-
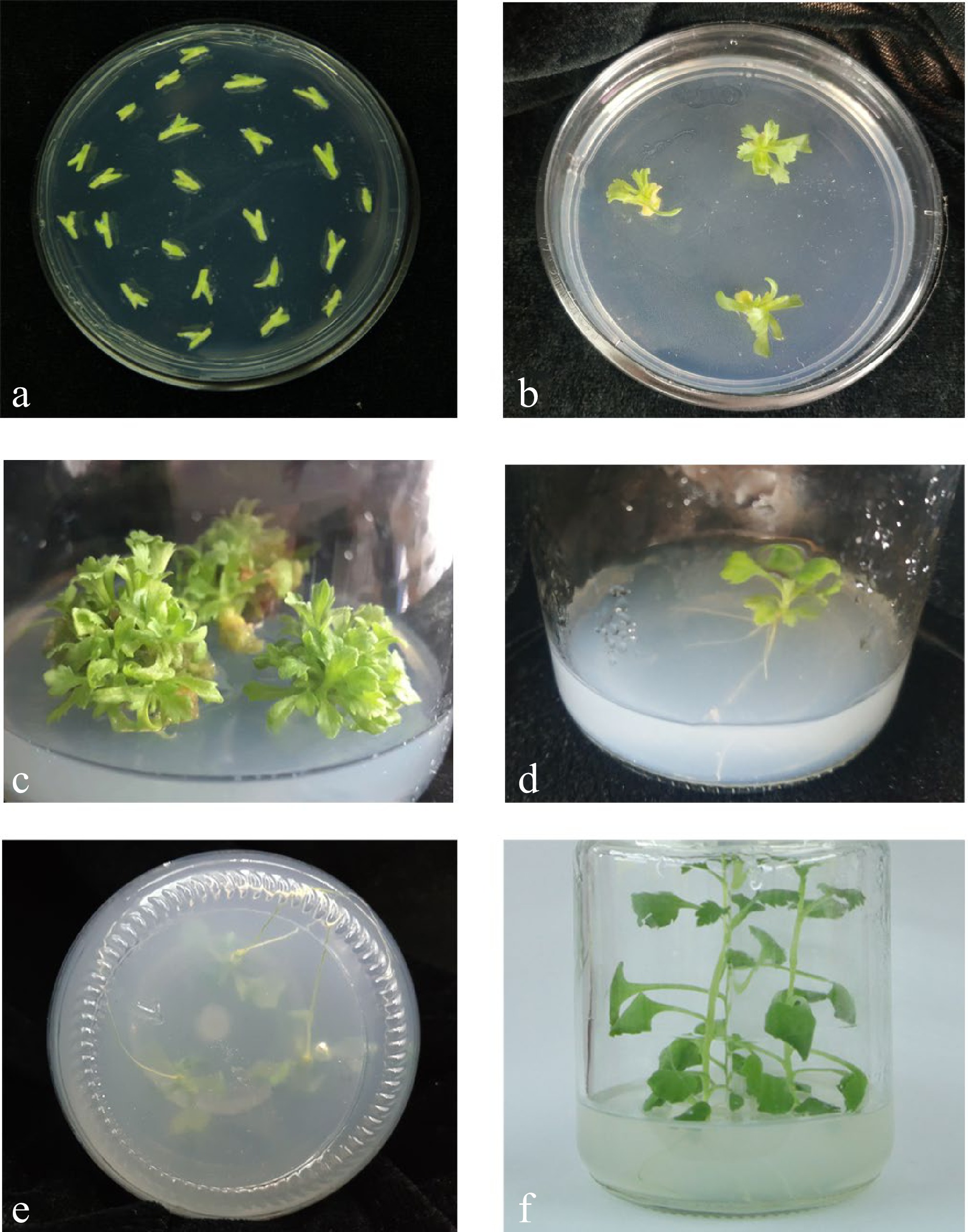

Figure 1.
The regeneration of stem internode explants. (a) The explants were cut from seedlings with undifferentiated axillary buds and without stem tips and stem leaves. The best age of the materials is 30 d. (b) The axillary buds of stem segments began to differentiate on the medium containing 6-BA and NAA. (c) Transformed buds rapidly formed a mass of shoots. (d) The transgenic shoots were unable to root in the rooting test. (e) Obvious root systems of the transformation. (f) The transgenic plants.
