-
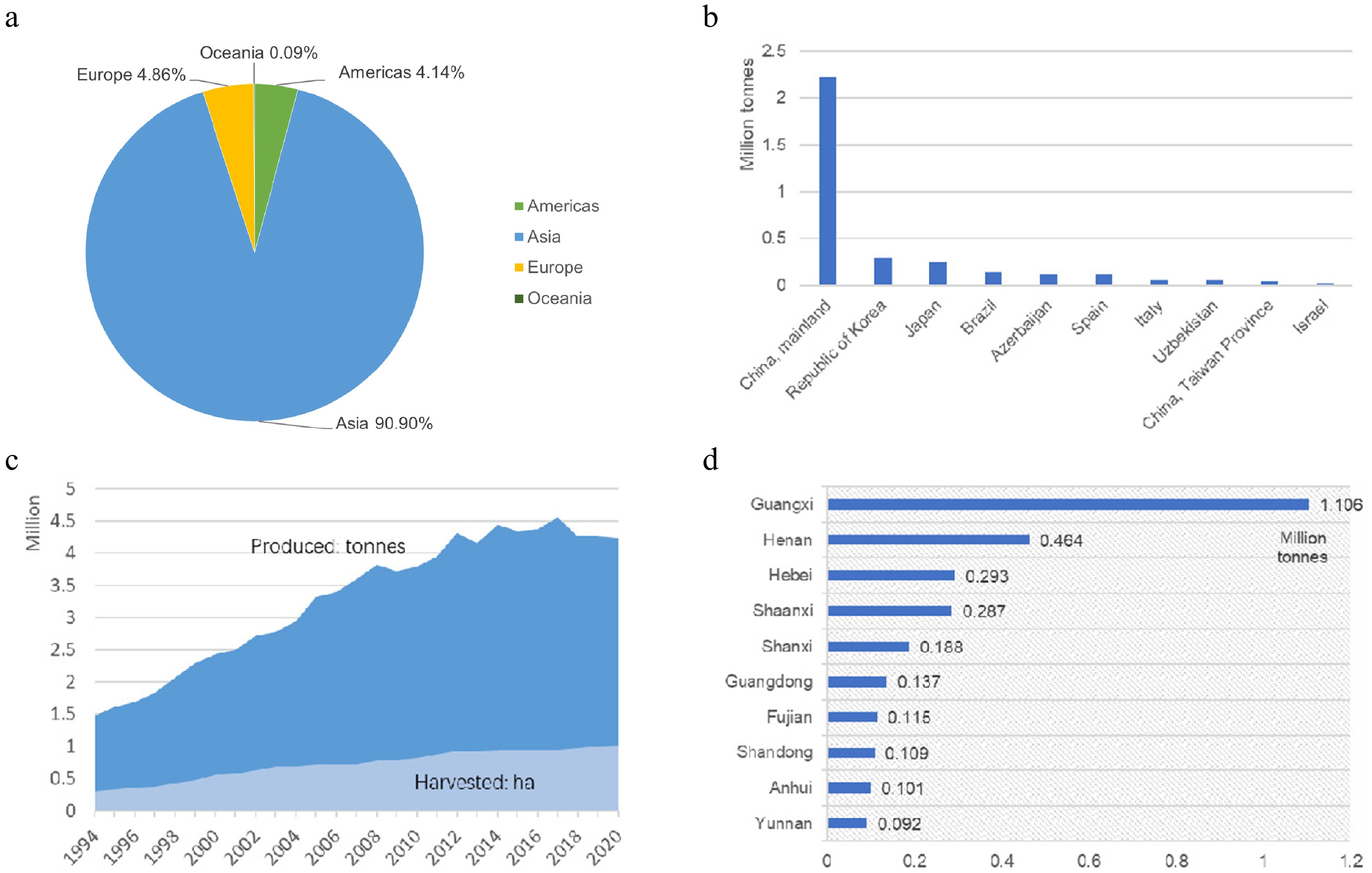
Figure 1.
Current status of the persimmon industry in the world and China. (a) Production share of persimmons by region (average 1994–2020). (b) Top 10 producers of persimmons (average 1994–2020). (c) Production quantities of persimmons in China (1994–2020). (d) Top 10 regions of persimmon production in China.
