-
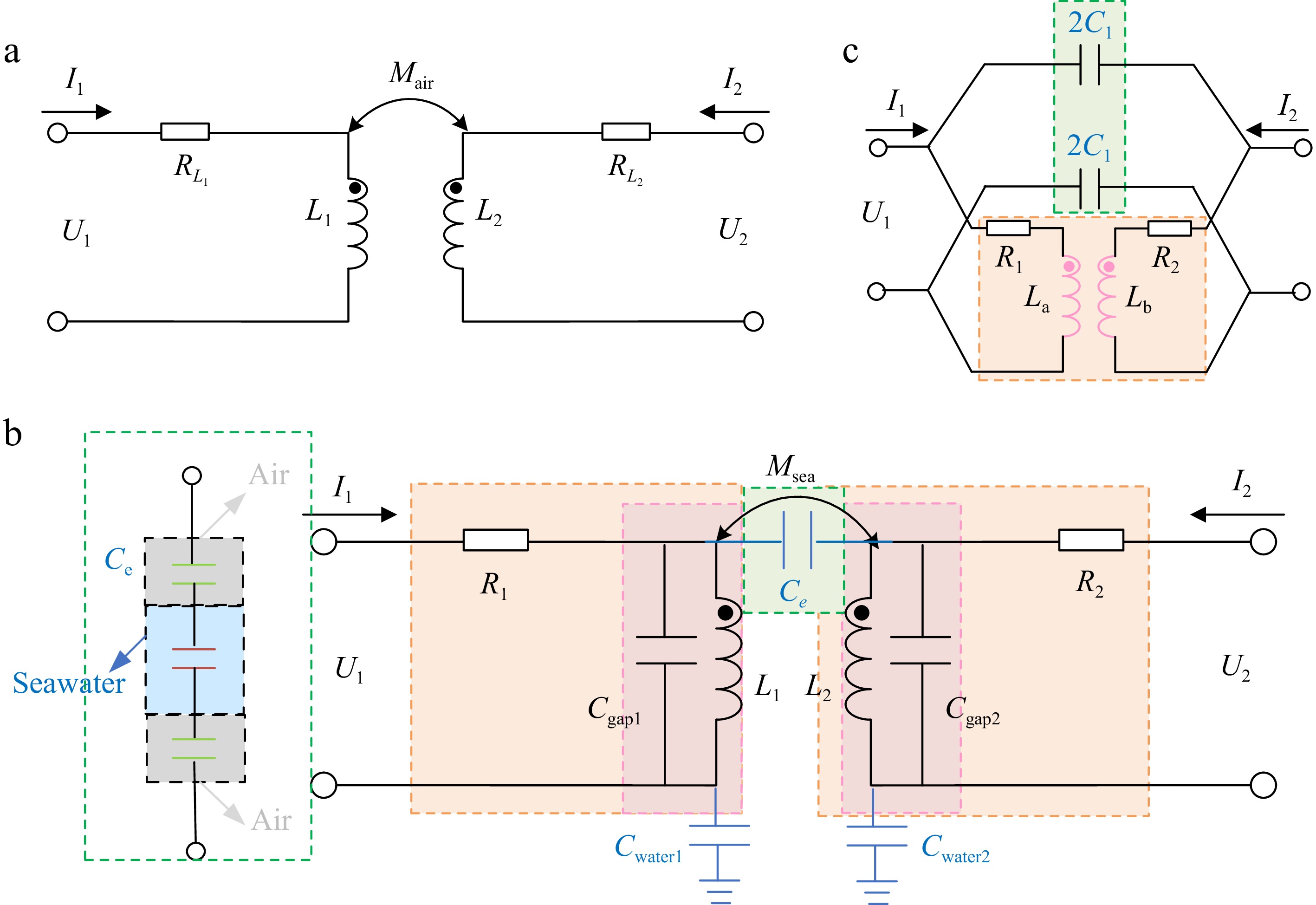
Figure 1.
Two-port models of WPT system. (a) Traditional mutual inductance model. (b) Model considering parasitic capacitance. (c) Simplified model considering parasitic capacitance.
