-
By reading the safety encyclopedias and safety technology terminology[1,2] in the field of safety science, one can see that there are very few number of general concepts used to express the whole safety and security characteristics or degree of a system. The commonly used general concepts currently include: sense of safety and security, safety atmosphere, safety culture, safety resilience, safety index, safety capacity, etc., as well as general concepts that are opposite to safety and security, such as danger and risk. In fact, the meanings of these general concepts that express the whole safety and security status of a system are not the same, and there are still certain differences in their application in specific time and space. With the rapid development of safety science, the existing general concepts of safety and security cannot meet today's needs, and more meaningful general concepts of safety and security need to be sought and applied. The above situation also indicates that proposing a new general concept to express comprehensive features of safety and security of a system is not an easy task. Even having invented a new general concept of safety science, it still needs a long period of promotion when the concept is widely accepted and widely used in practice.
Based on a long time research experience in safety culturology[3] and the search on the origin and propagating process of the concept of safety culture, the author believes that if a scientific definition of SSC can be provided and the complete connotation of SSC can be given, SSC can become an important new concept that expresses the comprehensive safety and security level of any system or at a certain time and space, and its significance is no less than that of the well-known concept of safety culture.
When searching the internet and typical literature databases, one can discover that the expression of safety civilization is not completely blank. For example, one can find a few research articles concerned with safety civilization production[4−7] in CNKI. However, by investigating relevant documents in detail, it is found that 'safety civilization production' in those documents is actually the abbreviations of the terms of 'safety production' and 'civilization production'. Furthermore, the term of 'civilization production' only means clean and hygienic production. In the Web of Science, the author has not yet found any literature that includes synthetic terms of safety civilization, security civilization, and safety and security civilization (SSC).
Through the above investigation and analysis, it can be concluded that the new concept and connotation of SSC proposed in the following text of this paper have not yet appeared in past research.
Therefore, the following will elaborate on the feasibility and significance of the compound word of civilization and safety and security, the concept and connotation of SSC, the classifications of SSC, and the comparison of SSC with safety culture, in order to hope that all safety and security researchers and professionals can recognize the term of SSC as a new general concept of safety and security science.
-
Civilization is a multidimensional concept, and its definition and connotation can be explained in various ways. Generally speaking, civilization can be understood as an advanced cultural status formed during the historical development of human society, including achievements and characteristics in social, economic, political, technological, moral, artistic, and other aspects. The connotation of civilization mainly includes the following aspects:
1) In terms of social organization and system, civilization means an organized social structure and system, including political system, legal system, social norms, etc, to ensure social order and stability;
2) In terms of economic prosperity and development, civilization reflects a prosperous economic mode and level of development, including achievements in agriculture, industry, commerce, finance, etc, to meet the material needs of the people and improve their living standards;
3) In terms of technological and knowledge progress, civilization represents human progress and innovation in the field of technology and knowledge, including scientific discoveries, technological applications, educational systems, etc, to promote social development and progress;
4) In terms of cultural and artistic achievements, civilization embodies a rich and diverse cultural expression and artistic achievements, including language, literature, music, painting, architecture, etc., in order to inherit and develop human cultural heritage.
Overall, civilization is a relativistic and general concept that emphasizes the development and progress of society, covers achievements and characteristics in multiple fields, and has a comprehensive and abstract significance. The concept of civilization can be defined as the stage of human social development and organization that is considered to be advanced, characterized by complex social and political structures, advanced technology, and socialized culture. So far, common synthetic terms related to civilization include human civilization, ecological civilization, economic civilization, modern civilization, technological civilization, etc. In recent decades, common synthetic terms related to civilization also include ecological environment civilization, ecological civilization, digital civilization, and cyber civilization, etc.
