-
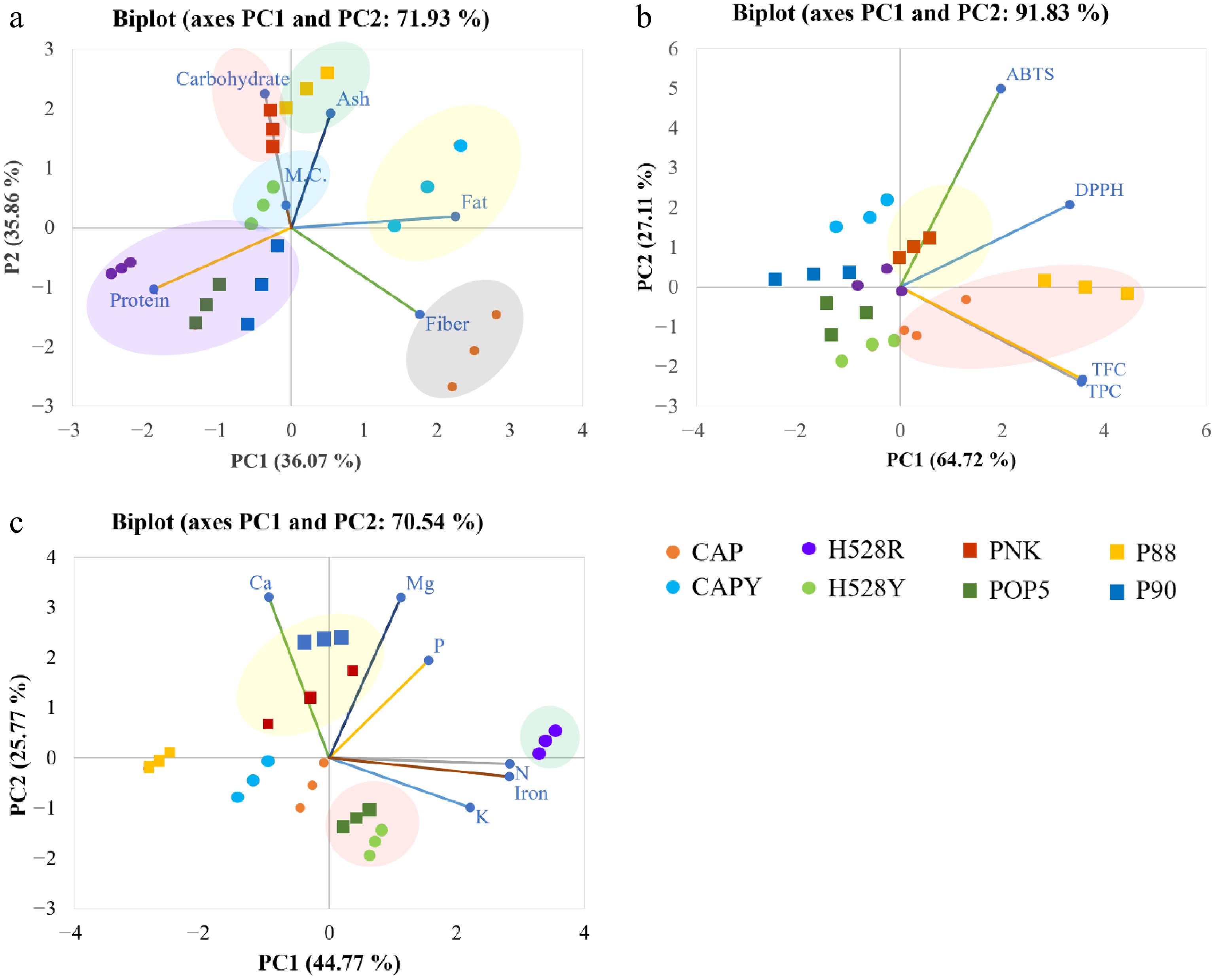
Figure 1.
