-
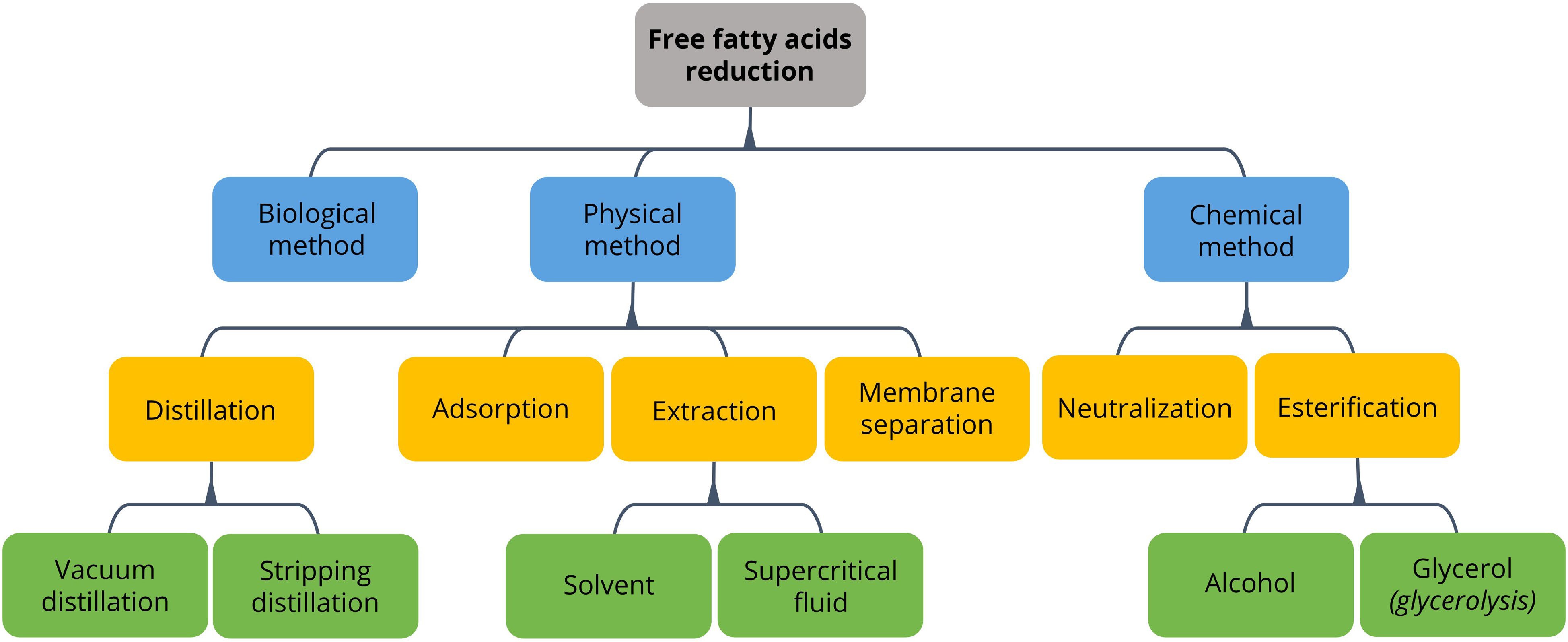
Figure 1.
Alternatives for free fatty acid reduction.
-
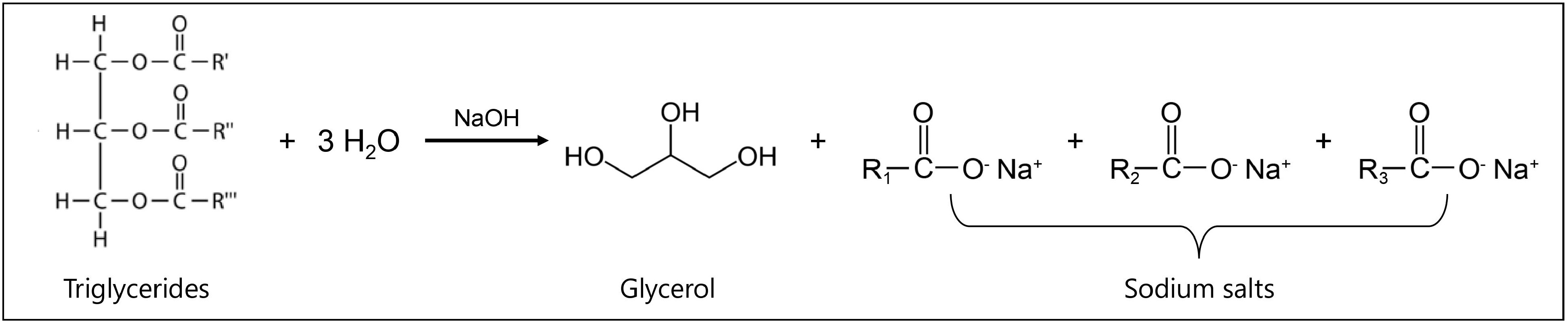
Figure 2.
Saponification process of waste cooking oil.
-
Techniques Process Pros Cons Acid removal References Chemical methods Neutralization Lesser energy usage Suitable for WCOs with different origins Higher removal selectivity Produce soaps and wastewater Reduce triglyceride content Large amount of water needed during washing process Up to < 1 wt% Pinzi[42],
Rodrigues and Meirelles[43], Shahidi[44], Tanzer et al.[45]Esterification Higher efficiency Suitable for WCOs from different origins Flexible working principle (simultaneous esterification-transesterification in biodiesel production) Higher processing costs Produce wastewater Cause corrosion if homogeneous acidic catalysts are used Able to achieve 100% acid conversion Mendecka et al.[21], Vaisali et al.[30], Divakar and Manohar[46], Elias et al.[47], Saravanan et al.[48] Physical methods Distillation Simple and universal applicability Simultaneous removal of other volatile components Less amount of waste generated Good quality of FFA High capital and operating costs Large energy consumption Vacuum system operates with steam jets and can generate higher wastewater Up to < 1 wt% Cárdenas et al.[24], Maddikeri et al.[35], Rodrigues and Meirelles[43], Shahidi[44], Yuan et al.[49] Extraction with solvent or supercritical fluid No generation of by-products Low energy consumption Low loss of WCO during extraction High capital and equipment costs Selection of solvent with low reactivity and high thermal stability is critical From 2−4 wt% to < 0.1 wt% Cárdenas et al.[24], Rodrigues and Meirelles[43], Bhosle and Subramanian[50], Meirelles[51] Adsorption Enhance the color of WCO by removing α and β unsaturated carbonyl compounds Applicable even under the presence of different impurities in WCO Large amount of absorbents are required Solid waste generation High separation effectiveness is required prior to industrial implementation Roughly 65%–80% efficiency Cárdenas et al.[24], Rahayu et al.[38], Rincón et al.[52], Sumnu and Sahin[53] Membrane separation Able to achieve selective FFA separation Lower energy consumption Improved FFA quality Higher yield of WCO Cost of membranes is very high High generation of solid waste Solvent is required to achieve separation Usually associated with solvent extraction with similar removal efficiency Cárdenas et al.[24],
Vaisali et al.[30], Bhosle and Subramanian[50],
Ladhe and Kumar[54]Table 1.
Pros and cons between the existing techniques for FFA removal from WCO.
Figures
(2)
Tables
(1)