The connotation of safety and security on contemporary
-
In contemporary times, safety and security issues are a complex and multi-dimensional intertwined problem[8]. Safety and security involve elements such as objects, time, space, subject and object, human nature, ideas, materials, energy, environment, cognition, management, information, culture, etc. Many dimensions of safety and security can be constructed from different perspectives and levels, and the conclusions drawn from defining and examining safety and security issues from different dimensions vary. From today's real world perspective, safety and security involves many fields, such as human rights, healthcare, health, food, ecology, environment, morality, culture, politics, national territory, military, economy, society, technology, information, resources, markets, property, assets, materials, etc. The complexity of safety and security has both multidimensional essential reasons and practical reasons for the diversity of expressions. Moreover, safety and security expressions from different fields or areas are often mixed together. So safety and security also has extremely complex connotations.
The interrelationship between civilization and safety and security
-
As can be seen from the above text, both civilization and safety and security have great inclusiveness. There is a close relationship between civilization and safety and security. Civilization is not only a cultural achievement and development of a society, but also involves social safety and security and stable development. The main relationship between civilization and safety and security is as follows:
1) Safety and security and stability are the foundation of civilization. The development of civilization requires a certain level of safety and security and stability. Only in a relatively safe society and international order can people better pursue the development of knowledge, art, and economy, and possibly pursue a more developed civilization.
2) Civilization and safety and security are interdependent and mutually influencing. Safety and security provides a guarantee for the development of civilization, and the development of civilization also needs to be carried out in a safe environment. Safety and security and civilization promote each other to achieve social stability and comprehensive development of human society.
3) The development of safety and security and civilization usually requires a relative balance. Overemphasizing safety and security may limit the development of civilization, while overemphasizing civilization may overlook safety and security issues. Therefore, it is necessary to seek a balance between safety and security and civilization, ensuring both promoting the development of safety and security and civilization.
4) The conflict of civilizations may lead to safety and security issues. Conflicts and frictions between different civilizations may pose a threat to safety and security. When there are differences and confrontations between civilizations, they may trigger conflicts and violent behavior, posing a threat to the safety of society and individuals.
5) Safety and security promotes civilized exchange and cooperation. The guarantee of safety and security can promote communication and cooperation among different civilizations. When people feel safe and protected, they are more willing to engage in dialogue, learning, and exchange with other civilizations, thereby promoting the diversity and development of civilizations.
6) Safety and security guarantees people's rights and freedoms. Only in a safe environment can people freely express their views, pursue knowledge, participate in social activities, and enjoy basic human rights. The guarantee of safety and security provides conditions for the development of individuals and all humanity.
7) Safety and security is one of the important goals of civilization. The development of civilization is not only about the progress of culture, art, and technology, but also involves the security and stability of society. By establishing a secure society and international order, people can better develop and realize the value of civilization. Thus safety and security is one of the important goals that people pursue for civilization.
In summary, the words of safety and security and civilization are comprehensive, multifaceted, general, abstract, and progressive. When safety and security and civilization are combined, the connotation of safety and security civilization (SSC) shall integrate the connotations of safety and security and civilization, and also has the characteristics of above two words.
-
SSC is a multi-dimensional complex issue and people can give various concepts from different views and levels. To make the concept being more convinced, the concept of SSC proposed in the following is based on reference to many concepts of culture, civilization, safety, and safety culture and their defining methods. The concept of SSC can be divided into narrow and generalized ones. Narrow concept of SSC can be defined as the level of civilization in people's safety and security ideas, safety and security behaviors, and comprehensive safety and security guarantee conditions at a certain period and space. The generalized concept of SSC can be defined as the level of civilization on safety and security aspects in the process of human survival, reproduction, and development, which includes the cognitive and behavioral patterns of human safety and security, the safety and security collaborative relationships formed among humans, the social safety and security guarantee system constructed by humans and its applications, and the vision of sustainable human safety and security development, etc. The generalized concept of SSC emphasizes the result of sustainable human safety and security as a whole, aiming to seek a coexistence world or district that is conducive to the harmonious and stable development of human security.
