Contactless power transfer system for sealed lead acid battery charging
-
Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, Guwahati – 781039, Assam, India
More Information
-
Author Bio:
 Gautam Rituraj
Gautam Rituraj received the B.Tech. degree in Electrical Engineering from the Uttar Pradesh Technical University, Lucknow, India, in 2012. He is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree with the Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering, IIT Guwahati, Guwahati, India. His current research interests include the analysis and design of stationary wireless power transfer systems and developing the power electronic circuits for electric vehicle charging.
 Brijesh Kumar Kushwaha
Brijesh Kumar Kushwaha received the B.Tech. degree in Electronics and Communication Engineering from the Uttar Pradesh Technical University, Lucknow, India, in 2010, and the M.Tech. degree in Power Electronics and Application Specified Integrated Circuit Design from the Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology, Allahabad, India, in 2012. He is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree with IIT Guwahati, Guwahati, India. His current research interests include the modeling of wireless power transfer systems, magnetic field theory, and power electronics.
 Praveen Kumar
Praveen Kumar received the B.Tech. degree in Electrical Engineering from the National Institute of Technology, Hamirpur, India, in 1998, the M.Tech. degree in Energy System from the IIT, Delhi, India, in 2000, and the Ph.D. degree from the Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands. He is currently an Associate Professor with IIT Guwahati, Guwahati, India. He was a Team Leader of Hybrid Systems with Drive Trains Innovation, Eindhoven, The Netherlands. His current research interests include optimization of electrical motors and drives, hybrid and electric vehicles, smart grid, and wireless charging of electric vehicles
-
Corresponding author:
G. Rituraj Email: g.rituraj@iitg.ernet.in
-
Abstract
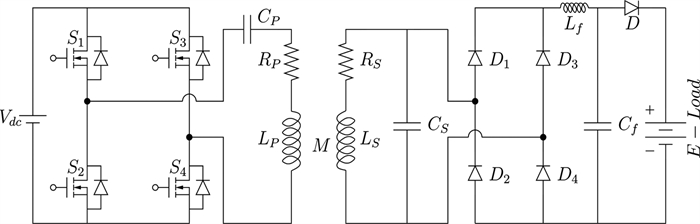
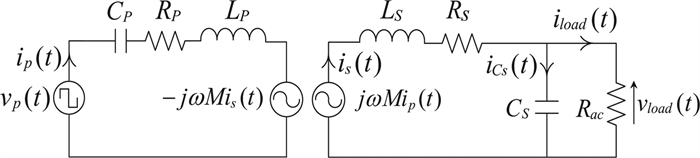
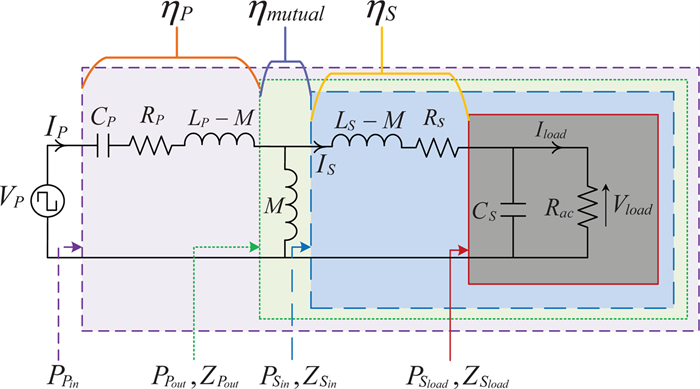
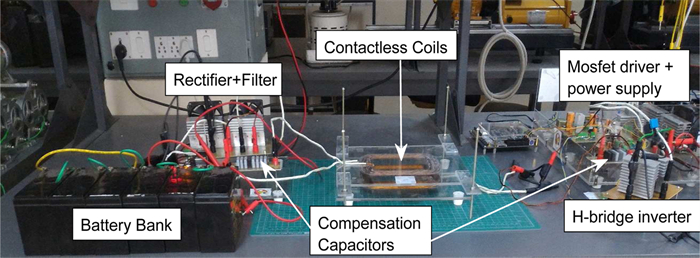
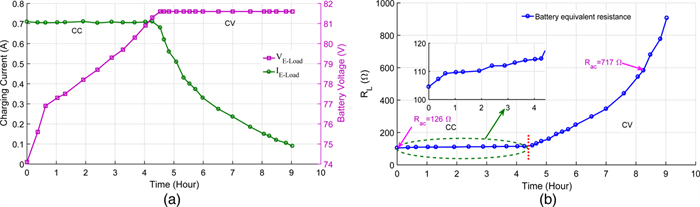
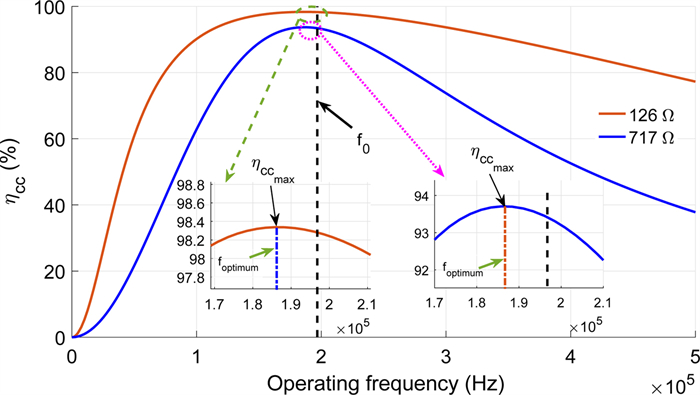
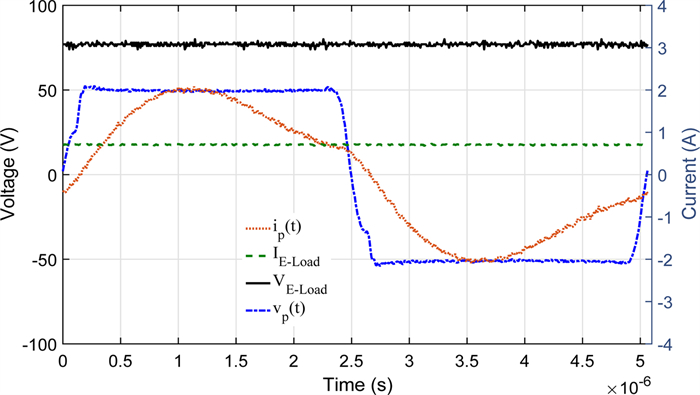
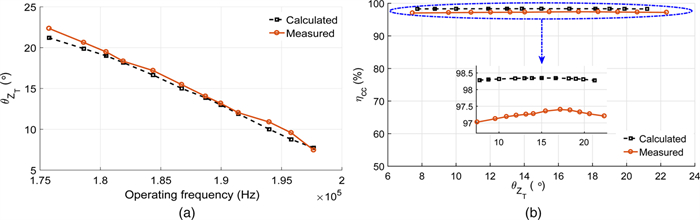
In this paper, an experimental study is carried out while charging the sealed lead acid battery bank using a series-parallel (SP) compensated contactless power transfer (CPT) system. Constant current (CC) and constant voltage (CV) modes are used for charging the battery bank. An expression of optimum operating frequency is derived to maintain the maximum compensated coil efficiency throughout the load variation in charging process. An experimental setup of SP compensated CPT system is built for charging the battery bank. The variation of compensated coil efficiency and the load phase angle with respect to different operating frequencies in CC and CV modes is verified with the measurement. Based on the analysis, the control parameters are identified.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Rituraj G, Kushwaha B K, Kumar P. 2018. Contactless power transfer system for sealed lead acid battery charging. Wireless Power Transfer 5(1): 20-26 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2017.18
|
Rituraj G, Kushwaha B K, Kumar P. 2018. Contactless power transfer system for sealed lead acid battery charging. Wireless Power Transfer 5(1): 20-26 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2017.18