-
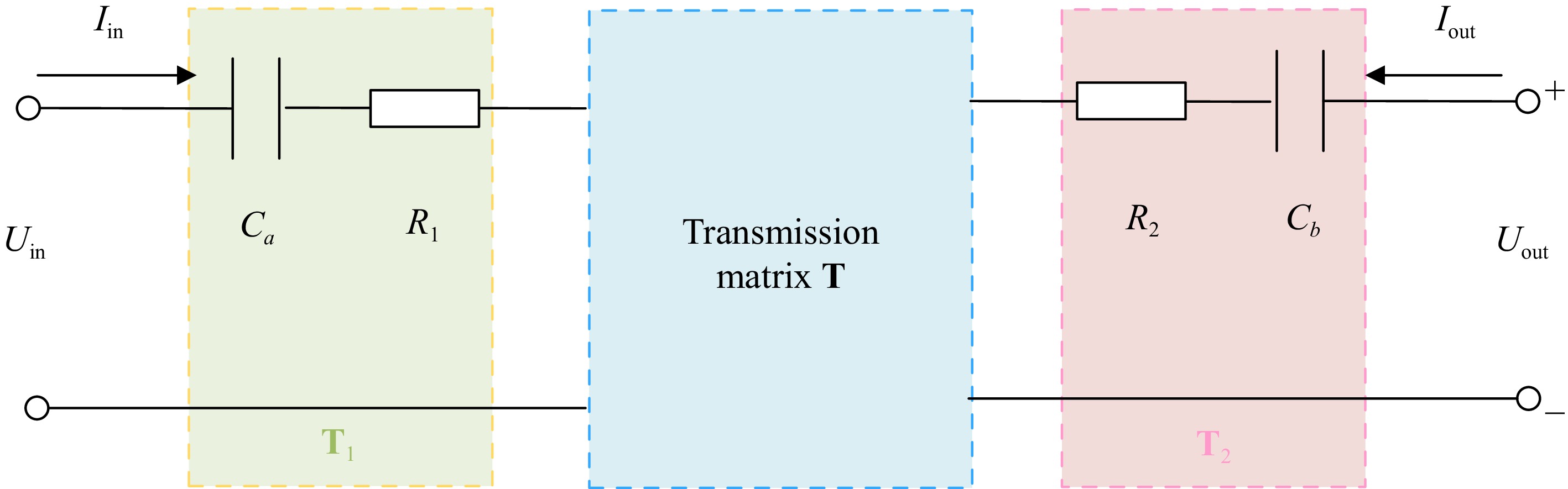
Figure 2.
Modeling of SWPT with S-S topology.
-
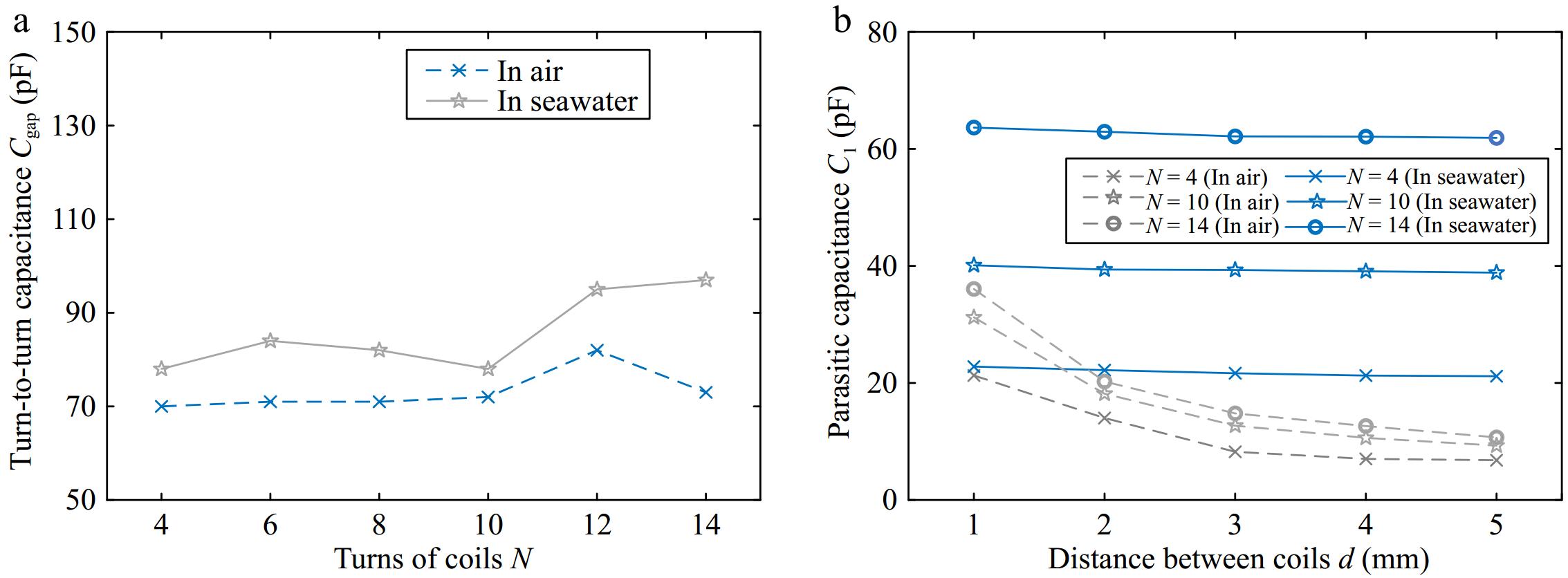
Figure 3.
