Microwave building as an application of wireless power transfer
-
1.
Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University, Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto 6110011, Japan. Phone: +81 774 38 3807
-
2.
Kajima Technical Research Institute, Kajima Corporation, Tobitakyu 2-19-1, Chofu, Tokyo 1820036, Japan
-
3.
Institute of Technology and Science, The University of Tokushima, Shinzo 2-24, Tokushima 7708501, Japan
-
4.
e-Devise Inc., Nijuyonken-Ichijo 4-1-10, Nishi, Sapporo 0630801, Japan
More Information
-
Author Bio:
 Naoki Shinohara
Naoki Shinohara received his B.E. degree in Electronic Engineering, the M.E. and Ph.D. (Eng.) degrees in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Japan, in 1991, 1993, and 1996, respectively. He was a research associate in the Radio Atmospheric Science Center, Kyoto University from 1998. He was a research associate of the Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere, Kyoto University by recognizing the Radio Atmospheric Science Center from 2000, and there he was an Associate Professor since 2001. He was an Associate Professor in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University by recognizing the Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere since 2004. From 2010, he has been a Professor in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University. He has been engaged in research on Solar Power Station/Satellite and Microwave Power Transmission system.
 Naoki Niwa
Naoki Niwa received his B.E. degree in Structural Engineering from Tsukuba University in 1982, and Ph.D. (Eng.) degree in Structural Engineering from Tsukuba University in 2000. He joined the Kajima Corporation in 1982, and has worked on the design of building structure. He was a research engineer of Kobori Research Complex, working on seismic response control from 1988. From 2003, he has been a chief research engineer in Kajima Technical of Research Institute (KaTRI), Kajima Corporation. He has been engaged in research on wireless power transfer in buildings, energy conversion, and seismic response control. In addition to his research activities, he worked on the project management of newly designed KaTRI H.Q. building. He has been a part-time lecturer, Tsukuba University from 2004. He is a P.E.Jp (Civil Engineering) and structural design 1st class architect.
 Kenji Takagi
Kenji Takagi received his B.E. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Keio University in 1986, and Ph.D. (Eng.) degree in Architecture and Building Science from Tohoku University in 1998. He joined the Kajima Corporation in 1986, and has worked on research of thermal fluid analysis. He was a researcher of Kajima Technical of Research Institute (KaTRI), Kajima Corporation from 1986. He was a visiting scientist in Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University from 1993 to 1994. He was a chief research engineer of KaTRI since 2005 and a lead researcher of Advanced Technology Incubation and Mechatronics Group of KaTRI since 2013. He has been engaged in research on wireless power transfer in buildings, energy conversion, and external wind forces to building.
 Kenniti Hamamoto
Kenniti Hamamoto received his B.E. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Kyoto University in 1995 and Ph.D. (Informatics) degree in Systems Science from Kyoto University in 2000. He joined Kajima Technical of Research Institute (KaTRI), Kajima Corporation in 2001, and has worked on the study of automonous control systems for building and civil construction equipments. Since 2004, he has been a Senior Research Engineer in KaTRI. He has been engaged in research on control for a power distribution system in buildings and control systems for civil construction equipments.
 Satoshi Ujigawa
Satoshi Ujigawa received his B.E. degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from Chiba University in 1999, M.E. degree in Natural Science from Chiba University in 2001, and Ph.D. (Eng.) degree in Electromagnetic Wave Engineering from Chiba University in 2011. He joined Kajima Technical of Research Institute (KaTRI) of Kajima Corporation as a research engineer in 2006, and has worked on Electromagnetic Compatibility in building environment. From 2013, he has been a Senior Research Engineer and a 3rd Class Electrical Chief Engineer. He is a member of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) EMC, AP, MTT, and MAG societies, and of American Geophysical Union(AGU).
