-
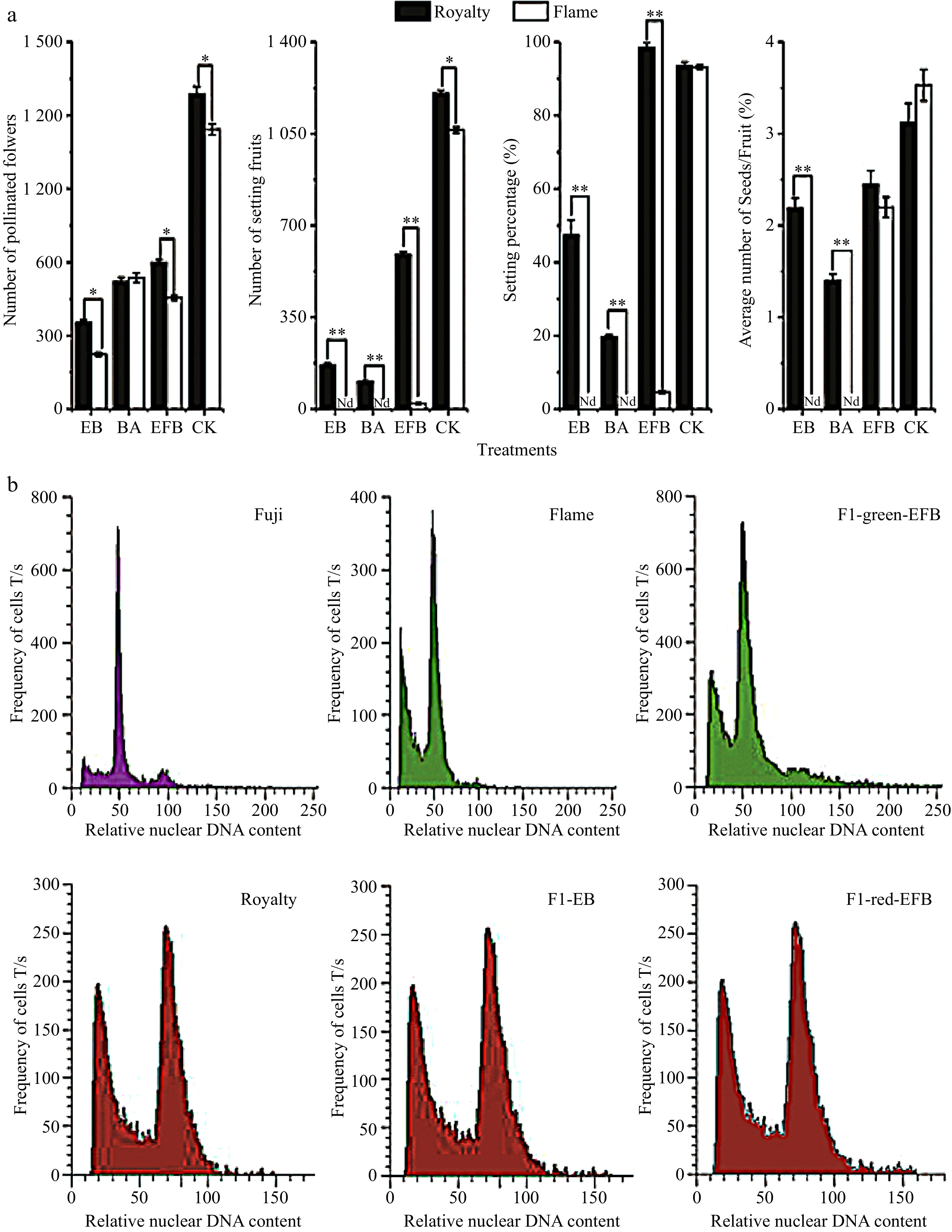
Figure 1. Fruit set and number of seeds across pollination treatments between Malus 'Royalty' and 'Flame' (a) and the fluorescence intensity distribution of nuclear DNA in the young leaf cells of the Malus cultivars (b). (a) The fruit setting rates and the average number of seeds/per fruit in Malus cultivars under different treatments. EB: bagging after emasculation; BA: bagging alone; EFB: pollination followed by bagging; and CK: untreated. All experiments were conducted with labelling at the large bud stage. The values represent the means from 2014 and 2015. The data (mean ± SD) are the sum of three biological repetitions for each treatment. (b) Fluorescence intensity distribution of nuclear DNA in the young leaf cells of the Malus cultivars 'Fuji', 'Flame', and 'Royalty', as well as their offspring. 'Fuji', a diploid Malus cultivar, was used as a reference to detect the ploidy of Malus crabapple 'Flame' and 'Royalty' by using flow cytometry. F1-EB: the F1 seedlings of 'Royalty' EB; F1-red-EFB: the F1 seedlings with a red phenotype from 'Royalty' EFB ('Royalty' (♀) × 'Flame' (♂)); and F1-green-EFB: the F1 seedlings with a green phenotype from 'Royalty' EFB ('Royalty' (♀) × 'Flame' (♂)).