Measurement results in air and seawater. (a) Using a vector analyzer to measure Cgap as a function of turns N. (b) Using a digital bridge to measure C1 as a function of distance d between coils.
-
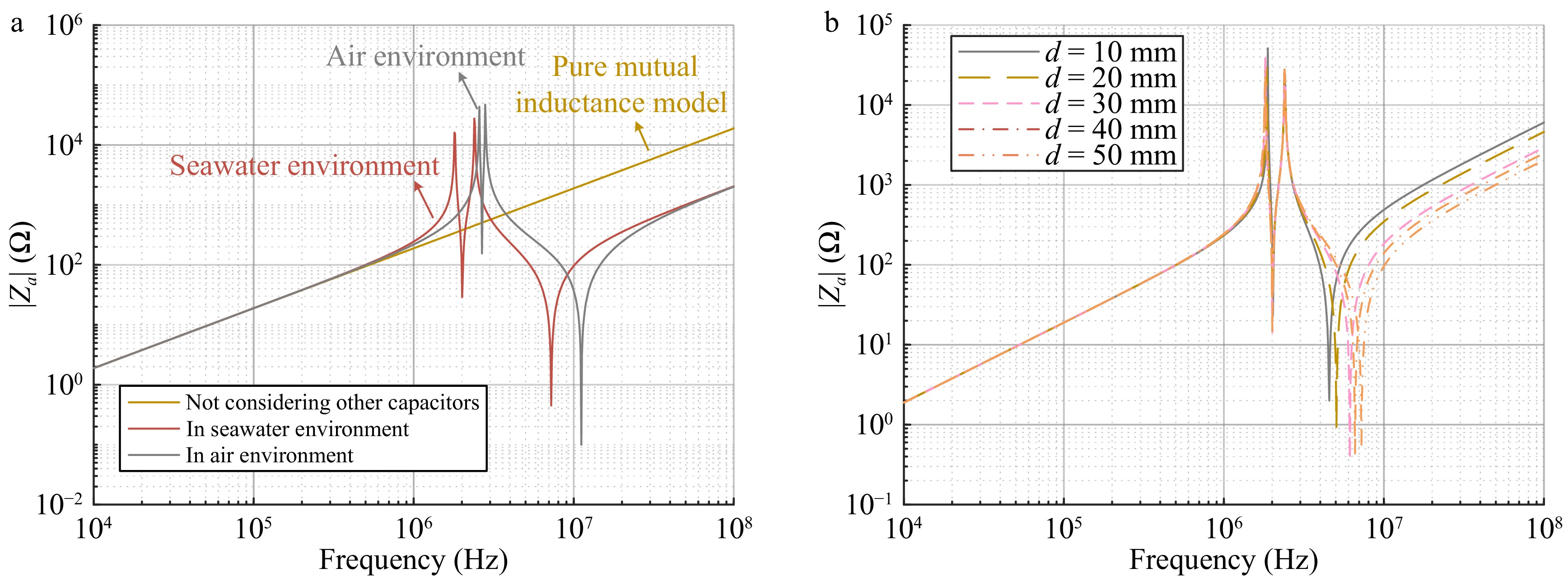
Figure 4.
Calculation results. (a) Frequency characteristics of impedance amplitude. (b) Frequency characteristics of impedance amplitude of distance d between coils.
