-
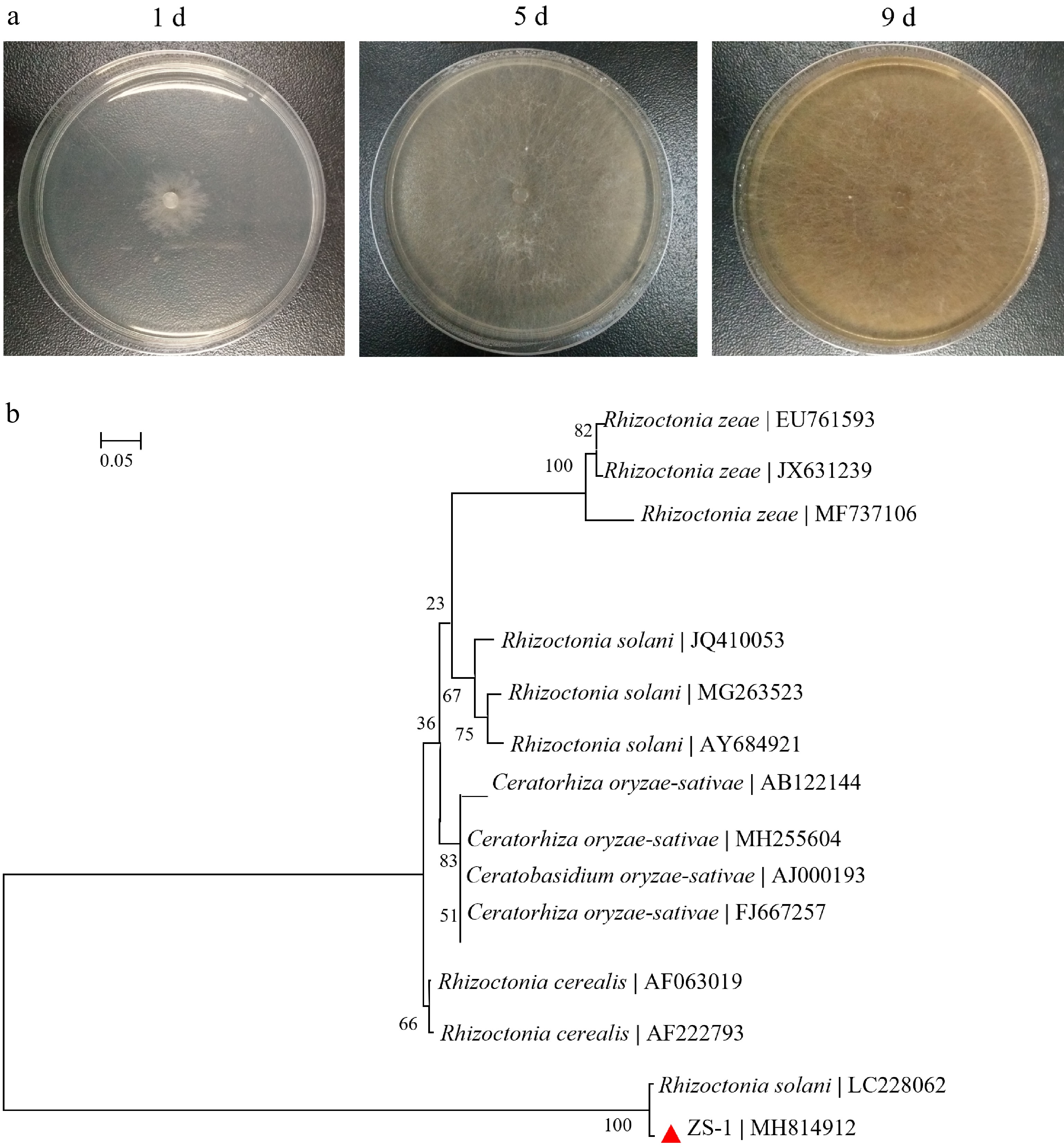
Figure 1.
(a) Colony morphology of the isolate ZS-1 on PDA causing Large Patch disease, and (b) phylogenetic tree of isolate ZS-1 and the related strains based on rDNA ITS sequences.