The chemometric PCA biplots of the (a) proximate, (b) phytochemicals, and (c) mineral compositions in different varieties of arabica coffee pulp. CAP = Catuai, CAPY = Caturra, H528Y = Cartimor H528 Yellow, H528R = Cartimor H528 Red, PNK = Bourbon Phanokkok, POP5 = Cartimor Populacao 5, P88 = Cartimor Progeny 88, P90 = Cartimor Progeny 90, TFC = Total flavonoid compound, TPC = Total phenolic compound.
-
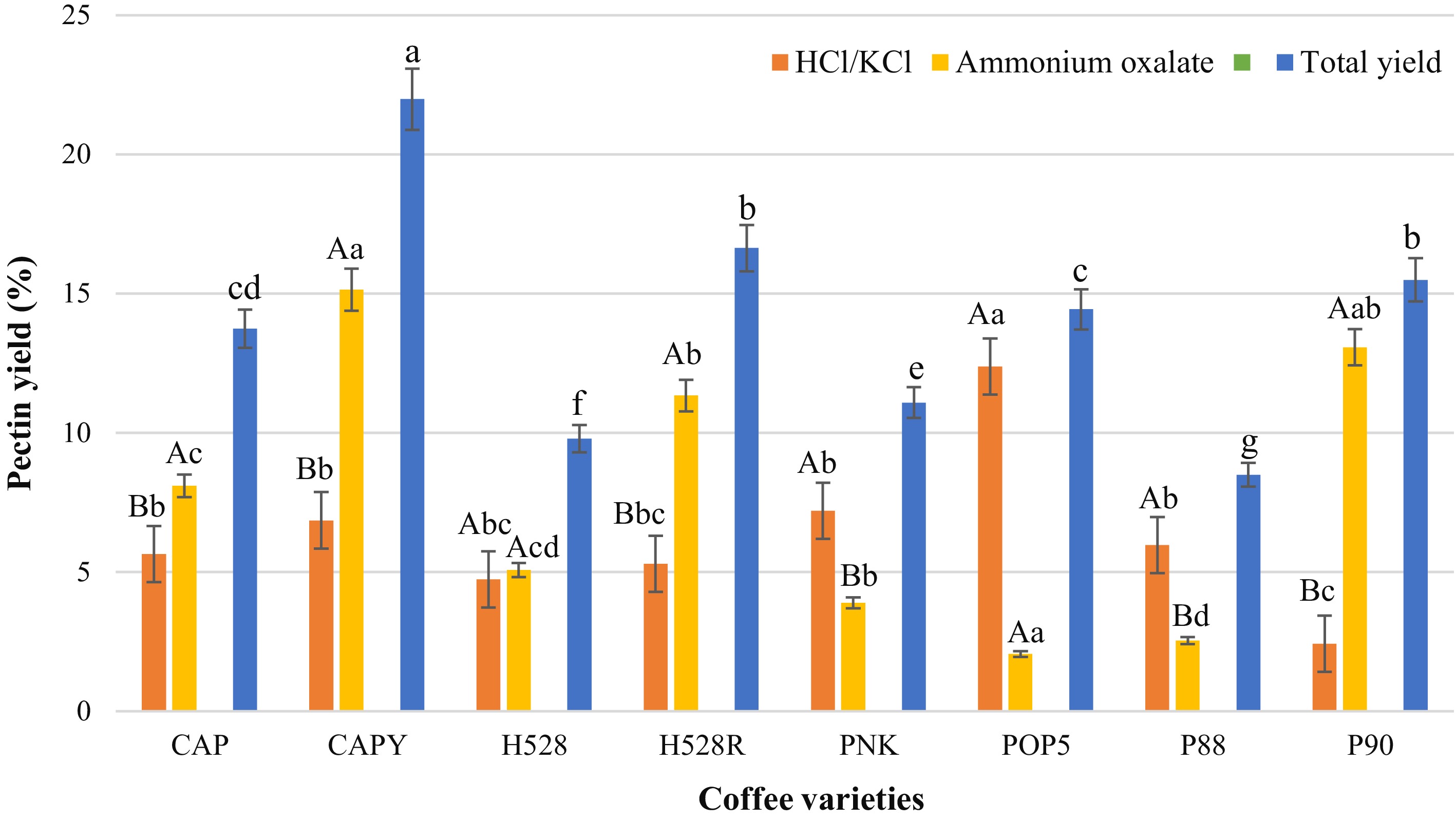
Figure 2.
