-
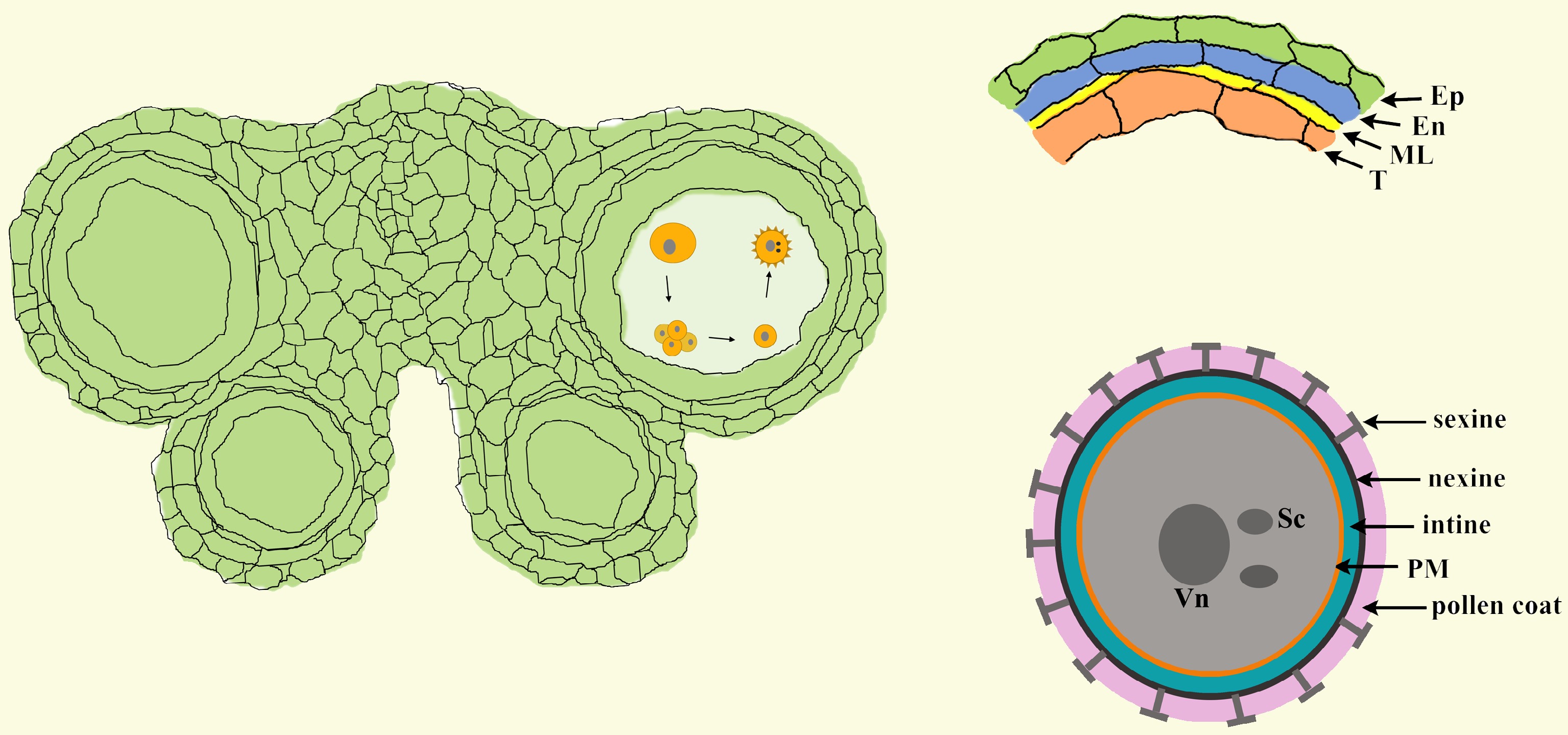
Figure 1.
The structure of anthers and pollen. In Arabidopsis, each anther has four anther locules (pollen sacs), and the anther wall around the anther locule is composed of the epidermis, endothecium, middle layer and tapetum. Mature pollen grains are produced inside the anther locule. A pollen grain has two sperm cells in the cytoplasm of the large vegetative cell and is covered with a complex pollen wall outside of the plasma membrane. Ep, epidermis; En, endothecium; ML, middle layer; T, tapetum; Vn, vegetative nucleus; Sc, sperm cell; PM, plasma membrane.
