Flat-topped beam forming experiment for microwave power transfer system to a vehicle roof
-
Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University, Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto, 6110011, Japan
More Information
-
Author Bio:
 Takaki Ishikawa
Takaki Ishikawa received the B.E. degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, the M.E. degree in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, in 2010 and 2012, respectively. He is presently a doctor course student of Electrical engineering in Kyoto University. His present research interests include microwave power transmission system.
 Naoki Shinohara
Naoki Shinohara received the B.E. degree in Electronic Engineering, the M.E. and Ph.D (Eng.) degrees in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Japan, in 1991, 1993, and 1996, respectively. He was a Research Associate in the Radio Atmospheric Science Center, Kyoto University from 1998. He was a Research Associate of the Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere, Kyoto University by recognizing the Radio Atmospheric Science Center from 2000, and there he was an Associate Professor since 2001. He was an Associate Professor in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University by recognizing the Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere since 2004. From 2010, he has been a professor in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University. He has been engaged in research on Solar Power Station/Satellite and Microwave Power Transmission system
-
Corresponding author:
T. Ishikawa Email: i-takaki@rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp
-
Abstract
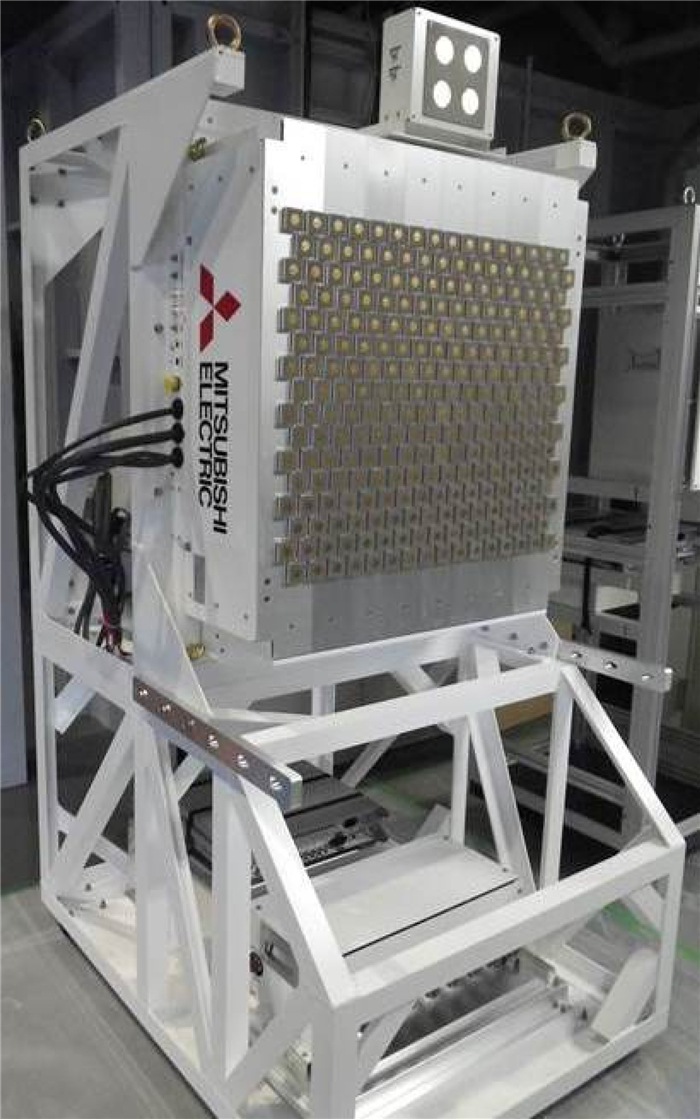
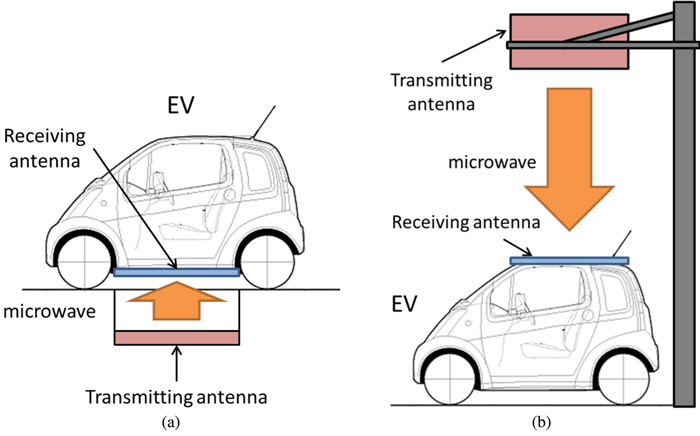
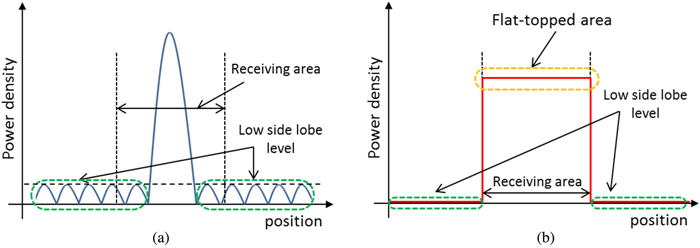
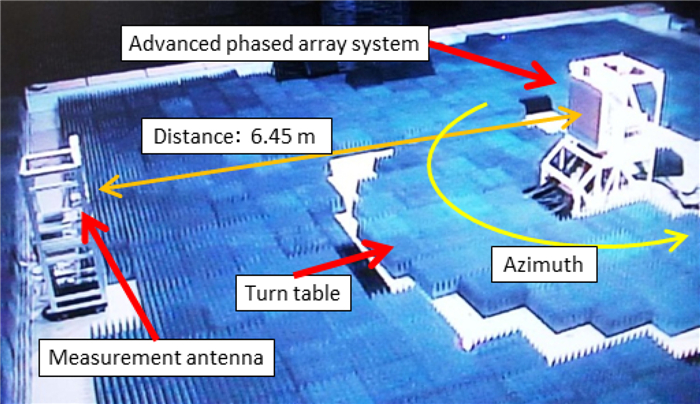
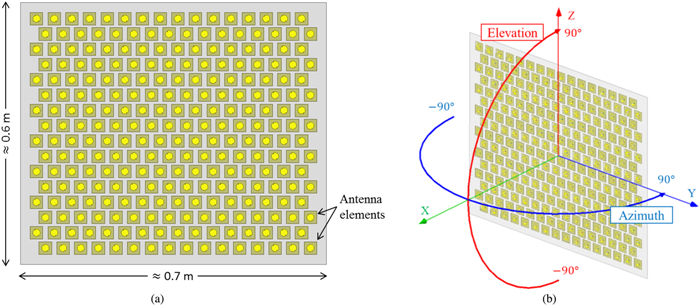
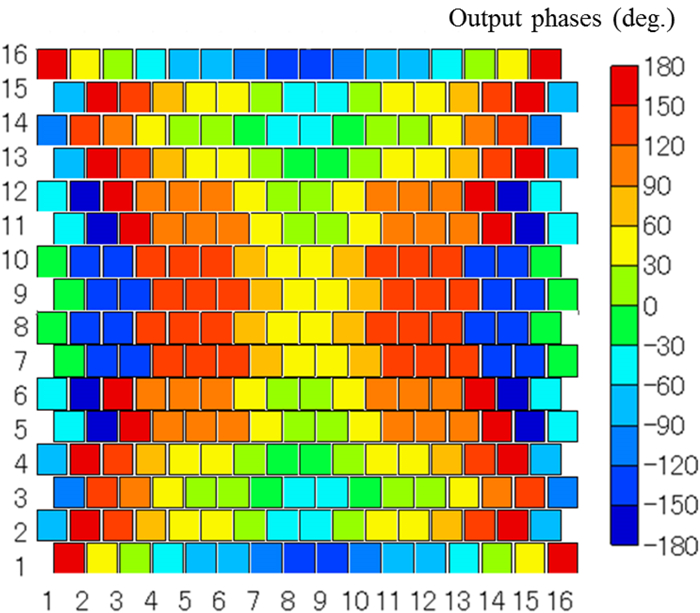
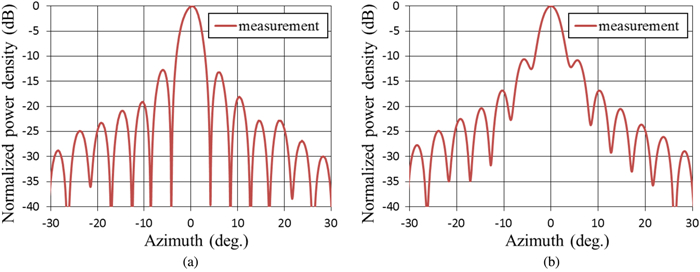
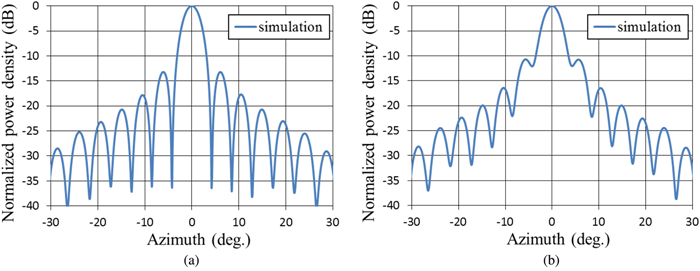
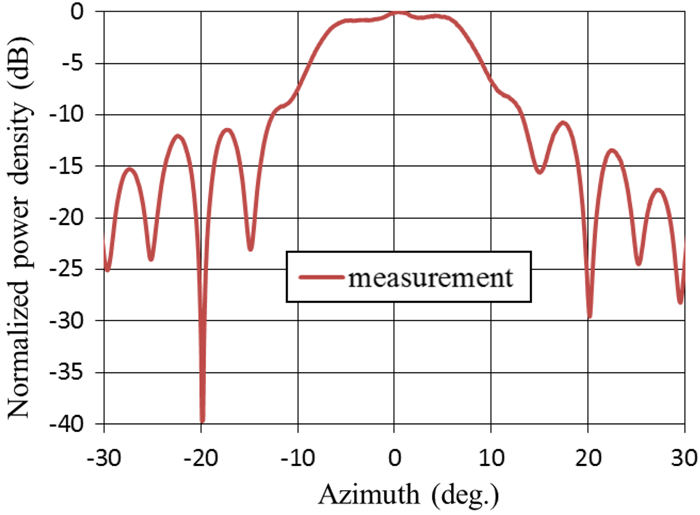
