-
Since its inception, for nearly a century, safety science has been developed and popularized in the field of workplace safety[1,2]. Safety theories, methods, principles, models, systems, standards, regulations, etc., have been gradually improved, and many safety science monographs and textbooks have been published during this period[3−7]. Beneficial practical effects have also been achieved in accident prevention, etc. However, when compared to other disciplines such as environment science, safety science is still slow to develop[8−10].
The world is currently in an unprecedented period of rapid development. Human-created innovations are being designed regularly, science and technology are advancing rapidly, and information networks, artificial intelligence, bioengineering, and other high-technology applications are used everywhere. Therefore, the social division of labor is constantly being refined. A variety of new knowledge and specialties are growing, converging, and developing while forming many new disciplines. As a result, integration of safety and security (SS) has been growing in potential over the last 20-30 years[11−13]. The development of SS science is an important objective need and attracts many opportunities[14−16]. Additionally, this enables fast development of SS science. Based on this background, the development of new disciplines in SS science is the highlight of a new era, both subjectively and objectively[17, 18].
The importance of SS has become increasingly prominent, and the connotation and extension of SS over the past 20-30 years have been continuously expanded and extended, both at the macro level of the world and the micro level of production and life[14−18]. However, many researchers generally pay more attention to the actual SS problems encountered than to the deep-seated upstream theories of SS science. Therefore, the theoretical development of SS science appears to lag far behind the actual needs. Pre-existing theories and disciplines of SS science are far from meeting the needs of current SS development[14−18].
SS science is a knowledge summary of revealing and re-understanding the SS objective world and SS laws from a specific perspective and focus. Furthermore, it is a knowledge system about SS phenomena and laws. SS science is a typical comprehensive interdisciplinary field. Additionally, it focuses on production safety, public security, disaster prevention, health, and epidemic prevention, national security, information security, and other fields, and has gradually shown a trend of developing a universal SS theory in the aforementioned fields. This development trend undoubtedly further reflects the necessity and importance of SS science research and the creation of new SS science disciplines. Conversely, the interdisciplinary characteristics of SS science endow SS science research with considerable time and space, while laying an objective feasibility and possibility for creating more new SS science disciplines[19, 20].
In the field of higher education in China, the SS discipline has seen the most rapid development of all disciplines in the last decade or two[21]. Since 2004, many colleges and universities in China have independently added numerous SS disciplines. In 2011, Safety Science and Engineering and Public Security Technology became a first-level discipline of national graduate education, followed by Cyberspace Security. In 2018, China established the Ministry of Emergency Management[22]. Emergency Management has also been approved as a secondary-level discipline under the first-level discipline of Public Management of graduate education[23, 24]. The emergence of COVID-19 has had a negative impact on the world, and since the end of 2019, the scientific theory of public health and safety has received unprecedented attention. In 2021, the Ministry of Education of China approved the setting up of a cross disciplinary category for postgraduate education with National Security Science as a first-level discipline. Therefore, the aforementioned SS disciplines urgently require the support of general SS science theories and the development of new disciplines.
We have been engaged in research on SS science theory and new discipline construction for many years, realizing that SS science as a new inter-discipline is far from perfect and more new sub-disciplines are urgently needed. Furthermore, we began to focus on the development of SS disciplines in 1999, and after 2003, continued to practice the development and research of new SS disciplines, accumulating extensive experience in the establishment of new SS science disciplines over many years of practice. The experiences are sorted and set into methodologies and paradigms for the creation of new disciplines of SS science accordingly.
-
The creation of a new discipline of safety and security (SS) science should be backed by research and be based on some causative factors, as shown by the following crucial conditions[25, 26]:
(1) There is a research team that focuses on the creation of new SS science disciplines. Researchers on the team must have a high level of scientific philosophy, research direction of general knowledge, scientific history, and practical experience in scientific research and discipline creation. Furthermore, a keen sense of innovation, a rich imagination, a very forward-looking vision, etc., is required to discover the signals of new SS science disciplines that have not yet emerged and anticipate their future development with extraordinary insight.
(2) The research team must be conscious of the guidance of building a new SS science discipline. New SS science disciplines that have recently been created lack the characteristics of pre-existing mature disciplines. However, there is potential to develop a new, mature discipline. Therefore, knowledge of the basic characteristics of mature SS science disciplines can help to consciously lead the creation and development of new disciplines to achieve twice the result with half the effort.
(3) The research team must determine the needs of society for new disciplines of SS science. Society is constantly developing and changing, and there are endless new demands on SS science. If researchers in new SS science disciplines can gain insight into new society's and human's changing needs, they can find and create genes or signals for a new SS science discipline in a timely manner.
(4) Researchers have to be very familiar with the scientific research paradigm of pre-existing disciplines and be aware of the interaction and integration between disciplines. Furthermore, research activities in various disciplines are ongoing, and collisions and hybridization occur occasionally, which has become the most direct and rapid way to create new SS science disciplines.
(5) The research method or methodology is very significant as it accelerates the creation of a new SS science discipline. Moreover, methods and methodologies are important tools for all scientific research as they are also crucial for research on the creation of new SS science disciplines.
(6) There are already preexisting sources of relevant knowledge. The creation of a new SS science discipline cannot be completely separated from the preexisting knowledge system. Additionally, it cannot be separated from the support of various knowledge systems and experience sharing. Therefore, researchers should have a broad knowledge of multiple-disciplines.
(7) External conditions should be provided to the extent possible during the creation of a new SS science discipline. Furthermore, research cannot be carried out without the support of human, material, and financial resources, particularly in the development stage of a new discipline. Only with the support of external factors can the new discipline grow in a healthy and rapid manner; otherwise, it may experience an early decline.