Note: In English, the meaning of safety and security are different in some ways. Safety pays more attention to the safety of life and production, including environmental safety, traffic safety, etc. Security emphasizes more on maintaining social security, national security, and personal public security, covering multiple aspects such as military security, political security, and economic security, etc. In order to make the meaning more complete, both two words of safety and security are used and combined into safety and security and then SSC is used throughout this paper. From the perspective of the connotation, the meaning of safety and security civilization (SSC) is more comprehensive than that of safety civilization or security civilization.
The connotation of SSC
-
As a general concept that expresses the whole safety and security of a system, SSC can more comprehensively and accurately describe the overall safety and security level of the system than others, especially for expressing the whole safety and security situation of society. The connotation and structure of SSC are shown in Fig. 1.
The further explanation of the 12 components that make up SSC (Fig. 1) is as below.
1) People's safety and security awareness. SSC requires people to have a keen sense of safety and security, be able to recognize that safety and security is everyone's responsibility, take proactive preventive measures, and avoid potential safety and security risks.
2) People's ideas of the rule of safety and security law. SSC emphasizes the governance of safety and security in accordance with the law. People should abide by safety and security laws and regulations, respect the rights and interests of others, and refrain from engaging in illegal or criminal activities. They should consciously participate in maintaining social safety and security and order.
3) People's risk management capabilities. SSC requires people to correctly evaluate and manage potential risks, take appropriate measures to prevent accidents and disasters, and reduce safety and security risks.
4) The level of people's participation on safety and security issues. SSC encourages public participation in safety and security affairs, increases public understanding and participation in various safety and security issues, and forms a joint force of all sectors of society to maintain safety and security.
5) The effectiveness of people's safety and security education and promotion. SSC emphasizes improving the public's safety and security literacy and knowledge through education and publicity, cultivating good safety habits and behaviors, and promoting the formation of SSC.
6) Lower crime rate and public security environment in society. The crime rate can measure the frequency of criminal behavior in society, such as violent crimes, property crimes, etc. A lower crime rate usually means a relatively safe society. The public security environment refers to the safe order and security situation of society, such as the effectiveness of police forces and social stability.
7) The level of social security and fairness. The level of social fairness is also related to security, and social inequality may lead to social tension and conflict, thereby reducing the level of social security.
8) The ability of society to prevent and reduce disasters. The risk of natural and man-made disasters is an important indicator for assessing social security, and the ability and preparedness of society to respond to disasters will affect the level of social security.
9) Good social public health and safety. The state of public health is also an important component of social security, for example, factors such as epidemic outbreaks and disease transmission can have an impact on social security.
10) The development level and innovation ability of safety technology. SSC advocates the use of technological means to improve social security levels, enhance security monitoring and early warning capabilities, such as developing intelligent security systems, big data analysis and other technologies, strengthening the protection of network security and information security, and preventing security risks such as network crime and data leakage.
11) The level of harmonious coexistence between countries and regions. SSC refers more to the civilization of the civilization of global safety and security. Only by achieving harmonious coexistence between countries and regions, reducing conflicts and contradictions, and eliminating wars can we achieve a broad common sense of SSC.
12) Others. The connotation of SSC is very broad, and it is difficult to fully summarize its connotation in the limited clauses mentioned above. There must be some content that has not been mentioned, namely other aspects.
The extension meaning of SSC
-
As a new concept with great inclusiveness and compatibility, the extension meaning of SSC mainly involves the following aspects:
1) Political stability. Political stability is the foundation of social security, and the stability of the political system, effective government governance, and fair law enforcement play an important role in social security, which is also an important manifestation of SSC.
2) Social fairness and justice. Social fairness and justice are the foundation for maintaining social security. Fair resource assignment, fair enforcement of laws, and social inclusiveness can all reduce social conflicts and unsafe factors, which is also an important manifestation of SSC.