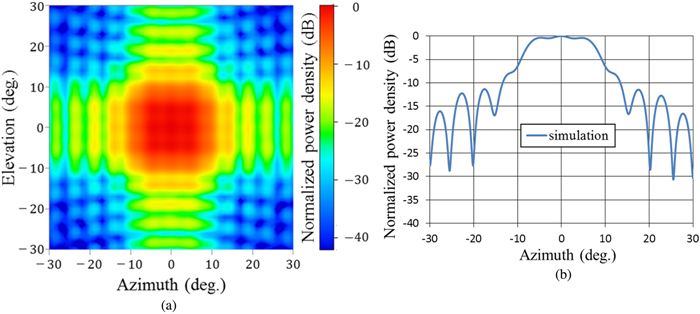
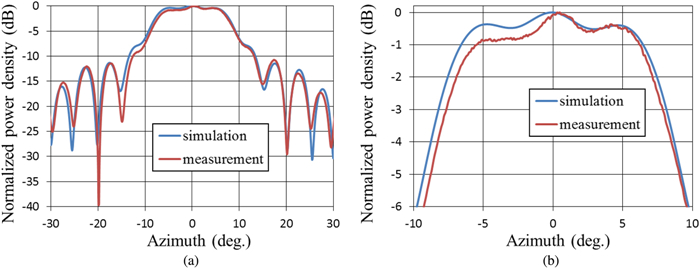
We proposed and examined a microwave power transfer system for electric vehicles (EVs). In this system, electricity is transmitted from a transmitting antenna over an EV to a receiving antenna on the roof of the EV. We used a rectenna to convert the received microwave power to direct current power. The conversion efficiency of a rectenna array is affected by the input power level distribution, and we have to form a flat-topped beam pattern to increase the conversion efficiency. We conducted an experiment to form a flat-topped beam pattern by using a phased array antenna. In this experiment, the output power of each antenna element is uniform and cannot be controlled independently. Hence, we controlled only the output phases of each antenna element and formed a flat-topped beam pattern. The distance between the transmitting antenna and the receiving area is 6.45 m, and the receiving area corresponds to a space in which the azimuth and elevation are in the range of −5°–5°.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Ishikawa T, Shinohara N. 2015. Flat-topped beam forming experiment for microwave power transfer system to a vehicle roof. Wireless Power Transfer 2(1): 15-21 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2015.5
|
Ishikawa T, Shinohara N. 2015. Flat-topped beam forming experiment for microwave power transfer system to a vehicle roof. Wireless Power Transfer 2(1): 15-21 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2015.5
|









 Takaki Ishikawa received the B.E. degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, the M.E. degree in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, in 2010 and 2012, respectively. He is presently a doctor course student of Electrical engineering in Kyoto University. His present research interests include microwave power transmission system.