Academic thought for creating a new discipline of SS science
-
The academic thought of establishing a new SS science discipline requires that the researcher have a bigger vision and aim at the upstream and unknown areas of the SS science field by relying on the foundation of scientific ideas with the help of previous research results, taking the approaches of absorbing other-disciplinary knowledge and creating new knowledge of self-discipline, and persisting in the end of goal realization.
The aforementioned academic thought is described more specifically below: (1) Researchers must be more ambitious in their research to create a new SS science discipline and focus on conducting universal knowledge innovation research; (2) The development of a new discipline of SS science requires researchers to have a broader vision and interdisciplinary thinking, as well as the ideas and research methods of the science of science, because the SS discipline involves a wide range of fields; (3) Researchers must fully utilize, rely, and draw on previous research achievements of various disciplines to achieve significant, systematic, basic, and theoretical achievements; (4) Many relevant disciplines have a great deal of knowledge that can be referenced in the creation of new SS disciplines as SS is a large-intercrossing and comprehensive discipline; (5) During the creation of a new SS discipline, researchers must follow two paths: they must create their own basic knowledge and absorb knowledge from other disciplines, and they must make unremitting efforts to conduct research until they succeed.
-
The common research methodology for the creation of new SS science disciplines includes: scientific thinking, theoretical analysis, various practical processes, mathematical and tools, and integration methods, etc. The specific research approaches are as follows:
(1) Researchers should focus on the unknown areas of the SS field to create a series of new SS science disciplines. Additionally, detailed work includes: discovering a possible breakthrough point for new SS science disciplines and naming of the new discipline, followed by elaborating their disciplinary theory and forming a blueprint for the potential new discipline. Furthermore, a good blueprint can attract more resources in the future. The developing pattern of the new discipline can learn from the judgment standards of the existing mature SS disciplines, allowing it to develop smoothly to serve human purposes.
(2) The comprehensive attributes of the SS discipline should be applied. Researchers may carry out interdisciplinary research in the fields of natural, technology, social sciences and humanities etc, to refine and pick up the relevant knowledge for the new discipline of SS science. Therefore, interdisciplinary research methods such as comparative safety research will be effective.
(3) Researchers should carry out research from the height and perspective of SS science and conduct basic theoretical research at the level of science, research, and methods for SS research results to be useful.
(4) Researchers should investigate general SS science problems in multi-spaces, such as universal issues in natural, artificial, social and cyberspaces, among others.
(5) Researchers should focus on SS system thinking and conduct basic theoretical research on SS science from the level of integrity and system creation to apply to SS science's system characteristics on the basis of reductionism thinking.
(6) Researchers should be the perfect combination of SS research and SS communication and make the basic theory of SS science a required learning subject for SS researchers, and let SS researchers promote and apply the basic theory of SS science and vice versa.
Research paradigm and its connotation for the creation of new disciplines of SS science
-
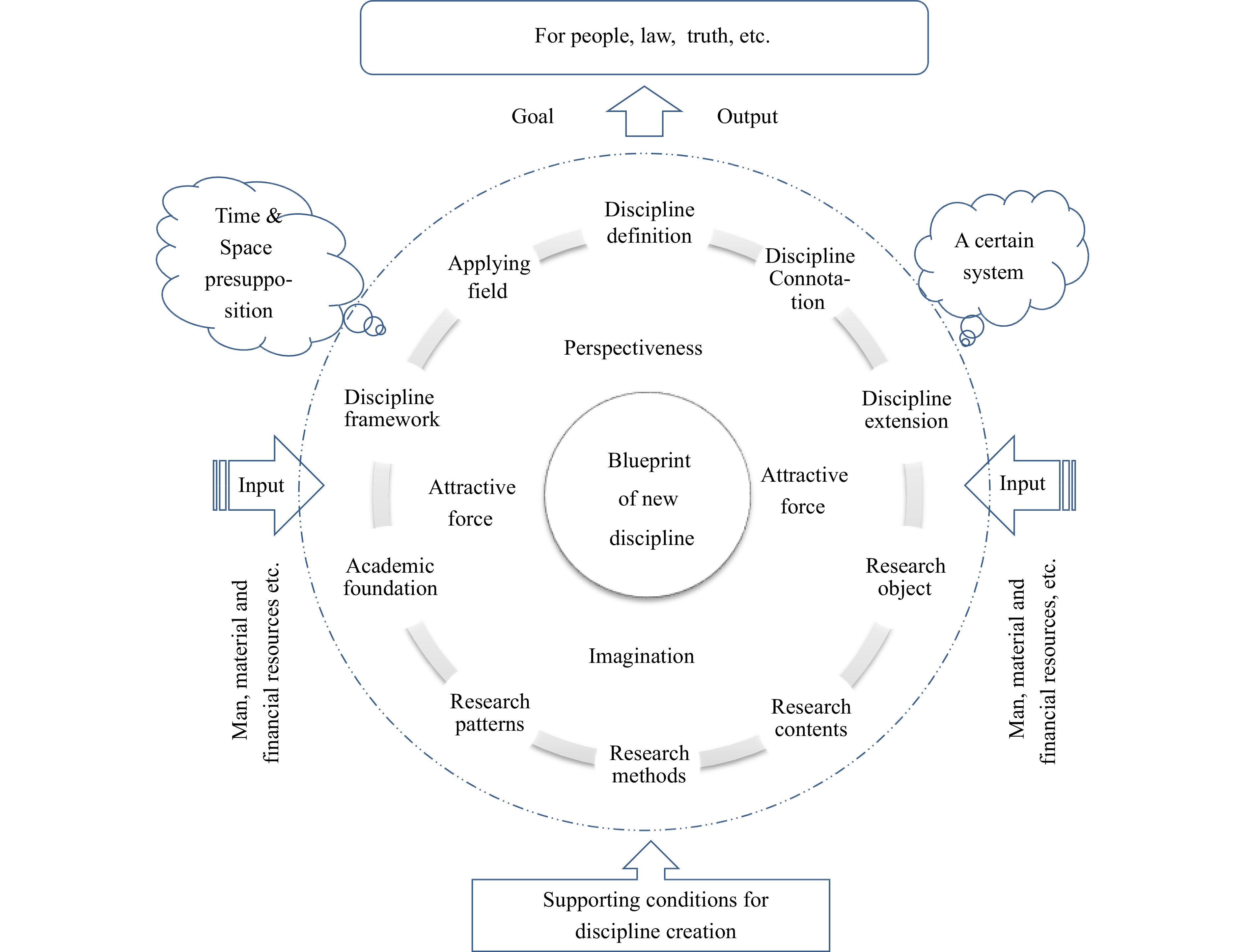
We extended our experiences from many years of research work in creating new SS science disciplines into a theory of creating new SS science disciplines. A summary of the research program or paradigm of the embryonic stage of a new discipline is shown in Fig. 1.