-
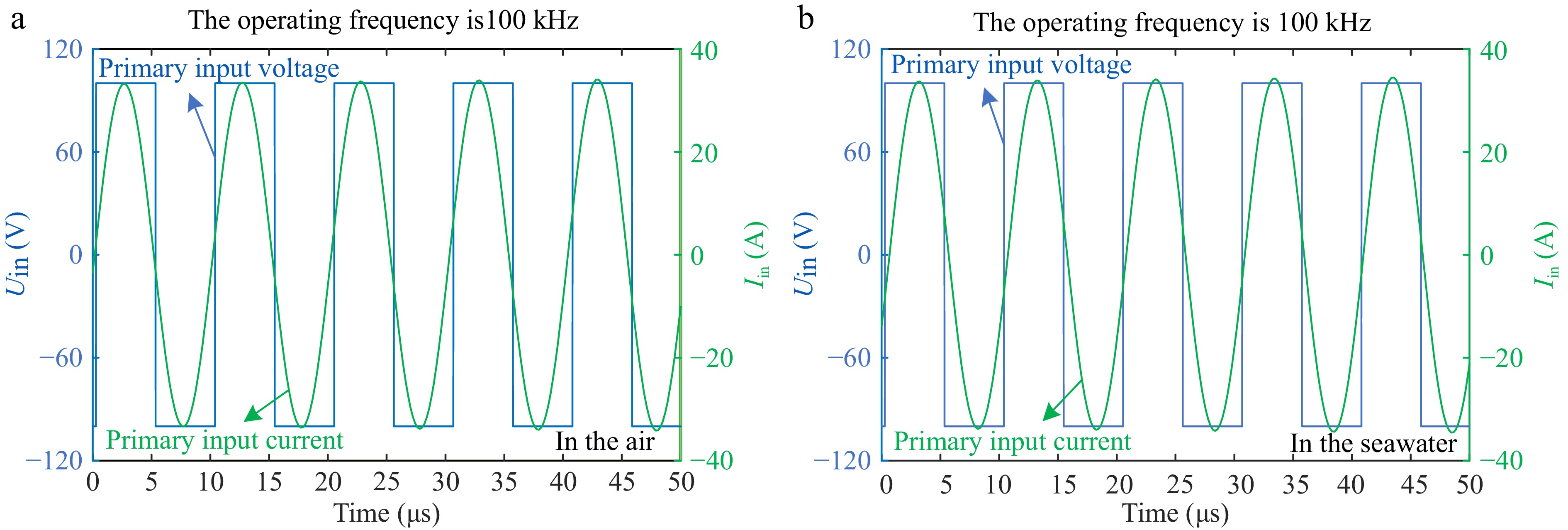
Figure 5.
Low-frequency simulation waveform. (a) In the air. (b) In the seawater.
-