-
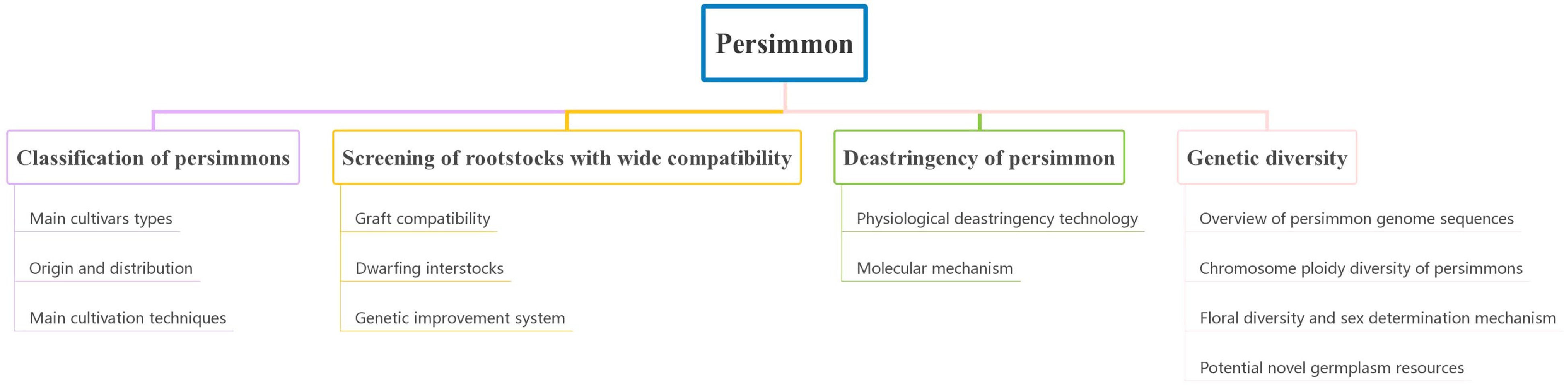
Figure 2.
Roadmap for persimmon improvement in China.
-
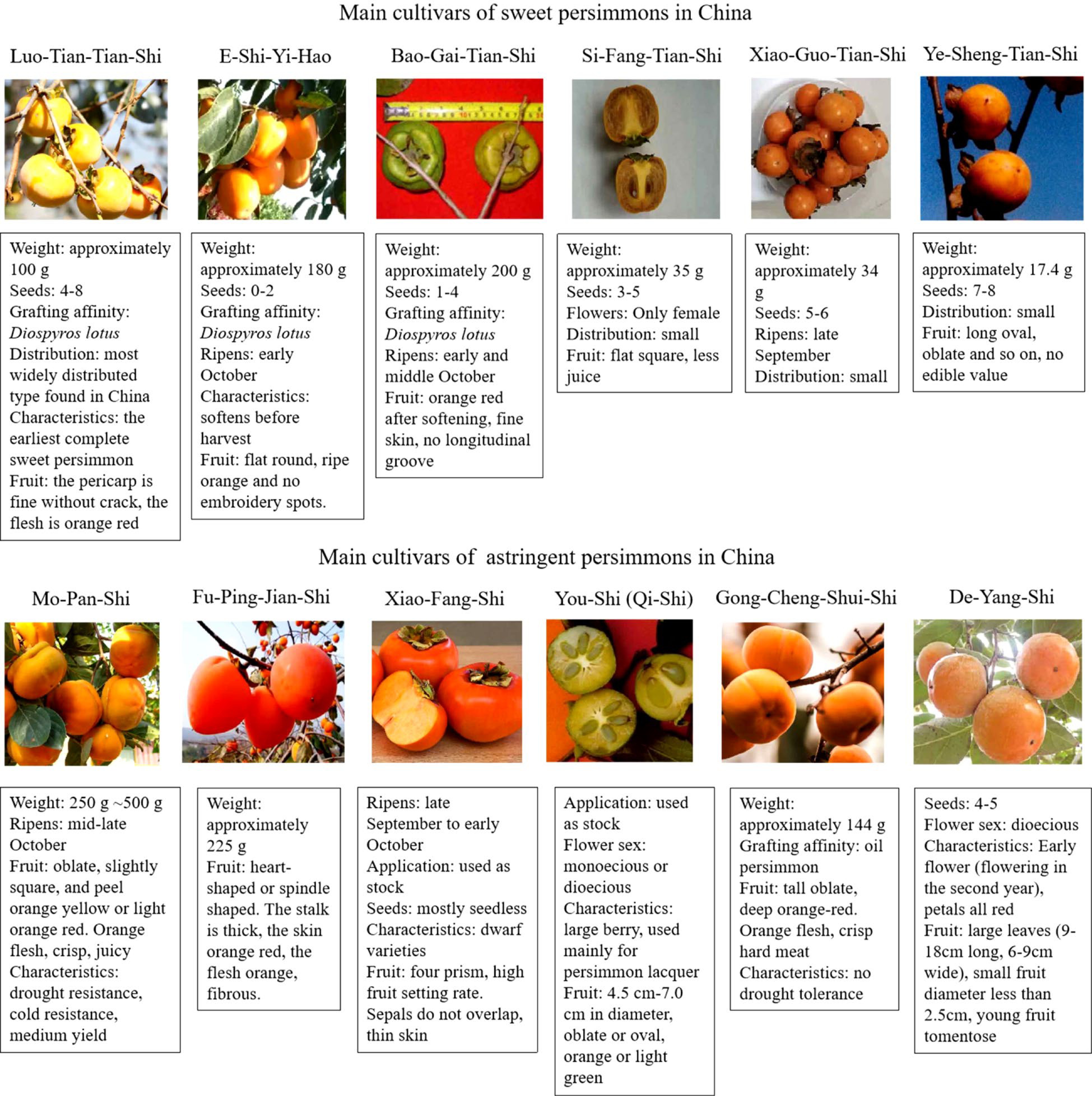