3) Stable and good economic development. The stability and development of the economy are crucial for social security. Economic development can provide employment opportunities, improve living standards, and reduce social instability factors, which is also an important manifestation of SSC.
4) Education and culture. The improvement of education and cultural level helps to cultivate the citizens' awareness of safety and security and the ideas of the rule of law, enhance citizens' safety literacy, which is also an important manifestation of SSC.
5) Public governance capabilities. The effective public governance capacity of the government is an important guarantee for ensuring social security, such as the construction and normal operation of public service agencies such as police, fire protection, medical treatment, and emergency rescue, which is also an important manifestation of SSC.
6) Awareness of public participation in social activities. The awareness of public participation is crucial for social security. Public security awareness, cooperation, and participation can improve the overall safety and security level of society, which is also an important manifestation of SSC.
7) Environmental protection. The health and sustainable development of the environment have a significant impact on social security, such as the protection of the natural environment, the rational utilization of resources, and the prevention and control of environmental pollution, which is also an important manifestation of SSC.
8) Technological innovation. The development of technology plays an important role in social security, such as the application of intelligent security systems, big data analysis, network security and other technologies, which can improve the level of social security, and which is also an important manifestation of SSC.
9) World peace. Peaceful coexistence among countries and nations around the world, proper handling of various conflicts and contradictions, mutual benefit, harmonious coexistence, and common development are also important manifestations of SSC.
It is worth noting that the extension of SSC is constantly developing and evolving, and with the changes in society and the emergence of new security challenges, the extension of SSC will further expand and change.
The significance of the new concept of SSC
-
The new concept of SSC is of great significance, mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1) SSC enriches the general concepts and comprehensive indicators to characterize the whole safety and security level of a system to safety science. The connotation of SSC concerns with a wide range of fields, including global security, traditional security, non-traditional security, etc. At the macro level and with SSC, it is possible to evaluate and compare the comprehensive security level and security development status of different regions and times.
2) SSC can be used to expand and innovate new theories of safety and security science. Based on the SSC, it is possible to construct a new theoretical system and framework of safety science, enrich and improve the existing knowledge of safety and security discipline, promote the development and innovation of new safety and security disciplines, and provide new ideas and methods for solving practical safety and security problems.
3) SSC can meet the needs of overall safety characterization in the new era. With the acceleration of social change, new safety and security issues are constantly emerging, and SSC can cover these new issues, which helps to promote the continuous progress of theory and practice in the field of safety and security.
4) SSC helps to broaden the perspective of safety and security concepts. SSC provides a more comprehensive perspective, broadens the dimensions of safety and security evaluation, promotes comprehensive analysis of safety and security risks, enables better understanding and response to safety and security issues in various fields, promotes the development of safety and security governance, and achieves sustainable development of safety and security.
5) SSC can provide new directions and prospects for the future development of related safety and security fields. SSC can stimulate people's imagination and exploration of future safety and security science and technology. Through in-depth research and application of SSC, it can promote innovation and progress in related safety and security fields and contribute to the safety and security development of future society.
6) SSC can promote communication and cooperation among relevant disciplines[9,10]. The study of SSC can stimulate intellectual collision and collaborative research among scholars, jointly research and solve complex system safety and security problems, promote the interdisciplinary development of safety and security disciplines with other disciplines, and improve the comprehensive and innovative capabilities of disciplines.
-
From different perspectives and dimensions, many classifications of SSC can be obtained, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Classifications of safety and security civilization (SSC) and examples.