The contents of the paradigm are described as follows: (1) Based on a certain space-time or system preset; (2) With a future vision; (3) Based on existing knowledge, information, scientific and technological development trends, social demand, and other practical bases; (4) Taking the general standards of existing mature disciplines as the conceptual model; (5) Depending on certain scientific methods or modes and discipline development laws; (6) Seeking, inferring, or predicting the possible formation of a new discipline of SS science in the future. Furthermore, the name of the potential new discipline of SS science, its definition, connotation, extension (relationship with adjacent disciplines), research objective, research content, research method and program, discipline basis and system framework, application field, etc., should be described thoroughly to form a blueprint of the new SS science discipline and attract more resources (human, financial, material, etc.) to create new disciplines. The afore mentioned research can be developed into a truly useful new SS science discipline and validated by the standards of existing mature disciplines to serve humanity or reveal new scientific laws and truths.
-
According to disciplinary ontology, a new discipline of SS science can be created because there is a gene and power for the discipline's creation. The gene for the new discipline of SS science is a new growth point formed by the development of existing disciplines and the integration of multidisciplinary groups. The discipline of social science is in high demand in society and humanity. The development of the new discipline depends on the synergy of internal dynamics and environmental mechanisms when there is a gene for a potential new SS science discipline. We summarized the 18 modes of breeding new disciplines of SS science by summarizing the creation processes of many new disciplines of SS science and the research experiences of predecessors[17,26]. These modes include the following: cross, edge, integrated, common, transverse, node, subdivision, crystallization, problem, demand, theoretical, conjecture, experimental, virtual, artificial intelligence, big data, combined multi-modes and uncertainty modes, etc. These modes are suitable for all disciplines, not just SS science.
(1) Cross mode. The cross mode is usually suitable for large multidisciplinary cases. It creates a new discipline that grows from the mutual blending of two (or more) existing disciplines. The newly generated discipline not only has its own independent connotation but also inevitably bears the imprint of existing disciplines. Furthermore, the cross mode is the most basic method of creating new disciplines. Many new disciplines are developed in this mode, such as computational sociology, physical chemistry, and material mechanics, among others. Additionally, there are also many examples in mature SS science disciplines, such as Safety Management, Safety Ergonomics, Safety & Security Jurisprudence, Safety Economics, etc.
(2) Edge mode, or lateral mode. This mode forms a new discipline by combining and integrating marginal knowledge of multiple related disciplines. Furthermore, it creates a new discipline that naturally comes into being when the boundaries of multiple disciplines expand knowledge by overlapping or colliding with each other.
(3) Integrated mode or cluster mode. This mode creates a new discipline because of the intersection and integration of multiple disciplines into a larger 'science block', such as SS and environmental sciences, which are the typical 'science block'.
(4) Common mode. This mode breeds a new discipline composed of the common contents of multiple disciplines. The new discipline contents not only come from multiple disciplines but also serve multiple disciplines and vice versa, while supporting each other to develop in a continuous cycle. For example, methodology is derived from the common methods of all disciplines while serving all disciplines. Another example is informatics, which is formed by all fields related to information while also serving all fields.
(5) Transverse mode. This is based on a certain perspective or level that communicates with other disciplines, followed by its extraction and development into a new discipline. For example, mechanics aims at the common problem of forces in the research objectives of various disciplines. Furthermore, pure mechanics is also an independent discipline.
(6) Node mode. There are many activities or evolutions in the form of similar chains or networks in the human social system and natural system that have become the development mode of a new discipline triggered by an important problem, link, process, etc. Other examples include a technique in the production process, a server in the network system, and an emergency act in the SS system.
(7) Subdivision mode, or cascade mode. Many disciplines are developing constantly, and their development is often in a deep and detailed direction, so it is natural to decompose many new disciplines. When these disciplines continue to grow, they gradually become a new discipline. For example, many new disciplines of medicine are generated by this mode.
(8) Crystallization mode. New disciplines can be created or precipitated during the evolution and practice of disciplines through natural fusion, collision and reaction. The initial incubation stage of creating new disciplines using this mode is generally not perceived by researchers.
(9) Problem mode. People will always encounter various problems or difficulties in long-term practical activities such as human production and survival. These problems or difficulties can be solved by humans by conducting special research. In this process, specialized knowledge for solving these problems or difficulties has gradually formed and become a new discipline. For example, the emergence of COVID-19 will lead to many new disciplines.
