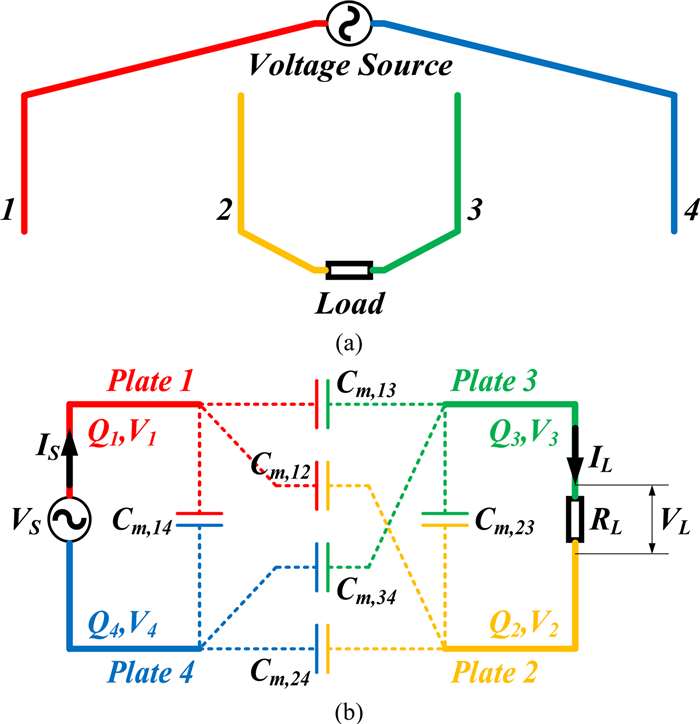
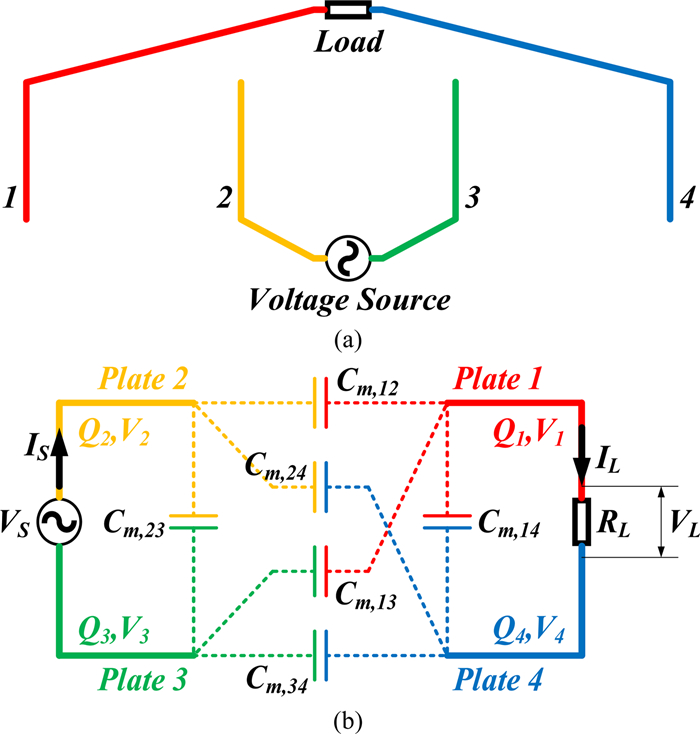
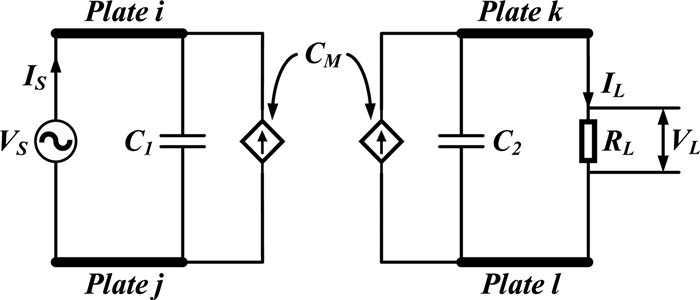
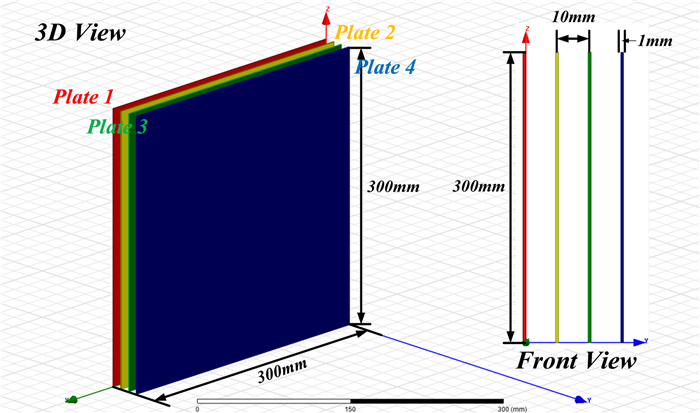
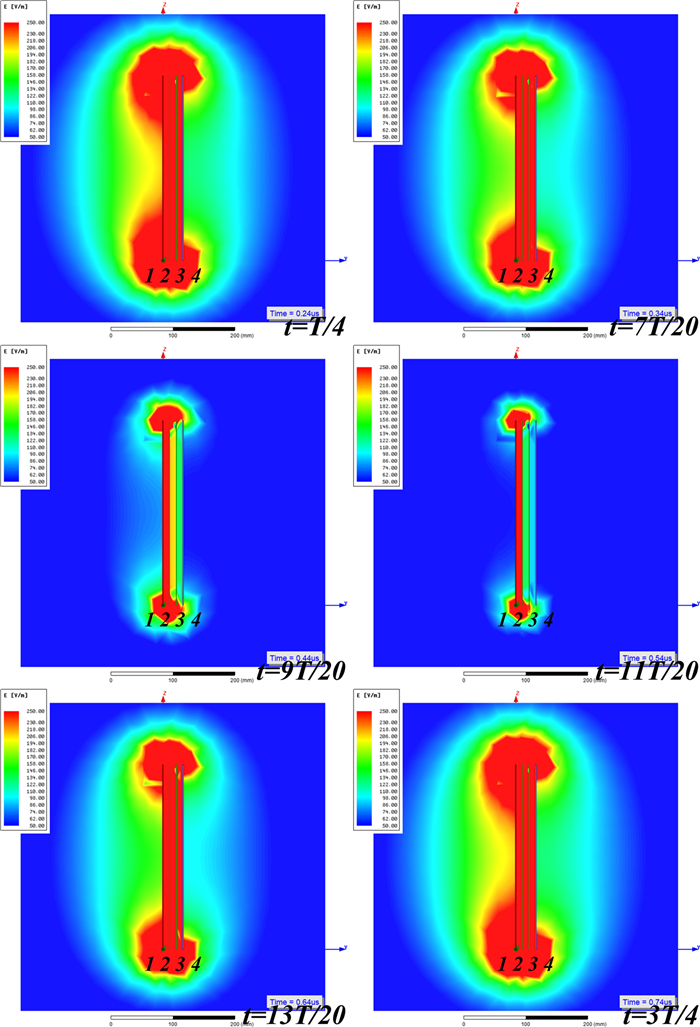