Figure 3.
Main cultivars of persimmons in China.
-
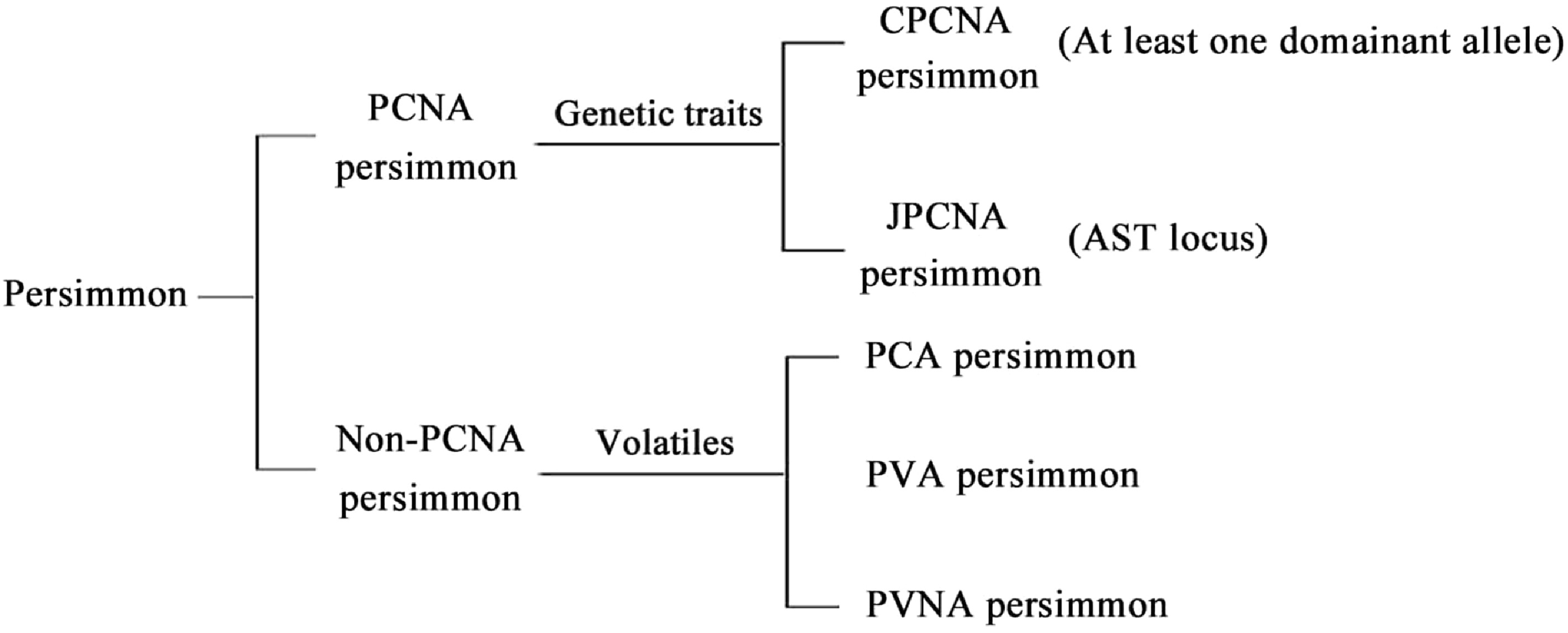
Figure 4.