-
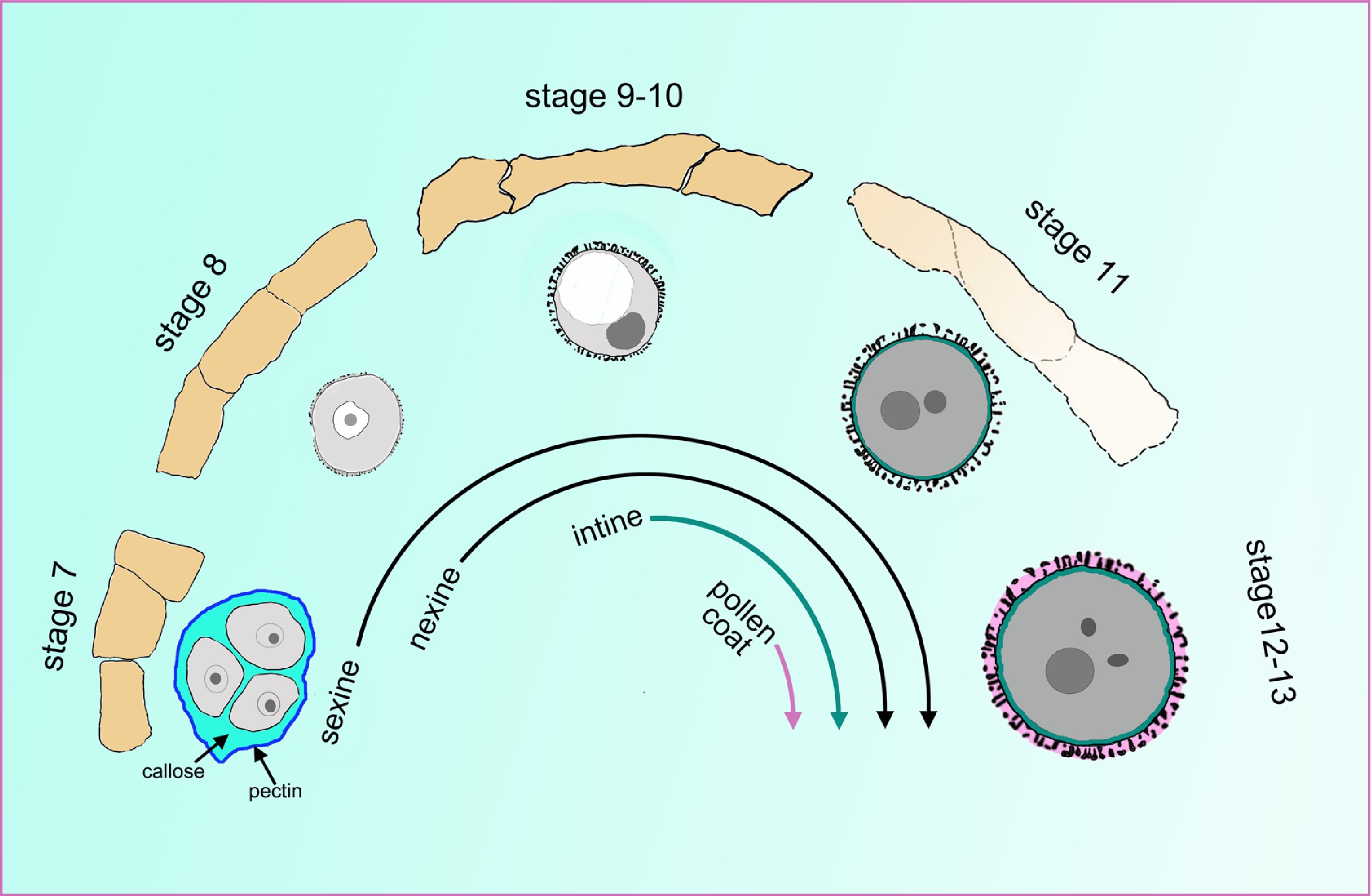
Figure 2.
The cell wall undergoes a tremendous change during pollen development. The orange quadrilaterals represent the tapetal cells, and the corresponding microspores or pollen at specific anther stages are shown under the tapetum cells. At stage 7, the four microspores are enclosed inside the callose wall and the outer pectin wall. At late stage 7, the sexine and nexine precursors start to deposit outside the membrane. During stages 9 to 10, the tapetum begins to degenerate and becomes spongy. The intine layer appears between the plasma membrane and nexine layer at stage 10. At stage 11, the tapetum evidently degenerates, and the pollen coat precursor start to fill the sculptured cavities of the sexine. At stages 12 and 13, the tapetum cell degenerates completely, and all layers of the pollen wall are established.