 Jing-Ping Ao
Jing-Ping Ao received his B.S. degree in Physics in Wuhan University in 1989, Wuhan, M.S. degree in semiconductor physics and semiconductor device physics in Hebei Semiconductor Research Institute (HSRI) in 1992, Shijiazhuang, and Ph.D. degree in Electronic Engineering from Jilin University in 2000, Changchun, China. He joined HSRI in 1992, working on high-speed compound semiconductor devices and integrated circuits, optoelectronic devices and optoelectronic integrated circuits. He joined The University of Tokushima, Japan, in February 2001, and currently he is an Associate Professor involved in the research and development of wide bandgap semiconductor (gallium nitride etc.) electronic devices, monolithic integrated circuits, chemical sensor, and optoelectronic devices. He has published more than 120 scientific papers, chapters of book and international conference presentations. He holds several patents on gallium nitride light-emitting diodes and electron devices. He was invited for scientific lectures by prestigious universities and institutes for more than 20 times. Dr. Ao is a senior member of the IEEE and a member of The Electrochemical Society, The Japan Society of Applied Physics and The Institute of the Electronics, Information, and Communication Engineers.
 Yasuo Ohno
Yasuo Ohno received his B.A. degree in Pure and Applied Science from Tokyo University in 1970, and his Ph.D. degree in Electrical Engineering from the Tokyo Institute of Technology in 1994. He joined NEC Corporation in 1970, and has worked on semiconductor devices including silicon LSIs, GaAs LEDs and FETs, and GaN FETs. He joined the University of Tokushima in 2001. He was a Professor in the Institute of Technology and Science, and worked on the research of GaN power devices and its application to microwave systems. In 2012, he established e-Device, Inc. in Sapporo, Japan, and now a director of e-Device, Inc. Dr. Ohno is a member of the Japan Society of Applied Physics and the IEEE, a fellow of the Institute of Electronics, Information, and Communication Engineers (IEICE)
-
Corresponding author:
N. Shinohara Email: shino@rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp
-
Abstract
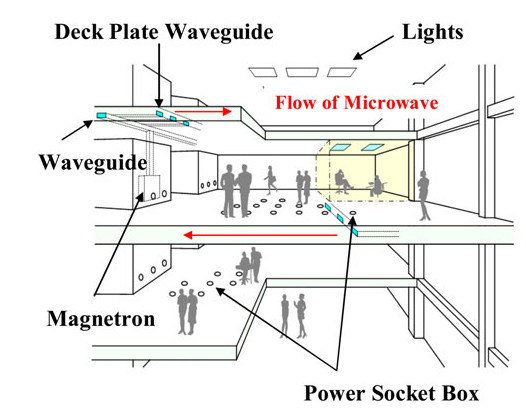
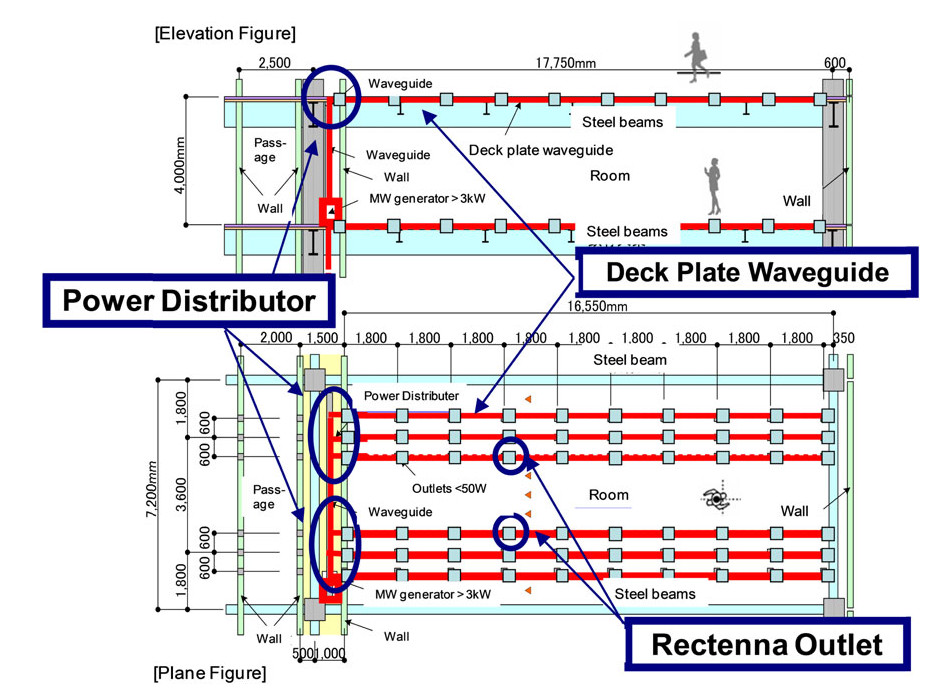
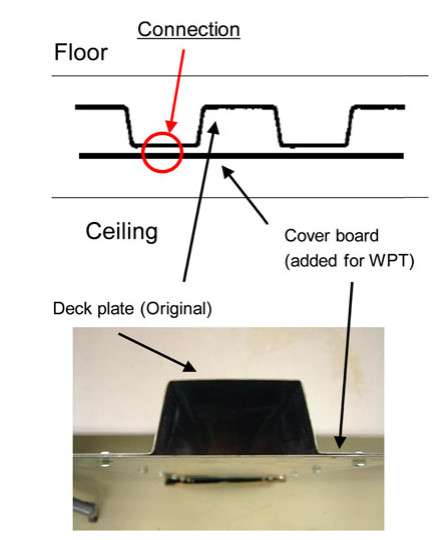
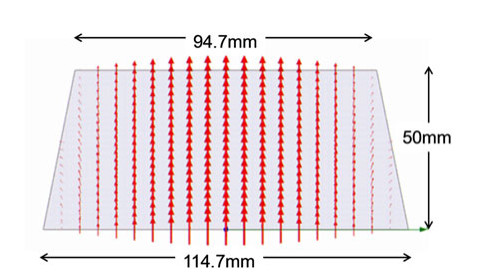
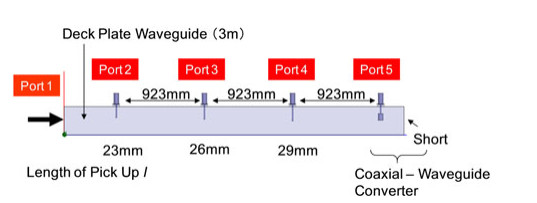
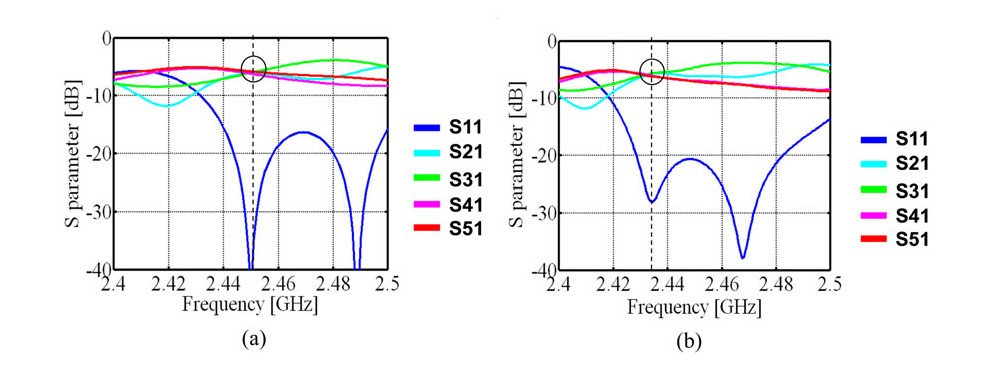
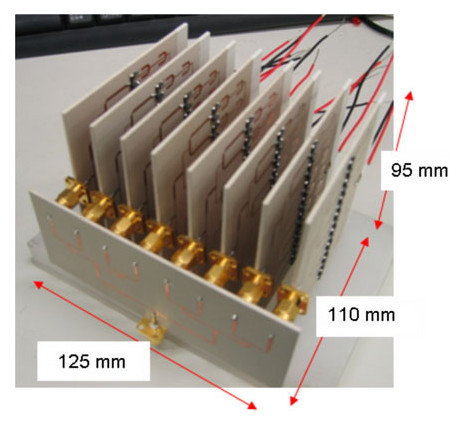
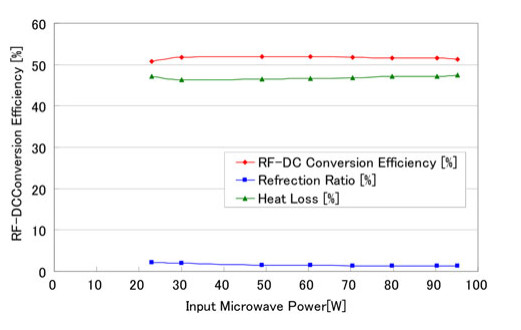
We propose a wireless power distribution system (WPDS) operating at 2.45 GHz CW in buildings instead of wired power distribution in order to reduce the initial cost of the building. Required technologies for the WPDS are (a) low-cost and low-loss deck plate waveguide, (b) variable microwave power distributor for the waveguide, and (c) high-power (> 100 W) rectifier at the outlet. We developed and tested the deck plate waveguide, power distributor, and high-power rectenna consisting of 256 Si Schottky barrier diodes and newly developed GaN diodes. Finally, a test WPDS was built and microwave power transmission experiments were conducted. The total efficiency of the test WPDS was estimated to be 52%.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Shinohara N, Niwa N, Takagi K, Hamamoto K, Ujigawa S, et al. 2014. Microwave building as an application of wireless power transfer. Wireless Power Transfer 1(1): 1-9 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2014.1
|
Shinohara N, Niwa N, Takagi K, Hamamoto K, Ujigawa S, et al. 2014. Microwave building as an application of wireless power transfer. Wireless Power Transfer 1(1): 1-9 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2014.1
|









 Naoki Shinohara received his B.E. degree in Electronic Engineering, the M.E. and Ph.D. (Eng.) degrees in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Japan, in 1991, 1993, and 1996, respectively. He was a research associate in the Radio Atmospheric Science Center, Kyoto University from 1998. He was a research associate of the Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere, Kyoto University by recognizing the Radio Atmospheric Science Center from 2000, and there he was an Associate Professor since 2001. He was an Associate