-
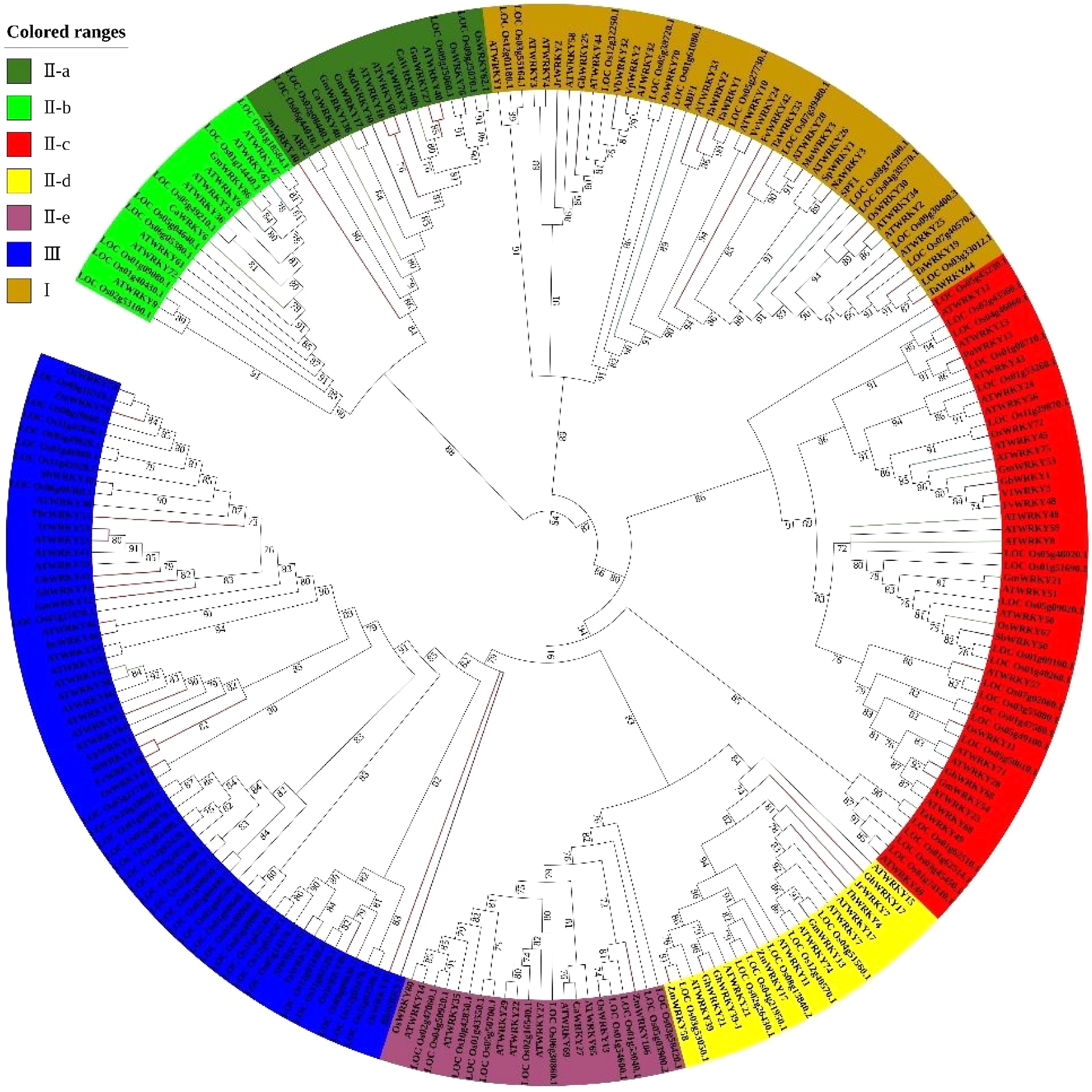
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of WRKY family proteins in Arabidopsis, rice, and other reported species.
-
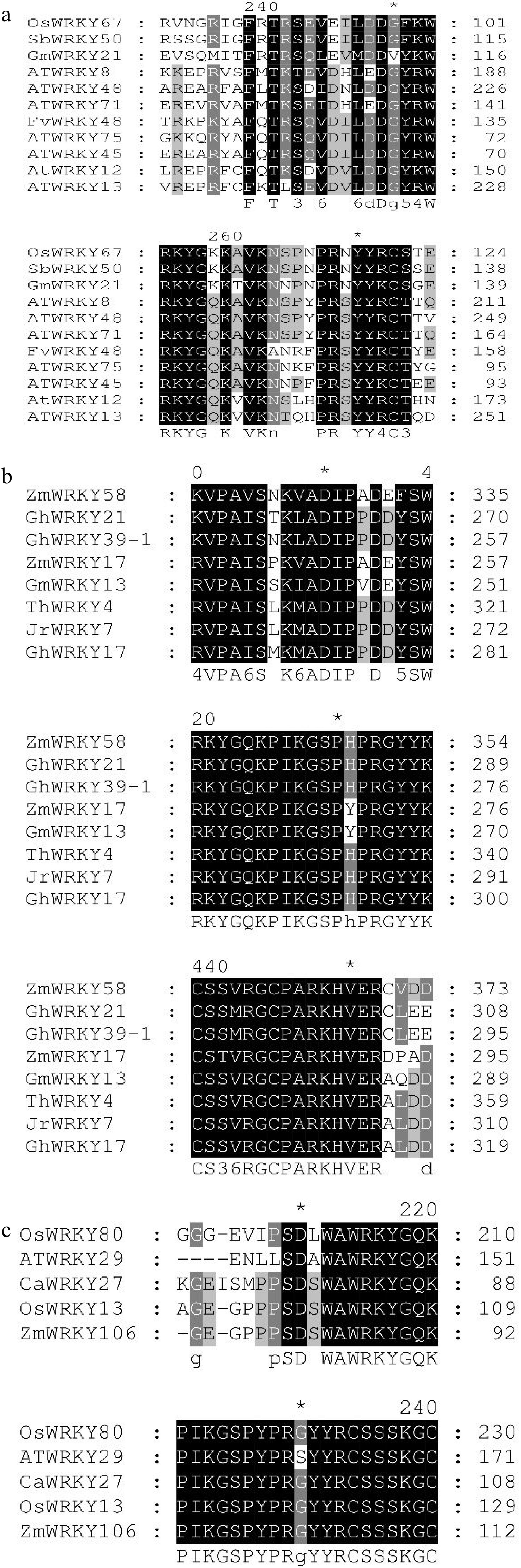
Figure 2.
