Sidelobe reduction with a GaN active array antenna
-
Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University, Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan. Phone: +81 774 38 3853
More Information
-
Author Bio:
 Naoki Hasegawa
Naoki Hasegawa was born in Aichi, Japan, on June 18, 1988. He received his B.E. degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from Ritsumeikan University, Siga, Japan, and his M.E. degree in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, in 2011 and 2013, respectively. He was a research associate in The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) from 2013 to 2015. He is a student member of the Institute of Electronics, Information and Communication Engineers (IEICE) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE). His research activities include RF GaN power amplifier and antenna design for wireless power transfer and up-link satellite communications.
 Naoki Shinohara
Naoki Shinohara received the B.E. degree in Electronic Engineering, the M.E. and Ph.D. (Eng.) degrees in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Japan, in 1991, 1993, and 1996, respectively. He was a research associate in Kyoto University from 1996. From 2010, he has been a professor in Kyoto University. He has been engaged in research on Solar Power Station/Satellite and Microwave Power Transmission system. He is IEEE MTT-S Technical Committee 26 (Wireless Power Transfer and Conversion) vice chair, IEEE MTT-S Kansai Chapter TPC member, IEEE Wireless Power Transfer Conference advisory committee member, International Journal of Wireless Power Transfer (Cambridge Press) executive editor, technical committee on IEICE Wireless Power Transfer, communications society member, Japan Society of Electromagnetic Wave Energy Applications vice president, Space Solar Power Systems Society board member, Wireless Power Transfer Consortium for Practical Applications (WiPoT) chair, and Wireless Power Management Consortium (WPMc) chair
-
Corresponding author:
N. Hasegawa Email: naoki_hasegawa@rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp
-
Abstract
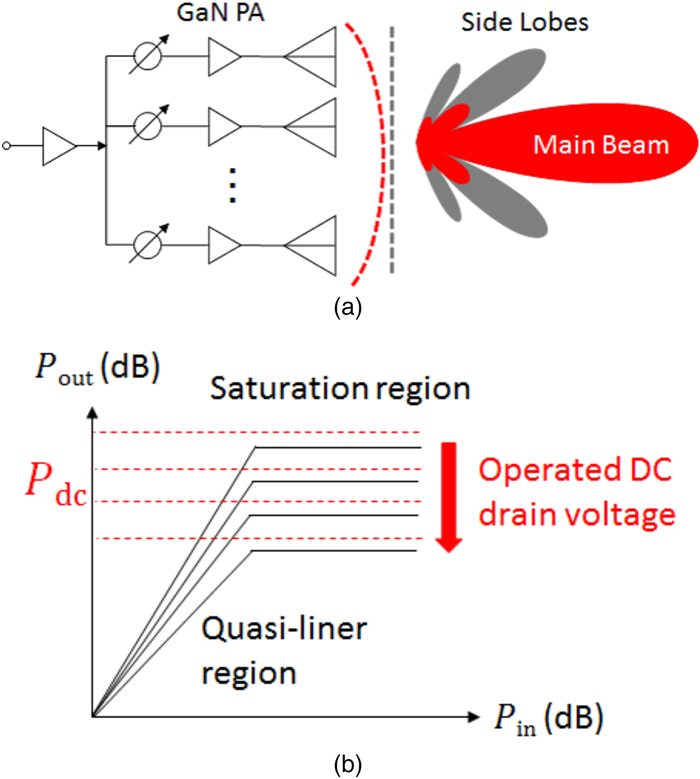
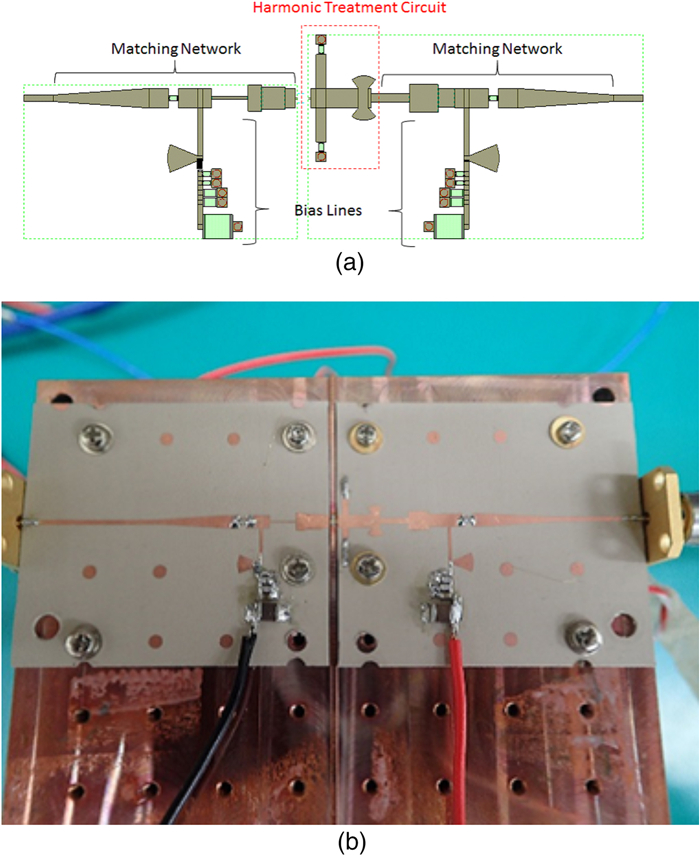
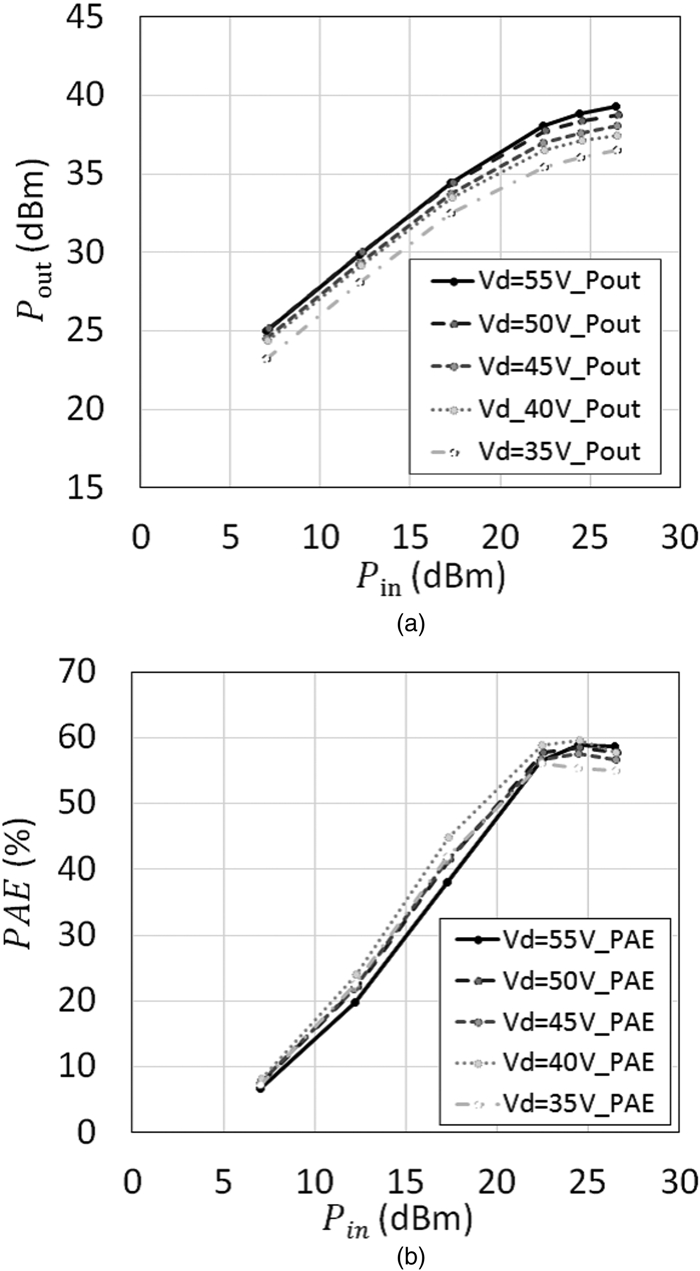
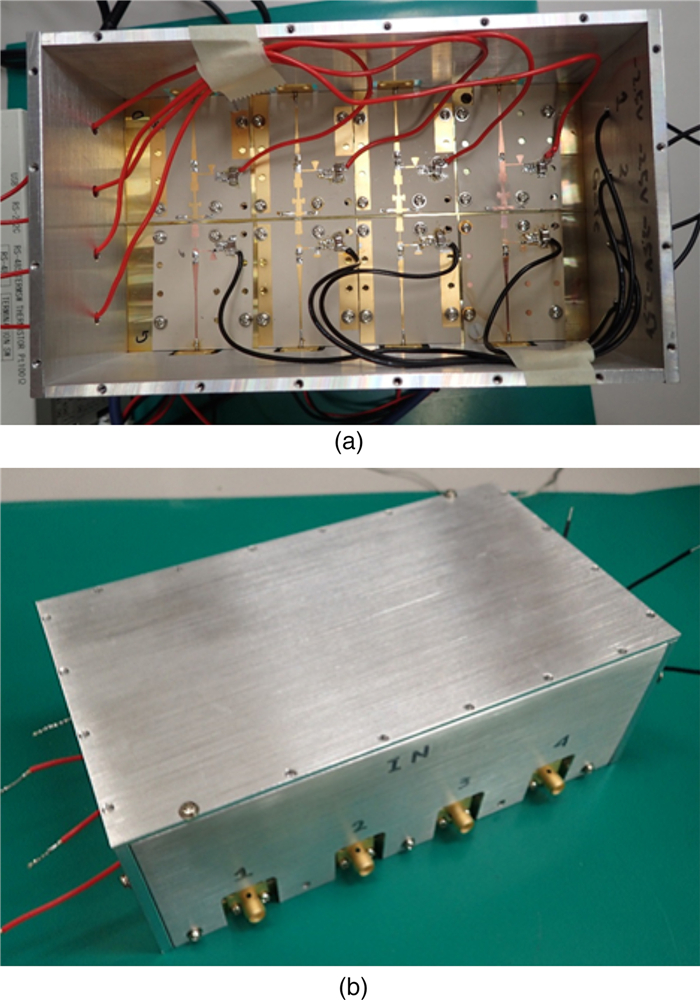
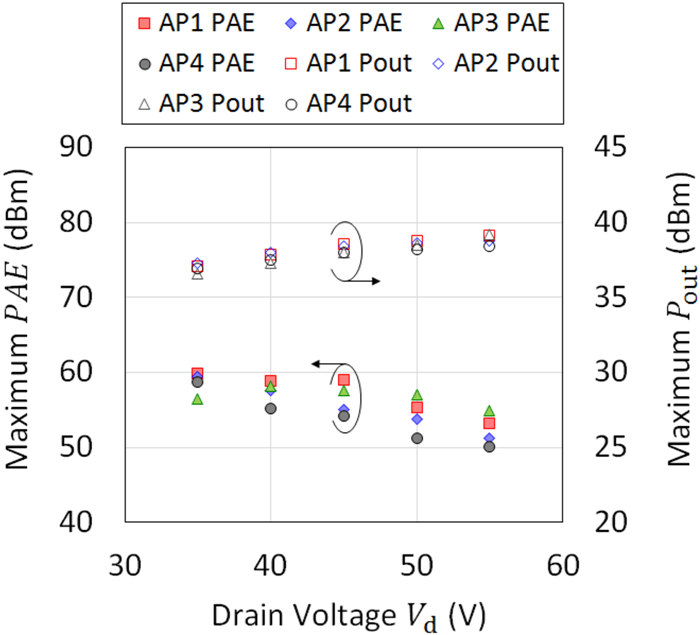
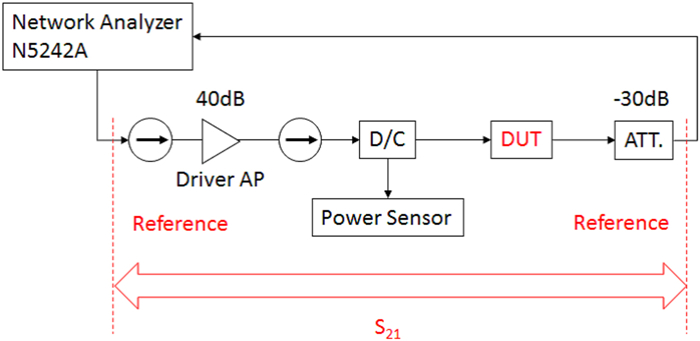
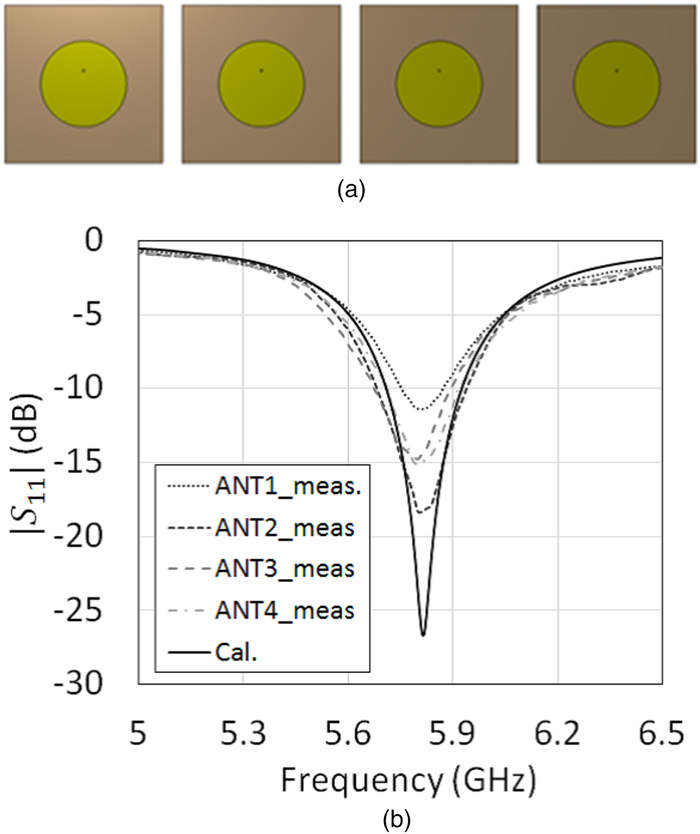
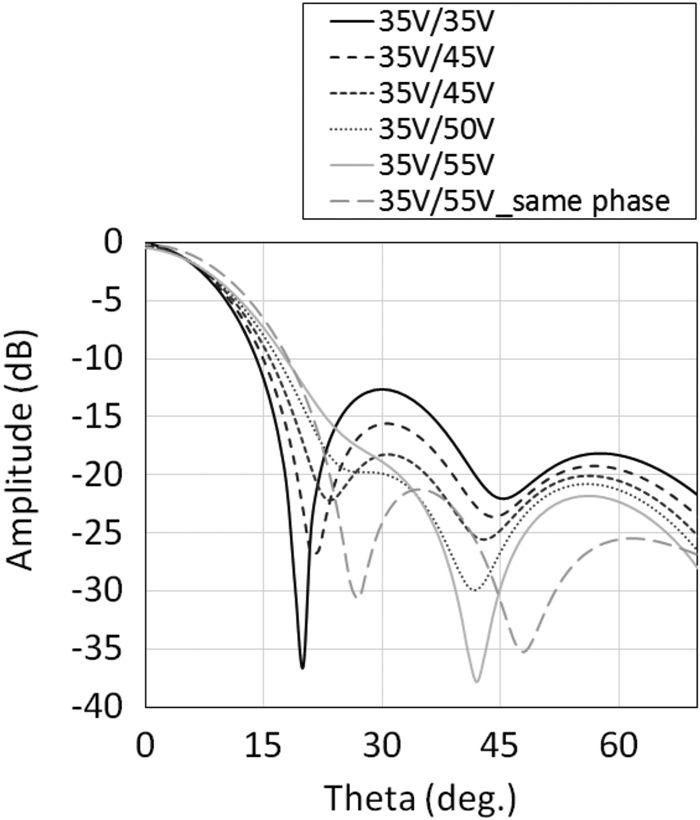
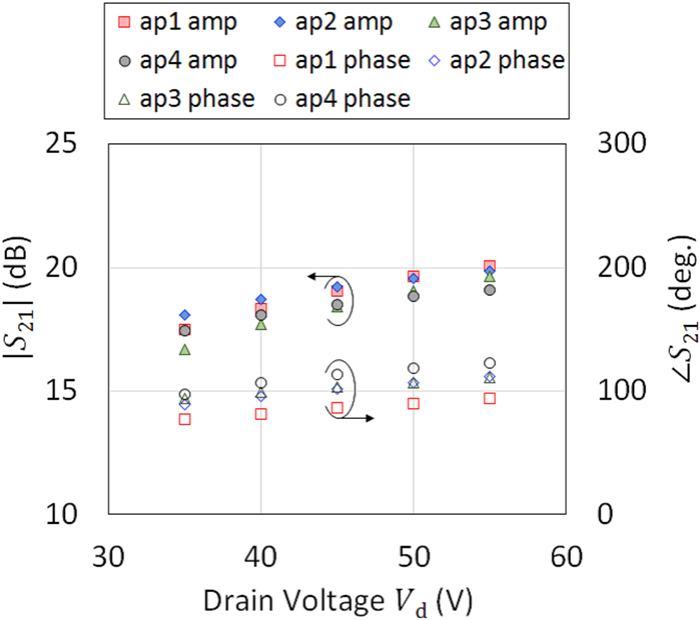
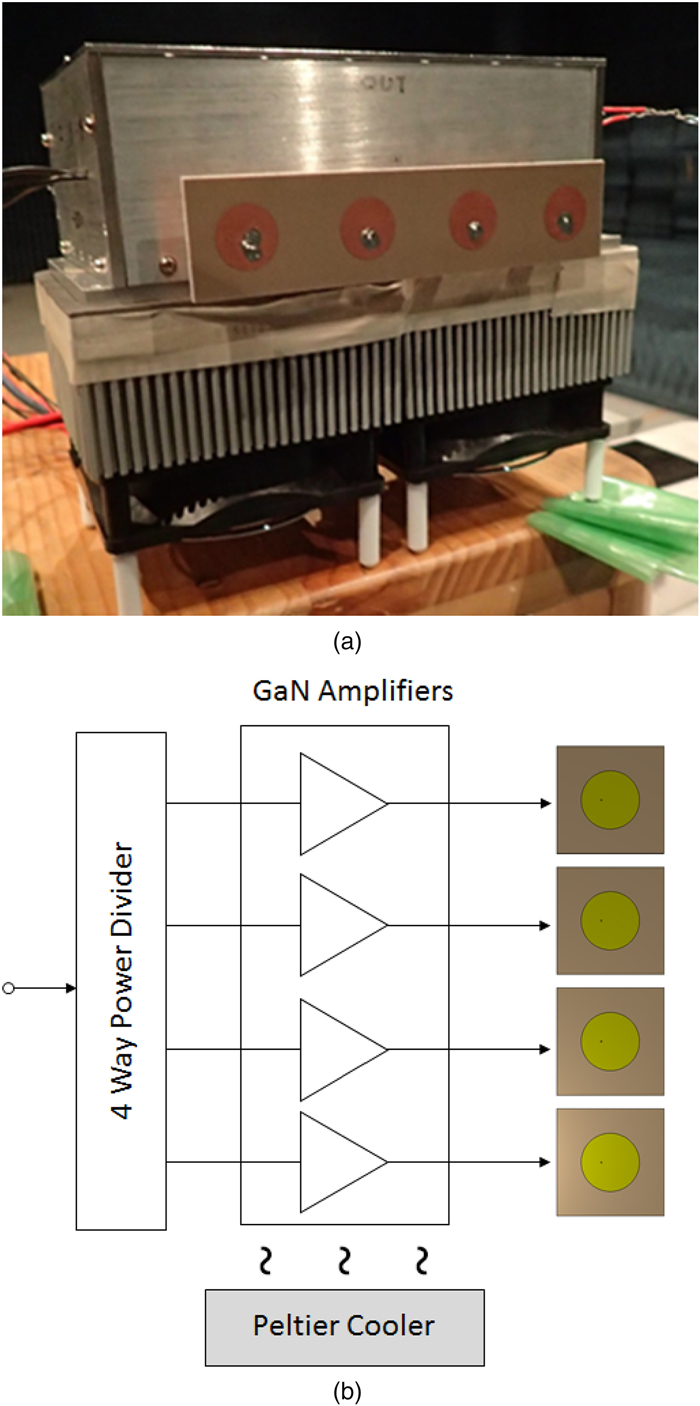
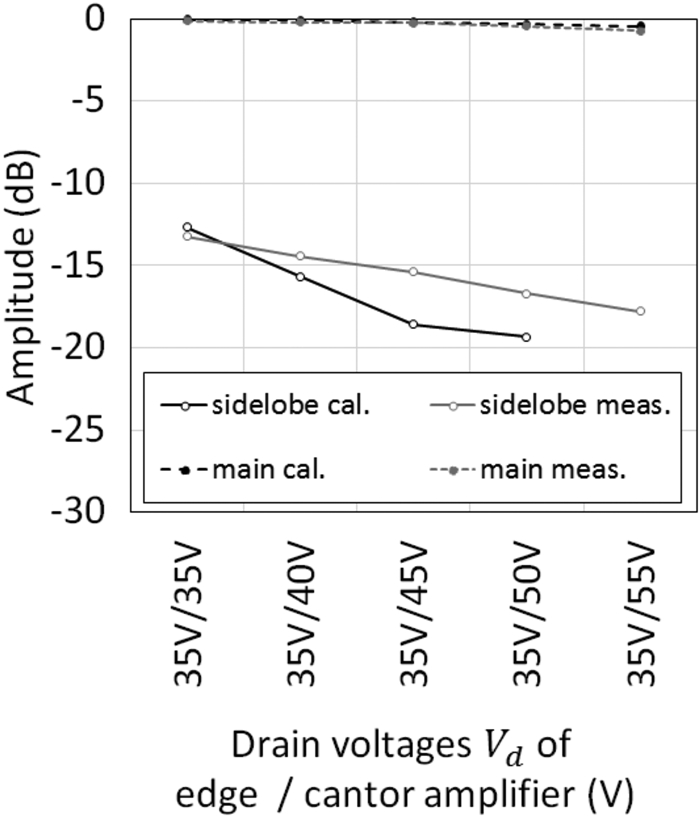
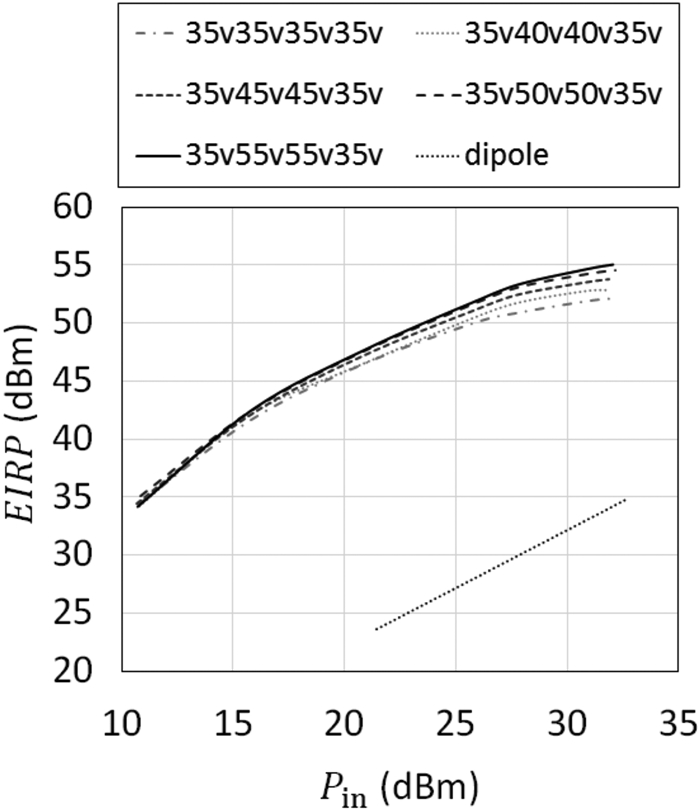
This work proposes a tunable sidelobe reduction method based on a GaN active-antenna technique, in which the output radio frequency power is controlled by the DC drain voltage of the amplifiers. In this study, a 1 × 4 array of active antenna with GaN amplifiers is designed and fabricated. GaN amplifiers capable of up to 10 W-class power output are fabricated and arranged for a four-way active-array antenna. The fabricated single-stage GaN amplifier offers a maximum power-added efficiency of 59.6% and a maximum