-
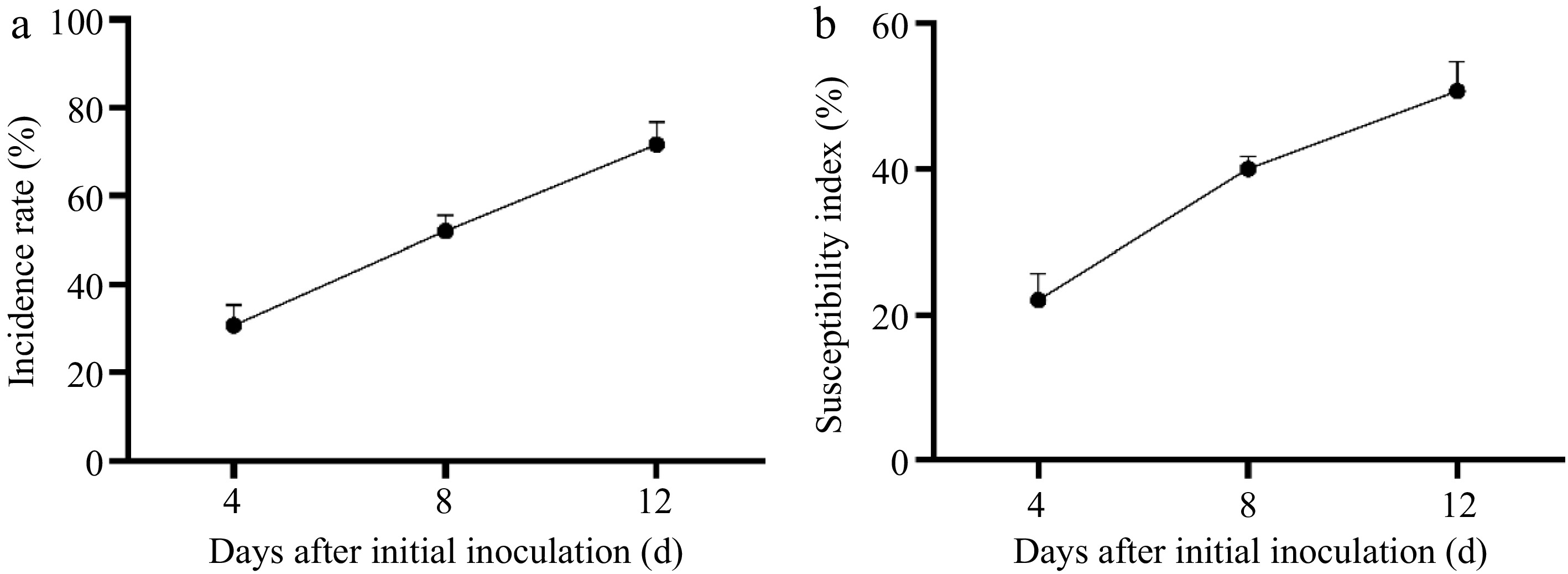
Figure 2.
(a) The incidence rate, and (b) severity index after ZS-1 strain invasion.
-
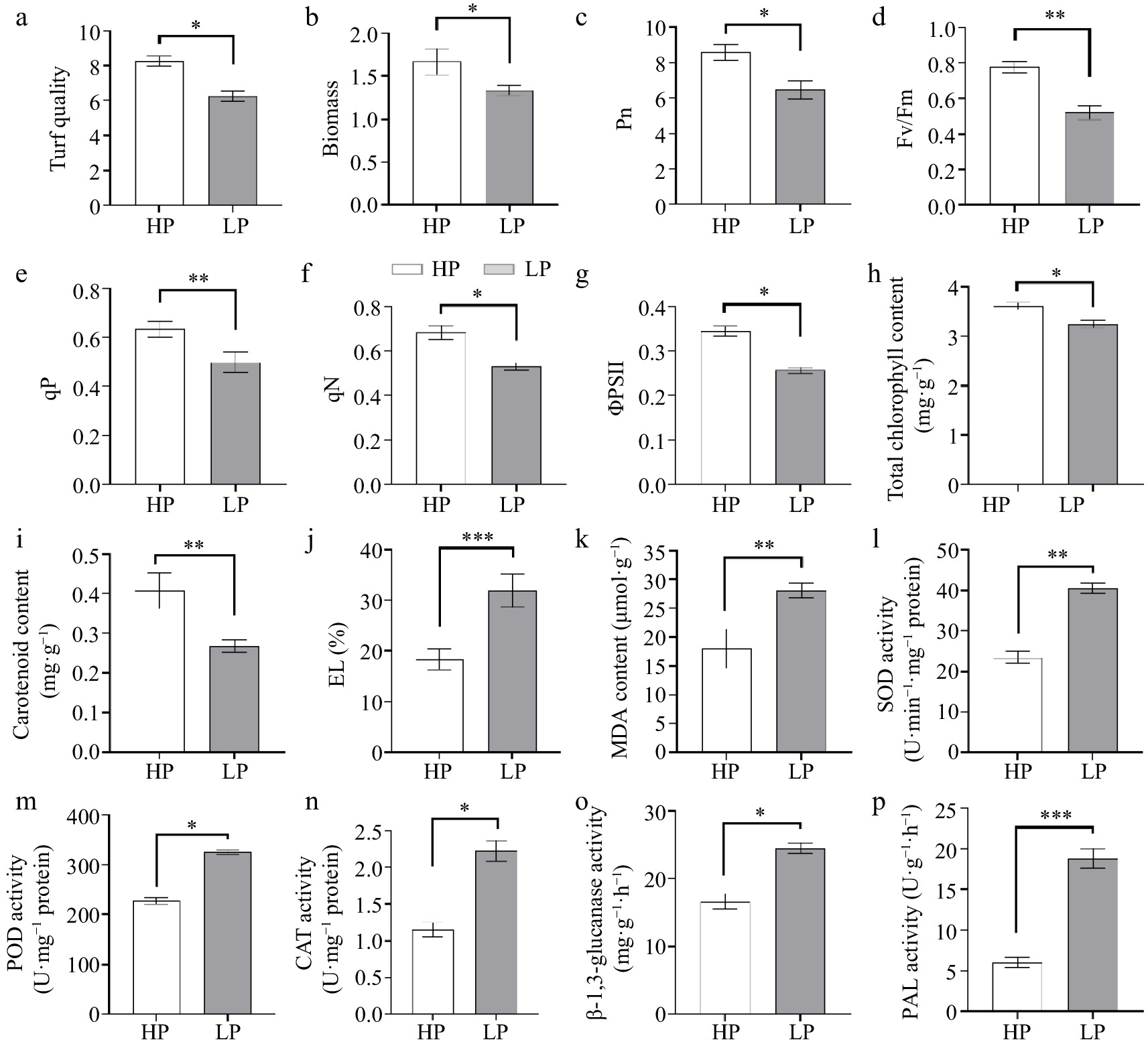
Figure 3.
Physiological indicators including (a) turf quality, (b) biomass, (c) net photosynthetic rate (Pn), (d) maximum quantum yield of PSII (Fv/Fm), (e) photochemical quenching (qP), (f) non-photochemical quenching (qN), (g) the photosystem II Efficiency (ΦPSII), (h) chlorophyll content, and (i) carotenoid content, (j) EL, (k) MDA level, (l) SOD, (m) POD, (n) CAT, (o) β-1,3-glucanase, and (p) PAL activities. (n = 3; 'LP' represents zoysiagrass grown with ZS-1 strain invasion; 'HP' represents zoysiagrass grown without ZS-1 strain invasion. '*', '**', '***', indicate significant differences at p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001, respectively).