Multiple sequence alignment of reported WRKY family proteins. (a) Multiple sequence alignment of reported WRKY proteins in group II-c. (b) Multiple sequence alignment of reported WRKY proteins in group II-d. (c) Multiple sequence alignment of reported WRKY proteins in group II-e.
-
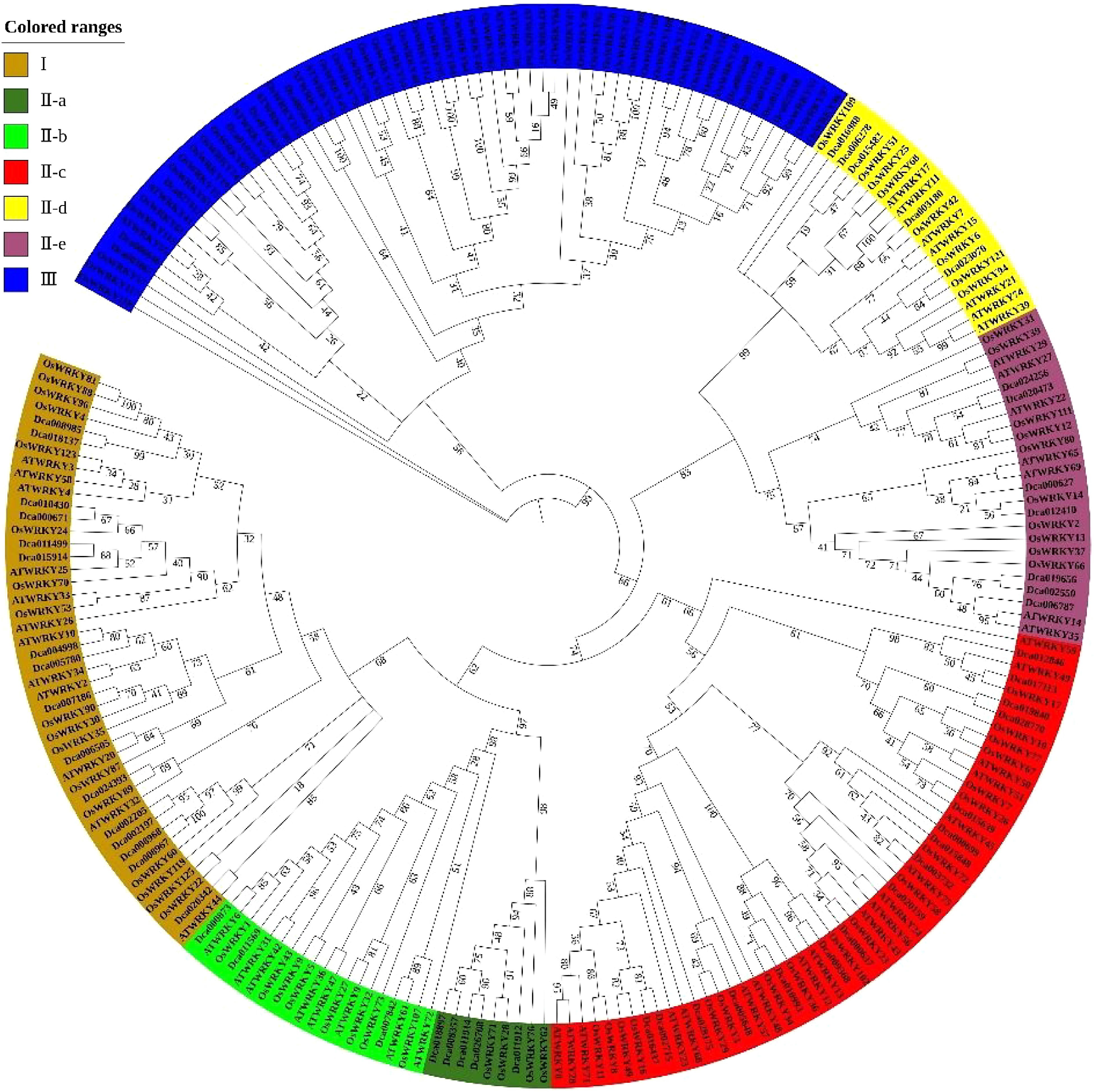
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of WRKY family proteins in D. catenatum.