Classification of persimmons. PCNA: pollination-constant nonastringent. CPCNA: Chinese-PCNA. JPCNA: Japanese-PCNA. PVNA: pollination variant nonastringent. PVA: pollination-variant astringent. PCA: pollination-constant astringent.
-

Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of 'Nan-Tong-Xiao-Fang-Shi' as interstocks. (a) Hypothetical model showing DKGA2ox1 transport in grafted plants (Kanshu/ Nan-Tong-Xiao-Fang-Shi/ D. lotus). (b) The diagram of D. kaki 'Youhou'/ Nan-Tong-Xiao-Fang-Shi/ D. lotus grafting.
-
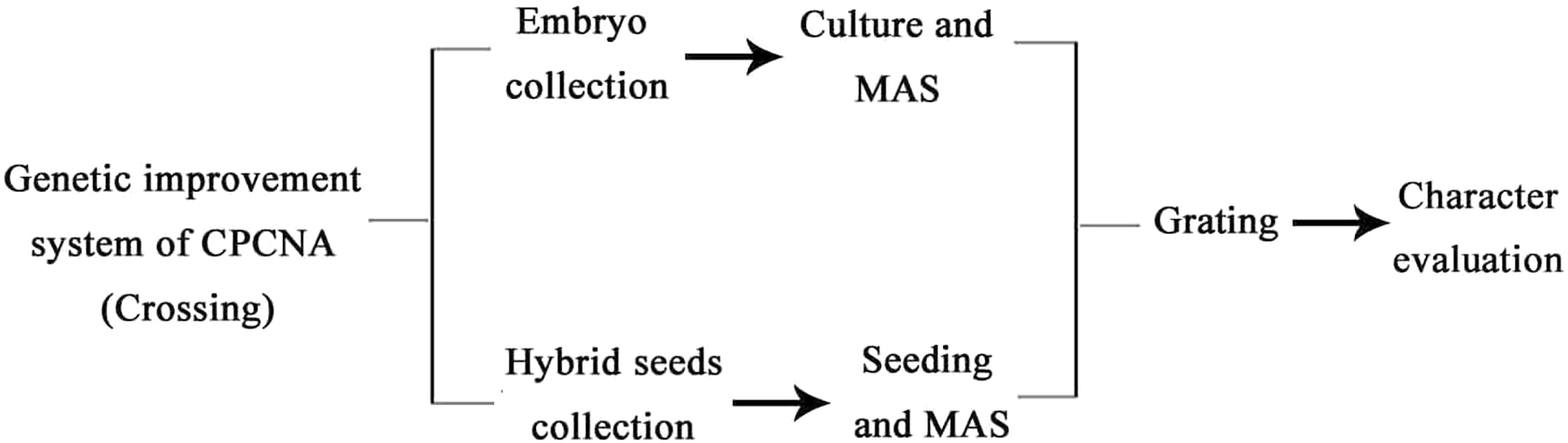
Figure 6.
Diagram of genetic improvement of CPCNA persimmon. MAS: marker-assisted selection.