Perspectives of classification Examples of classification Divided from binary structure Material SSC, spiritual SSC (non material SSC) Divided from the ternary structure Material SSC, institutional SSC, spiritual SSC Divide from the four element structure Material SSC, institutional SSC, behavioral SSC, and idea SSC From the visual binary perspective of humans Explicit SSC, implicit SSC From the time dimension Primitive SSC, ancient SSC, medieval SSC, modern SSC, future SSC Divided by scale and scope World SSC, national SSC, regional SSC, urban SSC, community SSC, etc By geographical region and cultural background Eastern SSC, Western SSC, Chinese SSC, Indian SSC, Islamic SSC, etc From the perspective of human activity functions Life SSC, production SSC, etc From a specific content perspective Scientific and technological SSC, economic SSC, environmental SSC, behavioral SSC, humanistic SSC, management SSC, health SSC, etc From the binary perspective of modern science and technology category Scientific SSC, technological SSC From the category of modern scientific disciplines Natural science SSC, social science SSC, life science SSC, technology science SSC, information science SSC, military science SSC, system science SSC, etc From the perspective of the production industry SSC in various industries, such as metallurgical SSC, construction SSC, etc More perspectives ……. It should be noted that the classifications in Table 1 can help us better understand and study the different aspects and characteristics of SSC. However, the classifications of SSC are made by a subjective approach, and different people and scholars may have different classification standards and perspectives. Therefore, the classifications of SSC in Table 1 are only a method or approach to better understand and study the development of human safety and security. In addition, the classifications of SSC in Table 1 are a simplified and generalized way, but in reality, SSC is complex and diverse. There may be mutual influence and communication among different SSC, and they have no absolute boundaries and divisions.
Examples of using the classification method of SSC
-
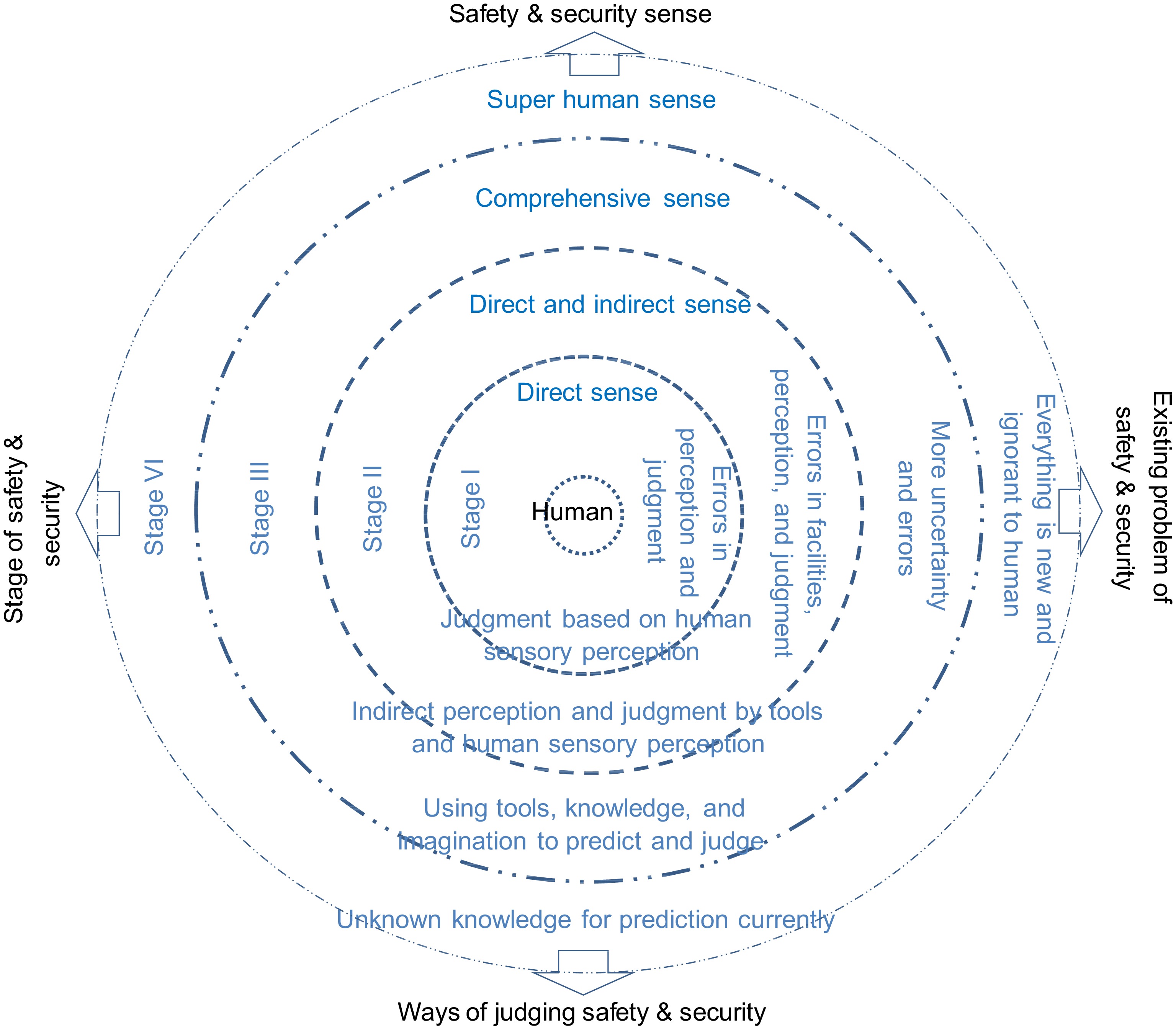
Based on the ways and time dimensions of human perception to judge safety and danger, SSC can be divided into four stages:
1) The first stage of SSC: Human judge safety and danger simply relying on human direct senses and experience. This stage of SSC belongs to the primary stage, and human judgment of safety and security and danger is limited by their own senses and experience, which may lead to large judgment errors.