Pectin content extracted from different CP varieties using HCl/KCl buffer and ammonium oxalate solution. CAP = Catuai, CAPY = Caturra, H528Y = Cartimor H528 Yellow, H528R = Cartimor H528 Red, PNK = Bourbon Phanokkok, POP5 = Cartimor Populacao 5, P88 = Cartimor Progeny 88, P90 = Cartimor Progeny 90. Means labelled with the same letters (uppercase, across different solutions; lowercase, across different coffee varieties), exhibit significant distinction based on Duncan's test. The error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean (p ≤ 0.05).
-
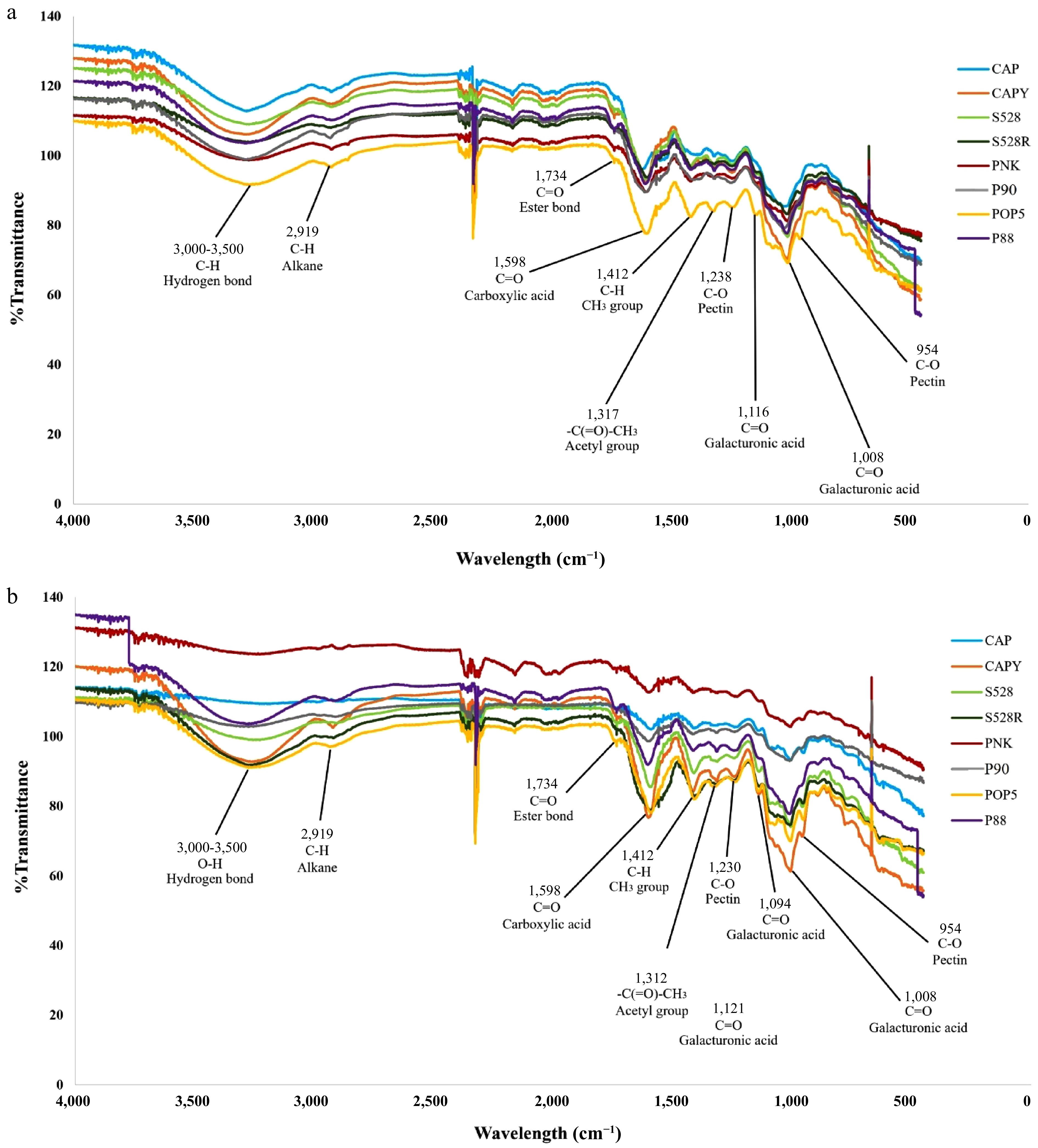
Figure 3.