-
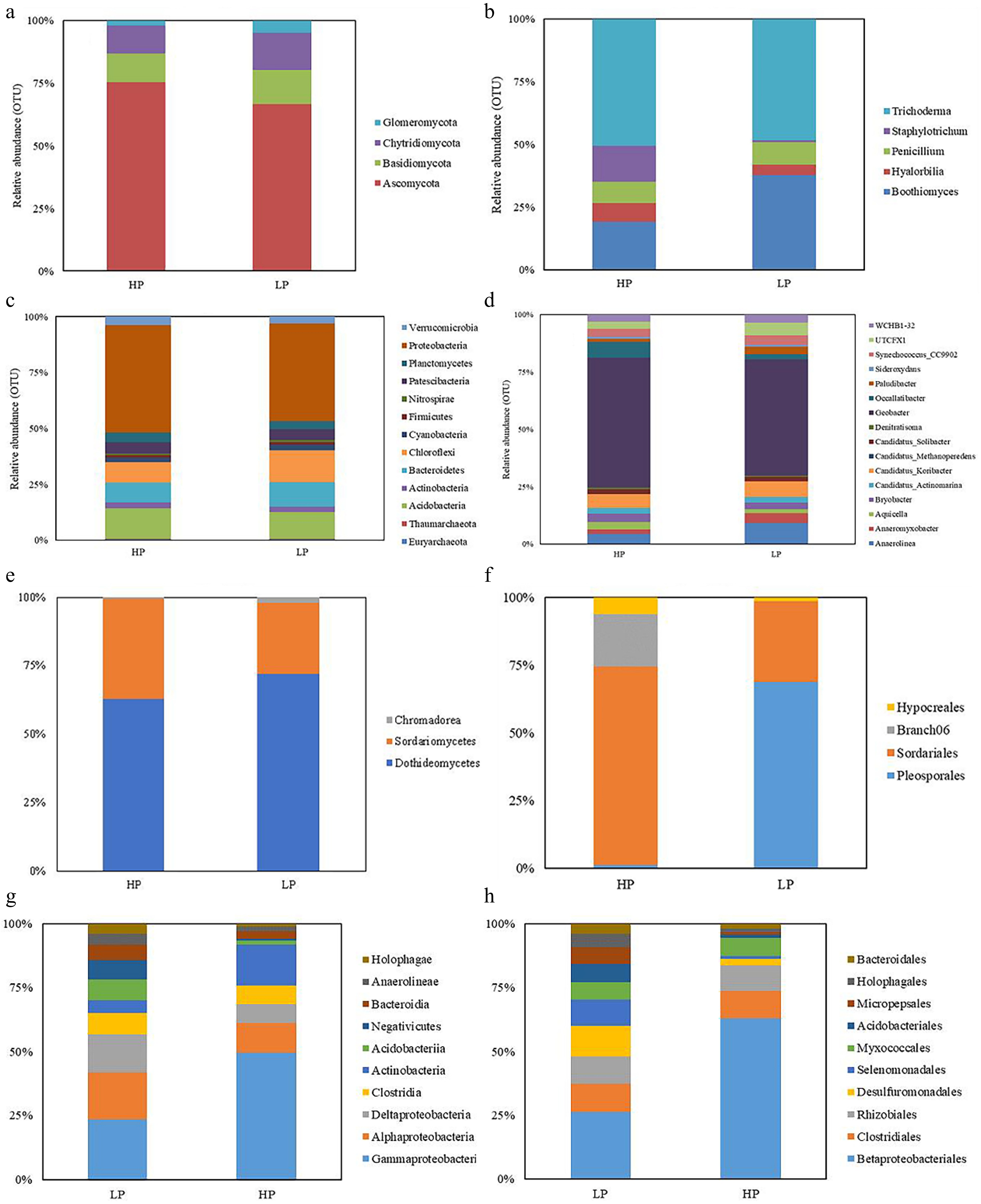
Figure 4.
The relative abundance of rhizosphere soil fungal (at the (a) phylum, and (b) genus level), and bacteria (at the (c) phylum, and (d) genus level) community as well as root fungal (at the (e) class, and (f) order level), and bacteria (at the (g) class, and (h) order level) community under ZS-1 strain invasion conditions. (n = 3; 'LP' represents zoysiagrass grown with ZS-1 strain invasion; 'HP' represents zoysiagrass grown without ZS-1 strain invasion).