-
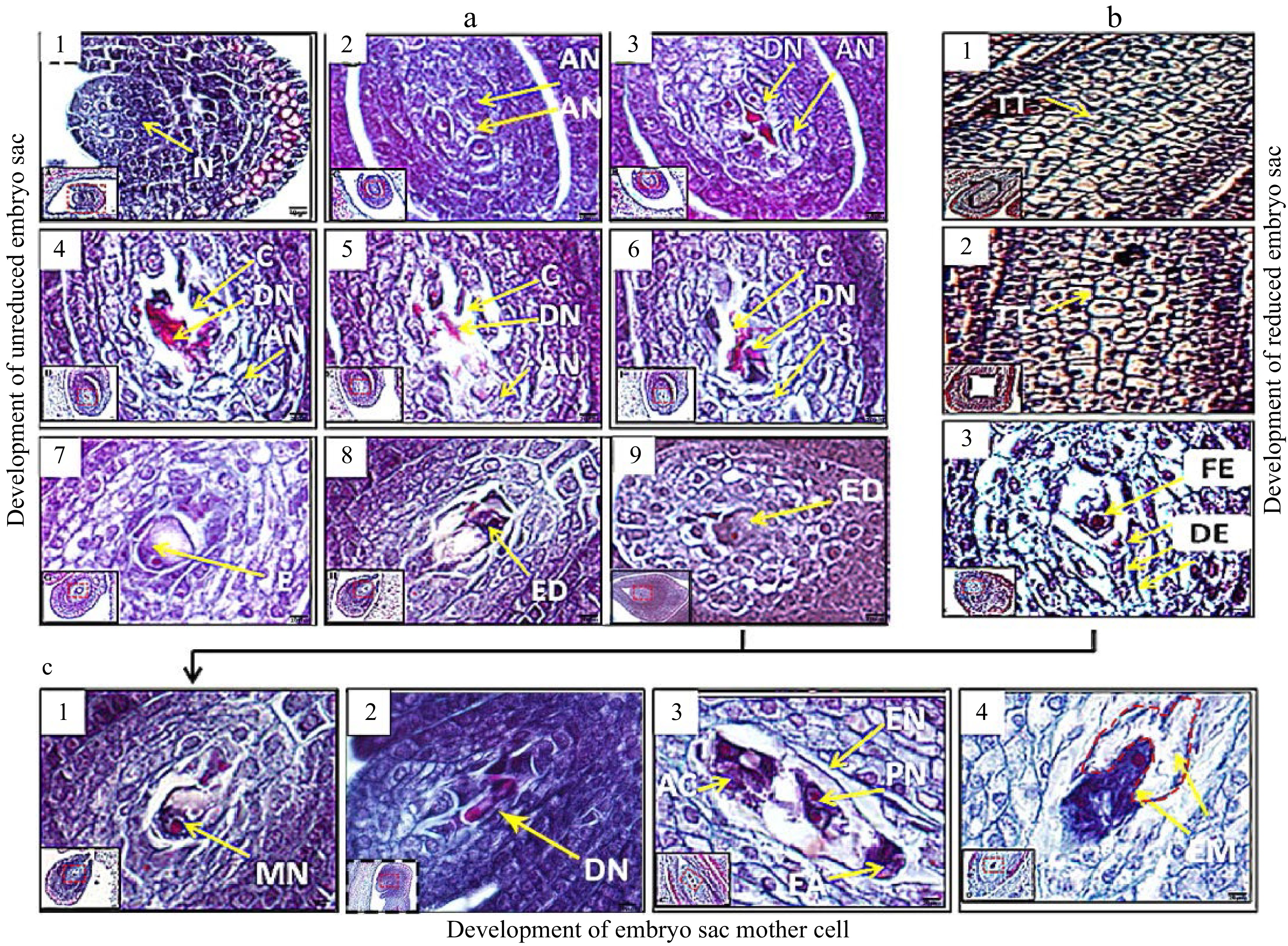
Figure 2. Paraffin sections of the development in the embryo mother sacs of 'Royalty' EB (a and c) and EFB (b) ovules. N: nucellus; AN: active nucellus cells; DN: disintegrated nucellus cells; TT: tetrads via meiosis; C: cavities left after nucellus cells disintegrated and died; S: sporogenous cells; E: embryo sac mother cells; ED: developing embryo sac mother cell; FE: functional embryo sac mother cells; DE: disintegrating embryo sac mother cells; MN: mononuclear embryo sac; DN: double nuclear