-
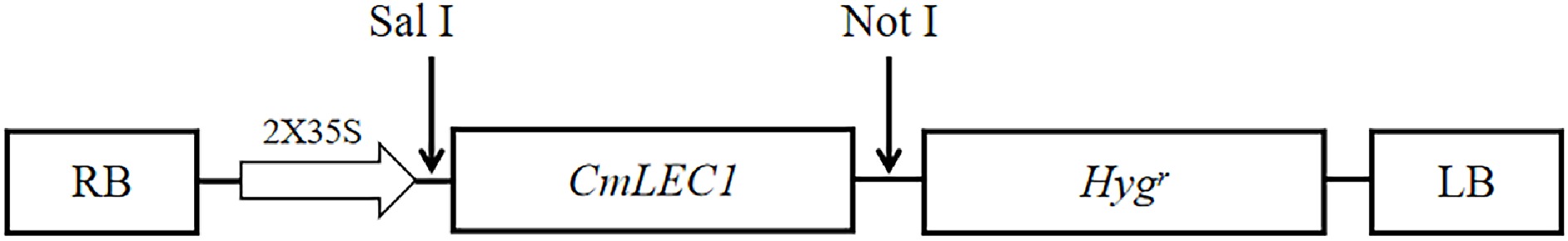
Figure 2.
Plant expression vector construction. Exogenous gene CmLEC1 was linked at the expression vector pMDC32, which contains the encoding sequence of hygromycin resistance. There is also a CaMV35S promoter, which can start the expression of CmLEC1.
-
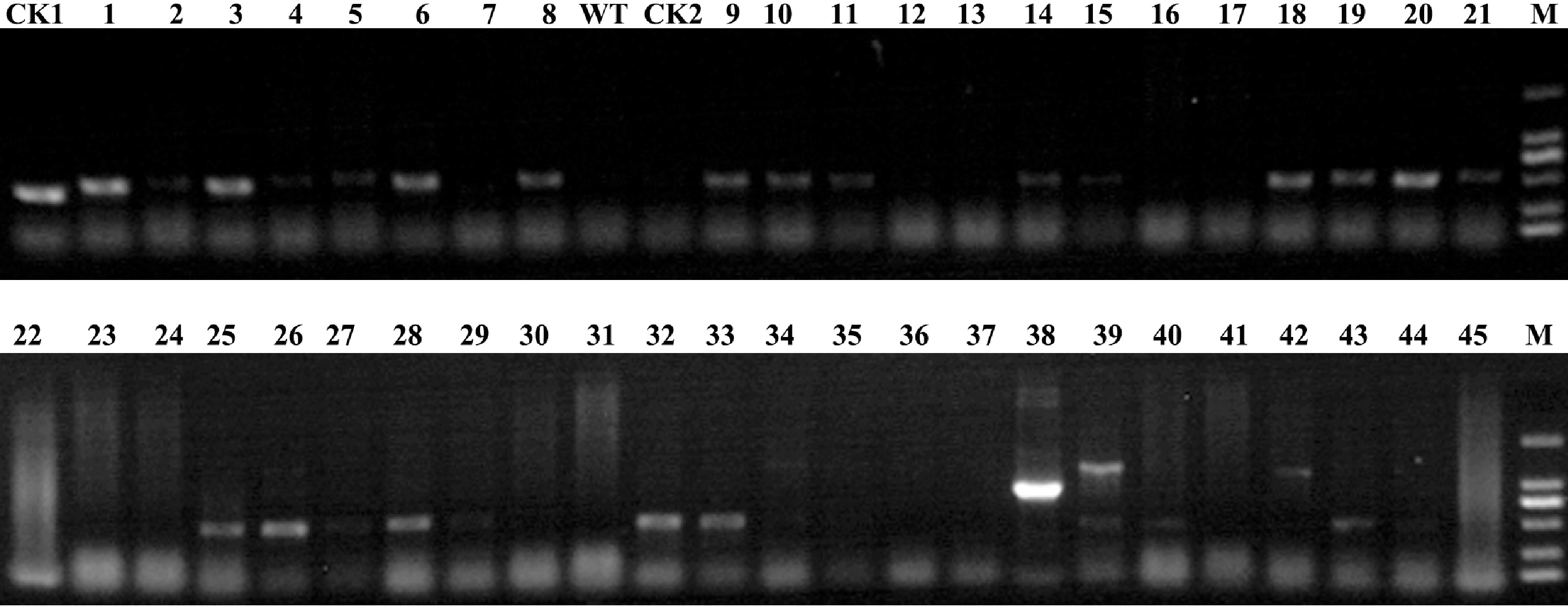
Figure 3.