-
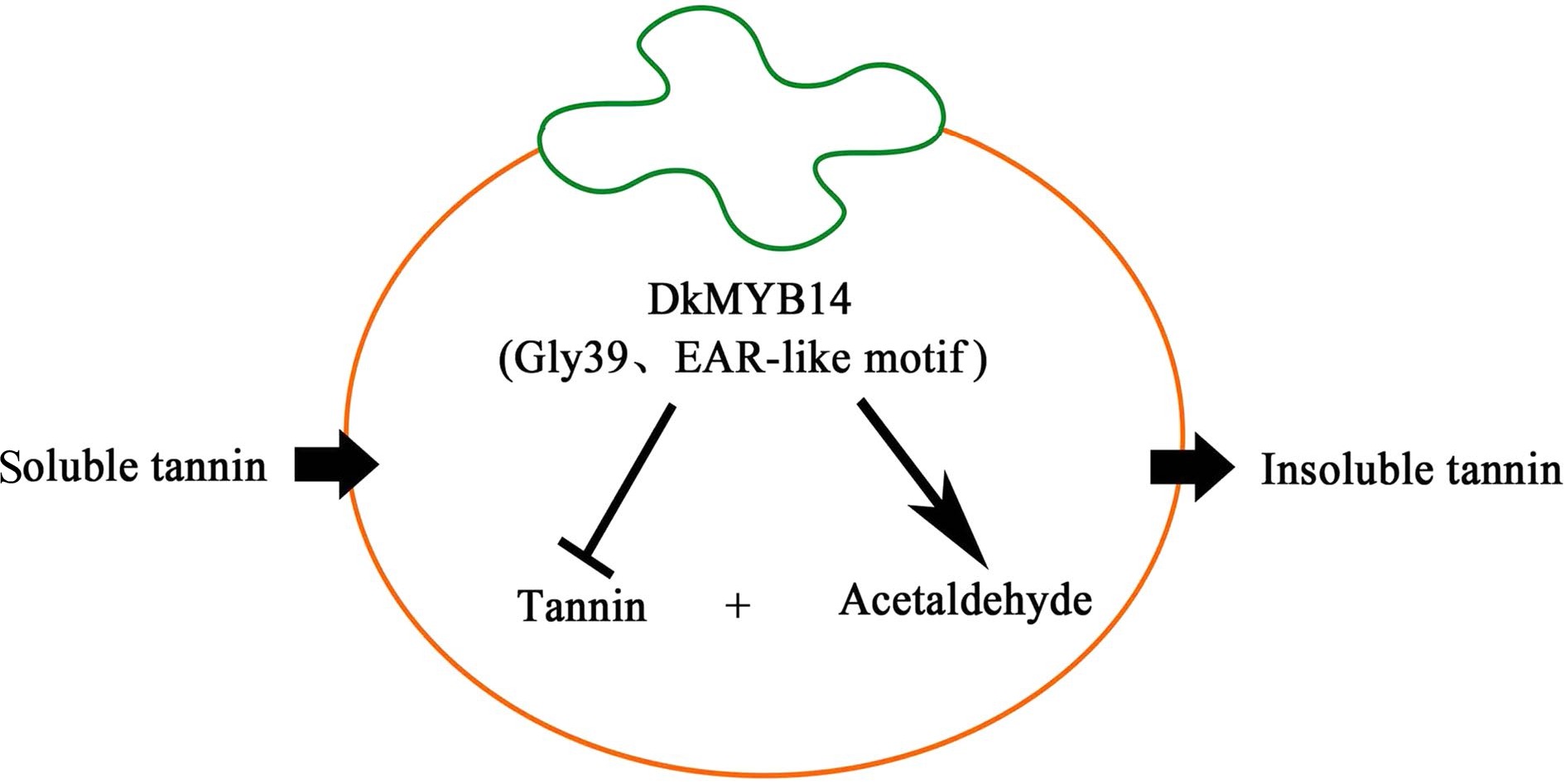
Figure 7.
Hypothetical model showing how DkMYB14 regulates the accumulation of proanthocyanidin (PA) in PCNA persimmon and non-PCNA persimmon.
