-
About this article
Cite this article
Xia Q, Yan L. 2016. Application of wireless power transfer technologies and intermittent energy harvesting for wireless sensors in rotating machines. Wireless Power Transfer 3(2): 93-104 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2016.6
Application of wireless power transfer technologies and intermittent energy harvesting for wireless sensors in rotating machines
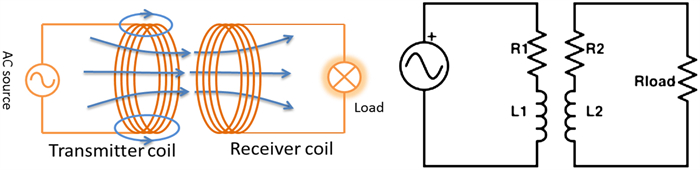
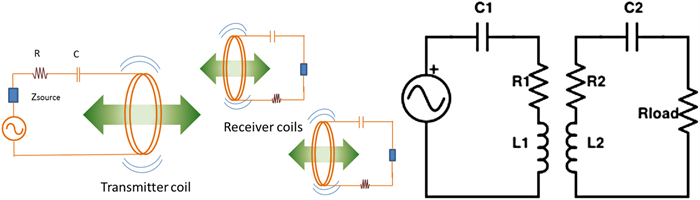
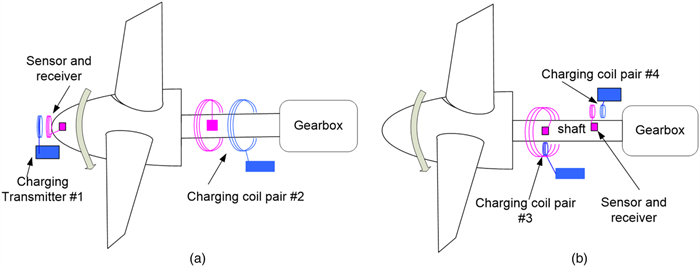
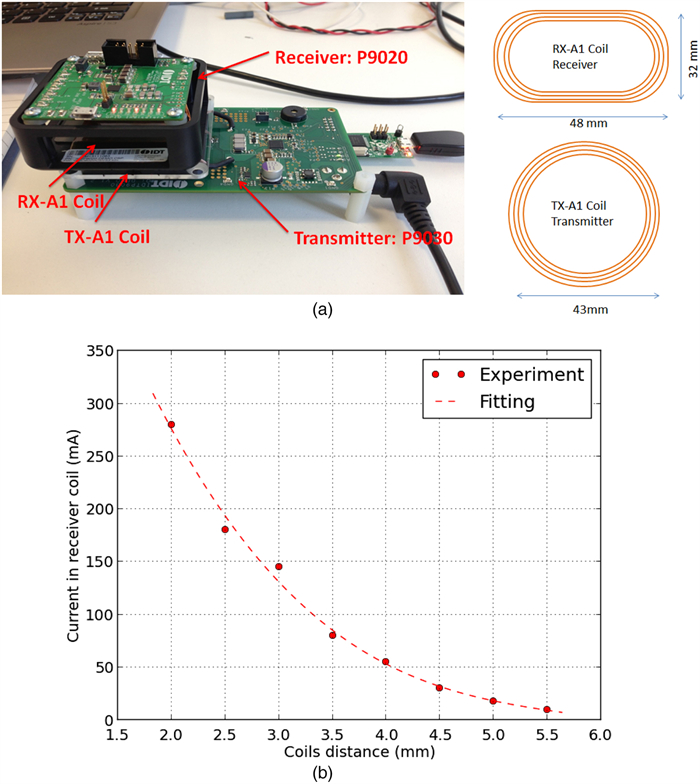
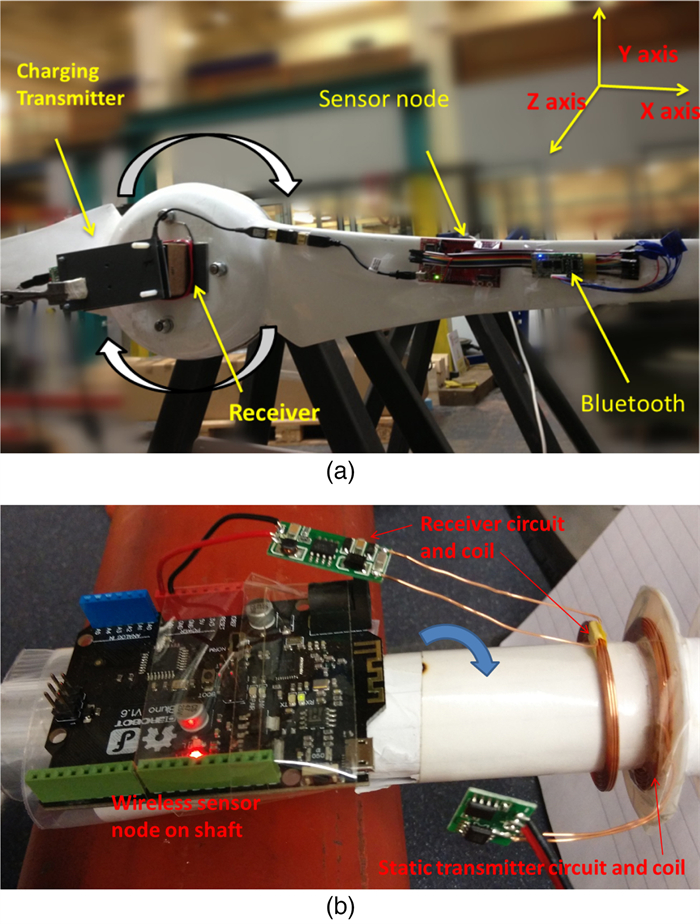
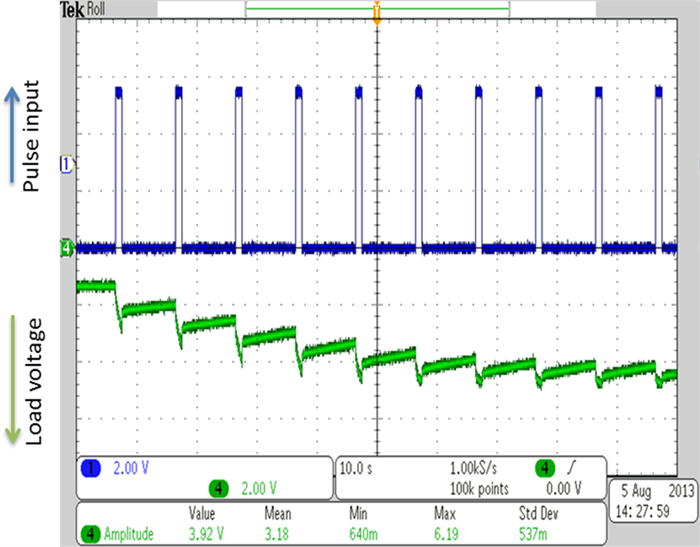
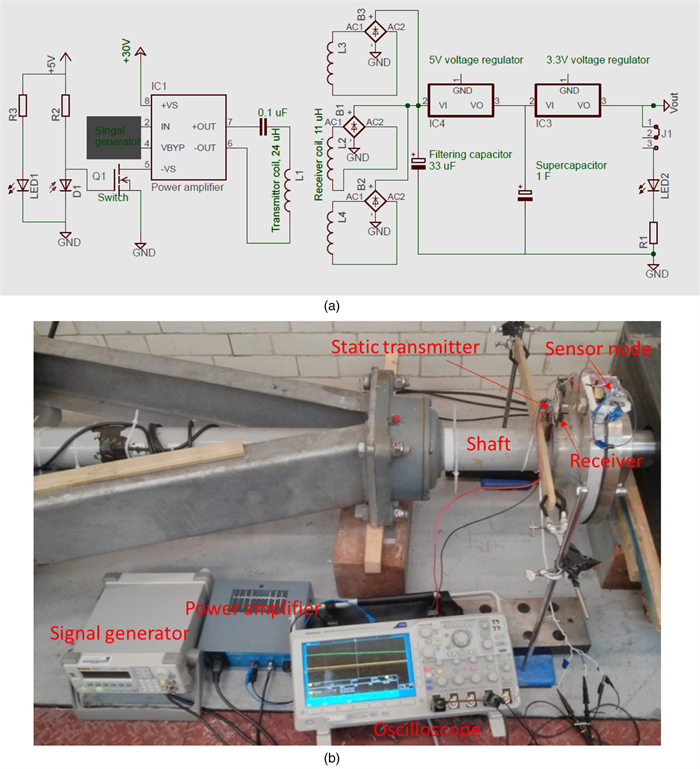
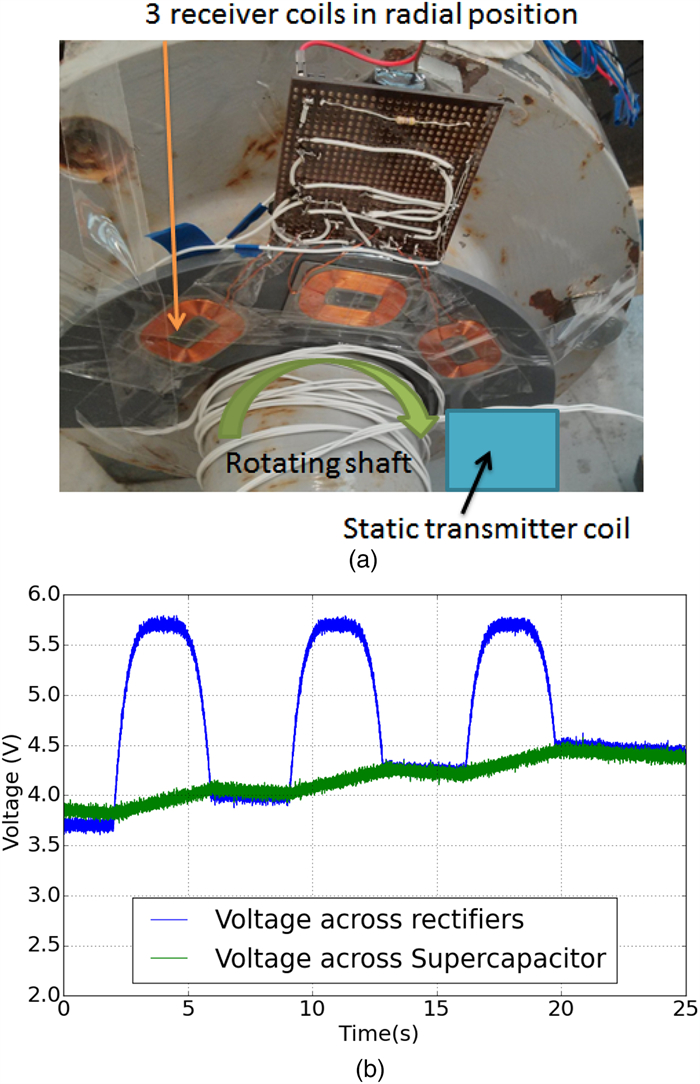
Abstract: Battery-powered wireless sensor networks have been extensively deployed in condition monitoring and structural health monitoring systems, but the performance of wireless sensors are limited by battery capacity and difficulty of application in rotating machines. In this paper, a variety of commercial wireless charging solutions and