Identification of transgenic plants at the DNA level. PCR analysis was carried out among the putative transgenic plants and control plants to confirm successful transformation. M: 2000 marker; 1−45: the putative transgenic plants to be identified; WT: 'Yuhualuoying' wild type plants; CK1: positive control; CK2: negative control.
-
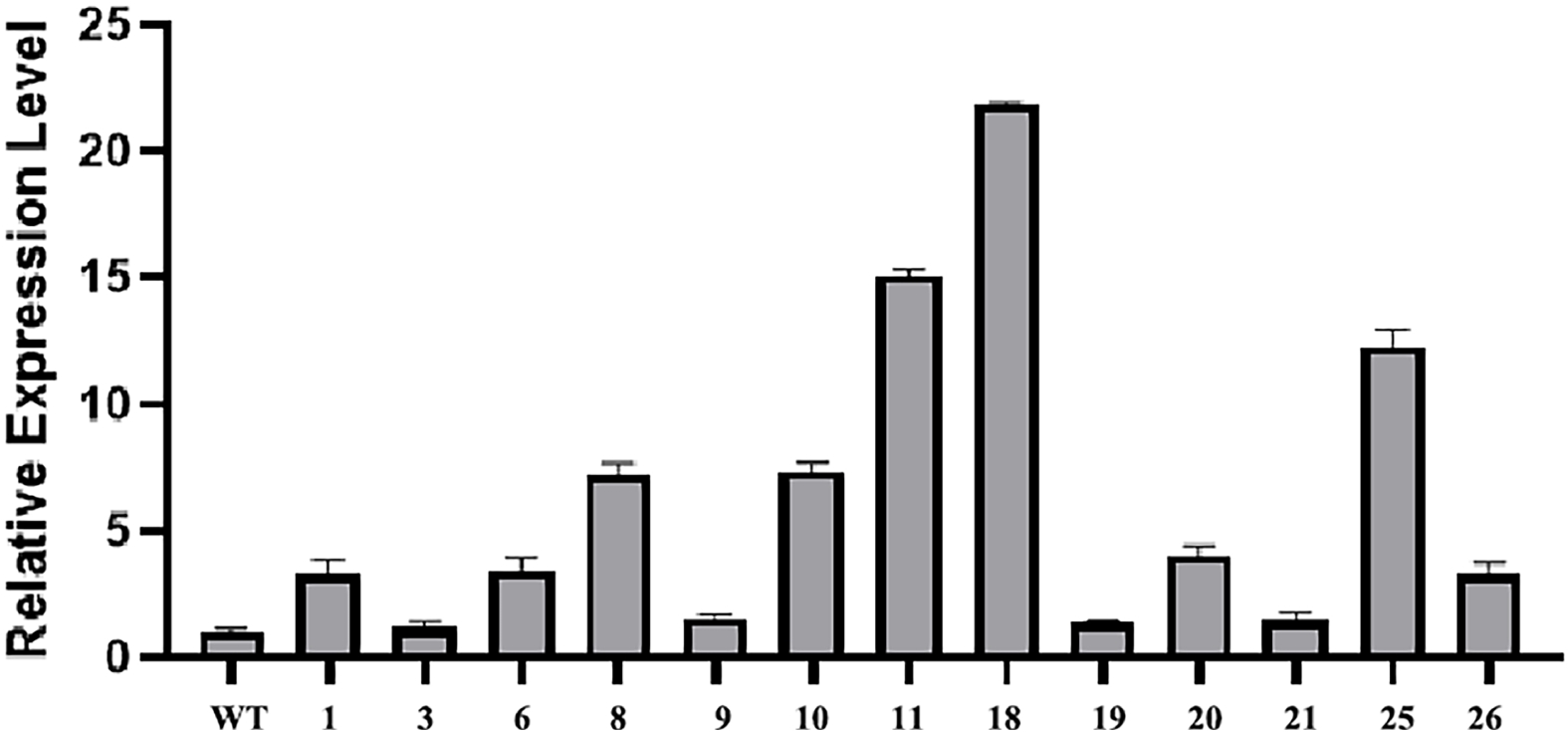
Figure 4.