-
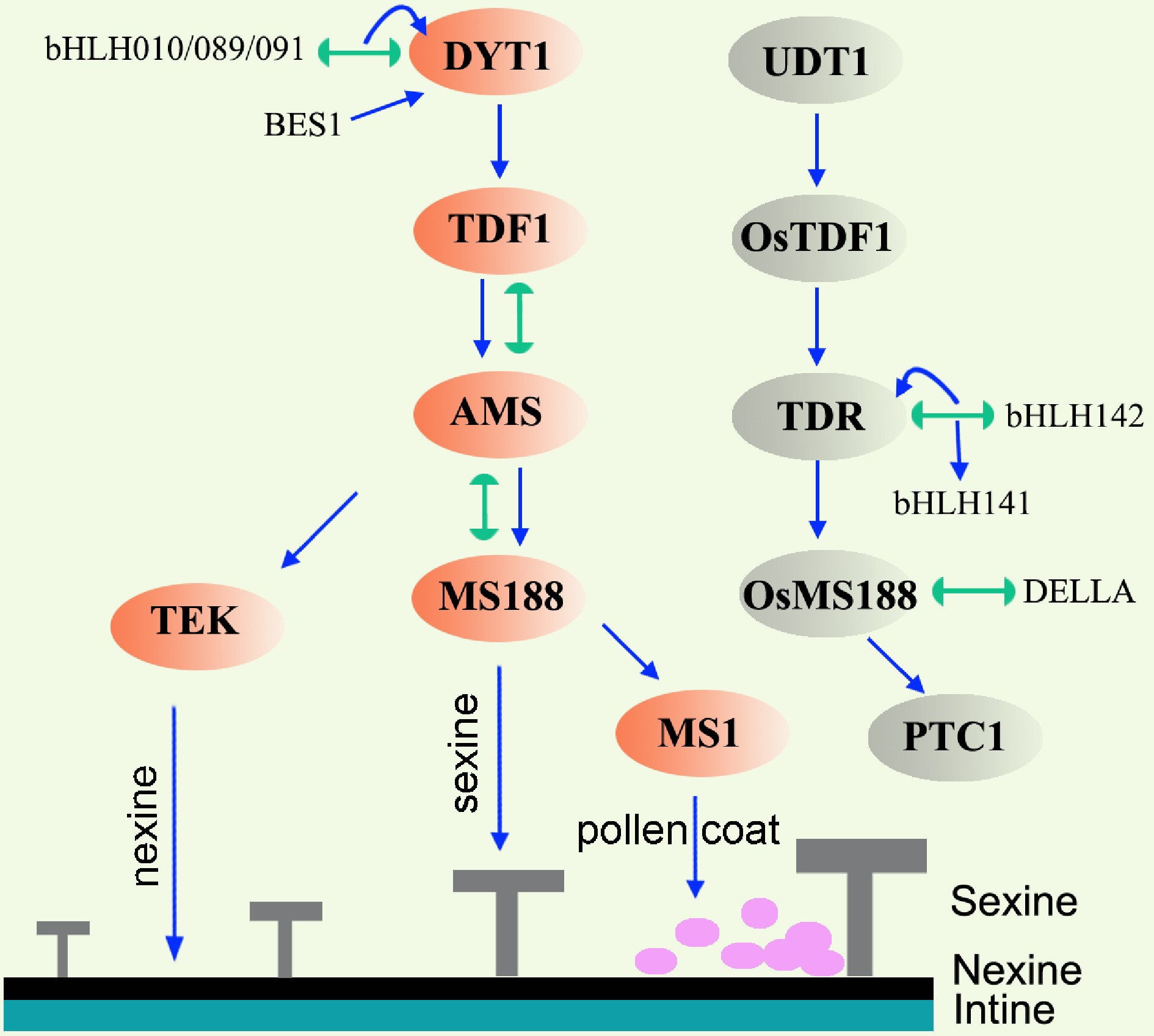
Figure 3.
Gene regulatory network in the tapetum of Arabidopsis and rice. Lines terminating in arrows represent positive regulation, lines with semicircle ends indicate interaction. Orange ovals and grey ovals mark the key transcription factors in Arabidopsis and rice respectively. In Arabidopsis, DYT1-TDF1-AMS are responsible for early tapetum development. AMS regulates nexine and sexine formation via TEK and MS188, respectively. MS1 is responsible for pollen coat formation. Abbreviations: TEK, transposable element silencing via AT-hook; BES1, BRI1 EMS SUPPRESSOR 1; UDT1, UNDEVELOPED TAPETUM 1; TDR, TAPETUM DEGENERATION RETARDATION; PTC1, PERSISTANT TAPETAL CELL 1.