-
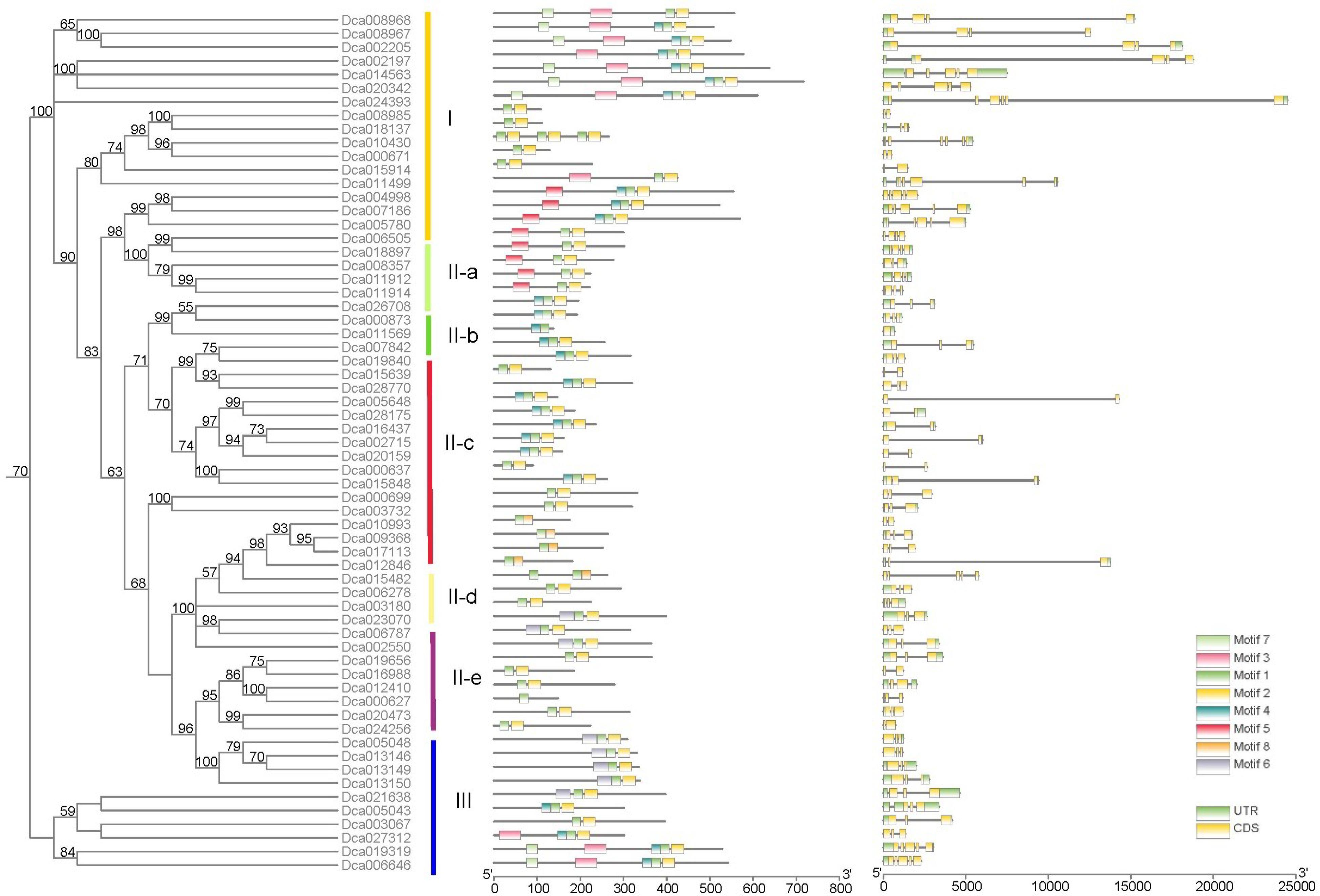
Figure 4.
Conserved motifs and gene structure of DcaWRKY genes according to phylogenetic relationships.
-

Figure 5.
Multiple sequence alignment of identified DcaWRKY proteins.