The FT-IR spectra of pectin obtained from different arabica coffee pulps using (a) HCl-KCl buffer and (b) ammonium oxalate solution, from 4,000 to 500 cm−1 (x-axis). %T presents the transmittance percentage (y-axis). CAP = Catuai, CAPY = Caturra, H528Y = Cartimor H528 Yellow, H528R = Cartimor H528 Red, PNK = Bourbon Phanokkok, POP5 = Cartimor Populacao 5, P88 = Cartimor Progeny 88, P90 = Cartimor Progeny 90.
-
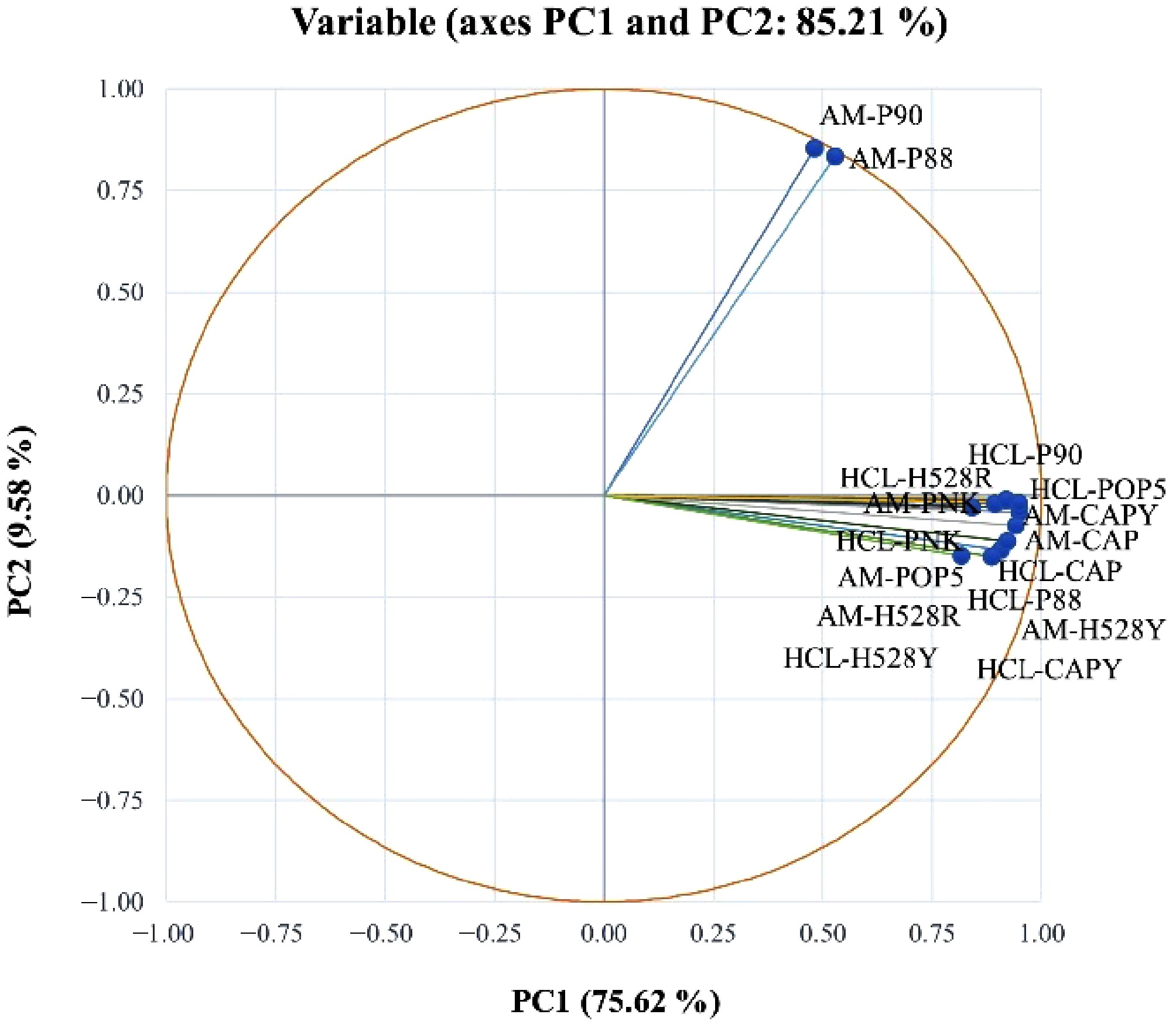
Figure 4.