embryo sac; AC: antipodal cells; EN: eight nuclear embryo sac; PN: polar nuclear; EA: egg apparatus; and EM: embryo. Bar = 5 μm. At least three biological replications were performed.
-
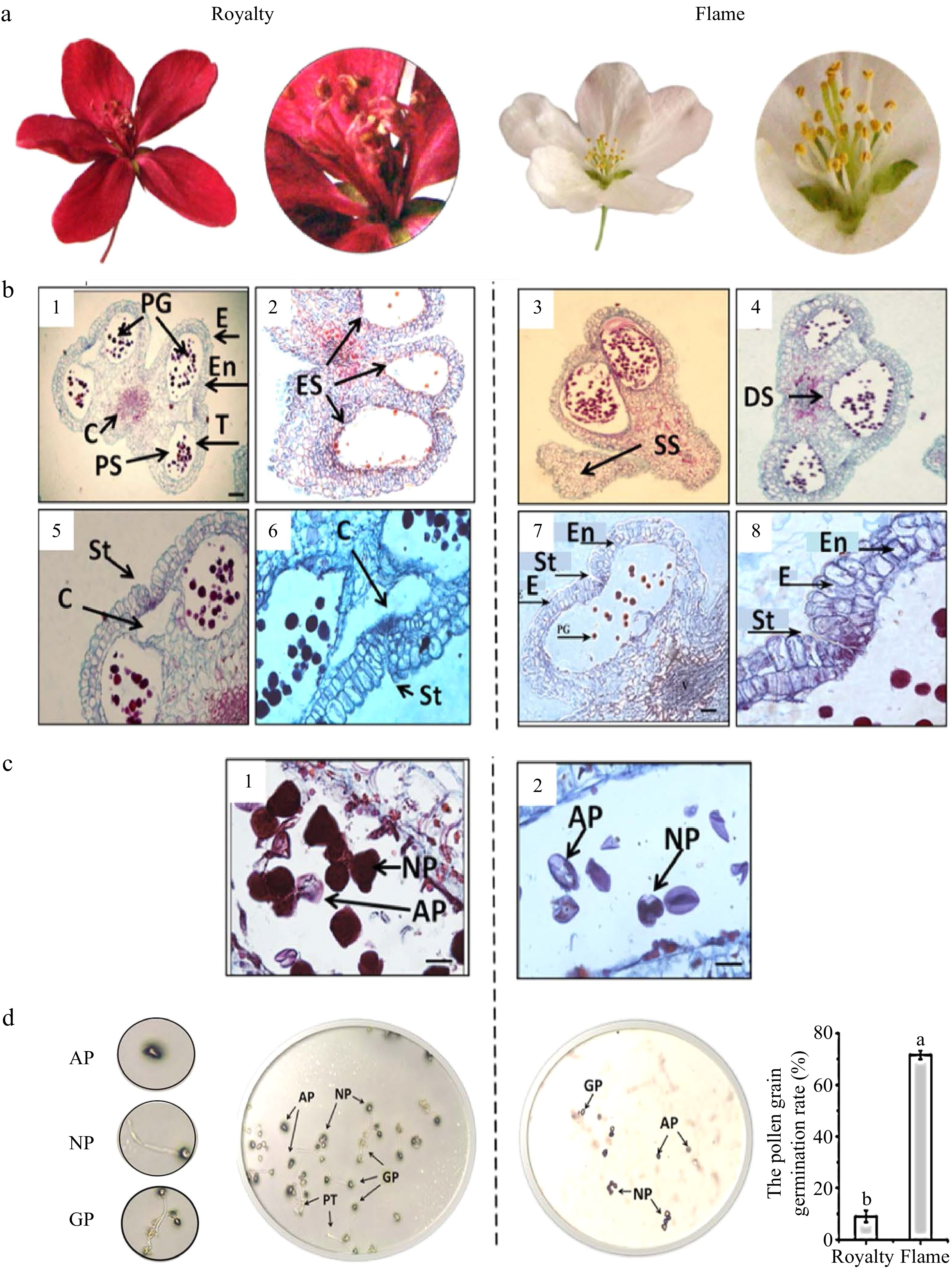
Figure 3. Morphological and anatomical characteristics of anther and pollen grains and pollen grain activity. (a−b) Morphological and anatomical images of anther and pollen grains in 'Royalty' and 'Flame'. (c−d) Pollen grain activity in 'Royalty' and 'Flame'. Note: E: epidermal layer; En: fibrous layer; T: tapetal layer; PG: pollen grains; C: connective tissue; PS: pollen sac; ES: empty sacs with few pollen grains; SS: solid pollen sacs not developed; DS: dissymmetrical pollen sacs without symmetric arrangement; St: stomium in the anther epidermis and intermediate layer adjacent to the cavity; C: cavity between 2 adjacent pollen sacs; NP: normal pollen grains; AP: abortive pollen grains; Gp: germinated pollen grains on culture medium; and PT: pollen tubes. Bar = 100 μm. At least three biological replications were performed.
-
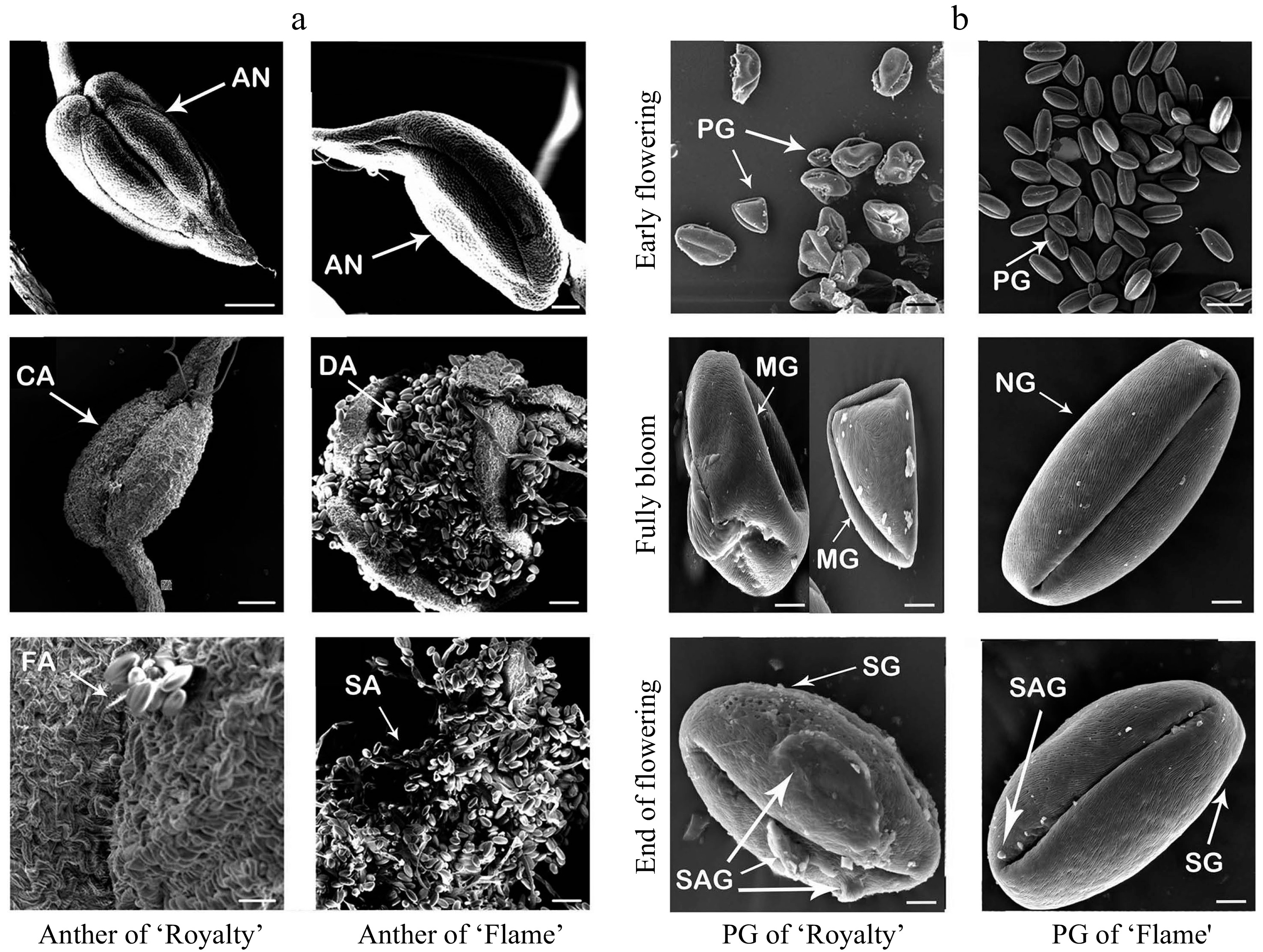
Figure 4. Scanning electron micrographs of anthers at different flowering stages (a) and pollen grains (b) during the blooming period of 'Royalty' and 'Flame'. AN: anther; CA: anthers that cannot split; DA: dehiscent anther and pollens; FA: anthers not fully split; SA: anthers with scattered pollen; PG: pollen grains; MG: malformed pollen grains; NG: normal pollen grains; SG: the surface of pollen grains; and SAG: the surface attachment of pollen grains. At least three biological replications were performed.