-
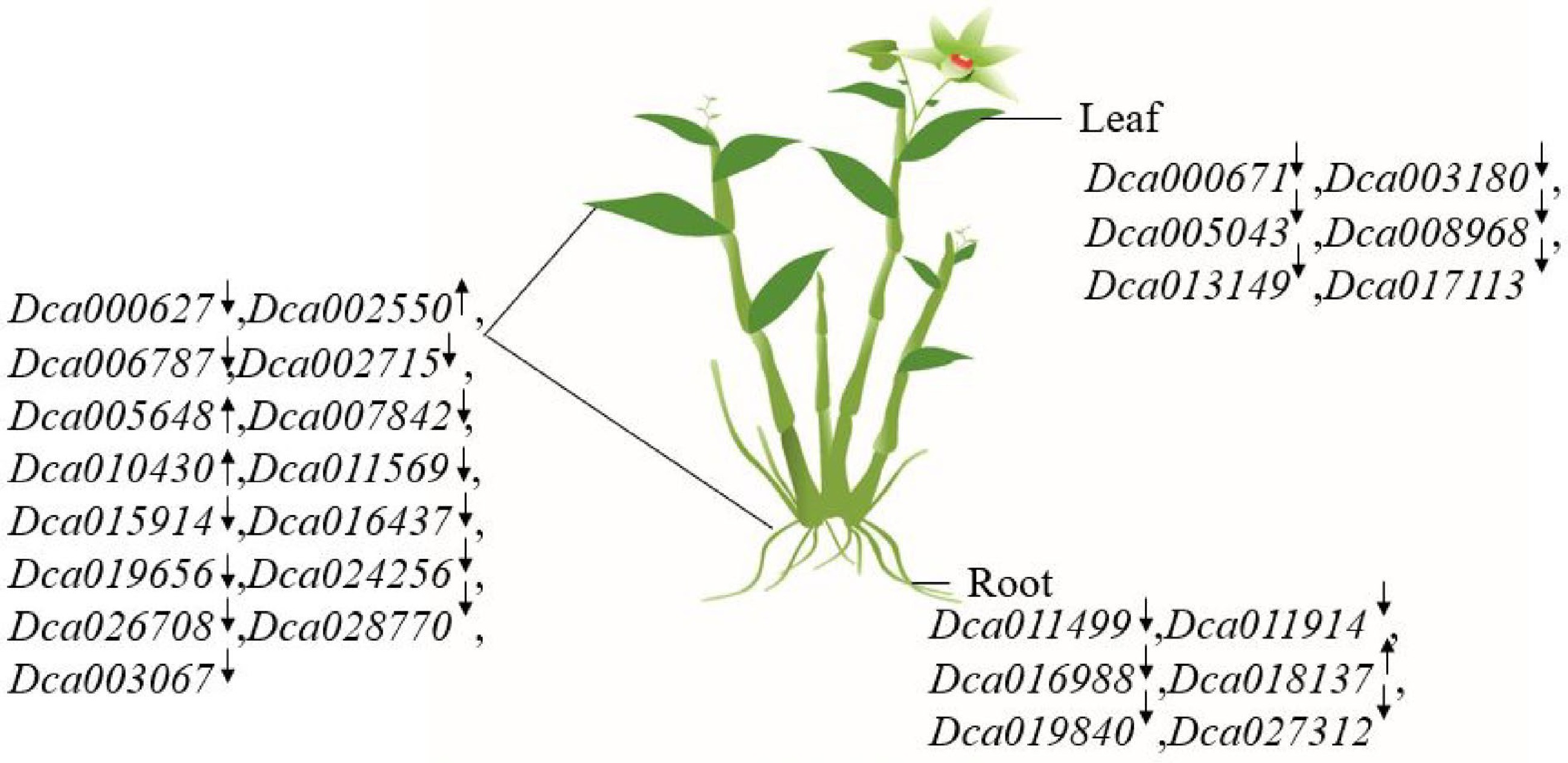
Figure 6.
The summarized figure of DcaWRKY genes expression in roots and leaves. '↑' indicates that gene expression increased under drought treatment. '↓' indicates decreased expression under drought treatment. Dca000671, Dca003180, Dca005043, Dca008968, Dca013149, and Dca017113 were differently expressed in leaves under drought treatment; similarly, Dca011499, Dca011914, Dca016988, Dca018137, Dca019840, and Dca027312 were differently expressed in