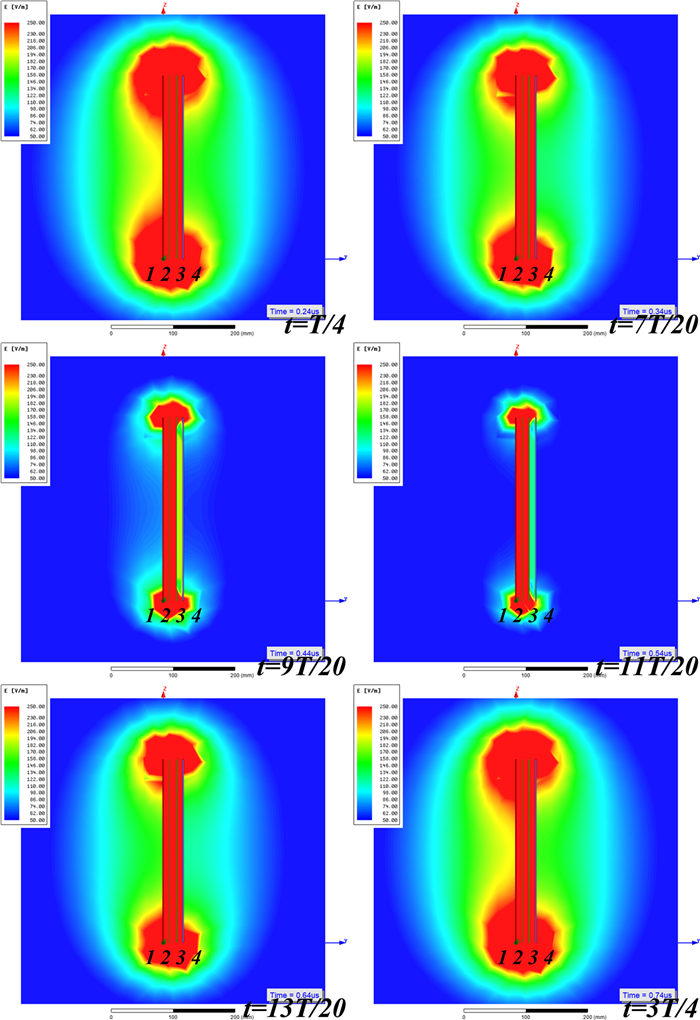
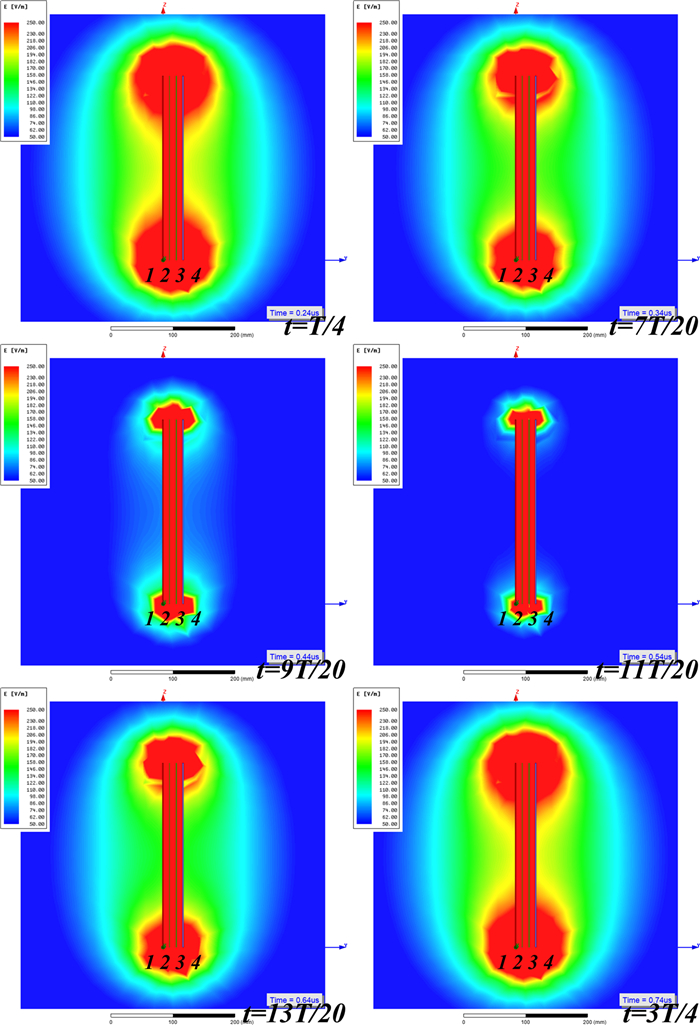
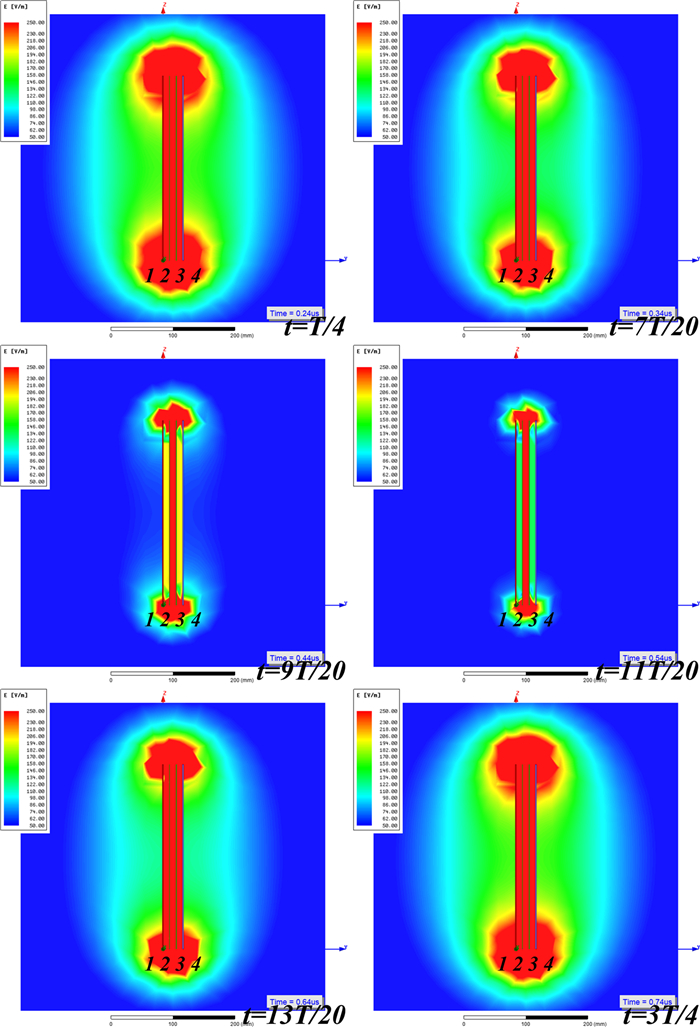
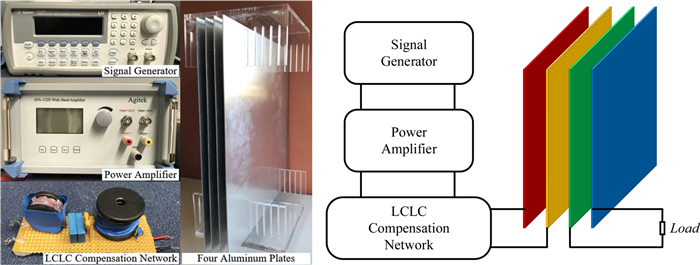
Study of coupling configurations of capacitive power transfer system with four metal plates
-
Qi Zhu1,2, ,
-
Shaoge Zang3, ,
-
Lixiang Jackie Zou3,
-
Guanguan Zhang4, , ,
-
Mei Su1,2 &
-
Aiguo Patrick Hu3,
-
1.
School of Automation, Central South University, Changsha, China
-
2.
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Power Electronics Equipment and Grid, Changsha, China
-
3.
Department of Electrical, Computer, and Software Engineering, the University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand
-
4.