-
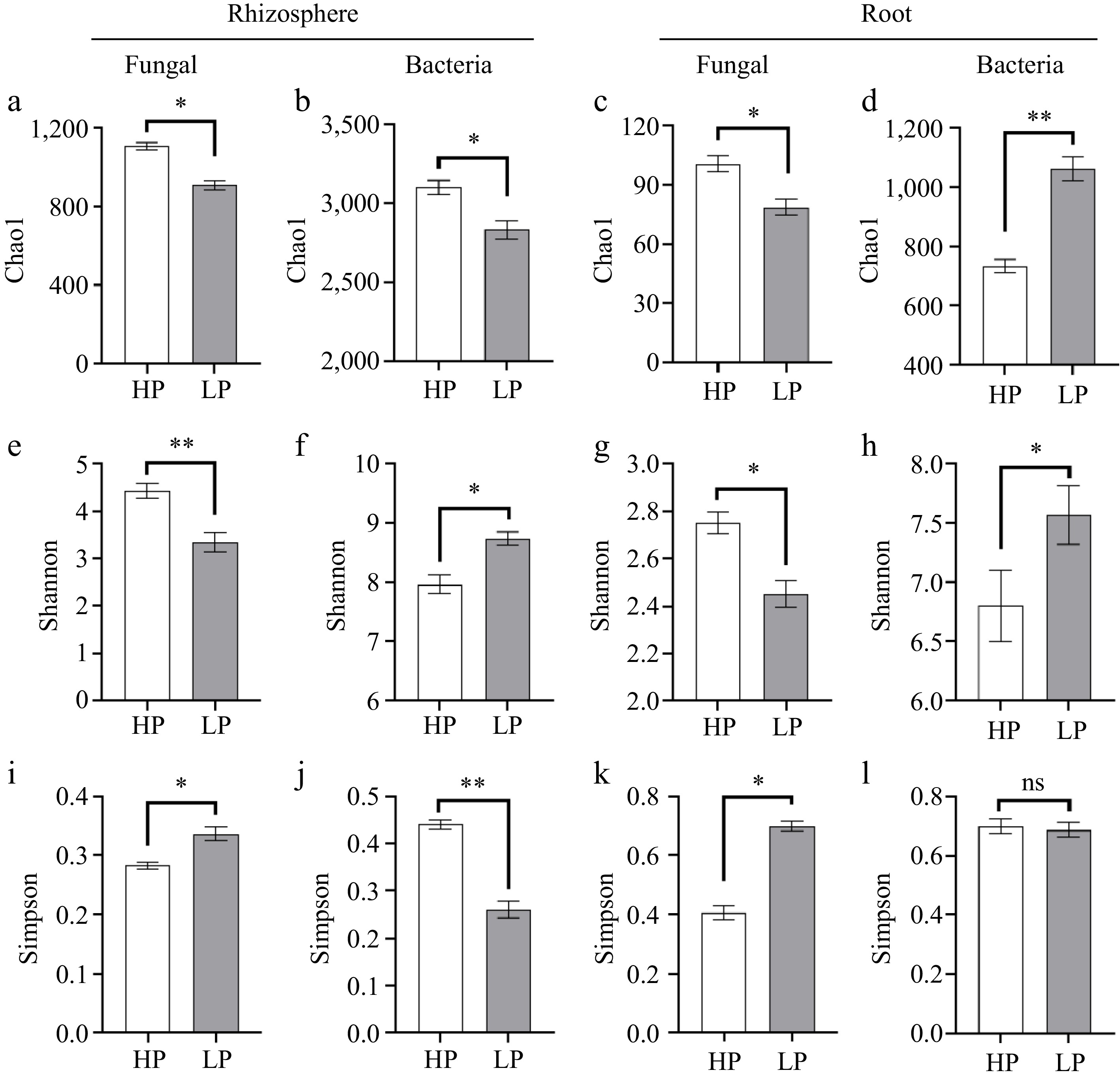
Figure 5.
Alpha diversity. Fungal and bacterial diversity and richness in rhizosphere soil and root. (a) Chao1, (e) Shannon, and (i) Simpson index of fungi in rhizosphere soil; (b) Chao1, (f) Shannon, and (j) Simpson index of bacteria in rhizosphere soil; (c) Chao1, (g) Shannon, and (k) Simpson index of fungi in root; (d) Chao1, (h) Shannon, and (l) Simpson index of bacteria in root. Bars denote means ± SE. (n = 3; 'LP' represents zoysiagrass grown with ZS-1 strain invasion; 'HP' represents zoysiagrass grown without ZS-1 strain invasion. '*', '**', indicate significant differences at p < 0.05, and p < 0.01, respectively and 'ns' represents no significant difference).