-
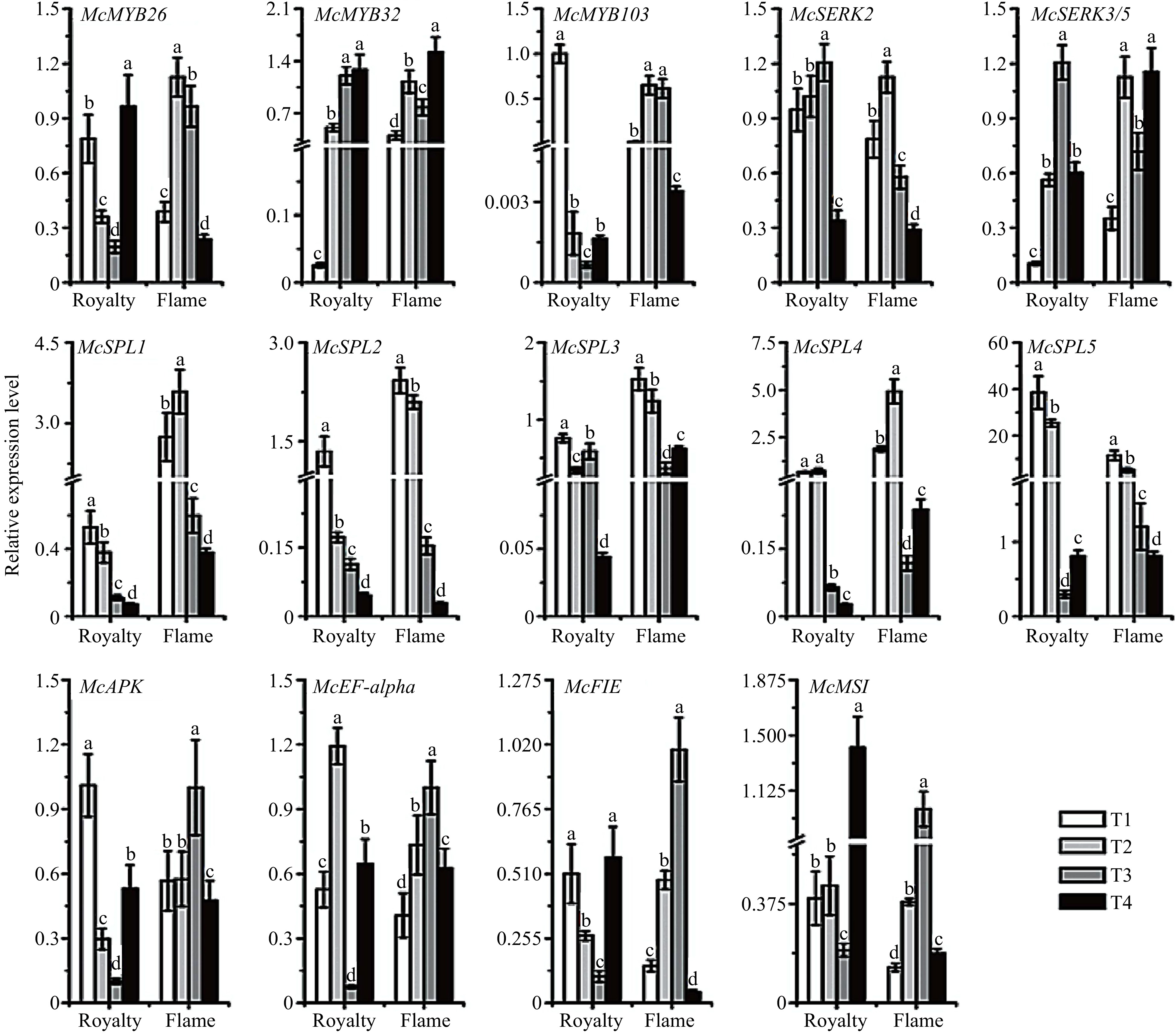
Figure 5. Relative expression profile of the genes related to apomixis in 'Royalty' and 'Flame' during flowering periods. T1-T4: flower organ developmental stages. The data (mean ± SD) are the sum of three biological repetitions for each treatment.