2) The second stage of SSC: In addition to the direct approach of sensing safety and danger in the first stage, human can sense safety and security and danger by indirect information through instruments, equipment, and tools to further determine safety and security and future hazards. Although the assessment of safety and danger in this stage has improved compared to the first stage, obtaining indirect information through instruments, equipment, tools, etc. still has errors caused by inaccuracy, incompleteness, or incorrect perception.
3) The third stage of SSC: In addition to the first and second approaches of sensing safety and security and danger, humans can actively plan and design safety and security systems, and can use various advanced scientific knowledge and human imagination to comprehensively judge and predict safety and security and future dangers.
4) The fourth stage of SSC: This stage can be referred to as the future SSC. Apart from the first, second, and third approaches of sensing safety and security and danger, humans currently don’t know what danger will come in the future and thus have no existing methods, tools, and knowledge to judge safety and security and predict future dangers, and they are currently ignorant of future dangers.
By above classification, a four dimensional SSC model can be derived as shown in Fig. 2.
-
The narrow and generalized definitions of SSC are as mentioned above. Because safety culture has rather long history. Habitually, safety culture also includes some content of security culture at present. Safety culture is a very meaningful and widely practiced concept in the field of safety science, and it is also very similar to the SSC. Therefore, it is necessary to make a comprehensive comparison between SSC and safety culture. The definition of safety culture varies from different fields, levels, and perspectives. Based on the reference to many definitions of safety culture, the author believes that the definitions of safety culture can be divided into two categories: narrow and generalized. According to this classification, the author provides two corresponding definitions of safety culture: narrow definition of safety culture refers to the common safety concept, safety behavior mode, and safety atmosphere formed by society, organizations and groups at a certain time and space. Generalized definition of safety culture refers to the integration of all soft and hard conditions that have formed and inherent safety attitudes and safety handling methods, as well as the protection of external harmful factors that pose a threat to human physical and mental health, at a certain stage of human social development and in all areas of human activity.
The basic connotations of SSC and safety culture have many similarities, but there are also some differences (as shown in Table 2).
Table 2. Comparison between safety and security civilization (SSC) and safety culture.