Principal component analysis of FT-IR spectra of pectin obtained from different arabica CP using HCl-KCl (HCL) and ammonium oxalate (AM). CAP = Catuai, CAPY = Caturra, H528Y = Cartimor H528 Yellow, H528R = Cartimor H528 Red, PNK = Bourbon Phanokkok, POP5 = Cartimor Populacao 5, P88 = Cartimor Progeny 88, P90 = Cartimor Progeny 90.
-
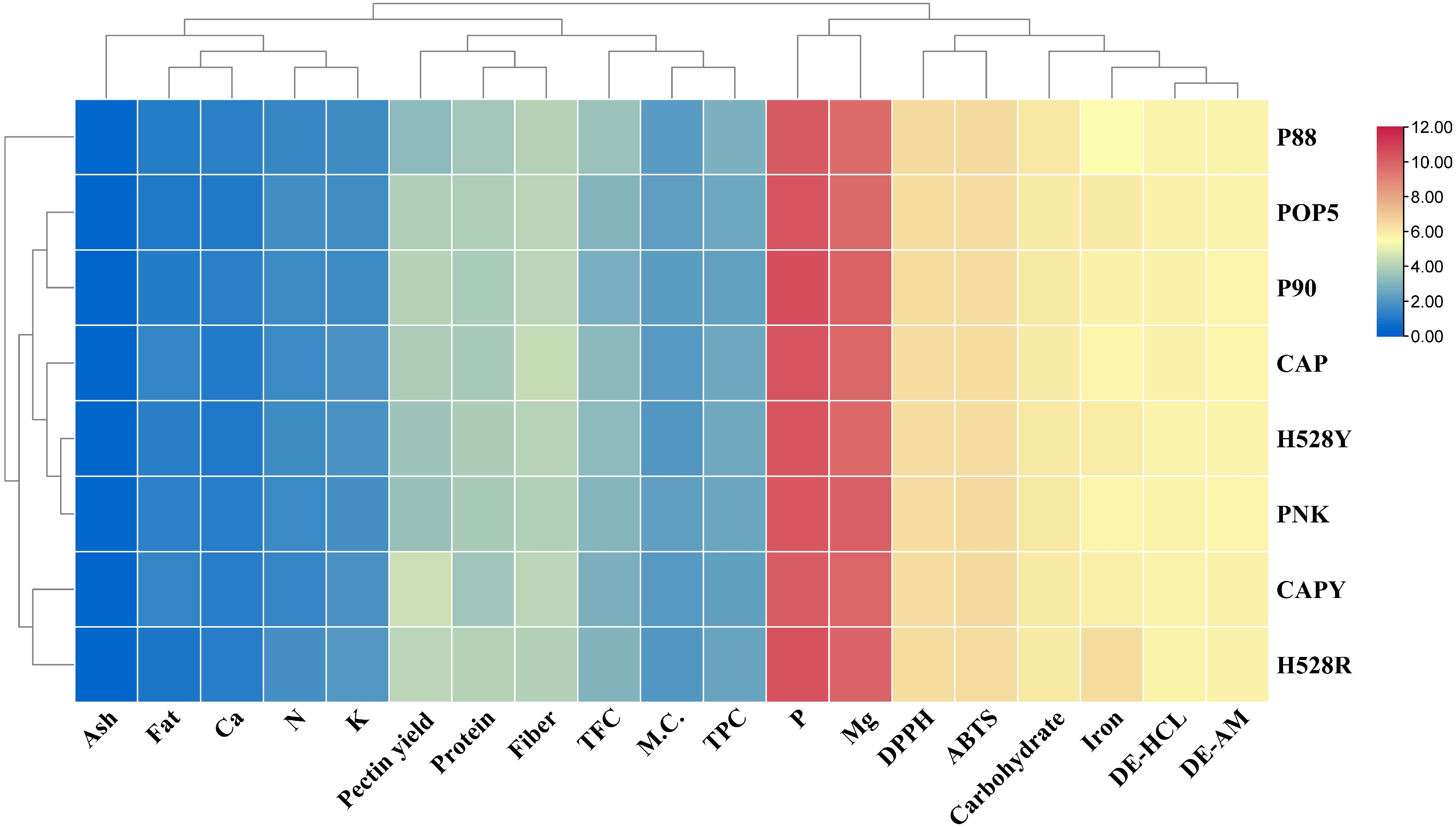
Figure 5.