(10) Demand mode. Nature and society are changing and developing constantly. Human desire is endless. Therefore, various new needs are constantly emerging. Many people need to think and practice how to meet this demand, conduct various studies, and create a new discipline.
(11) Theoretical model. According to the development based on existing discipline theory and practice, using logical, historical, system, structural, hierarchical, comparative, similarity analyses, and other methods, researchers can predict possible new disciplines in the future and use existing elements to create the framework of new disciplines while forming the embryonic form of new disciplines.
(12) Conjecture mode. Researchers can propose hypothetical propositions, make logical conjectures, and predict potential new disciplines while constructing new disciplines according to the elements of mature disciplines with a future perspective and based on the accumulation of researcher knowledge and experience, using innovative, associative, brainstorming, intuition, hypothesis, conjecture, image, and other thinking methods.
(13) Experimental mode. When researchers design experiments and control various environmental factors according to a certain purpose and the essential content of the research, they may obtain unknown and repeatable experimental phenomena and laws through experiments. A new discipline can be created using these phenomena and laws as the starting point.
(14) Virtual mode. Researchers conceive a new discipline for a certain purpose, use virtual reality methods and tools to carry out virtual experiments, preview and look forward to the development panorama and results of the discipline, and use these results as a starting point to create and develop a new discipline. This mode is applicable to the new discipline creation, which cannot continue to rely on experience and trial and error.
(15) Artificial intelligence mode. Researchers use artificial intelligence to replace and expand the limits of the human brain and to conduct research on the creation of new disciplines. This mode transcends human imagination and may be significant in the future.
(16) Big data mode. Researchers use high-speed computers to carry out rapid data analysis, identify multiple data types, and discover the possibility of creating a new discipline using massive data with an extremely low value density. This mode precedes the limitations of human practical experience and thinking data.
(17) Multi-mode combined mode. As the name implies, this mode combines and applies the aforementioned modes to create a new discipline model. Multi-mode combination methods are comparable to circular, spiral, dynamic, and static crossings. This mode is more flexible and practical for creating new disciplines. Furthermore, a large number of new disciplines are created using this mode.
(18) Uncertainty mode. This is the most popular mode for creating new disciplines, particularly for the micro-new disciplines created by project research. This mode is difficult to preset in advance because new disciplines are unknown before they are created and there is no mode to follow. Researchers usually create new disciplines based on various actual situations, personal talents, and abilities in the practice.
The 18 modes can be divided into several types according to their hierarchy and relevance. Modes (1) to (8) belong to the creation modes of new disciplines represented by morphological representation; modes (9) to (12) belong to the creation modes of new disciplines characterized by connotation; modes (13) to (16) belong to the creation modes of new disciplines with tools; and modes (17) to (18) belong to other modes.
-
Over the past ten years, we created 40 new SS science disciplines together with our research group. We edited most of them into a monograph[27]. Some of the new SS science disciplines have been investigated thoroughly and published as monographs and textbooks[28−39]. A series of new courses for graduate students in SS majors have been opened based on the aforementioned works. All new SS science disciplines fall into one of five categories: natural, technological, social, systematic and inter-cross SS sciences. The essentials of these new disciplines are as follows. Also, these new disciplines are critical research directions for basic SS theories.
Essentials of some new disciplines of natural SS Science
SS science principle[34, 40]
-
The principles of SS science are the basic rules that SS activities or work must follow, and is the objective laws of the development and change of SS things summarized based on experience or theory. Additionally, the relationships of five types of SS phenomena, laws and science are described on the perspective of the sciences of SS science and the multi-disciplines. The five first principles of SS science are the safety life science principle, the safety natural science principle, the safety technology principle, the safety social science principle and the safety system science principle. Furthermore, 25 second step safety science principles are summarized. Accordingly, the five first-step principles and the 25 second-step principles are created into a 'human shape' structure and a 'wheel pattern' structure, respectively. Additionally, the meanings, relations, cooperation, motivation, and development of the various step principles are given based on the 'human shape' structure and 'wheel pattern' structure.
SS logic[41]
-
SS logic is a science that uses common logic principles to study the form and structure of thinking involved in SS problems, the basic laws of logical thinking, the understanding of reality, and the use of logical methods. Nine core conceptions, five axioms, and five laws of safety theories are proposed based on general logic. Thirty inferences in macro-safety science are deduced tentatively. Furthermore, the principle system of safety theories, which is the deductive logic system of safety, is put forward for the first time. This study may guide the theoretical knowledge of SS science from a rough status to a rigorous system.
SS informatics[37, 42−44]
-
SS informatics is an interdisciplinary study of SS information phenomena, information dissemination laws, and application methods. A group of new concepts on SS science theory is deduced by the model. Furthermore, a new methodology of system analysis and control over SS information is established by studying a universal theoretical model on SS information cognition and taking the SS information distortion or asymmetry as problems. Ten basic discipline issues of SS informatics (including discipline name, definition, connotation, subject attribute, features, foundation, extension, task, research object, research contents, and research methods) are given at the creation of the discipline. Furthermore, there are six kinds of scientific principles in SS informatics. SS information theory is created by combining the attributes of SS science with the information asymmetry theory.
SS information economics[45]
-
The definition of SS information economics is refined, and its connotation is given based on the basic theory of SS information, SS economics and information economics; followed by the theoretical basis of the SS information economics is discussed and summarized; research methods of SS information economics are summarized from five aspects; research procedures of SS information economics are proposed and a detailed explanation is given. Additionally, the prospect of safety information economics from three aspects is prospected. The creation of SS information economics has a solid theoretical foundation and a wide range of application prospects, which can be used as a sub-discipline in SS informatics and SS economics in theory. It can also be used for optimal allocation of SS resources, SS management and risk decision-making.