School of Control Science and Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, China
More Information
-
Author Bio:
 Qi Zhu
Qi Zhu was born in Anhui Province, China, in 1993. He received the B.S. degree in electrical engineering and automation from Central South University, Changsha, China, in 2014, where he is currently working toward the Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering. From December 2017 till now, he is a joint Ph.D. student founded by China Scholarship Council at the University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand. His main research interest is wireless power transfer, including both inductive power transfer and capacitive power transfer.
 Shaoge Zang
Shaoge Zang received the B.E. (with first class honors) in Electrical and Computer Engineering from the University of Auckland, in 2018. He is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree in Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Auckland. His research interest includes inductive power transfer, capacitive power transfer, and the controller design for wireless power transfer application.
 Lixiang Jackie Zou
Lixiang Jackie Zou received the B.E. (Hons.) and M.E. (Hons.) degrees from the Electrical and Computer Department, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand, in 2009 and 2012, respectively. She is currently working towards the Ph.D. degree in the Electrical and Computer Department, University of Auckland. Her current research interests include inductive power transfer, capacitive power transfer, and electromagnetic field analysis.
 Guanguan Zhang
Guanguan Zhang received the B.S. degree and the Ph.D. degree in automation and power electronics and power transmission from Central South University, Changsha, China, in 2012 and 2018, respectively. From December 2016 to December 2017, she was a joint Ph.D. student supported by the China Scholarship Council with the Department of Energy Technology, Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark, where she focused on the reliability analysis of the wind power system. She is currently a Postdoctoral Research Fellow at the School of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, China. Her research interests include matrix converter, motor control, and high frequency converter.
 Mei Su