roots. Dca000627, Dca002550, Dca006787, Dca002715, Dca005648, Dca007842, Dca010430, Dca011569, Dca015914, Dca016437, Dca019656, Dca024256, Dca026708, Dca028770, and Dca003067 were expressed both in leaves and roots under drought treatment.
-
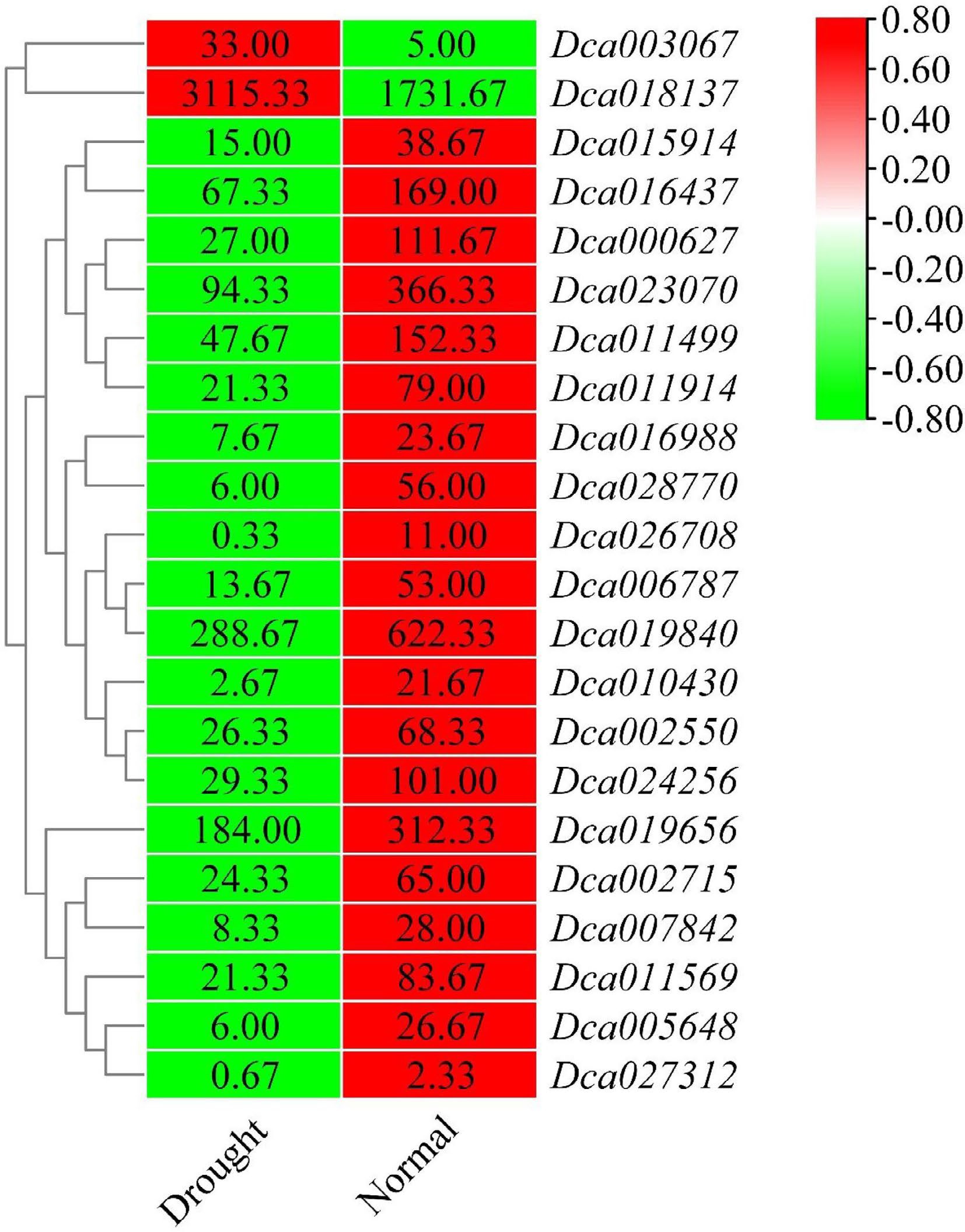
Figure 7.
Heatmap of differentially expressed DcaWRKY genes under drought stress in roots. The color scale shows increasing expression levels from green to red, which represents log2-transformed FPKM.
-
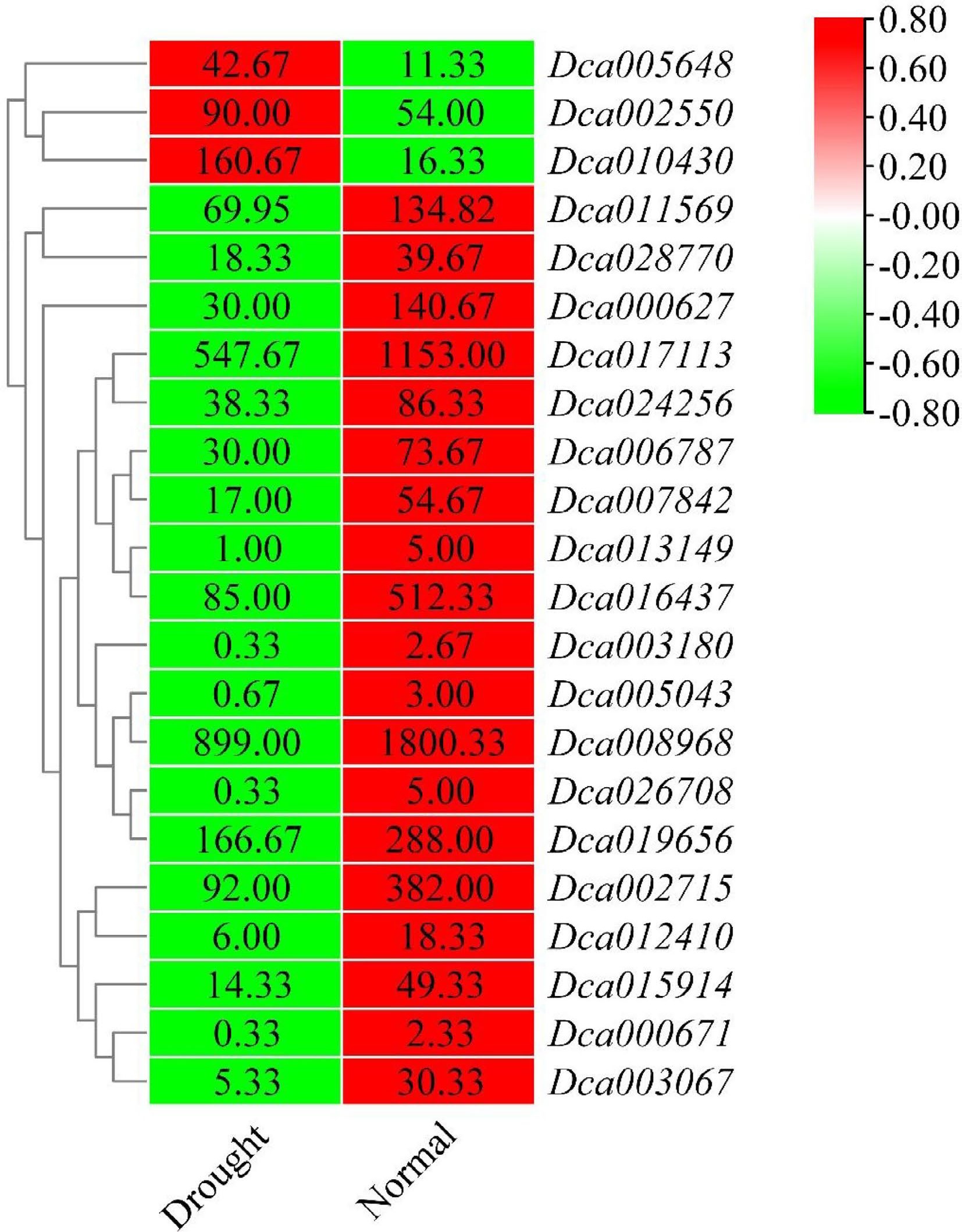
Figure 8.