coil-shaft configurations for magnetic coupling are compared, having in mind of the application of continuously charging wireless sensors on rotating machines. For the co-axial configuration of the transmitter coil and the receiver coil, a Qi standard compliant wireless charging kit and a custom charging circuit are successfully applied to charge wireless sensors on small rotating test rigs. In order to harvest and store intermittent energy input from the wireless power source, a prototype receiver circuit using a supercapacitor and low-dropout regulator is designed and validated. Based on the prototype circuit, the radial configuration of single transmitter coil and multiple receiver coils is demonstrated for wireless power transfer to the sensor nodes on the drivetrain of a small wind turbine test rig.
-
Key words:
- Condition monitoring /
- Rotating machine /
- Supercapacitor /
- WPT /
- Wireless sensor









 Qingfeng Xia obtained his Ph.D. degree from the University of Manchester in March 2012. Currently, he is a Research Associate at the Department of Engineering Science, the University of Oxford. His research interests include fluid visualization, condition monitoring of turbomachines, and sensor and instrumentations.
Qingfeng Xia obtained his Ph.D. degree from the University of Manchester in March 2012. Currently, he is a Research Associate at the Department of Engineering Science, the University of Oxford. His research interests include fluid visualization, condition monitoring of turbomachines, and sensor and instrumentations.  Longyang Yan received the B.Eng (2012) and M.Sc. degree (2013) from University of Strathclyde, UK. He is currently working for the China subsidiary of Safe Engineering Services & technologies Ltd (SES-China). His research interests include the computation of EM field, EMI analysis & power system grounding
Longyang Yan received the B.Eng (2012) and M.Sc. degree (2013) from University of Strathclyde, UK. He is currently working for the China subsidiary of Safe Engineering Services & technologies Ltd (SES-China). His research interests include the computation of EM field, EMI analysis & power system grounding