-
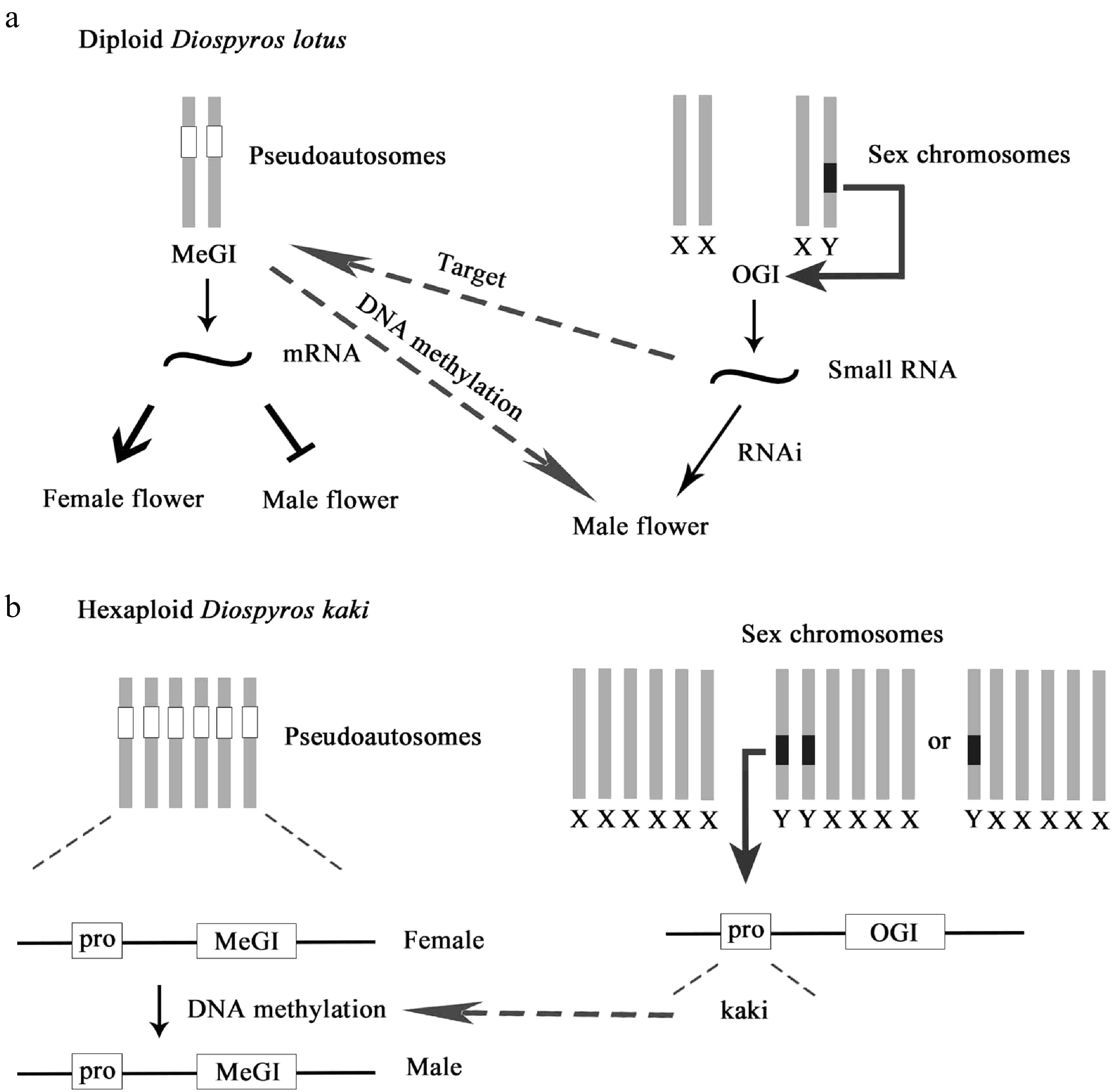
Figure 8.
Diagram of sex evolution model of persimmon. (a) Genetic sex determination in diploid D. lotus. (b) Epigenetic sex determination in genetic males of D. kaki.