Heatmap of differentially expressed DcaWRKY genes under drought stress in leaves. The color scale shows increasing expression levels from green to red, which represents log2-transformed FPKM.
-
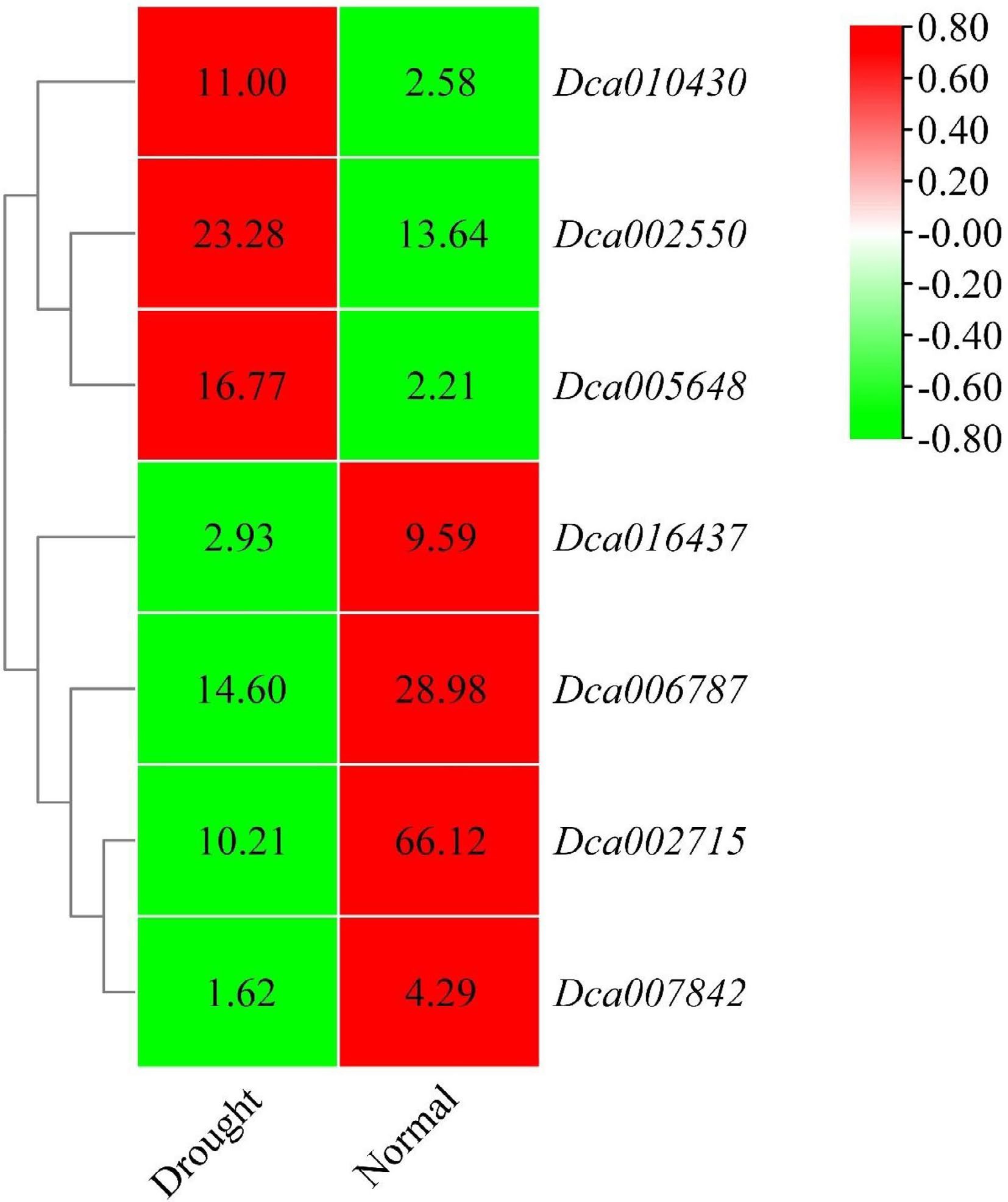
Figure 9.