-
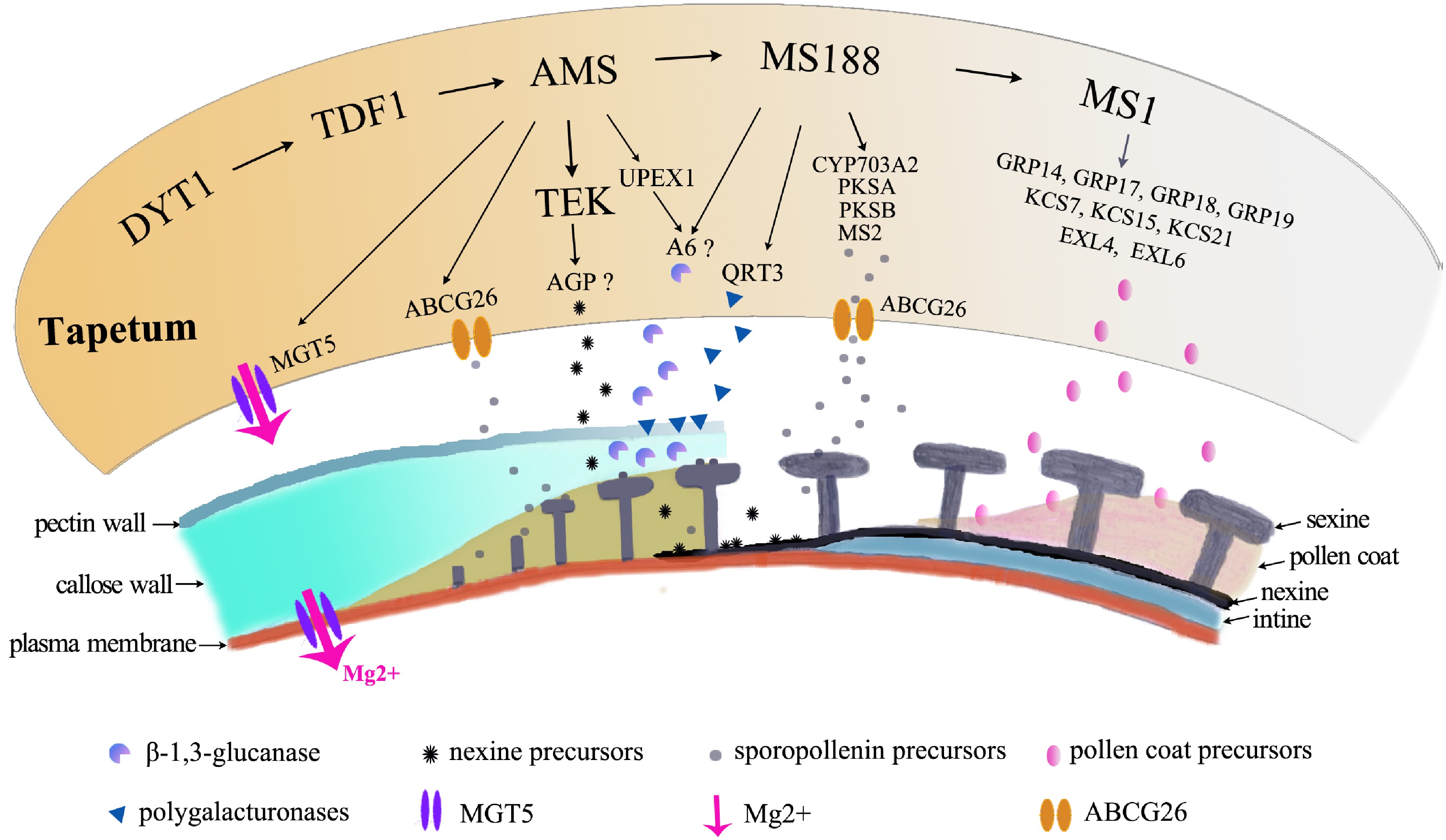
Figure 4.
Molecular pathways in tapetum contribution to pollen formation. The orange irregular shape represents the tapetal cell. The pathway regulates a large number of genes for pollen growth, which are shown below the tapetal cell, to provide Mg for pollen growth, to secrete enzymes for degradation of the pectin wall, for the callose wall to release microspores, to provide precursors of nexine and sexine, and to provide materials for pollen coat formation.