Mei Su was born in Hunan, China, in 1967. She received the B.S. degree in Automation, in 1989, M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in electric engineering, in 1992 and 2005 respectively, all from the School of Automation, Central South University. Since 2006, she has been a Professor with the School of Automation, Central South University. Her research interests include matrix converter, adjustable speed drives, and wind energy conversion system.
 Aiguo Patrick Hu
Aiguo Patrick Hu received the B.E. and M.E. degrees from Xian JiaoTong University, Xian, China, in 1985 and 1988, respectively, and the Ph.D. degree from the University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand, in 2001, He was a Lecturer, a Director of China Italy Cooperative Technical Training Center, Xian, and the General Manager of a technical development company. Funded by Asian2000 Foundation, he was with the National University of Singapore for a semester as an exchange Postdoctoral Research Fellow. He is currently in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Auckland, and also the Head of Research of PowerbyProxi, Ltd. He holds 15 patents in wireless/contactless power transfer and microcomputer control technologies, published more than 200 peer-reviewed journal and conference papers, authored a monograph on wireless inductive power transfer technology, and contributed four book chapters
-
Corresponding author:
Guanguan Zhang, School of Control Science and Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, China. E-mail: dr_zgg@163.com
-
Abstract
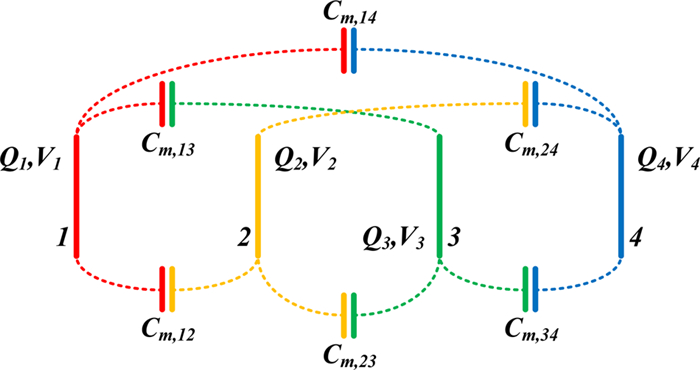
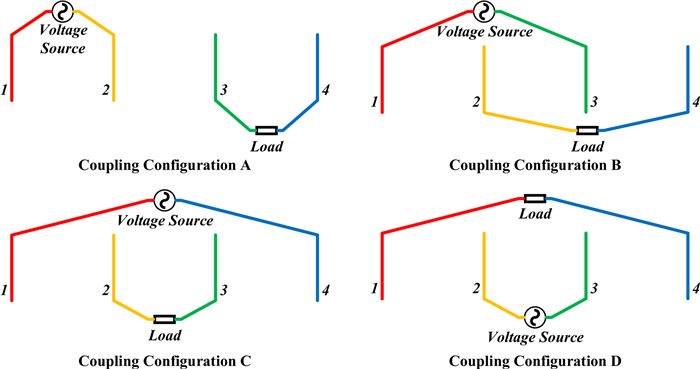
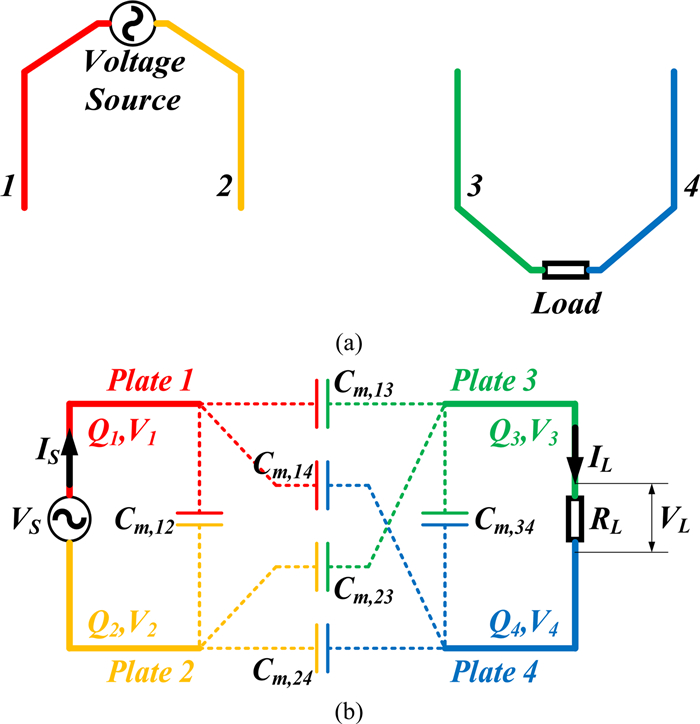
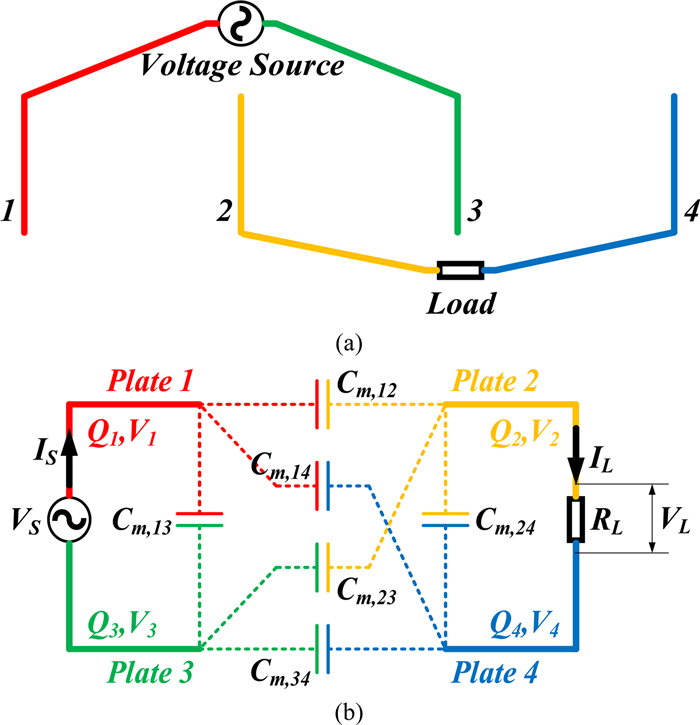
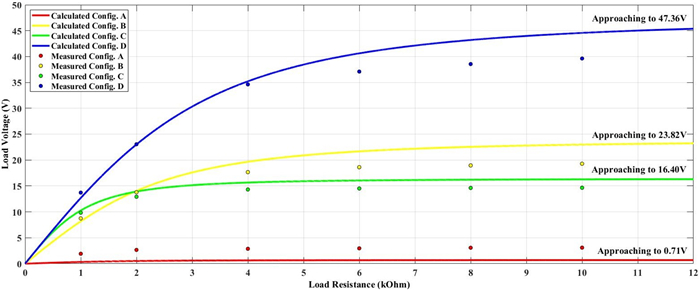
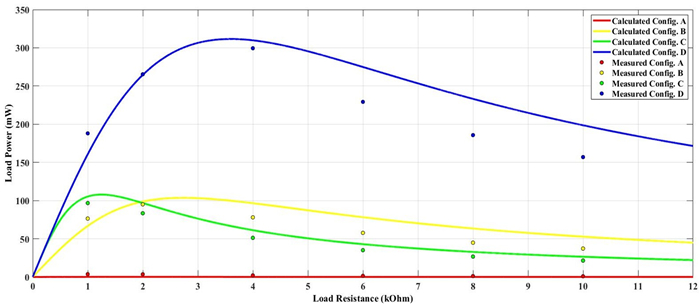
In this paper, possible coupling configurations of a four-plate capacitive power transfer system are studied by varying the combinations of its input and output ports. A voltage source is applied between two of the four plates, and a load is connected to the other two to form different circuit topologies. A mathematical model based on a 4 × 4 mutual capacitance matrix is established for equidistantly placed four identical metal plates. Based on the proposed model, four separate circuit topologies are identified and analysed in detail and described in a general form. The electric field distributions of the coupling configurations are simulated by ANSYS Maxwell. The theoretical modeling and analysis are then verified by a practical system, in which four aluminum plates of 300 mm × 300 mm are used and placed with a gap