Comparing items Narrowly defined SSC Narrowly defined safety culture Generalized SSC Generalized safety culture Definition example Narrow SSC is defined as
the level of civilization in people's safety and security ideas, safety and security behaviors, and comprehensive safety and security guarantee conditions at a certain period and space.Safety culture refers to the common safety concept, safety behavior mode, and safety atmosphere formed by society, organizations and groups at a certain
time and space.Generalized SSC can be defined as the level of civilization on safety and security aspects in the process of human survival, reproduction, and development, which includes the cognitive and behavioral patterns of human safety and security, the safety and security collaborative relationships formed among humans, the social safety and security guarantee system constructed by humans and its applications, and the vision of sustainable human safety and security development. Safety culture refers to the integration of all soft and hard conditions that have formed and inherent safety attitudes and safety handling methods, as well as the protection of external harmful factors that pose a threat to human physical and mental health, at a certain stage of human social development and in all areas of human activity. Word property Commendatory, progressiveness Neutral, containing both advanced and backward contents Commendatory, progressiveness Neutral, containing both advanced and backward contents Characteristic Dynamic, developing Inherent status at a certain time and space, continuous and slow changes Dynamic, developing Inherent status at a certain time and space, continuous and slow changes Emphasis Emphasizing the advanced level of civilization in people's safety and security ideas, behaviors, and conditions Emphasizing the existence of safety ideas, behaviors, and atmosphere Emphasizing the results of overall sustainable human security, aiming to pursue a coexisting world or space that is conducive to the harmonious and stable development of human safety and security Emphasize the sum and status of overall software and hardware for human safety and security Applying scale Commonly used for expressing safety and security levels at large scale Commonly used for expressing small-scale of safety status Commonly used for expressing safety and security levels at large
scaleCommonly used for expressing large-scale safety and security status Main purpose Used for evaluation of comprehensive and advanced characterization and safety and security levels, etc Used for evaluation of comprehensive characteristics and safety status, etc Used for evaluation of comprehensive, advanced and sustained characteristics and safety and security levels at a large scale Used for evaluation of comprehensive, status of safety and security at a large scale Relevance and inclusiveness SSC is the essence and an advanced part of safety culture Contents of safety culture including
SSC and is bigger than SSCSSC is the essence and an advanced part of safety culture at a large scale Contents of safety culture is greater than SSC in the scope and including SSC at a large scale Mutual learning between SSC and safety culture and promoting SSC
-
Since SSC is the essence and advanced parts of safety culture, SSC can be used to guide the construction of safety culture and experiences of safety culture can support the promotion of SSC. Also the promotion of SSC is a systematic project that requires multiple efforts and cooperation. At the same time, the power of safety culture can be utilized to transform and develop into SSC. Some specific promotion approaches of SSC are listed below:
1) Emphasizing the promotion and education of public security and civilization. Through publicity and education, people can enhance the public safety and security literacy and mastery of safety knowledge, such as conducting safety publicity and education in schools, communities, media, and other channels, and strengthening the cultivation of people's awareness of safety, legal ideas, and risk management.
2) Establishing a sound system of safety and security laws and regulations, and clarifying safety and security and legal responsibilities. For example, governments should strengthen the crackdown and punishment of illegal and criminal acts, enhance the awareness of the rule of law, and maintain social security order.
3) Strengthening safety risk management. For example, governments should establish a scientific risk assessment and management mechanism, develop preventive measures and emergency plans, and improve society's ability to identify and respond to potential risks, and strengthen risk management of natural disasters, public health, and other fields.
4) Encouraging the public to actively participate in safety affairs. For example, governments should encourage the public to actively participate in safety affairs, increase their understanding and participation in safety issues, such as through community safety patrols, volunteer services, etc., to form a joint force of all sectors of society to maintain safety and security.
5) Increasing the innovation in safety technology. For example, governments should utilizing technological means to enhance social security, such as developing intelligent security systems and security big data analysis technologies, and improving security monitoring and early warning capabilities.