SS chaos science[46]
-
Modern scientific knowledge in chaos science is applied tentatively in the study of SS science based on the comparison of their basic characteristics. Furthermore, the definition of 'SS chaos science' is put forward and its connotation is analyzed. The theoretic branch system of SS chaos science is created from a perspective of modern nonlinear theory. Conversely, the corresponding study contents and methods for each branch are elaborated. The broad prospect and outstanding significance are illustrated for the application and research of the SS chaos science. SS chaos science is a result of combining various nonlinear theories from the SS research field. Furthermore, it integrates the function and relationships of various nonlinear theories, deepens the understanding of SS systems, renovates the SS concept, and develops traditional safety science principles.
SS forecasting science[47]
-
SS forecasting science is created from a systematic perspective. The definition of SS forecasting is proposed, and its connotation is explained and, its connotation and establishment evidence are thoroughly analyzed. Additionally, four basic issues in SS forecasting science (including discipline features, research content, classifications, and foundations) are systematically discussed. The essence of SS forecasting is the methodology of the research and practice of SS science. SS forecasting science is a new inter-discipline that is specialized in studying the developmental and variable rules of future SS states of systems.
SS popularization science[48]
-
The establishment of SS popular science is researched from the perspective of discipline creation. The definition of SS popularization science is put forward, and its connotation is analyzed thoroughly. Five basic issues in SS popularization science (including research scope, discipline features, research object, research content, and research purpose) are systematically discussed. SS popularization science is a new inter-discipline specialized in studying the laws of SS popularization science, and its research can provide the diagnostic information necessary for an important theoretical basis.
Essentials of some new disciplines of technological SS science
SS statistics[49]
-
SS statistics is a subject that studies the quantitative expression, relationship, and law of information related to SS issues in the fields of production and life. Furthermore, it is a cross-disciplinary discipline of SS science, system science and statistics. The statistical range of SS systems, the typical industry safety statistics, specific statistical objects, and statistical indicators, these branches of SS statistics are the focus of statistical research. The main content of each branch are systematically described. The advantages, disadvantages, and applicability of different methods are obtained through the comparison of the SS statistical research and the analysis methods. Some common practice studies are proposed in the fields of industry safety statistics, casualty statistics, natural disasters statistics, occupational health and safety statistics, safety and economic statistics and social security statistics.
SS big data science[50]
-
Big data and technology have great effects on SS science and engineering. The definition of 'SS big data' is proposed based on the connotation of the term. The basic paradigm of SS science research based on SS big data is created and analyzed. Reconstruction ideas for the SS science discipline system are proposed accordingly based on SS big data. The definition of 'SS big data science' is provided, and its three dimensional structure model is created to point out its main research contents. SS big data is very helpful for studying macroscopical safety rules and workplace safety, etc.
SS intelligence science[51−53]
-
SS intelligence is a new interdisciplinary science that studies SS information, movement laws, and applications. In recent years, SS-related intelligence studies have become a new growth point and extension point in intelligence science and SS science. The background and foundation for creating SS-related intelligence science are described using a theoretical thinking method. On the disciplinary construction level, origin, the definition and understanding of basic disciplinary concepts, identity, and the disciplinary created perspective are provided. Furthermore, the system for SS-related intelligence science is constructed and expressed by models on the theoretical level according to the general characteristics and functions of the intelligence system.
SS material science[54]
-
The definition of the SS materials science is defined, its meaning is deduced, and discipline system of the SS materials science is created. The discipline system of the SS materials science is created with following aspects: the SS materials principle, the disaster science of materials, the essence safety of materials science and the human-material-environment safety systematics. The corresponding concept, connotation, and research contents for each branch are elaborated. The research methods of the SS materials science are analyzed from perspectives of safety material identification, hazard analysis, hazard assessment and materials safety function defense. The SS materials science system is established, and the research methods of the safety materials science have been systemized on this basis.
Material safety assessment science[55]
-
The definition of assessment science for material safety is defined, its meaning is analyzed, and the sub-branches are established both in theory and application. The disciplinary branches of material safety assessment science consist of material risk evaluation and material risk control theories, as well as material health, material ecology, and material accident risk assessments. The research program in assessment science for material safety is established. It consists of material hazard identification, material risk analysis, material risk assessment, and material risk control.
Materials safety management science[56]
-
The definition of materials safety management science is defined, and its connotation and theoretical basis are analyzed. They are classified into disaster-causing materials, disaster-avoiding material, and disaster-bearing materials according to the properties of the materials and the ways in which the materials affect safety. Four module management methods should be used to manage disaster-causing materials. Disaster-avoiding materials should be managed by the process management method. Disaster-bearing materials should be managed through a comprehensive management method that includes aspects of technology, routine repair and maintenance, education, and the environment.
Materials-caused disaster chemistry[57]
-
The definition of materials-caused disaster chemistry is defined based on the definition of safety materials science and chemistry. The purposes, discipline foundation, and discipline frame are introduced. The main research contents and methods of the materials-caused disaster chemistry are analyzed from four aspects, including the similarity and peculiarity of the accident-causing materials, hazard analysis of the accident-causing materials, risk evaluation and prediction of the material system, and material safety principles and measures. The theoretical foundation of the chemistry disaster caused by materials is profound, the research content and method are rich, and it will become a new discipline of both safety science and chemistry.