output power of 39.3 dBm. The maximum output power is decreased to 36.5 dBm upon decreasing the operating drain voltage from 55 to 35 V. In this study, a 4.5 dB sidelobe reduction is demonstrated in a 1 × 4 active antenna based on this output power difference for each amplifier.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Hasegawa N, Shinohara N. 2017. Sidelobe reduction with a GaN active array antenna. Wireless Power Transfer 4(2): 113-119 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2017.8
|
Hasegawa N, Shinohara N. 2017. Sidelobe reduction with a GaN active array antenna. Wireless Power Transfer 4(2): 113-119 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2017.8
|









 Naoki Hasegawa was born in Aichi, Japan, on June 18, 1988. He received his B.E. degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from Ritsumeikan University, Siga, Japan, and his M.E. degree in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, in 2011 and 2013, respectively. He was a research associate in The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) from 2013 to 2015. He is a student member of the Institute of Electronics, Information and Communication Engineers (IEICE) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE). His research activities include RF GaN power amplifier and antenna design for wireless power transfer and up-link satellite communications.
Naoki Hasegawa was born in Aichi, Japan, on June 18, 1988. He received his B.E. degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from Ritsumeikan University, Siga, Japan, and his M.E. degree in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, in 2011 and 2013, respectively. He was a research associate in The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) from 2013 to 2015. He is a student member of the Institute of Electronics, Information and Communication Engineers (IEICE) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE). His research activities include RF GaN power amplifier and antenna design for wireless power transfer and up-link satellite communications.  