of 10 mm between adjacent plates. The experimental results show that the measured output voltage and power under the four coupling configurations are in good agreement with the theoretical results. It has found that the voltage gain is the highest when the two inner plates are connected to the source, and this coupling configuration also has the lowest leakage electric field.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu Q, Zang S, Zou L J, Zhang G, Su M, et al. 2019. Study of coupling configurations of capacitive power transfer system with four metal plates. Wireless Power Transfer 6(2): 97-112 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2019.10
|
Zhu Q, Zang S, Zou L J, Zhang G, Su M, et al. 2019. Study of coupling configurations of capacitive power transfer system with four metal plates. Wireless Power Transfer 6(2): 97-112 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2019.10
|









 Qi Zhu was born in Anhui Province, China, in 1993. He received the B.S. degree in electrical engineering and automation from Central South University, Changsha, China, in 2014, where he is currently working toward the Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering. From December 2017 till now, he is a joint Ph.D. student founded by China Scholarship Council at the University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand. His main research interest is wireless power transfer, including both inductive power transfer and capacitive power transfer.
Qi Zhu was born in Anhui Province, China, in 1993. He received the B.S. degree in electrical engineering and automation from Central South University, Changsha, China, in 2014, where he is currently working toward the Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering. From December 2017 till now, he is a joint Ph.D. student founded by China Scholarship Council at the University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand. His main research interest is wireless power transfer, including both inductive power transfer and capacitive power transfer.  Shaoge Zang received the B.E. (with first class honors) in Electrical and Computer Engineering from the University of Auckland, in 2018. He is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree in Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Auckland. His research interest includes inductive power transfer, capacitive power transfer, and the controller design for wireless power transfer application.