Essentials of some new disciplines of social SS science
Safety pedagogy[58]
-
Safety pedagogy is a cross-disciplinary field that studies the theory, methods, educational law, and application practice of safety education. Safety pedagogy is a human-centered, interdisciplinary subject that originates from practice. By comparing and referring to the two disciplines as education and safety science, the properties, characteristics, functions, and relations with other disciplines of safety pedagogy are described. The theoretical frame work with six research areas at three levels for safety pedagogy is described. The horizontal and vertical disciplinary system of safety pedagogy, referring to the disciplinary systems of safety science and education are created according to the disciplinary classification and creation.
Safety culturology[59]
-
Safety culturology is a cross-disciplinary field that studies and discusses the origin, characteristics, functions, evolution, development, dissemination, and role of safety culture and guides its practice. Its connotation is analyzed by defining the safety culturology. Four basic issues of safety culturology (including research object, research scope, research content, and research purpose) are discussed. The safety culturology disciplinary foundation and five discipline branches (including safety folklore culturology, safety culture semiotics, safety culture historiography, safety culture psychology, and comparative safety culturology) are discussed in detail. The development of safety culturology has a theoretical and practical solid foundation, and the safety culturology discipline system provides a clear outline of the safety culturology basic issues, disciplinary foundation and discipline branches.
Safety culture semiotics[60,61]
-
From the perspective of semiotics and safety culture, the definition of safety culture semiotics is proposed, and its connotation is explained. The theoretical basis of safety culture semiotics is analyzed, and the subject contents of safety culture semiotics are elaborated based on this. The multidimensional structure system of methodology of safety culture semiotics is made up of five dimensions, such as time and theory dimensions. Safety culture semiotics is the tangible manifestation of the safety culture. The subject contents of safety culture semiotics are studied widely and have broad application prospects.
Safety folklore culturology[62]
-
The definitions of safety folklore culture and safety folklore culturology are proposed. The basic issues of the subject of safety folklore culturology are analyzed, which are research objects, research purposes, research contents, and research methods, among others. The three aspects of the application prospect of safety folklore culturology (including safety culturology research, safety publicity and education, and safety management) are discussed. Safety folklore culturology is a new approach to safety culturology research that is a branch discipline of the safety culturology with abundant research content and great research value.
Family safety culturology[63]
-
The definition and connotations of family safety culturology are proposed based on the connotations of both safety culture and family culture. The functions and hierarchy of family safety culture are analyzed. A four-layer structure of functions of family safety culture and its inner structure are created. Furthermore, basic and practical ideas about the creation of a family safety culture are provided, which can be divided into 29 specific ideas and classified into 22 key elements. The foundation of family safety culture is family love; its core is family safety values; its subject is the family organization system; and its functions include four levels, such as basic and consciousness levels, and that family safety culture consists of five aspects, such as emotion and idea safety culture of family.
Safety culture psychology[64]
-
The definition of safety culture psychology is proposed based on that of safety culture and safety psychology. The connotation, research object, disciplinary foundation, and research content of safety culture psychology are analyzed. Safety culture psychology is a new research strategy or paradigm of safety culture and safety psychology, and studies on it can enhance the scientificity, aboriginality, compatibility, and applicability of safety culture and safety psychology.
Safety culture historiography[65]
-
Safety historiography is a science that studies the history of safety, analyzes the process of human understanding, mastering, and avoiding dangerous disasters, and finds out the development law of human safety activities. Safety culture historiography is the study of historiography from the perspective of safety culture and is the intercross science of safety culture and safety historiography. Therefore, the connotation of safety culture historiography and five basic issues, including disciplinary foundation, research object, research content, research method, and research step are analyzed. Safety culture historiography is a new research strategy in safety culture and safety historiography. The safety culture historiography research can effectively correct defects and deficiencies in their traditional research.
Psychic trauma assessment science[66,67]
-
The definitions of trauma and psychic trauma are proposed from the perspective of SS science, and their connotations are analyzed. Furthermore, the definition of psychic trauma assessment science is proposed, and its connotation is explained. Additionally, four basic issues in the psychic trauma assessment science are discussed: the research object, scope, content and purpose. The disciplinary foundation and research process are discussed in detail. The establishment of a science of psychic trauma assessment can provide a significant scientific foundation and operational method for the legislation, compensation, treatment, intervention, and prevention of psychic trauma.
Psychological safety contract theory[68]
-
The definitions of 'safety contract' and 'psychological safety contract' are proposed based on definitions of 'contract' and 'psychological contract', and their connotations are explained. Furthermore, related concepts of psychological safety contract theory are defined, and the characteristics, functions, and types of psychological safety contract are thoroughly analyzed. The psychological safety contract theory is worth full consideration in fields of safety science branches such as safety management, safety psychology, and safety culturology, and psychological safety contract have a significant influence on safety attitudes and behaviors of organization's members.
Safety humanology[69,70]
-
Human nature has a more obvious impact on safety. The connotation and functions of safety humanology are inducted based on principles of SS science and humanology. A framework of safety humanology is put forward, and a model is built for the relationship among all subjects in six dimensions. The basic principles and rules, engineering applications and subordinate cultural areas, corresponding discipline branches of safety humanology are established, the academic foundation and features of safety humanology are elaborated. The safety humanology enriches the SS sciences and build a new humanology research perspective.
Essentials of some new disciplines of systematic SS science
Science of SS science[71]
-
From the perspective of developing SS discipline, SS science is a discipline that takes SS science as its main research object, studies and understands the general theories, principles, and methods of the extension, characteristics, attributes, functions, structure, system, and movement of SS science, and promotes the development and application of SS science. Five axioms are deduced according to the comprehensive property of SS discipline. Furthermore, the methodology of SS science can be selected as a break-through point during the study of SS science. Additionally, the SS comparison science can be regarded as an incision during investigating the methodology of SS science. However, SS science classification from multi-directions is a crucial and basic research approach. SS science is very valuable in guiding the study of SS science.