6) Paying attention to non-traditional security issues. For example, governments should strengthen research and response to non-traditional security issues, in order to reduce disasters, crises, environmental and social security.
7) Defending human rights. The construction of a safe and civilized society requires attention to human rights protection, improving people's quality of life, reducing social instability factors, and enhancing the public's sense of security happiness.
8) Improving international security rules. The construction of a safe and civilized society requires compliance with international security regulations, respect for national sovereignty and territorial integrity, such as by maintaining international order and stability, reducing the occurrence of conflicts and disputes, and better responding to new security challenges and threats.
9) Strengthening international cooperation. Security issues have global and transnational characteristics, and it is necessary to strengthen international cooperation and exchange, enhance mutual trust and understanding among countries, such as through sharing experiences and resource assistance, to jointly address security challenges and promote the development of global SSC.
-
1) The compound word of 'safety and security civilization (SSC)' has comprehensive, multifactorial, general, abstract, and progressiveness properties to express the whole safety and security level of any system or at a certain time and space. As a new concept, SSC enriches the general concepts of safety science, and can better represent the comprehensive characteristics of safety and security integrity of a system. It has a wide application fields in the future.
2) Narrowly defined SSC is the level of civilization in people's safety and security ideas, safety and security behaviors, and comprehensive safety and security guarantee conditions at a certain period and space. Generalized SSC is the level of civilization on safety and security aspects in the process of human survival, reproduction, and development, which includes the cognitive and behavioral patterns of human safety and security, the safety and security collaborative relationships formed among humans, the social safety and security guarantee system constructed by humans and its applications, and the vision of sustainable human safety and security development, etc.
3) From different perspectives and dimensions, SSC can be classified by many patterns, including by structural binary, structural ternary, structural quaternary, visual binary, time dimension, scale and scope, geographical region and cultural background, human activity function, specific content, scientific discipline category, production industry perspective, etc.
4) There are many similarities and differences between SSC and safety culture in word property, characteristic, emphasis, applying scale, purpose, relevance and inclusiveness etc. SSC is commendatory and progressiveness word, which are the main characteristics of different from safety culture. SSC is an advanced part of generalized safety culture and can guide the construction of safety culture. Through the construction of advanced safety culture, the development of SSC will be promoted.
-
The author confirms sole responsibility for the following: study conception and design, analysis and interpretation of results, and manuscript preparation.
-
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
The author would like to thank reviewers and editors cordially for their comments and suggestions. This study is supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (No. 22ZDA121) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51534008).
-
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest. Wu Chao is the Editorial Board member of Emergency Management Science and Technology who was blinded from reviewing or making decisions on the manuscript. The article was subject to the journal's standard procedures, with peer-review handled independently of this Editorial Board member and the research groups.
- Copyright: © 2023 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press on behalf of Nanjing Tech University. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Wu C. 2023. Why should safety and security civilization (SSC) be a new concept of safety and security science? Emergency Management Science and Technology 3:14 doi: 10.48130/EMST-2023-0014
Why should safety and security civilization (SSC) be a new concept of safety and security science?
- Received: 26 August 2023
- Accepted: 17 October 2023
- Published online: 31 October 2023
Abstract: In order to increase the number of general concepts of safety and security science which can be used to represent the comprehensive safety and security level of a system, a compound word of safety and security civilization (SSC) is proposed, based on the connotation and attributes of words of civilization, safety and security. Then, the narrow and generalized definitions and their connotations of SSC are given respectively. Further analysis shows that properties of SSC have implications of comprehensiveness, generality, abstractness and progressiveness. On this basis, various classifications of SSC are made from different perspectives and dimensions, and the similarities and differences between SSC and safety culture are compared. SSC is an advanced part of generalized safety culture and can be used to guide the construction of safety culture. The research shows that the new concept of SSC can be widely used to express the whole safety and security level at a certain time and space, and has important value in practical applications.