-
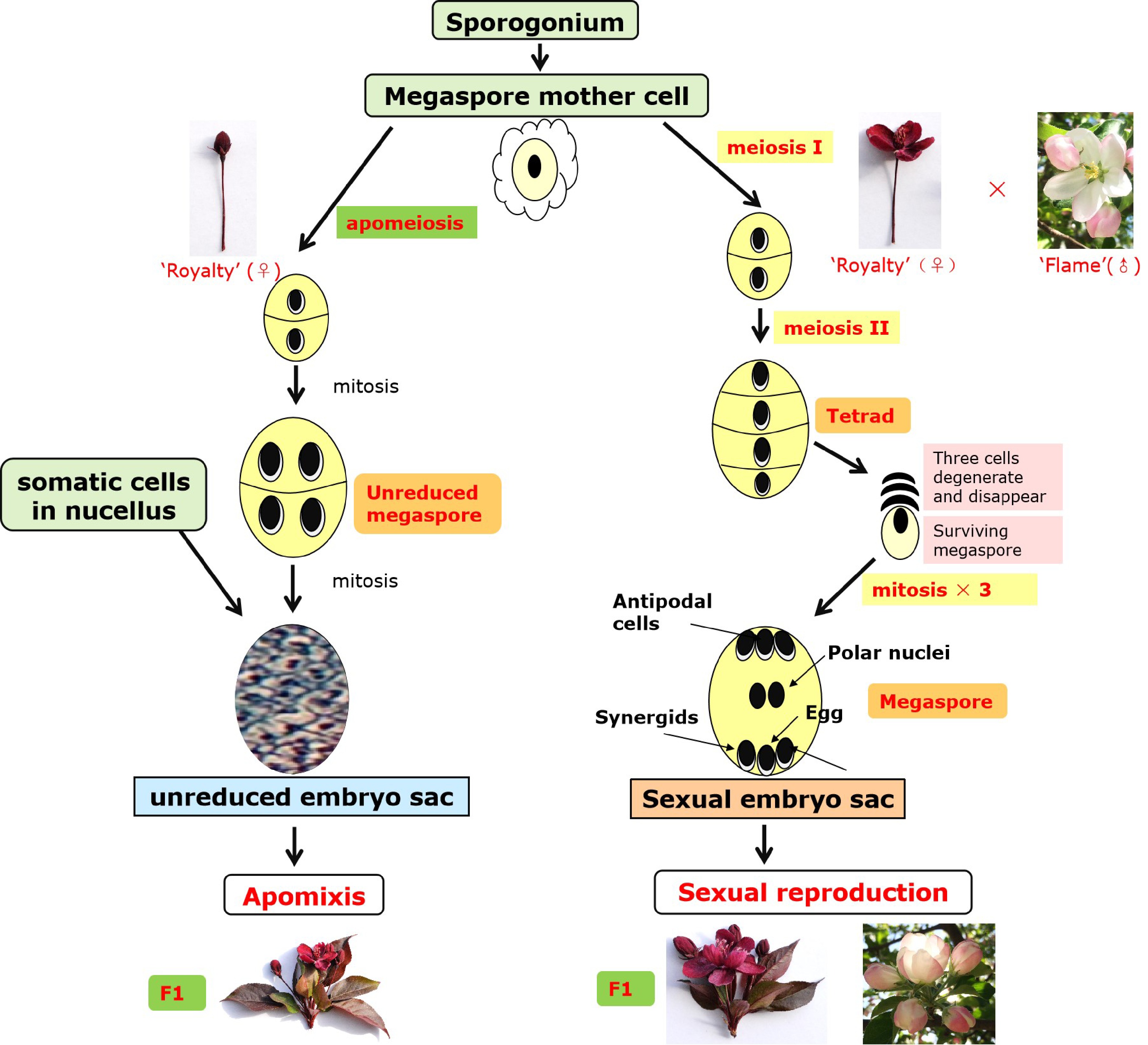
Figure 6. Mechanism of apomixis and sexual reproduction in 'Royalty'.