SS systematology[72]
-
The differences and connections between SS-system thinking are discussed. Furthermore, a theoretical system framework of SS systematology is developed. The connotations of system-SS thinking are different from those of SS-system thinking. SS systematology contains eight cognitive-typed basic theories at the SS-aspect and eight practical-typed basic theories at the system-aspect; the theoretical system framework of SS systematology is developed by combining SS systems different in size with the two research directions and their sub theory branches.
SS operations research[73]
-
The definition of SS operations research is provided and its connotations are analyzed. The disciplinary foundation of SS operations research is also discussed. The major subjects of SS operations research are theories, academic disciplines and applications. The discipline foundation framework of SS operations research is provided, as well as its application prospects. SS operations research is an inter-discipline subject that continues to solve SS problems, uses operational research theory as its foundation, and solves the SS operations problems by using optimization methods.
SS synergy theory[74]
-
The theory of SS synergy is provided, and the research category of SS synergy theory with the correlation dimension of SS objectives is summarized. Seven important subordinate application principles of SS synergy, namely: the SS collaboration competition principle, SS instability principle, SS fluctuation principle, SS order parameter principle, SS servo principle, SS self-organization principle, and SS synergistic effect principle, are elaborated on its connotation, respectively. The SS synergy theory can reveal the operating mechanism and the general rules of the SS system, which can provide a new method for the analysis, evaluation, and counter measures of the SS system.
SS relations science[75]
-
The definition of SS relations is proposed, and its connotation, types, and characteristics are analyzed depending on the features of the SS relations architecture. The definition of SS relations science is proposed; its basic subject issues and theoretical basis are analyzed. Six methods of SS relations representation, such as object and logical representation, are extracted, and the branch disciplines of the science of SS relations are created with 11 different aspects. The research of SS relations science has a profound theoretical basis and practical basis and has wide application fields and development prospects, especially in accident prevention in the big data era.
SS planning science[76]
-
The definition of SS planning science is provided based on SS science and planning science. Furthermore, its connotation is analyzed from five aspects, such as logical starting point, research purpose, and research object. The basic problems relating to SS planning science are discussed from three perspectives: discipline properties, foundation and characteristics. Research content of the science are derived from basic theory and application practice. A three-dimensional structure system for the methodology of SS planning science is created, and the general research procedures and methods are refined.
SS system management science[77]
-
SS system management science is a science that studies the laws and methods of SS system management activities. It takes people, objects, information, environment, culture, system and other elements in the determined system as well as their relationship with SS as the research object, and studies the reasonable and effective configuration of various elements and their relationship to ensure the continuous realization of the SS status in the system. The theoretical basis of SS system management is SS science, system science, and management; the research object is SS systems; the research tasks are to use the theory and methods of modern management to reveal the law of SS system management activities and to establish SS system management models. Therefore,the methodology of SS system management is very important.
SS complexity science[78]
-
SS complexity is a science that studies SS complexity. SS complexity discipline, or SS complexity science, is a growing topic for SS research in the future. Four ways to judge safety complex problems, and eight basic principles to be followed in safety complexity studies are provided. Five core concepts, and nine basic definitions of safety complexity, and nine typical methods of such research are summarized. A general model and super logic structure diagram for expressing safety complexity system are created, and five controlling strategies are proposed. Furthermore, branches of the discipline are put forward from eight perspectives. These findings are crucial for the development of safety complexity science, and they serve as the theoretical foundation for it.
Essentials of some new disciplines of tran-sectional SS science
SS comparison science[79]
-
SS comparison science is a scientific method to reveal the common points and differences of elements, components, or subsystems in the SS system and draw conclusions that are conducive to mutual reference and SS optimization decision-making. The sub-disciplines of the SS comparison science are created accordingly. The corresponding study content for each sub-discipline are elaborated. The framework of the SS comparison science is created. The broad prospect is illustrated based on the comparison study on SS science and by the synthesis of SS comparison literature. Many new SS measures can be invented by using multi-angle SS comparison science. SS comparison science will become one of the most important foundations of SS science methodology.
SS comparison jurisprudence[80]
-
SS jurisprudence is a science that takes SS laws, regulations, phenomena, and their laws as its research content, and is a cross-discipline of law and SS science. SS comparison jurisprudence is combined with the comparison sciences, jurisprudence and SS jurisprudence. SS comparison jurisprudence is the study of SS jurisprudence comparison. Furthermore, the horizontal branch systems and the vertical branch systems of SS comparison jurisprudence are established. The comparison dimensions, time and space dimensions, and knowledge dimension of the SS comparison jurisprudence are proposed. The research layers, structure, and space of SS comparison jurisprudence are determined, and the four-dimension methodology system is created. Several comprehensive comparison paths are given.
Safety comparison culturology[81]
-
The definition of safety comparison culturology is proposed based on the definitions of comparison science and safety culturology, and its connotations and theoretical basis are analyzed. Comparison dimensions and research content of safety comparison culturology are proposed. The structure system of safety comparison culturology methodology is created, and the research process of safety comparison culturology is analyzed. Safety comparison culturology is an important way to conduct safety culturology research, and safety comparison culturology can promote safety culturology research and development.