-
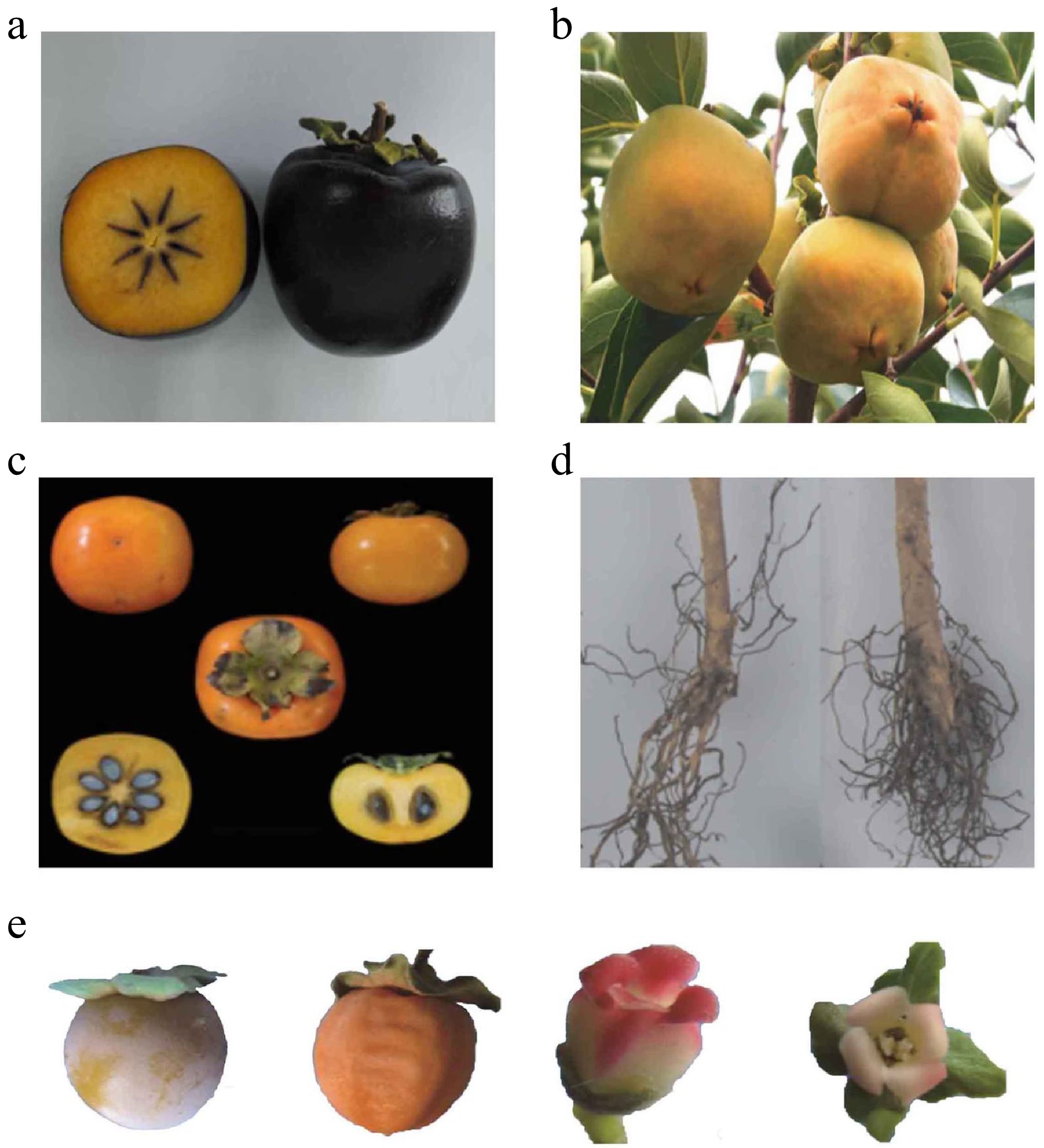

Figure 9.
Potential novel germplasm resources in China. (a) A new persimmon cultivar ‘Heishi No. 1’. (b) A new persimmon cultivar ‘Zhongshi 2’. (c) A new persimmon cultivar ‘Male 8’. (d) ‘Yalin 6’ as a potential widely compatible rootstock. (e) A new persimmon cultivar ‘De-Yang-Shi.’ From left to right: ripening fruit with fluff, ripe fruit, male flower, and female flower.
Figures
(9)
Tables
(0)