Professor in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University by recognizing the Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere since 2004. From 2010, he has been a Professor in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University. He has been engaged in research on Solar Power Station/Satellite and Microwave Power Transmission system.
Naoki Shinohara received his B.E. degree in Electronic Engineering, the M.E. and Ph.D. (Eng.) degrees in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Japan, in 1991, 1993, and 1996, respectively. He was a research associate in the Radio Atmospheric Science Center, Kyoto University from 1998. He was a research associate of the Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere, Kyoto University by recognizing the Radio Atmospheric Science Center from 2000, and there he was an Associate Professor since 2001. He was an Associate Professor in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University by recognizing the Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere since 2004. From 2010, he has been a Professor in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University. He has been engaged in research on Solar Power Station/Satellite and Microwave Power Transmission system.  Naoki Niwa received his B.E. degree in Structural Engineering from Tsukuba University in 1982, and Ph.D. (Eng.) degree in Structural Engineering from Tsukuba University in 2000. He joined the Kajima Corporation in 1982, and has worked on the design of building structure. He was a research engineer of Kobori Research Complex, working on seismic response control from 1988. From 2003, he has been a chief research engineer in Kajima Technical of Research Institute (KaTRI), Kajima Corporation. He has been engaged in research on wireless power transfer in buildings, energy conversion, and seismic response control. In addition to his research activities, he worked on the project management of newly designed KaTRI H.Q. building. He has been a part-time lecturer, Tsukuba University from 2004. He is a P.E.Jp (Civil Engineering) and structural design 1st class architect.