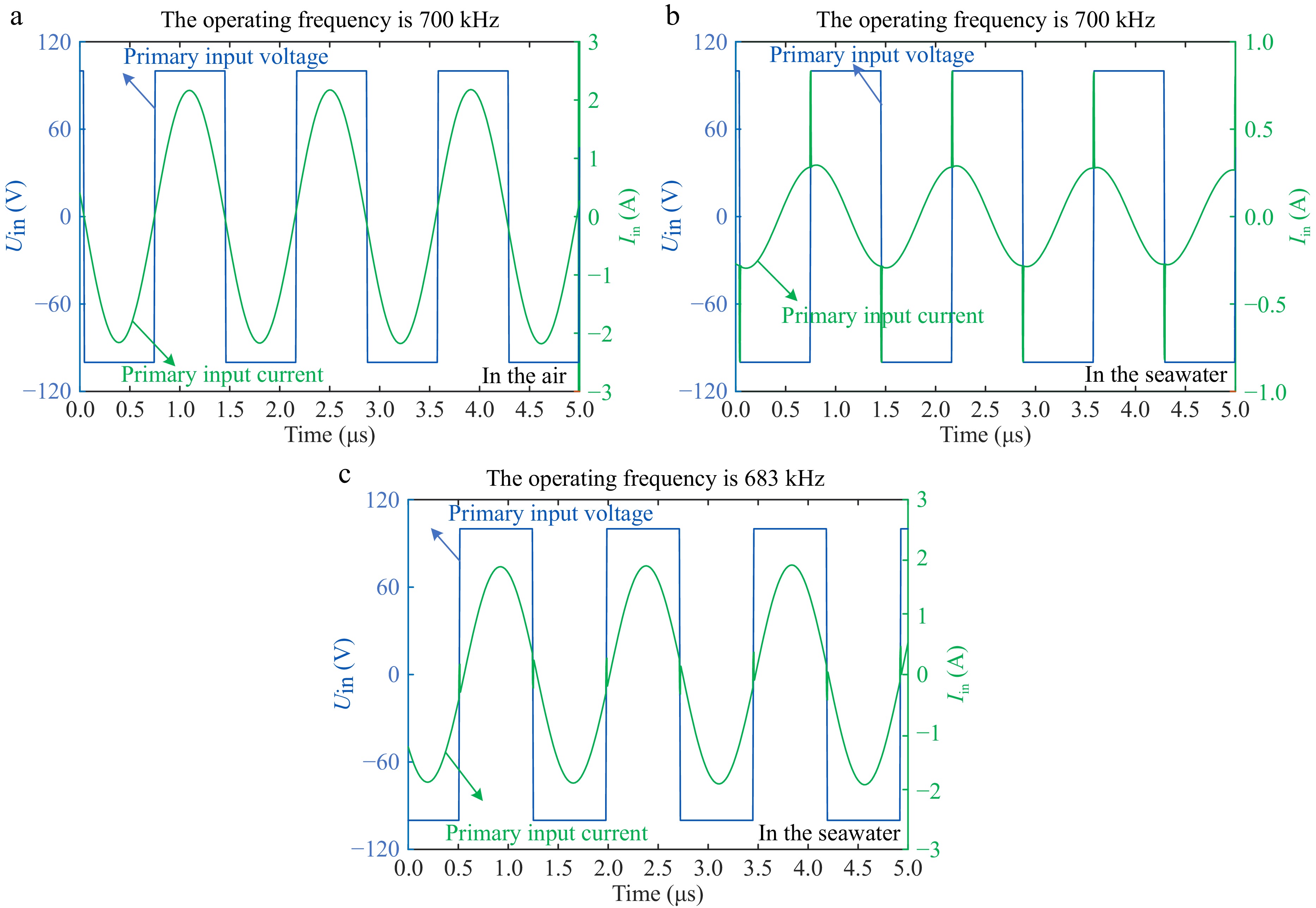
Figure 6.
High-frequency simulation waveform. (a) In the air. (b) In the seawater. (c) Readjust back to the resonance state.