Identification of positive transformants. Relative expression of CmLEC1 in chrysanthemum 'Yuhualuoying' was confirmed by qRT-PCR analysis.
-
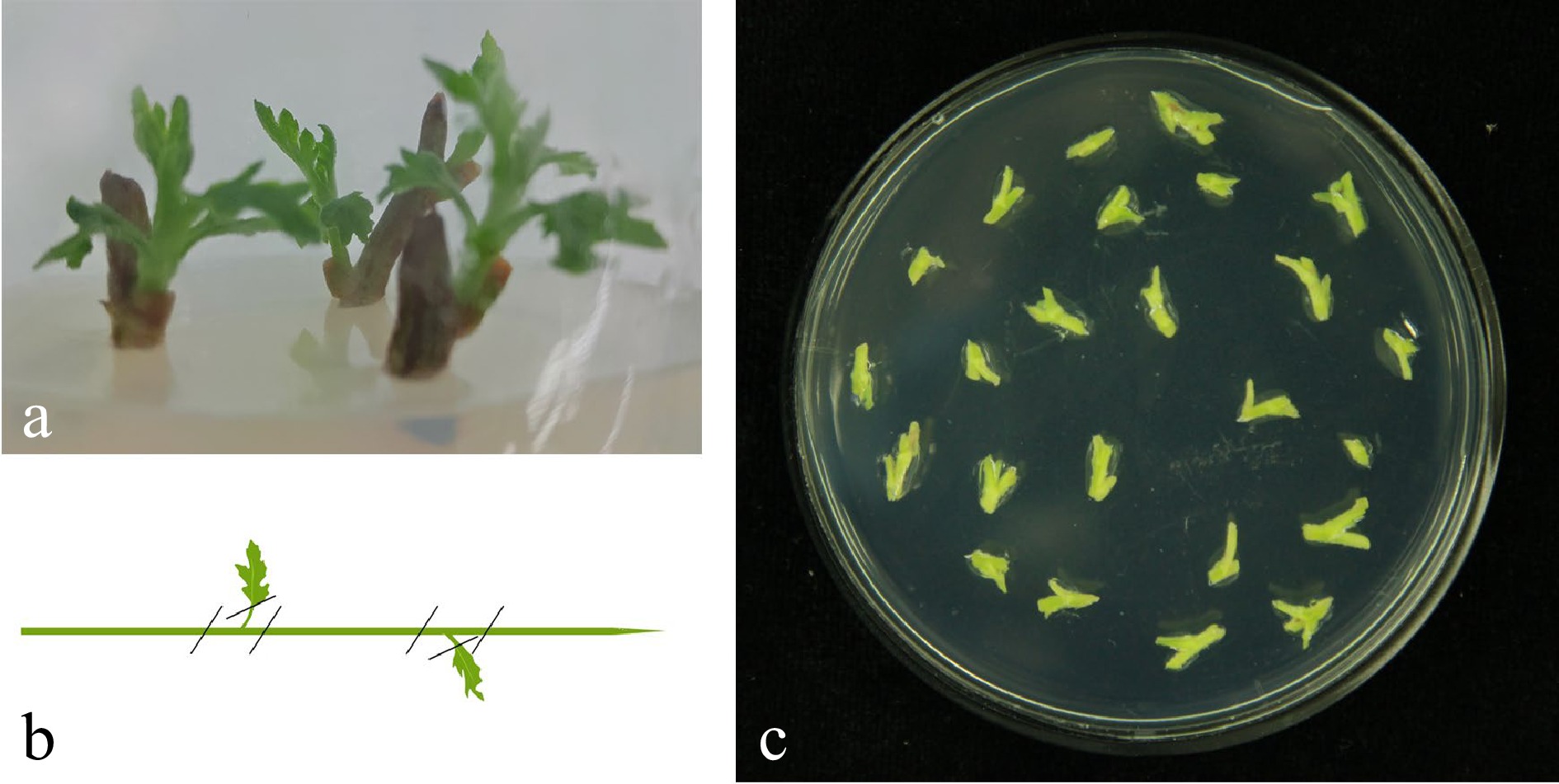
Figure 5.