Naoki Niwa received his B.E. degree in Structural Engineering from Tsukuba University in 1982, and Ph.D. (Eng.) degree in Structural Engineering from Tsukuba University in 2000. He joined the Kajima Corporation in 1982, and has worked on the design of building structure. He was a research engineer of Kobori Research Complex, working on seismic response control from 1988. From 2003, he has been a chief research engineer in Kajima Technical of Research Institute (KaTRI), Kajima Corporation. He has been engaged in research on wireless power transfer in buildings, energy conversion, and seismic response control. In addition to his research activities, he worked on the project management of newly designed KaTRI H.Q. building. He has been a part-time lecturer, Tsukuba University from 2004. He is a P.E.Jp (Civil Engineering) and structural design 1st class architect.  Kenji Takagi received his B.E. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Keio University in 1986, and Ph.D. (Eng.) degree in Architecture and Building Science from Tohoku University in 1998. He joined the Kajima Corporation in 1986, and has worked on research of thermal fluid analysis. He was a researcher of Kajima Technical of Research Institute (KaTRI), Kajima Corporation from 1986. He was a visiting scientist in Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University from 1993 to 1994. He was a chief research engineer of KaTRI since 2005 and a lead researcher of Advanced Technology Incubation and Mechatronics Group of KaTRI since 2013. He has been engaged in research on wireless power transfer in buildings, energy conversion, and external wind forces to building.
Kenji Takagi received his B.E. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Keio University in 1986, and Ph.D. (Eng.) degree in Architecture and Building Science from Tohoku University in 1998. He joined the Kajima Corporation in 1986, and has worked on research of thermal fluid analysis. He was a researcher of Kajima Technical of Research Institute (KaTRI), Kajima Corporation from 1986. He was a visiting scientist in Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University from 1993 to 1994. He was a chief research engineer of KaTRI since 2005 and a lead researcher of Advanced Technology Incubation and Mechatronics Group of KaTRI since 2013. He has been engaged in research on wireless power transfer in buildings, energy conversion, and external wind forces to building.  Kenniti Hamamoto received his B.E. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Kyoto University in 1995 and Ph.D. (Informatics) degree in Systems Science from Kyoto University in 2000. He joined Kajima Technical of Research Institute (KaTRI), Kajima Corporation in 2001, and has worked on the study of automonous control systems for building and civil construction equipments. Since 2004, he has been a Senior Research Engineer in KaTRI. He has been engaged in research on control for a power distribution system in buildings and control systems for civil construction equipments.
Kenniti Hamamoto received his B.E. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Kyoto University in 1995 and Ph.D. (Informatics) degree in Systems Science from Kyoto University in 2000. He joined Kajima Technical of Research Institute (KaTRI), Kajima Corporation in 2001, and has worked on the study of automonous control systems for building and civil construction equipments. Since 2004, he has been a Senior Research Engineer in KaTRI. He has been engaged in research on control for a power distribution system in buildings and control systems for civil construction equipments.  Satoshi Ujigawa received his B.E. degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from Chiba University in 1999, M.E. degree in Natural Science from Chiba University in 2001, and Ph.D. (Eng.) degree in Electromagnetic Wave Engineering from Chiba University in 2011. He joined Kajima Technical of Research Institute (KaTRI) of Kajima Corporation as a research engineer in 2006, and has worked on Electromagnetic Compatibility in building environment. From 2013, he has been a Senior Research Engineer and a 3rd Class Electrical Chief Engineer. He is a member of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) EMC, AP, MTT, and MAG societies, and of American Geophysical Union(AGU).