-
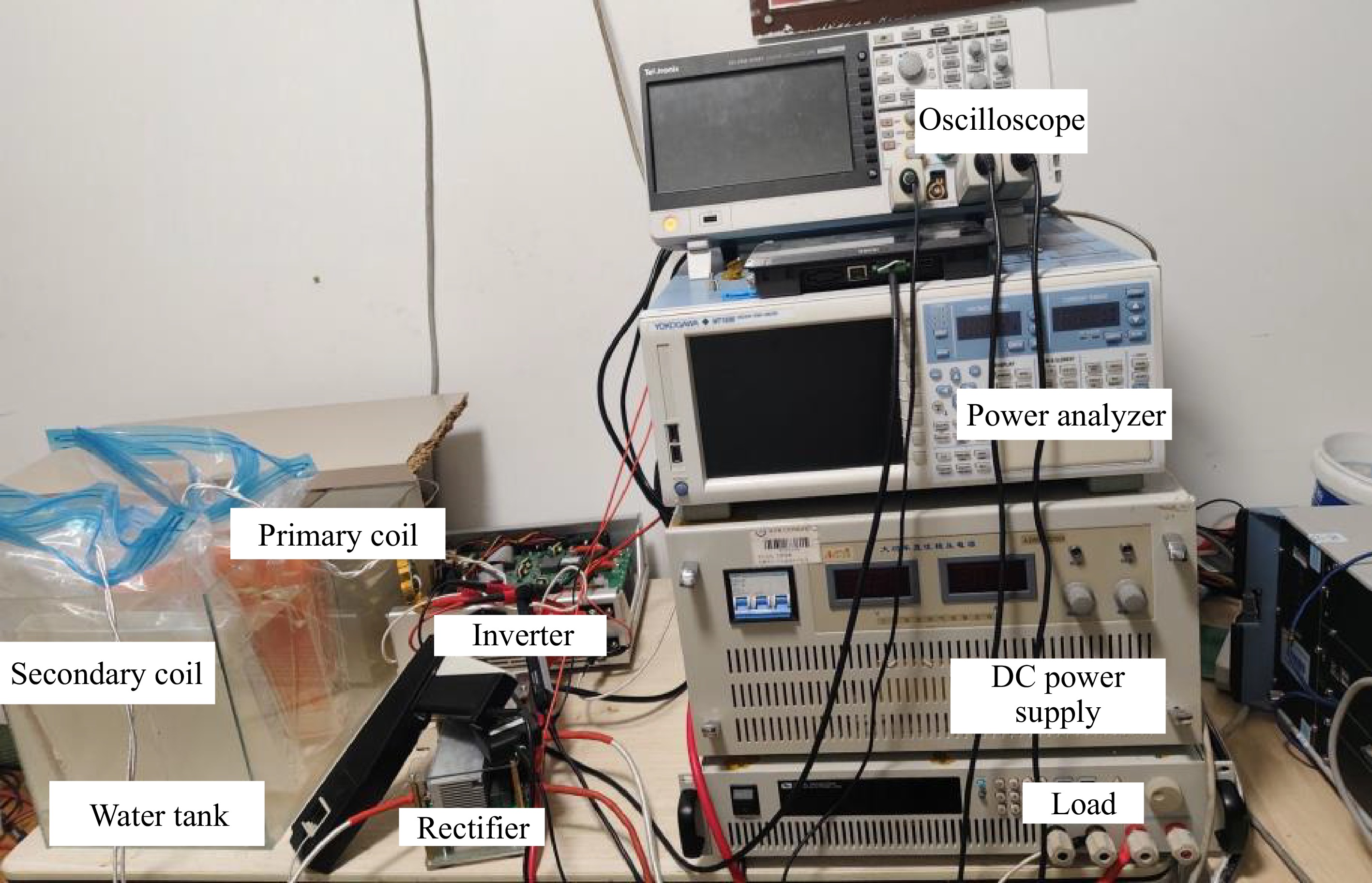
Figure 7.
The experimental setup for SWPT system.
-
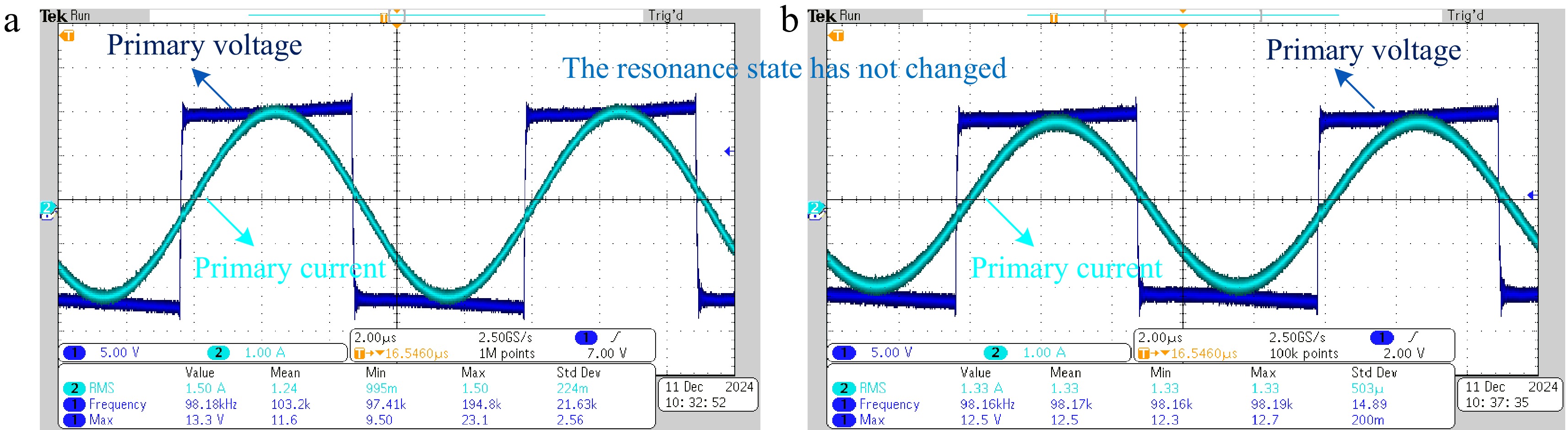
Figure 8.