-
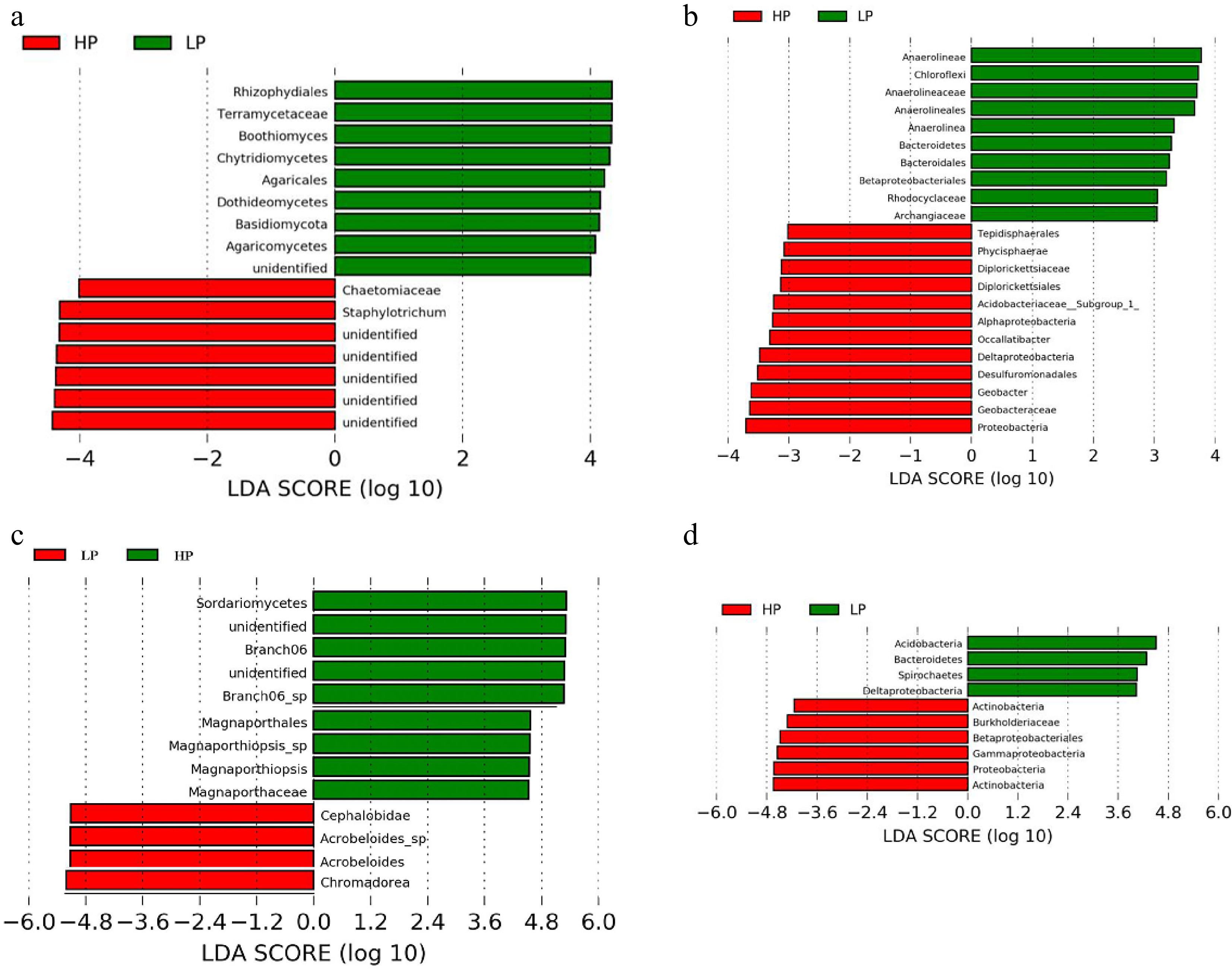
Figure 6.
The taxonomic differences between treatments based on ZS-1 strain invasion in zoysiagrass. Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size (LEfSe) of fungi and bacteria in (a), (b) rhizosphere soil, and (c), (d) root. LEfSe map is a linear discriminant analysis based on the composition of sample taxonomy according to different grouping conditions. p < 0.05, LDA > 4 as the standard. ('LP' represents zoysiagrass grown with ZS-1 strain invasion; 'HP' represents zoysiagrass grown without ZS-1 strain invasion).