Tissue culture seedlings from explants sterilized and stem material preparation. (a) Stem explants were taken from plants growing on land, young shoots were surface sterilized and tissue seedlings were cultured in a sterile environment. Note: steam internode explants with a seedling age of 30−40 d were used. (b) Remove the steam tips and steam leaves and cut the explants into 0.5 cm sections containing undifferentiated axillary buds. (c) Pre-culture the explants on MS basal medium containing 2.0 mg/L 6-BA and 0.1 mg/L NAA.
-
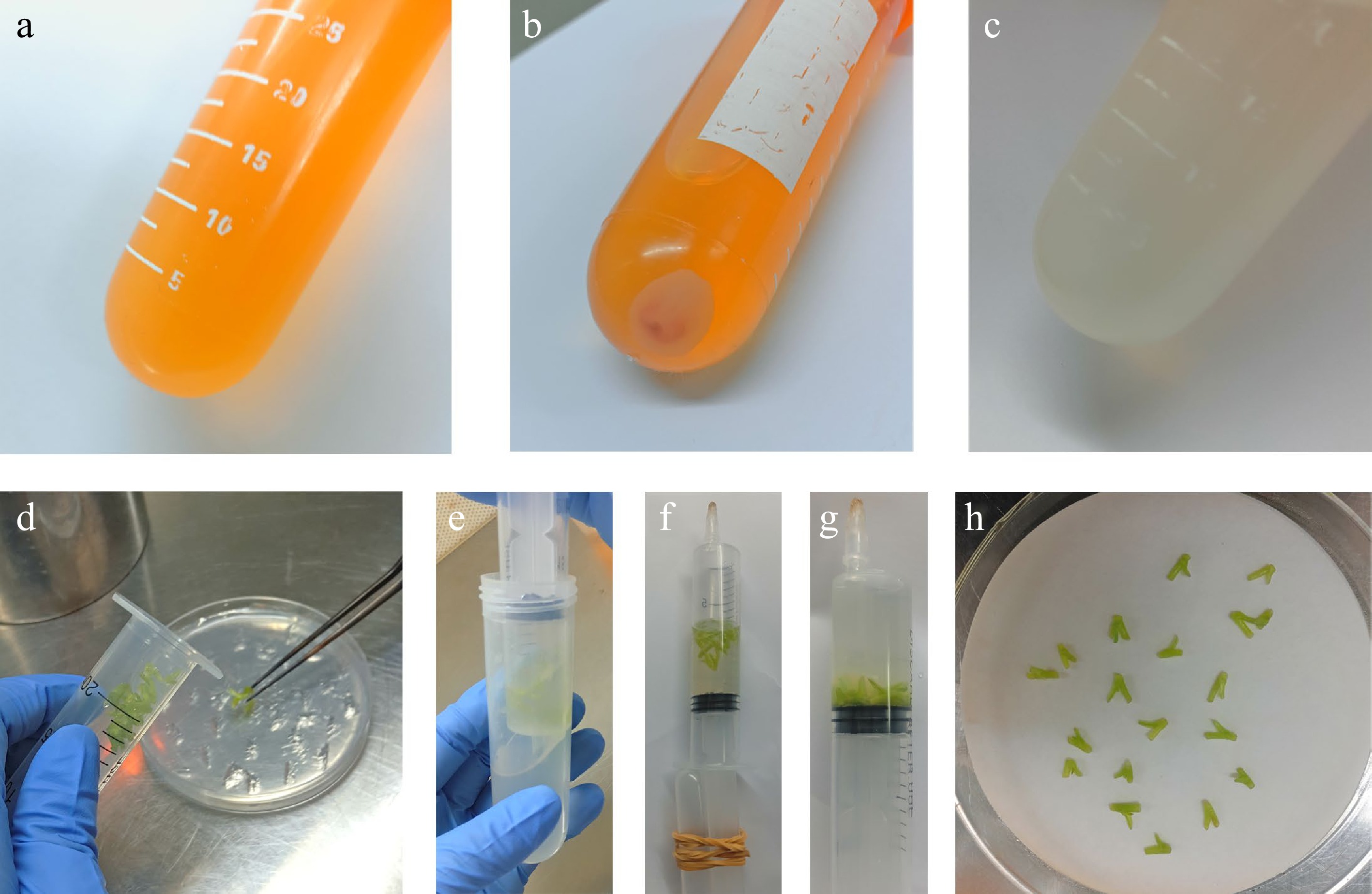

Figure 6.