Heat map illustrates the clustering of different arabica coffee pulps according to their chemical compositions, phytochemical profiles, and pectin characteristics. CAP = Catuai, CAPY = Caturra, H528Y = Cartimor H528 Yellow, H528R = Cartimor H528 Red, PNK = Bourbon Phanokkok, POP5 = Cartimor Populacao 5, P88 = Cartimor Progeny 88, P90 = Cartimor Progeny 90, M.C. = Moisture, TFC = Total flavonoid compound, content, TPC = Total phenolic compound, DE-HCL = DE of pectin obtained from HCl/KCl extraction, DE-AM = DE of pectin obtained from ammonium oxalate extraction.
-
Coffee varieties Origin Feature Catuai (CAP) The Catuai coffee variety originated in Brazil and was developed by the Instituto Agronomico in the Campinas region of São Paulo. It was crossed from two natural arabica mutations: the compact and smaller Caturra and the highly productive Mundo Novo. This breeding aimed to combine Caturra's compact growth with Mundo Novo's yield and quality, resulting in a robust, high-yielding plant ideal for dense planting and efficient harvesting[3,4]. 
Caturra (CAPY) Originating as a natural Bourbon mutation found in Brazil (1915−1918), this variety's compact form and dense secondary branching immediately attracted plant breeders. These characteristics are advantageous as they permit closer plant spacing, which translates directly into higher overall fruit yields per area[5,6]. 
CaturraCatimor Catimor designates a range of cultivars resulting from a cross between the Timor hybrid and Caturra, a breeding effort driven primarily by the need for resistance to coffee leaf rust. The Catimor group includes several cultivars and breeding lines, such as H528, Populacao 5, and Progenies 88 and 90[22−24]. 
CatimorH528R and H528Y
A hybrid, H528, was created by crossing yellow-fruited Catuai with HW26. The H 528/21 cultivar produces beans comparable in weight and size to Caturra, while the H 528/46 cultivar shows resistance to coffee leaf rust in its fourth generation. This hybrid fruits later than Caturra[23, 25].
Catimor H528R
Catimor H528YPopulacao 5 (POP5)
This variety was developed through the selection of the fifth filial generation (F5) derived from ICFC 7958 (F4), which in turn originated from progenies of CIFC HW 26/5-3-45. Its lineage traces back to the Catimor variety from the Coffee Institute of Portugal[23,26].
Populacao 5Progeny 88 (P88) and Progeny 90 (P90)
Both Catimor coffee varieties originated in Colombia; however, the fourth filial generation (F4) seeds were obtained from a coffee research station in Kenya. Unlike the commonly known Catimor types developed primarily in Brazil and Portugal, these hybrids have a distinct parentage. Their genetic background includes hybrids such as Hybrido de Timor, Caturra, and HDT-CIFC 832/1 Portugal F6[23].