Safety comparison ethics[82]
-
Safety ethics is the knowledge about safety morality. Furthermore, it is the knowledge system concerning ethical principles, ethical categories and moral norms of dealing with the social relations between people, and people to society in safety activities. Safety comparison ethics is the study of safety from the perspective of comparison and is the intercross science of safety science, safety comparison science and safety ethics. The differences between the study objects of safety ethics and safety law are pointed out accordingly. The sub-disciplines and theoretical system of safety comparison ethics are established in perspective of both theory and application, and each sub-discipline has been elaborated. The basic research process, models, and methods are listed, classified, and described. The safety comparison ethics not only provides a new perspective for the research of ethics, but also has the potential to overcome research errors caused by time and space differences.
Safety comparison economics[83]
-
Safety economics is a discipline that studies the relationship between safety and various economic activities from the perspective of safety. Safety comparison economics uses the perspective of comparison to study safety economics and is based on the basic theories of comparison science and safety economics. Ten aspects of studying safety comparison economics are presented based on the attributes of safety comparison economics. A four-dimensional structure system is established which includes the method, knowledge, step and logic of safety comparison economics. Safety comparison economics is a new sub-discipline of safety science formed by the fusion of safety economics and comparison science.
Safety similarity systematology[84]
-
Safety systematology is a discipline that analyzes, evaluates, controls, and optimizes the system safety risks to achieve the safety objectives of the system and its whole process. Safety similarity systematology is studied from the perspective of similarity of safety systems. The feasibility and significance of establishing a safety similarity systematology are explained through a disciplinary attribute and system feature. The foundations of safety similarity systematology are described, the concept system, research levels, and application fields Furthermore, the disciplinary branches are classified within a multi view. Development direction and related subjects extended from safety similarity systematology are prospected. Safety similarity systematology provides new methods for the research of safety systematology.
Safety similarity management science[85]
-
The feasibility of creating a safety similarity management science is demonstrated, and the definition and connotation of safety similarity management science are analyzed. The necessity of dynamic similarity analysis is made clear by analyzing the object and content of the research. Therefore, a tapered structure of similarity analysis is created on the basis of time and the other six dimensions. Furthermore, the comparison method is ascertained as the basic research means of safety similarity management science, and a methodology system of safety similarity management science and four a stage research procedure are created.
Safety similarity psychology[86]
-
The definition of safety similarity psychology is defined and its connotation is analyzed. The disciplinary foundations of safety similarity psychology are analyzed, and the concept system and research levels are created. The state and nature of safety similarity psychology, the dimension system of quantity, category and nature are defined based on study objects scope. The research approach of safety similarity psychology is described from different perspectives. According to research, safety similarity psychology is a direct cross fusion of safety psychology and safety similarity to form a new branch of safety science.
-
(1) SS science is a new interdisciplinary and comprehensive discipline. Its interdisciplinary nature provide SS science with ample time and space for research and development, and the objective feasibility and possibility for creating new disciplinary branches. Furthermore, as society evolves, new SS issues emerge endlessly, and the fields and categories involved in SS become increasingly broad. The aforementioned reasons form the objective conditions for creating new SS science disciplinary branches.
(2) The creation of new disciplines of SS science requires researchers who can focus on creating SS disciplines and are aware of the need to lead in terms of social and human needs, interdisciplinary, suitable research methods, relevant knowledge support, and external conditions. The gene of creating new SS science discipline is a new growth point formed by the integration of existed multiple disciplines, and the driving force for creating new SS science disciplines is the new need of society and humanity.
(3) The creation of new SS science disciplines needs practice. It needs to be based on the science of science; moreover, it needs to be guided by new science disciplines. Using the intercross attributes of SS science and new interdisciplinary thought will achieve twice the result with half the effort to create new disciplinary branches of SS science.
(4) The important elements of creating a new discipline of SS science include the following: disciplinary space-time presupposition, definition, connotation, extension, research objective, research content, research method, research program, basis, system framework, and application field of the new discipline.
(5) Cross, edge, integrated, common, transverse, node, subdivision, crystallization, problem, demand, theoretical, conjecture, experimental, virtual, artificial intelligence, big data, combined multi and uncertainty modes are among the knowledge breeding modes for creating new disciplinary branches of SS science.
(6) Our research group's 40 new SS science disciplines fill many gaps in the theory of SS science, laying a foundation and having a leading and lasting significance. Furthermore, these new disciplines demonstrate that our new SS science disciplinary theories are correct and effective.
(7) The definition, connotation, extension, research objective, research content and method, research paradigm, discipline foundation, framework, environment, development conditions, application fields, etc., of each new SS science discipline form a blueprint for the development of new disciplines, which can attract more resources to the creation of new disciplines that can be rapidly developed into mature disciplines.
The authors would like to thank reviewers and editors cordially for their comments and suggestions. This study is supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (No. 22ZDA121) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51534008).
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
- Copyright: © 2023 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press on behalf of Nanjing Tech University. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Wu C, Wang B. 2023. Theory of creating new disciplines of safety and security (SS) science and essentials of 40 practical examples. Emergency Management Science and Technology 3:2 doi: 10.48130/EMST-2023-0002
Theory of creating new disciplines of safety and security (SS) science and essentials of 40 practical examples
- Received: 13 January 2023
- Accepted: 21 February 2023
- Published online: 28 February 2023
Abstract: The development of society and the demand for the improved safety and security (SS) of people in the SS research field have been constantly changing and growing, resulting in the emergence of new SS science disciplines. In this study, the conditions, academic thought, methodology, paradigm, and modes for creating new disciplines of SS science, based on the practical experiences of creating new disciplines of SS science by the authors and methods of analysis and induction over the past ten years are summarized. The essentials of 40 new disciplines of SS science created are presented. The aforementioned theoretical analysis can encourage the development of more new disciplines of SS science and shorten the incubation and growth cycle of new disciplines in this research field. The results also enrich the discipline construction theory of SS science and are crucial in promoting the development of SS science in the future.