Satoshi Ujigawa received his B.E. degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from Chiba University in 1999, M.E. degree in Natural Science from Chiba University in 2001, and Ph.D. (Eng.) degree in Electromagnetic Wave Engineering from Chiba University in 2011. He joined Kajima Technical of Research Institute (KaTRI) of Kajima Corporation as a research engineer in 2006, and has worked on Electromagnetic Compatibility in building environment. From 2013, he has been a Senior Research Engineer and a 3rd Class Electrical Chief Engineer. He is a member of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) EMC, AP, MTT, and MAG societies, and of American Geophysical Union(AGU).  Jing-Ping Ao received his B.S. degree in Physics in Wuhan University in 1989, Wuhan, M.S. degree in semiconductor physics and semiconductor device physics in Hebei Semiconductor Research Institute (HSRI) in 1992, Shijiazhuang, and Ph.D. degree in Electronic Engineering from Jilin University in 2000, Changchun, China. He joined HSRI in 1992, working on high-speed compound semiconductor devices and integrated circuits, optoelectronic devices and optoelectronic integrated circuits. He joined The University of Tokushima, Japan, in February 2001, and currently he is an Associate Professor involved in the research and development of wide bandgap semiconductor (gallium nitride etc.) electronic devices, monolithic integrated circuits, chemical sensor, and optoelectronic devices. He has published more than 120 scientific papers, chapters of book and international conference presentations. He holds several patents on gallium nitride light-emitting diodes and electron devices. He was invited for scientific lectures by prestigious universities and institutes for more than 20 times. Dr. Ao is a senior member of the IEEE and a member of The Electrochemical Society, The Japan Society of Applied Physics and The Institute of the Electronics, Information, and Communication Engineers.
Jing-Ping Ao received his B.S. degree in Physics in Wuhan University in 1989, Wuhan, M.S. degree in semiconductor physics and semiconductor device physics in Hebei Semiconductor Research Institute (HSRI) in 1992, Shijiazhuang, and Ph.D. degree in Electronic Engineering from Jilin University in 2000, Changchun, China. He joined HSRI in 1992, working on high-speed compound semiconductor devices and integrated circuits, optoelectronic devices and optoelectronic integrated circuits. He joined The University of Tokushima, Japan, in February 2001, and currently he is an Associate Professor involved in the research and development of wide bandgap semiconductor (gallium nitride etc.) electronic devices, monolithic integrated circuits, chemical sensor, and optoelectronic devices. He has published more than 120 scientific papers, chapters of book and international conference presentations. He holds several patents on gallium nitride light-emitting diodes and electron devices. He was invited for scientific lectures by prestigious universities and institutes for more than 20 times. Dr. Ao is a senior member of the IEEE and a member of The Electrochemical Society, The Japan Society of Applied Physics and The Institute of the Electronics, Information, and Communication Engineers.  Yasuo Ohno received his B.A. degree in Pure and Applied Science from Tokyo University in 1970, and his Ph.D. degree in Electrical Engineering from the Tokyo Institute of Technology in 1994. He joined NEC Corporation in 1970, and has worked on semiconductor devices including silicon LSIs, GaAs LEDs and FETs, and GaN FETs. He joined the University of Tokushima in 2001. He was a Professor in the Institute of Technology and Science, and worked on the research of GaN power devices and its application to microwave systems. In 2012, he established e-Device, Inc. in Sapporo, Japan, and now a director of e-Device, Inc. Dr. Ohno is a member of the Japan Society of Applied Physics and the IEEE, a fellow of the Institute of Electronics, Information, and Communication Engineers (IEICE)
Yasuo Ohno received his B.A. degree in Pure and Applied Science from Tokyo University in 1970, and his Ph.D. degree in Electrical Engineering from the Tokyo Institute of Technology in 1994. He joined NEC Corporation in 1970, and has worked on semiconductor devices including silicon LSIs, GaAs LEDs and FETs, and GaN FETs. He joined the University of Tokushima in 2001. He was a Professor in the Institute of Technology and Science, and worked on the research of GaN power devices and its application to microwave systems. In 2012, he established e-Device, Inc. in Sapporo, Japan, and now a director of e-Device, Inc. Dr. Ohno is a member of the Japan Society of Applied Physics and the IEEE, a fellow of the Institute of Electronics, Information, and Communication Engineers (IEICE)