Catimor progeny 90
Catimor progeny 88Bourbon variety Bourbon (Coffea arabica var. bourbon) is believed to have originated as a natural mutation of the Typica variety. Bourbon is thought to have emerged naturally in the highlands of Ethiopia and was introduced to Bourbon Island (now Réunion) in 1740 CE. Bourbon leaves are broad with green-coloured young shoots. While the variety is susceptible to coffee leaf rust and environmental stresses[23,27].
Phanokkok (PNK)
Phanokkok, also known as orange Bourbon, is a cultivar of the Bourbon coffee variety characterised by its distinctive orange cherry colour. Bourbon itself is a natural mutation of the Typica coffee variety, originating originally from Ethiopia. This unique cultivar has been introduced to northern Thailand, where it is being developed and cultivated primarily by the Highland Agricultural Research and Training Center in Khun Chang Kian, Chiang Mai[23,27].
PhanokkokTable 1.
Characteristics and origin of arabica coffee.
-
Coffee varieties Moisture content (%) Carbohydrate (%) Crude fat (%) Crude fibre (%) Crude protein (%) Ash (%) CAP 3.43 ± 0.04cd 62.54 ± 0.36e 1.78 ± 0.03a 19.42 ± 0.41a 12.50 ± 0.12e 0.35 ± 0.02ab CAPY 3.34 ± 0.06d 66.22 ± 0.37b 1.72 ± 0.11a 17.07 ± 0.24b 11.34 ± 0.09f 0.33 ± 0.02bc H528Y 3.14 ± 0.02e 65.94 ± 0.03b 1.34 ± 0.04cd 15.71 ± 0.00d 13.53 ± 0.03c 0.35 ± 0.01ab H528R 3.11 ± 0.02e 65.05 ± 0.62c 0.93 ± 0.04g 15.18 ± 0.44ef 15.41 ± 0.22a 0.33 ± 0.00bc PNK 4.02 ± 0.01a 66.55 ± 0.24b 1.44 ± 0.01bc 14.72 ± 0.06f 12.91 ± 0.28d 0.36 ± 0.01a POP5 3.92 ± 0.03a 63.93 ± 0.29d 1.05 ± 0.04fg 16.51 ± 0.21c 14.28 ± 0.16b 0.32 ± 0.01c P88 3.49 ± 0.08c 67.77 ± 0.09a 1.25 ± 0.08de 15.57 ± 0.19de 11.59 ± 0.09f 0.35 ± 0.01ab P90 3.72 ± 0.02b 64.94 ± 0.18c 1.17 ± 0.02ef 16.80 ± 0.07bc 13.03 ± 0.03d 0.34 ± 0.02abc The data are given as the mean ± standard deviation. a–f Within each column, values with different letters denote statistically significant differences between the means (p ≤ 0.05, Duncan's multiple range test). CAP = Catuai, CAPY = Caturra, H528Y = Cartimor H528 Yellow, H528R = Cartimor H528 Red, PNK = Bourbon Phanokkok, POP5 = Cartimor Populacao 5, P88 = Cartimor Progeny 88, P90 = Cartimor Progeny 90. Table 2.
Nutritional composition of different arabica coffee pulp varieties.
-
Coffee
varietiesTotal phenolic
content
(mgGAE/gDW)Total flavonoid
content
(mgCE/gDW)Antioxidant activity (%) DPPH ABTS CAP 5.09 ± 0.10cd 8.14 ± 0.25bcd 85.65 ± 3.59b 84.08 ± 0.87c CAPY 4.21 ± 0.06f 6.55 ± 0.34ef 85.58 ± 1.74b 88.80 ± 0.27a H528Y 5.30 ± 0.10b 8.44 ± 0.36bc 83.10 ± 0.43b 84.88 ± 0.56c H528R 4.66 ± 0.13e 7.17 ± 0.24de 83.63 ± 0.86b 86.37 ± 1.06bc PNK 4.90 ± 0.03d 7.50 ± 0.25cde 85.41 ± 0.11b 88.52 ± 0.74a POP5 4.94 ± 0.06d 7.30 ± 0.43de 84.08 ± 0.87b 84.97 ± 1.41c P88 6.41 ± 0.04a 10.28 ± 1.14a 88.81 ± 1.22a 88.80 ± 0.00a P90 4.31 ± 0.29f 6.07 ± 0.67f 83.58 ± 0.11b 85.72 ± 1.01c The data are given as the mean ± standard deviation. a–f Within each column, values with different letters denote statistically significant differences between the means (p ≤ 0.05, Duncan's multiple range test). CAP = Catuai, CAPY = Caturra, H528Y = Cartimor H528 Yellow, H528R = Cartimor H528 Red, PNK = Bourbon Phanokkok, POP5 = Cartimor Populacao 5, P88 = Cartimor Progeny 88, P90 = Cartimor Progeny 90. Table 3.