-
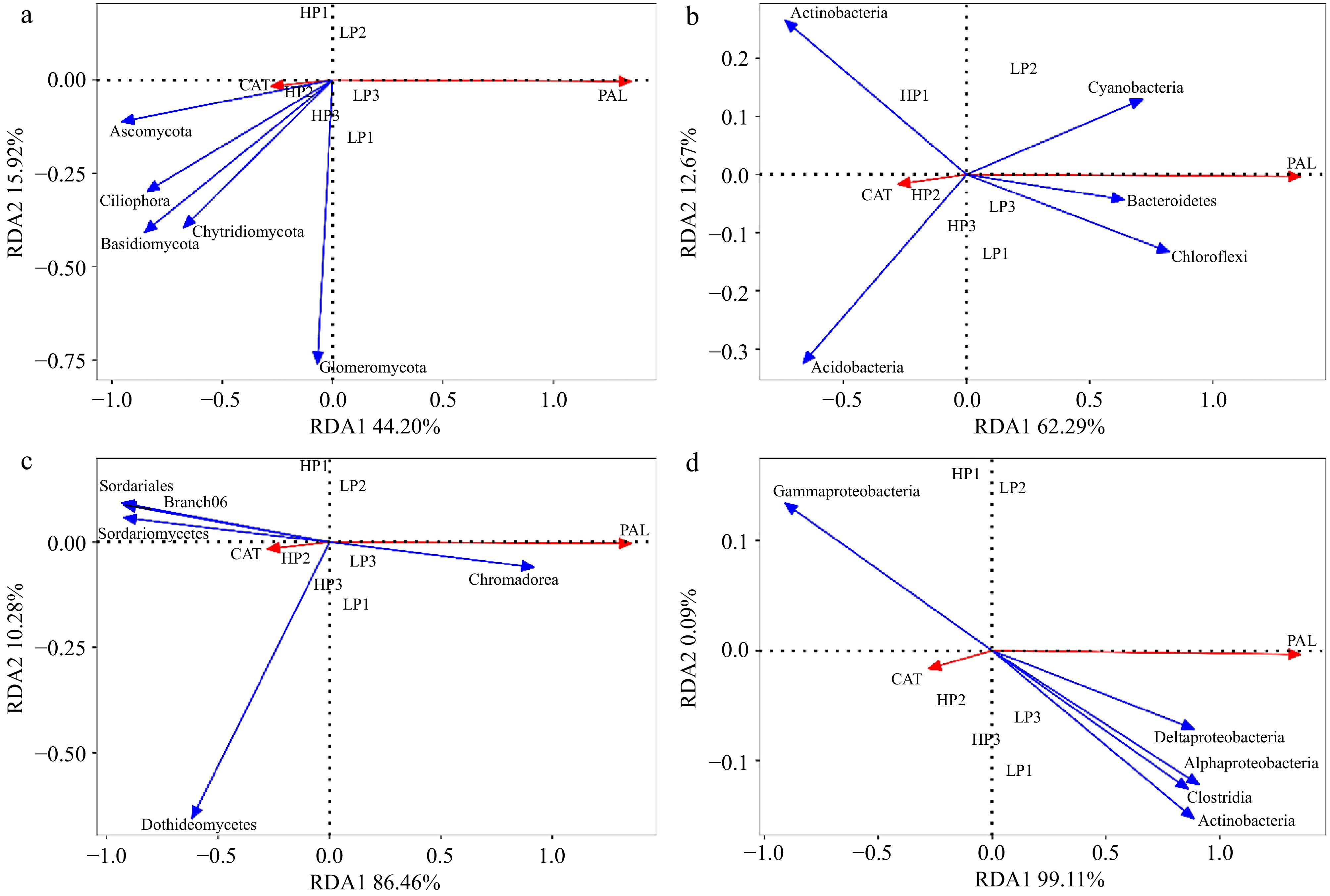
Figure 7.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) of relative abundance of fungi and bacteria in rhizosphere soil and root. and physiological indicators. (a) RDA between relative abundance of fungi in rhizosphere soil and physiological indicators; (b) RDA between relative abundance of bacteria in rhizosphere soil and physiological indicators; (c) RDA between relative abundance of fungi in root and physiological indicators; (d) RDA between relative abundance of bacteria in root and physiological indicators. (n = 3; 'LP' represents zoysiagrass grown with ZS-1 strain invasion; 'HP' represents zoysiagrass grown without ZS-1 strain invasion. CAT = catalase activity; PAL = phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activity).