Takaki Ishikawa received the B.E. degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, the M.E. degree in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, in 2010 and 2012, respectively. He is presently a doctor course student of Electrical engineering in Kyoto University. His present research interests include microwave power transmission system.  Naoki Shinohara received the B.E. degree in Electronic Engineering, the M.E. and Ph.D (Eng.) degrees in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Japan, in 1991, 1993, and 1996, respectively. He was a Research Associate in the Radio Atmospheric Science Center, Kyoto University from 1998. He was a Research Associate of the Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere, Kyoto University by recognizing the Radio Atmospheric Science Center from 2000, and there he was an Associate Professor since 2001. He was an Associate Professor in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University by recognizing the Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere since 2004. From 2010, he has been a professor in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University. He has been engaged in research on Solar Power Station/Satellite and Microwave Power Transmission system
Naoki Shinohara received the B.E. degree in Electronic Engineering, the M.E. and Ph.D (Eng.) degrees in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Japan, in 1991, 1993, and 1996, respectively. He was a Research Associate in the Radio Atmospheric Science Center, Kyoto University from 1998. He was a Research Associate of the Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere, Kyoto University by recognizing the Radio Atmospheric Science Center from 2000, and there he was an Associate Professor since 2001. He was an Associate Professor in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University by recognizing the Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere since 2004. From 2010, he has been a professor in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University. He has been engaged in research on Solar Power Station/Satellite and Microwave Power Transmission system