-
Name ID Protein Function Reference DYT1 AT4G21330 bHLH transcription factor Early tapetum development [30] TDF1 AT3G28470 MYB transcription factor Early tapetum development [32] AMS AT2G16910 bHLH transcription factor Early tapetum development [29,31] MS188/MYB80/MYB103 AT5G56110 MYB transcription factor Tapetum PCD, microspore release, exine formation [24,35,47] MS1 AT5G22260 PHD-finger transcription factor Tapetum PCD, exine and pollen coat formation [33,34] OsUDT1 Os07g0549600 bHLH transcription factor DYT1 ortholog; early tapetum development [49] OsTDF1 Os03g18480 MYB transcription factor TDF1 ortholog; early tapetum development [53] OsTDR Os02g0120500 bHLH transcription factor AMS ortholog; tapetum development [50,54] OsMS188/OsMYB80 Os04g39470 MYB transcription factor MS188 ortholog; tapetum PCD, exine formation [51,55,56] OsPTC1/OsMS1 Os09g0449000 PHD-finger transcriptional factor MS1 ortholog; tapetum PCD, exine formation [50,52,54] ZmMs32 GRMZM2G163233 bHLH transcription factor DYT1 ortholog; tapetum development [21,57,62] ZmMs9 GRMZM2G308034 MYB transcription factor TDF1 ortholog; tapetum development [57,61] ZmbHLH51 Zm00001d053895 bHLH transcription factor AMS ortholog; tapetum development [57] ZmMYB84 Zm00001d025664 MYB transcription factor MS188 ortholog; tapetum development [57] ZmMs7 GRMZM5G890224 PHD-finger transcriptional factor MS1 ortholog; tapetum development [57−59] MYB33 AT5G06100 GAMYB transcription factor Tapetum and pollen development [39] MYB65 AT3G11440 GAMYB transcription factor Tapetum and pollen development [39] bHLH010 AT2G31220 bHLH transcription factor bHLH010, bHLH089 and bHLH091 redundantly required for tapetum and pollen development [40] bHLH089 AT1G06170 bHLH transcription factor [40] bHLH091 AT2G31210 bHLH transcription factor [40] EAT1/DTD1/bHLH141 Os04g0599300 bHLH transcription factor Tapetum PCD [63,64] TIP2/bHLH142 Os01g0293100 bHLH transcription factor Tapetum PCD [65,66] MGT5 AT4G28580 Transmembrane magnesium transporter Transport Mg from tapetum to anther locule [91] QRT3 AT4G20050 polygalacturonase Pectin dissolution [10,98] A6 AT4G14080 β-1,3-glucanase Callose dissolution [107,110] UPEX1/KNS4/RES3 AT1G33430 Arabinogalactan β-(1,3)-galactosyltransferase Influence the secretion of A6 from tapetum [110] ACOS5 AT1G62940 Fatty acyl-CoA synthetase Sporopollenin synthesis [112] CYP703A2 At1G01280 Hemethiolate monooxygenase (P450) Sporopollenin synthesis [47,113] CYP704B1 AT1G69500 Hemethiolate monooxygenase (P450) Sporopollenin synthesis [114] PKSA AT1G02050 Acyltransferase Sporopollenin synthesis [116,118] PKSB AT4G34850 Acyltransferase Sporopollenin synthesis [116,118] TKPR1 AT4G35420 Tetraketide alpha-pyrone reductase Sporopollenin synthesis [117] TKPR2 AT1G68540 Tetraketide alpha-pyrone reductase Sporopollenin synthesis [117] MS2 AT3G11980 Fatty acid reductase Sporopollenin synthesis [115,116] ABCG26 AT3G13220 ATP binding cassette transporter Sporopollenin transportation [120,121] ABCG15 AT3G21090 ATP binding cassette transporter Sporopollenin transportation [123] TEK AT2G42940 AT-hook nuclear localized (AHL) protein Nexine formation [44,103] OsOSC12 Os08g0223900 Bicyclic triterpene poaceatapetol synthase Pollen coat formation [139] GRP17 AT5G07530 Glycine-rich protein Pollen coat protein [140,141] EXL4 AT1G75910 Lipase protein Pollen coat protein [140,142] EXL6 AT1G75930 Lipase protein Pollen coat protein [140] CER1 AT1G02205 Decarbonylases Pollen coat synthesis: very long chain alkane synthesis [152,153] CER3/FLP1/WAX2/YRE AT5G57800 Decarbonylases Pollen coat synthesis: very long chain alkane synthesis [149−151,153] KCS7 AT1G71160 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase Pollen coat synthesis: fatty acid elongation [146] KCS15 AT3G52160 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase Pollen coat synthesis: fatty acid elongation [146] KCS21 AT5G49070 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase Pollen coat synthesis: fatty acid elongation [146] Dcl5 Zm00001eb104810 Endoribonuclease Generation of 24-nt phasiRNAs in the tapetum in maize [181] CLSY3 AT1G05490 Helicase Generation of 24-nt siRNAs in the anther in Arabidopsis [182] Table 1.
The summary of the key genes and their functions during anther or pollen development.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(1)