Experimental waveforms for the SWPT system. (a) In the air. (b) In the seawater.
-
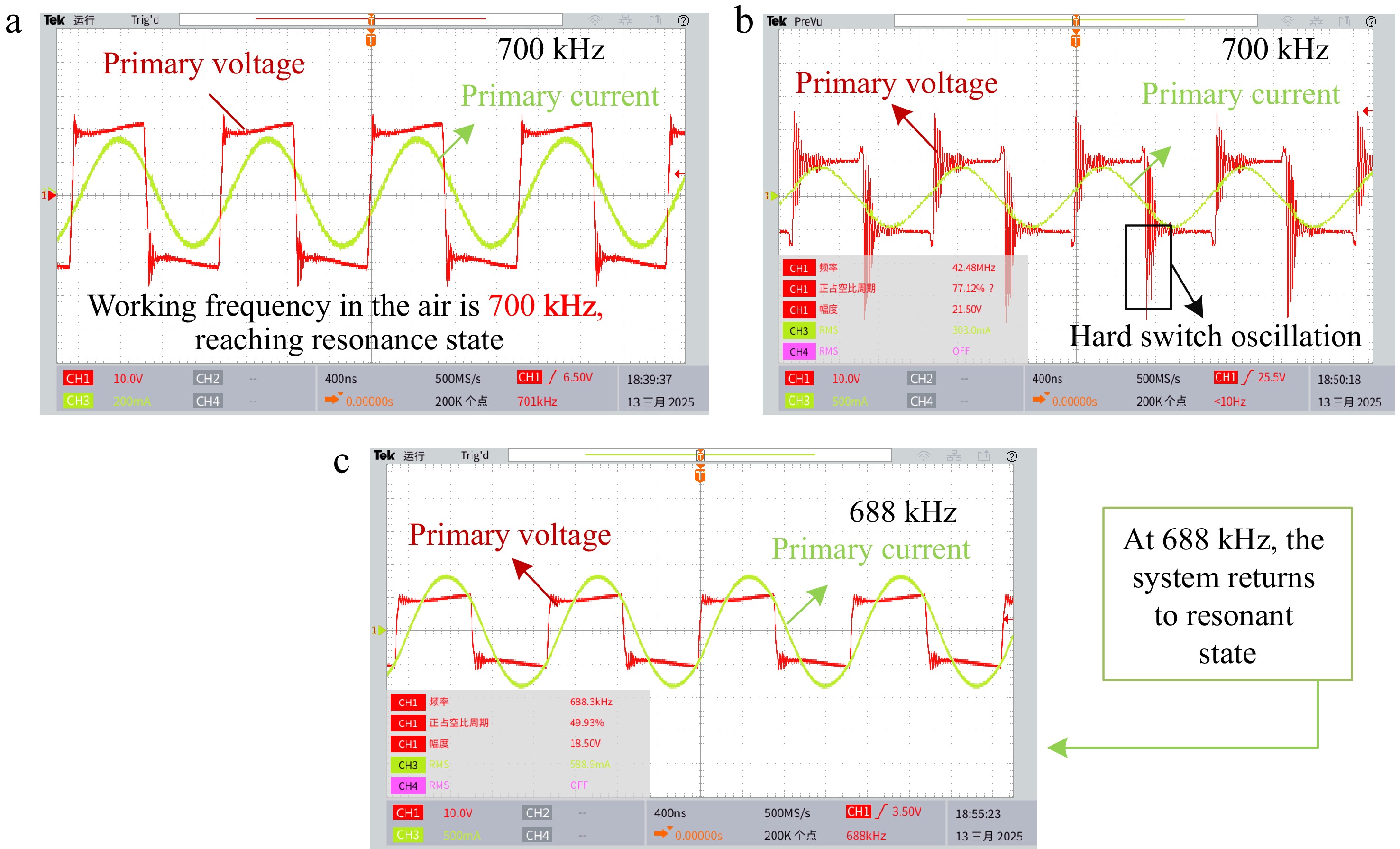
Figure 9.