-
Pollination type Crossing groups Number of pollinated flowers Number of
fruitsSetting percentage (%) Average number of seeds Bagging after emasculation (EB) 'Royalty' (♀) 354 168 47.46 2.19 Bagging after emasculation (EB) 'Flame' (♀) 224 0 0.00 0.00 Bagging alone ('Royalty' BA)) 'Royalty'(♀) × 'Royalty' (♂) 521 104 19.70 1.40 Bagging alone (Flame' BA) 'Flame'(♀) × 'Flame' (♂) 537 0 0.00 0.00 Pollination followed by bagging after emasculation (EFB) 'Royalty' (♀) × 'Flame' (♂) 589 589 98.44 2.45 Pollination followed by bagging after emasculation (EFB) 'Flame' (♀) × 'Royalty' (♂) 455 21 4.62 2.20 Untreated (CK) 'Royalty' (♀) × '?'(♂) 1,287 1,204 93.55 3.10 Untreated (CK) 'Flame' (♀) × '?'(♂) 1,143 1,065 93.18 3.50 Notes: Average number of seeds is average seed number per fruit. At least three biological replications were performed. Table 1. Statistical results of the pollination test for Malus 'Royalty' and 'Flame'.
-
Cultivars Mean G1 Relative nuclear DNA content Ratio Chromosome ploidy level Ratio Fuji 50.01 ± 1.36b 100.00 1.00 2x 1.00 Royalty 76.04 ± 1.07a 152.05 1.52 3x 1.52 Flame 51.21 ± 0.75b 102.04 1.02 2x 1.02 F1-EB 78.48 ± 0.87a 149.01 1.49 3x 1.49 F1-red-FEB 77.38 ± 1.21a 150.66 1.51 3x 1.51 F1-green-FEB 54.34 ± 1.45b 108.66 1.09 2x 1.09 Notes: Mean G1: mean fluorescence intensity; F1-EB: F1 seedlings of 'Royalty' EB; F1-red-EFB: F1 seedlings with the red phenotype of 'Royalty' from 'Royalty' (♀) × 'Flame' (♂) EFB; and F1-green-EFB: F1 seedlings with the green phenotype of 'Royalty' from 'Royalty' (♀) × 'Flame' (♂) EFB. At least three biological replications were performed. Table 2. Relative nuclear DNA content and chromosome ploidy level of 'Royalty' and 'Flame' as well as their offspring.
-
Gene description F/R_20d F/R_90d SPL domain class transcription factor, SBP domain 1.5155** −1.9002 SPL domain class ranscription factor, Mlo family//NUDIX domain//PSK 0.0018** 0.7627 Putative WD-40 repeat protein, MS12, WD domain, G-beta repeat 0.1297** −0.6362 Elongation factor 1 alpha subunit −0.482** −0.0517 MYB-like DNA-binding domain −1.0009** −0.0038 Nodulation protein S //Methyltransferase domain//Thiopurine S-methyltransferase −1.6507 −1.7201 Anther-specific gene, CcmE −2.0335** 0.0536 Putative pollen surface protein, Peptidase//Delta Atracotoxin 2.003* 3.6557 MYB domain class transcription factor −0.2966** 0.5912 MYB transcription factor, Cytotoxic 0.7377 0.4173 Methyltransferase domain//Putative methyltransferase 0.9047* 1.6914 Anther-specific gene, TAP42-1ike family −0.9796** −0.3826 Methylransferase domain//Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase class-1 −0.7489 −0.8379 Probable methyltransferase PMTI-like, Methyltransferase domain −0.8516** −0.0800 MYM-type Zinc finger //Methyltransferase domain 0.8559** −0.2436 Peroxidase//Methyltransferase domain −0.263** 0.2461 Hypothetical methyltransferase//ER lumen protein retaining receptor//Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine Ca binding 0.3528** 1.1421 Methyltransferase domain//Methyltransferase small domain −0.5462** 0.3341 Sigma-70, region 4//MYB like DNA-binding domain 0.166** −0.5268 Stromal cell-derived factor 2-like protein MIR domain 0.2252** −0.5918 Somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 3B precursor, Leucine Rich Repeat//Protein kinase domain −0.9486** 0.4198 Notes: F/R-20d: the related gene expression ratios of 'Flame' to 'Royalty' fruits at 20 days after the blooming period; F/R-90d: the related gene expression ratios of 'Flame' to 'Royalty' fruits at 90 days after the blooming period. At least three biological replications were performed. Table 3. The results of RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) of 'Royalty' and 'Flame' fruits.
Figures
(6)
Tables
(3)