Heatmap of
the selected DcaWRKY genes in leaves. The color scale shows increasing expression levels from green to red, which represents log2-transformed FPKM. -
Group Gene ID Species Function References III GhWRKY33 Gossypium hirsutum Tolerance to drought [58] III PbrWRKY53 Pyrus betulaefolia Tolerance to drought [38] II C GmWRKY54 Glycine max Tolerance to drought [59] II A GmWRKY27 Glycine max Tolerance to drought [58] III AtWRKY63 Arabidopsis thaliana Tolerance to drought [60] I TaWRKY2 and TaWRKY19 Triticum aestivum Tolerance to drought [61] II C OsWRKY11 Oryza sativa Tolerance to drought [57] III OsWRKY45 Oryza sativa Tolerance to drought [62] II A WRKY18, WRKY40 and WRKY60 Arabidopsis thaliana Tolerance to drought [63,64] I WRKY1 Arabidopsis thaliana Tolerance to drought [65] III WRKY46, WRKY54, and WRKY70 Arabidopsis thaliana Tolerance to drought [42] II C AtWRKY57 Arabidopsis thaliana Tolerance to drought [37] I A OsWRKY30 Oryza sativa Tolerance to drought [66] II OsWRKY80 Oryza sativa Tolerance to drought [67] III OsWRKY47 Oryza sativa Tolerance to drought [68] I FvWRKY42 Fragaria vesca Tolerance to drought [39] II D ZmWRKY58 Zea mays Tolerance to drought [41] II E ZmWRKY106 Zea mays Tolerance to drought [69] II A ZmWRKY40 Zea mays Tolerance to drought [69] II E CmWRKY10 Chrysanthemum morifolium Tolerance to drought [70] III and I TaWRKY1 and TaWRKY33 Triticum aestivum Tolerance to drought [71] II D ThWRKY4 Tamarix hispida Tolerance to drought [72] I MuWRKY3 Macrotyloma uniflorum Tolerance to drought [73] II D GhWRKY17 Gossypium hirsutum Tolerance to drought [34] III GhWRKY41 Gossypium hirsutum Tolerance to drought [74] I TaWRKY44 Triticum aestivum Tolerance to drought [75] III FcWRKY70 Fortunella crassifolia Tolerance to drought [40] II C GmWRKY12 Glycine max Tolerance to drought [76] III ZmWRKY79 Zea mays Tolerance to drought [77] II D GhWRKY21 Gossypium hirsutum Tolerance to drought [78] III SlWRKY81 Solanum lycopersicum Tolerance to drought [79] I SPF1 Ipomoea batatas Root development [43] I and II A ABF1 and ABF2 Avena fatua Seed germination [45] II B WRKY42 and WRKY6 Arabidopsis thaliana Plant nutrient [42] II C WRKY45 and WRKY75 III and II E WRKY74 and WRKY80 Oryza sativa Plant nutrient [42] III AtWRKY53 Arabidopsis thaliana Leaf senescense [46] II C OsWRKY11 Oryza sativa Floral development [41] II C AtWRKY12 and AtWRKY13 Arabidopsis thaliana Floral development [44] II C AtWRKY71 Arabidopsis thaliana Floral development [47] I AtWRKY2 Arabidopsis thaliana Reproductive development [80] I OsWRKY70 Oryza sativa Defense response [81] II C FvWRKY48 Fragaria vesca Pectin degradation [82] II E OsWRKY13 Oryza sativa Regulated ABA signaling and tolerance to salt [83] II C VlWRKY3 Vitis vinifera Response to Golovinomyces cichoracearum and tolerant to salt [84] II C GhWRKY68 Gossypium hirsutum Reduced salt tolerance and drought resistance [85] I GhWRKY25 Gossypium hirsutum Tolerance to salt [86] I VvWRKY24 Vitis vinifera Tolerance to cold [29] I AtWRKY25 and AtWRKY33 Arabidopsis thaliana Tolerance to heat [25] I AtWRKY34 Arabidopsis thaliana Negative regulator in cold stress [31] III AtWRKY53 Arabidopsis thaliana Reduced drought resistance [87] III AtWRKY63 Arabidopsis thaliana Regulated ABA signaling [60] III AtWRKY54 Arabidopsis thaliana Response to heat stress [28] II C OsWRKY72 Oryza sativa Sensitive to salt, sucrose, and ABA [88] III OsWRKY74 Oryza sativa Tolerance to cold and Pi deprivation [89] II A OsWRKY76 Oryza sativa Tolerance to cold [90] III OsWRKY89 Oryza sativa Tolerance to UV [91] II A GmWRKY17 Glycine max Reduced salt tolerance [34] III BcWRKY46 Brassica campestris Tolerance to salt [92] III BhWRKY1 Boea hygrometrica Tolerance to salt [93] III and I VpWRKY1 and VpWRKY2 Vitis pseudoreticulata Tolerance to salt and cold [94] II A VpWRKY3 Vitis pseudoreticulata Tolerance to salt [95] III TcWRKY53 Thlaspi caerulescens Negative regulator in osmotic stress [96] I NaWRKY3 Nicotiana attenuata Sensitive to mechanical damage [97] I and II D JrWRKY2 and JrWRKY7 Juglans regia Tolerance to drought and cold [98] III SbWRKY30 Sorghum bicolor Tolerance to salt and drought [99] II C SbWRKY50 Sorghum bicolor Tolerance to salt [100] II A MdWRKY30 Malus domestica Tolerance to salt and osmotic stress [101] II C GbWRKY1 Gossypium barbadense Tolerance to salt [35] I VbWRKY32 Verbena bonariensis Tolerance to cold [28] II C OsWRKY67 Oryza sativa Negative regulator of innate defense response [22] II A OsWRKY62.1 Oryza sativa Positive regulator of PTI and ETI against pathogens [12] III AtWRKY38 and AtWRKY62 Arabidopsis thaliana Response to bacterial pathogen [11] II A,II C, and II B GmWRKY136, GmWRKY53, and GmWRKY86 Glycine max Tolerance to SCN [23] II C and III TaWRKY49 and TaWRKY62 Triticum aestivum Tolerance to stripe rust [102] II A CaWRKY40b and CaWRKY40 Capsicum annuum Negative regulation of plant immunity [17,24] II B CaWRKY6 Capsicum annuum Tolerance to R. solanacearum [15] I SpWRKY1 Solanum pimpinellifolium Tolerance to Phytophthora infestans [16] II D ZmWRKY17 Zea mays Negative regulator of salt stress [103] II D GhWRKY39-1 Gossypium hirsutum Tolerance to salt [33] II C AtWRKY8 Arabidopsis thaliana Defense response [13] II E CaWRKY27 Capsicum annuum Response to Ralstonia solanacearum infection [14] II C AtWRKY48 Arabidopsis thaliana Tolerance to P. syringae [20] II E AtWRKY29 Arabidopsis thaliana Resistance to P. syringe [18] II C PoWRKY13 Populus Response to heat stress [26] tomentosa III SlWRKY33 Solanum lycopersicum Tolerance to cold [30] II D GmWRKY13 Glycine max Response to salt and mannitol [9] Table 1.