Agrobacterium infection solution preparation and manual vacuum infiltration treatment. (a) Agrobacterium was cultured overnight with YEB medium. (b) Bacteria were selected by centrifugation. (c) Bacteria were resuspended in liquid MS medium. (d) Stem segments were picked and placed in a 30 mL syringe. (e) Infection liquid was drawn in the syringe. (f) Through a series of simple operations to create a vacuum environment. (g) Pull the syringe plunger and shake to release the interstitial air, keeping the negative pressure state for 5−10 min, until all steam sections sink to the bottom of the liquid. (h) Dry the infected stem and replace on new medium.
-
Medium name Code Medium composition Pre-culture and co-culture medium MS1 MS + 6-BA 2.0 mg/L + NAA 0.1 mg/L Decarboxylation medium MS2 MS + 6-BA 2.0 mg/L + NAA 0.1 mg/L + Carb 350 mg/L Select medium MS3 MS + 6-BA 2.0 mg/L + NAA 0.1 mg/L + Carb 350 mg/L Select medium MS4 MS + 6-BA 2.0 mg/L + NAA 0.1 mg/L + Carb 80 mg/L + Hyg 8 mg/L rooting medium MS5 MS + Hyg 9 mg/L MS: Murashige and Skoog basal medium (Potassium Nitrate 1,900 mg/L, Ammonium Nitrate 1,650 mg/L, Potassium Phosphate Monobasic 170 mg/L, Magnesium Sulfate 370 mg/L, Calcium Chloride 440 mg/L, Potassium Iodide 0.83 mg//L, Boric Acid 6.2 mg/L, Manganese Sulfate 22.3 mg/L, Zinc Sulfate 8.6 mg/L, Sodium Molybdate 0.25 mg/L, Cupric Sulfate 0.025 mg/L, Cobalt Chloride·6H2O 0.025 mg/L, Ferrous Sulfate 27.8 mg/L, Myo-Inositol 100 mg/L, Glycine 2 mg/L, Thiamine Hydrochloride 0.1 mg/L, Pyridoxine Hydrochloride 0.5 mg/L, Nicotinic Acid 0.5 mg/L, Sucrose 30 g/L, Sugar 6.5−7 g/L, PH = 5.8, adjusted with NaOH); 6-BA: 6-benzylaminopurine; Carb: Carbenicillin; NAA: Napthaleneacetic acid; Hyg: hygromycin. Table 1.
Several culture mediums used during the training process.
-
Primer Sequence (5'-3') CmLEC1 forward ATGGGTTACAATTGTGATTACTGTGG CmLEC1 reverse TCAGAAACTTGTTGCTTCATTCATGG CmLEC1-SalI forward TTCAGTCGACATGGGTTACAATTGTGATTA CmLEC1-NotI reverse GAGTGCGGCCGCGAGAAACTTGTTGCTTCATTCA Table 2.
Primers used in CmLEC1gene isolation and vector construction.
-
Primer Sequence (5'-3') 35S GACGCACAATCCCACTATCC CmLEC1-TESTreverse ACATTCTTGGATGGTTTCTTTT CmLEC1-RT Forward GGCCATGAGCAAACTAGGGT CmLEC1-RT Reverse ACGTTCTCCGCCATCAAACT CmEF1α Forward TTTTGGTATCTGGTCCTGGAG CmEF1α Reverse CCATTCAAGCGACAGACTCA Table 3.
Specific primers designed for identification.
Figures
(6)
Tables
(3)