Experimental waveforms for SWPT system. (a) In the air. (b) In the seawater. (c) Readjust back to resonance state.
-
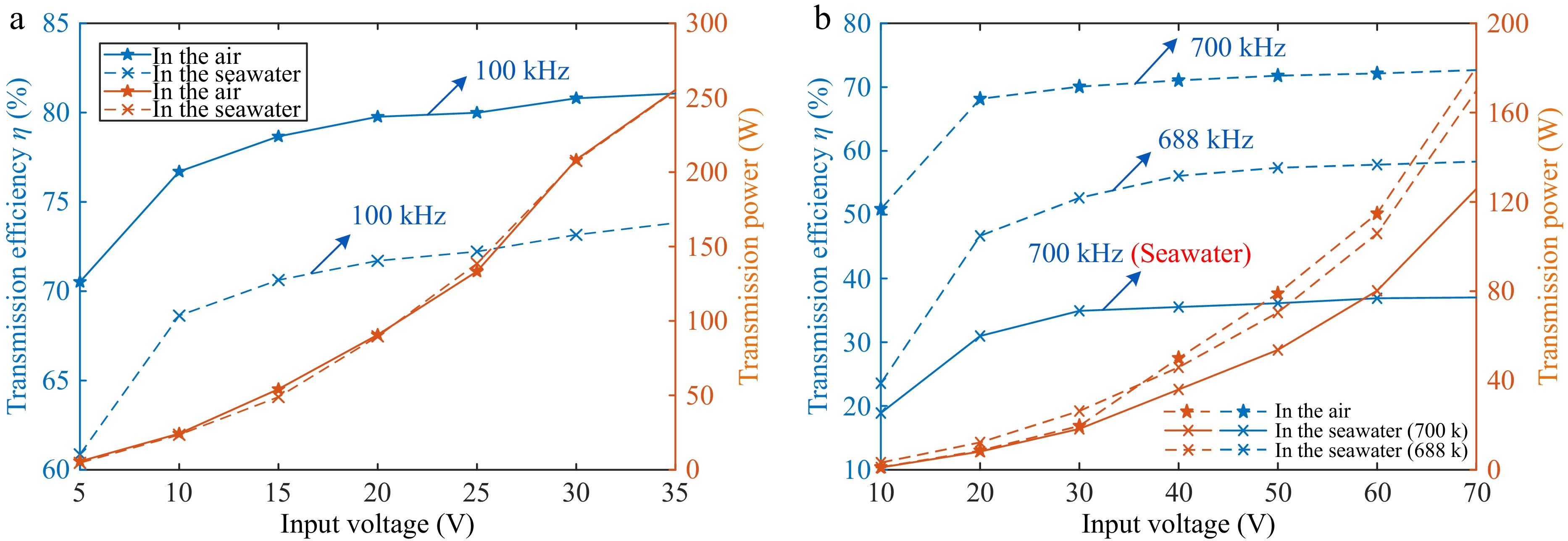
Figure 10.
System efficiency and transmission power. (a) Low frequency. (b) High frequency.
-
Note Symbol Value Primary/secondary inductance La/Lb 100 k 233.2 μH / 229.5 μH 700 k 490.5 μH / 461 μH Coupling coefficient kps 100 k 0.0443 700 k 0.0449 Resonant capacitor Ca/Cb 100 k 5.5 nF / 5.16 nF 700 k 112 pF / 105 pF Litz wire standard 0.1 × 550 Litz wire diameter 4 mm Number of turns N1/N2 14 Coil diameter d1 200 mm Seawater region 500 mm × 270 mm × 300 mm Gap d 100 mm Operating frequency f 100 kHz / 700 kHz Conductivity of seawater σ 4 S/m Table 1.
System parameters.
-
System operating frequency 100 kHz 700 kHz Air Calculate 100 kHz 700 kHz Simulation 100 kHz 700 kHz Experiment 100 kHz 700 kHz Seawater Calculate 100 kHz 689 kHz Simulation 100 kHz 683 kHz Experiment 100 kHz 688 kHz Transmission efficiency Air 81.065% 72.667% Seawater 73.82% (100 kHz) 37.02% (700 kHz) Efficiency after adjusting frequency / 58.313% (688 kHz) Efficiency improvement points / 21.0293% Table 2.
Experimental results.
Figures
(10)
Tables
(2)