Shaoge Zang received the B.E. (with first class honors) in Electrical and Computer Engineering from the University of Auckland, in 2018. He is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree in Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Auckland. His research interest includes inductive power transfer, capacitive power transfer, and the controller design for wireless power transfer application.  Lixiang Jackie Zou received the B.E. (Hons.) and M.E. (Hons.) degrees from the Electrical and Computer Department, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand, in 2009 and 2012, respectively. She is currently working towards the Ph.D. degree in the Electrical and Computer Department, University of Auckland. Her current research interests include inductive power transfer, capacitive power transfer, and electromagnetic field analysis.
Lixiang Jackie Zou received the B.E. (Hons.) and M.E. (Hons.) degrees from the Electrical and Computer Department, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand, in 2009 and 2012, respectively. She is currently working towards the Ph.D. degree in the Electrical and Computer Department, University of Auckland. Her current research interests include inductive power transfer, capacitive power transfer, and electromagnetic field analysis.  Guanguan Zhang received the B.S. degree and the Ph.D. degree in automation and power electronics and power transmission from Central South University, Changsha, China, in 2012 and 2018, respectively. From December 2016 to December 2017, she was a joint Ph.D. student supported by the China Scholarship Council with the Department of Energy Technology, Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark, where she focused on the reliability analysis of the wind power system. She is currently a Postdoctoral Research Fellow at the School of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, China. Her research interests include matrix converter, motor control, and high frequency converter.
Guanguan Zhang received the B.S. degree and the Ph.D. degree in automation and power electronics and power transmission from Central South University, Changsha, China, in 2012 and 2018, respectively. From December 2016 to December 2017, she was a joint Ph.D. student supported by the China Scholarship Council with the Department of Energy Technology, Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark, where she focused on the reliability analysis of the wind power system. She is currently a Postdoctoral Research Fellow at the School of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, China. Her research interests include matrix converter, motor control, and high frequency converter.  Mei Su was born in Hunan, China, in 1967. She received the B.S. degree in Automation, in 1989, M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in electric engineering, in 1992 and 2005 respectively, all from the School of Automation, Central South University. Since 2006, she has been a Professor with the School of Automation, Central South University. Her research interests include matrix converter, adjustable speed drives, and wind energy conversion system.
Mei Su was born in Hunan, China, in 1967. She received the B.S. degree in Automation, in 1989, M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in electric engineering, in 1992 and 2005 respectively, all from the School of Automation, Central South University. Since 2006, she has been a Professor with the School of Automation, Central South University. Her research interests include matrix converter, adjustable speed drives, and wind energy conversion system.  Aiguo Patrick Hu received the B.E. and M.E. degrees from Xian JiaoTong University, Xian, China, in 1985 and 1988, respectively, and the Ph.D. degree from the University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand, in 2001, He was a Lecturer, a Director of China Italy Cooperative Technical Training Center, Xian, and the General Manager of a technical development company. Funded by Asian2000 Foundation, he was with the National University of Singapore for a semester as an exchange Postdoctoral Research Fellow. He is currently in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Auckland, and also the Head of Research of PowerbyProxi, Ltd. He holds 15 patents in wireless/contactless power transfer and microcomputer control technologies, published more than 200 peer-reviewed journal and conference papers, authored a monograph on wireless inductive power transfer technology, and contributed four book chapters
Aiguo Patrick Hu received the B.E. and M.E. degrees from Xian JiaoTong University, Xian, China, in 1985 and 1988, respectively, and the Ph.D. degree from the University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand, in 2001, He was a Lecturer, a Director of China Italy Cooperative Technical Training Center, Xian, and the General Manager of a technical development company. Funded by Asian2000 Foundation, he was with the National University of Singapore for a semester as an exchange Postdoctoral Research Fellow. He is currently in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Auckland, and also the Head of Research of PowerbyProxi, Ltd. He holds 15 patents in wireless/contactless power transfer and microcomputer control technologies, published more than 200 peer-reviewed journal and conference papers, authored a monograph on wireless inductive power transfer technology, and contributed four book chapters