-
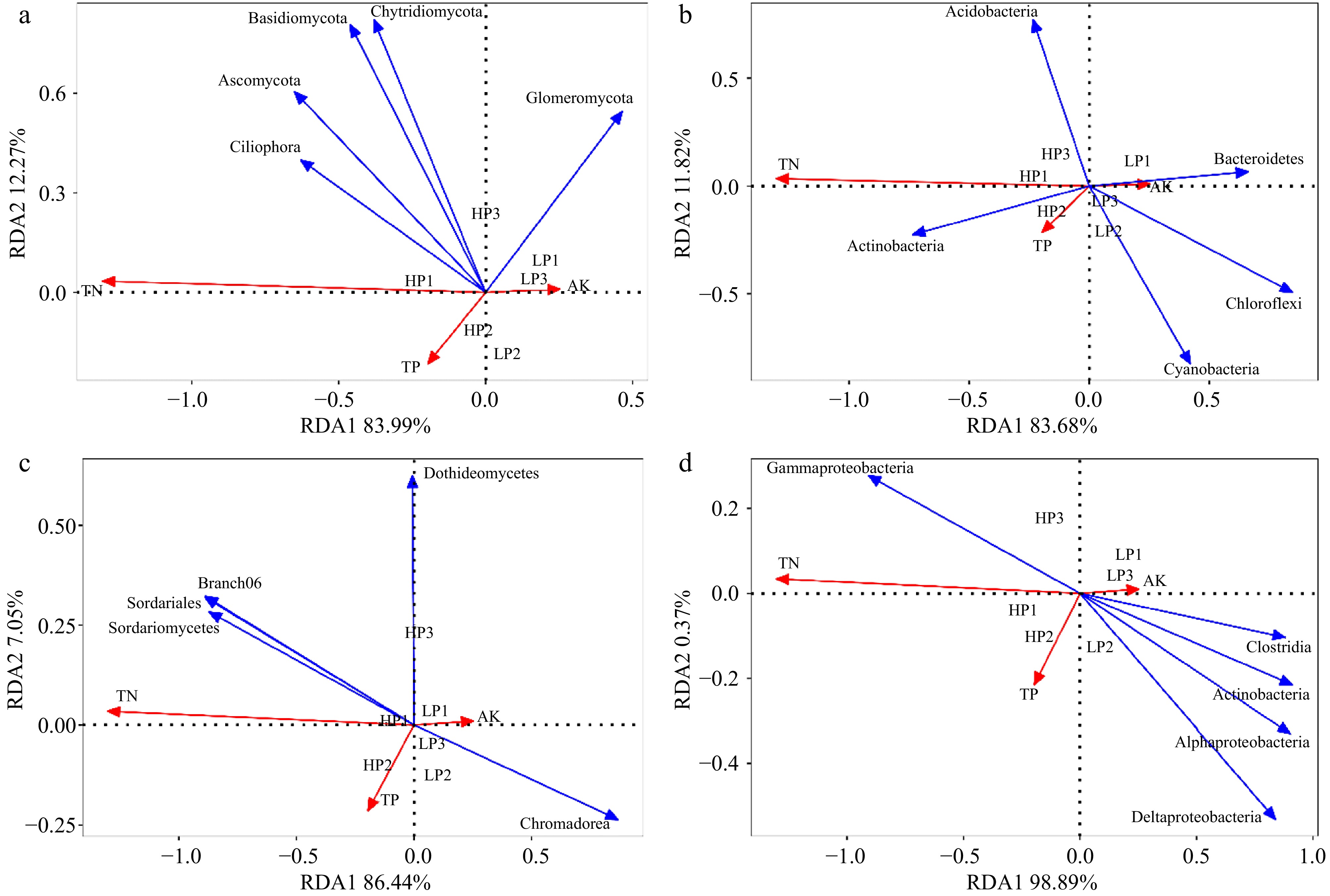
Figure 8.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) of relative abundance of fungi and bacteria in rhizosphere soil and root, and soil properties. (a) RDA between relative abundance of fungi in rhizosphere soil and soil properties; (b) RDA between relative abundance of bacteria in rhizosphere soil and soil properties; (c) RDA between relative abundance of fungi in root and soil properties; (d) RDA between relative abundance of bacteria in root and soil properties. (n = 3; 'LP' represents zoysiagrass grown with ZS-1 strain invasion; 'HP' represents zoysiagrass grown without ZS-1 strain invasion. AK = available potassium; TN = total nitrogen; TP = total phosphorus).
Figures
(8)
Tables
(0)