|









 Gautam Rituraj received the B.Tech. degree in Electrical Engineering from the Uttar Pradesh Technical University, Lucknow, India, in 2012. He is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree with the Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering, IIT Guwahati, Guwahati, India. His current research interests include the analysis and design of stationary wireless power transfer systems and developing the power electronic circuits for electric vehicle charging.
Gautam Rituraj received the B.Tech. degree in Electrical Engineering from the Uttar Pradesh Technical University, Lucknow, India, in 2012. He is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree with the Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering, IIT Guwahati, Guwahati, India. His current research interests include the analysis and design of stationary wireless power transfer systems and developing the power electronic circuits for electric vehicle charging.  Brijesh Kumar Kushwaha received the B.Tech. degree in Electronics and Communication Engineering from the Uttar Pradesh Technical University, Lucknow, India, in 2010, and the M.Tech. degree in Power Electronics and Application Specified Integrated Circuit Design from the Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology, Allahabad, India, in 2012. He is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree with IIT Guwahati, Guwahati, India. His current research interests include the modeling of wireless power transfer systems, magnetic field theory, and power electronics.
Brijesh Kumar Kushwaha received the B.Tech. degree in Electronics and Communication Engineering from the Uttar Pradesh Technical University, Lucknow, India, in 2010, and the M.Tech. degree in Power Electronics and Application Specified Integrated Circuit Design from the Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology, Allahabad, India, in 2012. He is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree with IIT Guwahati, Guwahati, India. His current research interests include the modeling of wireless power transfer systems, magnetic field theory, and power electronics.  Praveen Kumar received the B.Tech. degree in Electrical Engineering from the National Institute of Technology, Hamirpur, India, in 1998, the M.Tech. degree in Energy System from the IIT, Delhi, India, in 2000, and the Ph.D. degree from the Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands. He is currently an Associate Professor with IIT Guwahati, Guwahati, India. He was a Team Leader of Hybrid Systems with Drive Trains Innovation, Eindhoven, The Netherlands. His current research interests include optimization of electrical motors and drives, hybrid and electric vehicles, smart grid, and wireless charging of electric vehicles
Praveen Kumar received the B.Tech. degree in Electrical Engineering from the National Institute of Technology, Hamirpur, India, in 1998, the M.Tech. degree in Energy System from the IIT, Delhi, India, in 2000, and the Ph.D. degree from the Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands. He is currently an Associate Professor with IIT Guwahati, Guwahati, India. He was a Team Leader of Hybrid Systems with Drive Trains Innovation, Eindhoven, The Netherlands. His current research interests include optimization of electrical motors and drives, hybrid and electric vehicles, smart grid, and wireless charging of electric vehicles