Phytochemical contents of different arabica coffee pulp varieties.
-
Coffee varieties Nitrogen (%) Phosphorus (mg/kg) Potassium (%) Calcium (%) Magnesium (mg/kg) Iron (mg/kg) CAP 2.00 ± 0.02e 1343.75 ± 38.25c 2.73 ± 0.02b 1.14 ± 0.06d 918.50 ± 6.50c 50.14 ± 1.40e CAPY 1.82 ± 0.02f 1125.50 ± 2.50h 2.66 ± 0.01b 1.28 ± 0.03c 936.25 ± 31.25c 58.34 ± 2.18c H528Y 2.17 ± 0.01c 1310.50 ± 9.50d 2.73 ± 0.06b 1.03 ± 0.04e 867.50 ± 7.51de 61.92 ± 0.04b H528R 2.47 ± 0.04a 1376.50 ± 5.50b 3.21 ± 0.03a 1.28 ± 0.04c 1001.50 ± 4.01b 83.44 ± 0.26a PNK 2.07 ± 0.05d 1282.50 ± 3.50e 2.50 ± 0.22c 1.47 ± 0.05a 1065.00 ± 62.50a 51.50 ± 2.60e POP5 2.29 ± 0.03b 1347.25 ± 9.75c 2.26 ± 0.02d 1.09 ± 0.02d 841.25 ± 8.75e 62.27 ± 1.37b P88 1.86 ± 0.02f 1190.25 ± 6.25g 2.17 ± 0.03de 1.40 ± 0.02b 834.00 ± 8.50e 44.46 ± 1.23f P90 2.09 ± 0.01d 1534.50 ± 12.50a 2.11 ± 0.08e 1.38 ± 0.00b 1021.25 ± 8.75b 55.38 ± 1.98d The data are given as the mean ± standard deviation. a–f Within each column, values with different letters denote statistically significant differences between the means (p ≤ 0.05, Duncan's multiple range test). CAP = Catuai, CAPY = Caturra, H528Y = Cartimor H528 Yellow, H528R = Cartimor H528 Red, PNK = Bourbon Phanokkok, POP5 = Cartimor Populacao 5, P88 = Cartimor Progeny 88, P90 = Cartimor Progeny 90. Table 4.
Mineral constituents of different arabica coffee pulp varieties.
-
Coffee varieties Degree of esterification (%) HCl-KCl Ammonium oxalate CAP* 54.30 ± 0.59ab 50.95 ± 0.14e CAPY* 53.28 ± 0.54cd 55.74 ± 0.19a H528Y* 53.68 ± 0.24bc 53.07 ± 0.10c H528R* 52.60 ± 0.21de 55.76 ± 0.17a PNK* 52.65 ± 0.10de 51.03 ± 0.13e POP5* 54.82 ± 0.22a 53.74 ± 0.28b P88* 52.81 ± 0.28de 53.22 ± 0.18c P90* 54.23 ± 0.23ab 51.96 ± 0.22d * There is no statistically significant difference within the same row using pair sample t-test analysis. a–e Different letters in the same column indicate significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) between means (one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test). CAP = Catuai, CAPY = Caturra, H528Y = Cartimor H528 Yellow, H528R = Cartimor H528 Red, PNK = Bourbon Phanokkok, POP5 = Cartimor Populacao 5, P88 = Cartimor Progeny 88, P90 = Cartimor Progeny 90. Table 5.
Degree of esterification of different arabica coffee pulp pectins using HCl-KCl buffer and ammonium oxalate solutions.
Figures
(5)
Tables
(5)