Naoki Shinohara received the B.E. degree in Electronic Engineering, the M.E. and Ph.D. (Eng.) degrees in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Japan, in 1991, 1993, and 1996, respectively. He was a research associate in Kyoto University from 1996. From 2010, he has been a professor in Kyoto University. He has been engaged in research on Solar Power Station/Satellite and Microwave Power Transmission system. He is IEEE MTT-S Technical Committee 26 (Wireless Power Transfer and Conversion) vice chair, IEEE MTT-S Kansai Chapter TPC member, IEEE Wireless Power Transfer Conference advisory committee member, International Journal of Wireless Power Transfer (Cambridge Press) executive editor, technical committee on IEICE Wireless Power Transfer, communications society member, Japan Society of Electromagnetic Wave Energy Applications vice president, Space Solar Power Systems Society board member, Wireless Power Transfer Consortium for Practical Applications (WiPoT) chair, and Wireless Power Management Consortium (WPMc) chair
Naoki Shinohara received the B.E. degree in Electronic Engineering, the M.E. and Ph.D. (Eng.) degrees in Electrical Engineering from Kyoto University, Japan, in 1991, 1993, and 1996, respectively. He was a research associate in Kyoto University from 1996. From 2010, he has been a professor in Kyoto University. He has been engaged in research on Solar Power Station/Satellite and Microwave Power Transmission system. He is IEEE MTT-S Technical Committee 26 (Wireless Power Transfer and Conversion) vice chair, IEEE MTT-S Kansai Chapter TPC member, IEEE Wireless Power Transfer Conference advisory committee member, International Journal of Wireless Power Transfer (Cambridge Press) executive editor, technical committee on IEICE Wireless Power Transfer, communications society member, Japan Society of Electromagnetic Wave Energy Applications vice president, Space Solar Power Systems Society board member, Wireless Power Transfer Consortium for Practical Applications (WiPoT) chair, and Wireless Power Management Consortium (WPMc) chair