Reported functional WRKY genes summarized in this study.
-
Gene ID WRKY domain No. of
domainsNo. of
exonsNo. of
intronsGroup Conserved heptapeptide Zinc finger Zinc finger type Dca000627 WRKYGQK − − 1 3 2 II E Dca000637 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 2 1 II C Dca000671 WRKYGQK/WRKYGQK C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX22HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 5 4 I Dca000699 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 2 1 II C Dca000873 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 5 4 II B Dca002197 WKKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 2 1 I Dca002205 WRKDGTH/WRKYATN C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX23HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 6 5 I Dca002550 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 3 2 II E Dca002715 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 3 2 II C Dca003067 WRKYGQK C2HC CX7CX23HXC 1 3 2 III Dca003180 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 3 2 II D Dca003732 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 2 1 II C Dca004998 WRKYGQK/WRKYGQK C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX22HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 4 3 I Dca005043 WRKYGQK C2HC CX7CX23HXC 1 3 2 III Dca005048 WRKYGEK C2HC CX7CX23HXC 1 2 1 III Dca005648 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 3 2 II C Dca005780 WRKYGQK/WRKYGQK C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX22HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 5 4 I Dca006278 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 3 2 II D Dca006505 WRKYGQK/WRKYGQK C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX22HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 6 5 I Dca006646 WRKYGQK C2HC CX7CX23HXC 1 3 2 III Dca006787 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 3 2 II E Dca007186 WRKYGQK/WRKYGQK C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX22HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 5 4 I Dca007842 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 5 4 II B Dca008357 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 4 3 II A Dca008967 WTKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 3 2 I Dca008968 WNKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 2 1 I Dca008985 WRKYGQK/WRKYGQK C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX22HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 4 3 I Dca009368 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 3 2 II C Dca010430 WRKYGQK/WRKYGQK C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX22HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 5 4 I Dca010993 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 2 1 II C Dca011499 WRKYGQK/WRKYGQK C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX22HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 3 2 II C Dca011569 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 5 4 II B Dca011912 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 3 2 II A Dca011914 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 4 3 II A Dca012410 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 3 2 II E Dca012846 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 3 2 II C Dca013146 WRKYGQK C2HC CX7CX23HXC 1 3 2 III Dca013149 WRKYGQK C2HC CX7CX23HXC 1 3 2 III Dca013150 WRKYGEK C2HC CX7CX23HXC 1 3 2 III Dca014563 WRKYGQK C2HC CX7CX23HXC 1 2 1 III Dca015482 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 3 2 II D Dca015639 WRKYGKK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 3 2 II C Dca015848 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 2 1 II C Dca015914 WRKYGQK/WRKYGQK C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX22HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 3 2 II C Dca016437 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 2 1 II C Dca016988 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 2 1 II E Dca017113 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 3 2 II C Dca018137 WRKYGQK/WRKYGQK C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX22HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 4 3 I Dca018897 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 4 3 II A Dca019319 WRKYGQK C2HC CX7CX23HXC 1 3 2 III Dca019656 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 3 2 II E Dca019840 WRKYGKK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 3 2 II C Dca020159 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 2 1 II C Dca020342 WRKYGQK/WRKYGQK C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX22HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 5 4 I Dca020473 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 3 2 II E Dca021638 WRKYGEK/WRKYGEK —/C2HC —/CX7CX23HXC 2 5 4 III Dca023070 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 3 2 II D Dca024256 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX5CX23HXH 1 2 1 II E Dca024393 WRKYGQK/WRKYGQK C2H2/C2H2 CX4CX22HXH/CX4CX23HXH 2 4 3 I Dca026708 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 4 3 II A Dca027312 WRKYGQK C2HC CX7CX23HXC 1 3 2 III Dca028175 WRKYGQK C2H2 CX4CX23HXH 1 3 2 II C Dca028770 WRKYGKK - - 1 1 0 II C Table 2.
Characteristics of WRKY genes in D. catenatum.
-
Primer name Sequence (5'-3') Dca002550-F GTGTTCGAGCTCAACCATCA Dca002550-R TGATCGTGATCTCCCATGAA Dca005648-F GGCCGATTCACCGAATAATA Dca005648-R TTTCAACACGCTTCTTCACG Dca006787-F GCGATCTCTTTGCCTCAAAC Dca006787-R TTCCTTGCTGAGCATCCTTT Dca007842-F GCTCCTCTACCACCCATTCA Dca007842-R GTGAGGTCGAGGGTGATTGT Dca010430-F AGGAAGTCTGACGACGGCTA Dca010430-R CGAGTGGACTGAGGCTTAGG Dca016437-F ATCGTTGCACCACACAGAAG Dca016437-R AAGTCATGGTGGAAGCTTGG Table 3.
qRT-PCR primers of DcaWRKYs.
Figures
(9)
Tables
(3)