-
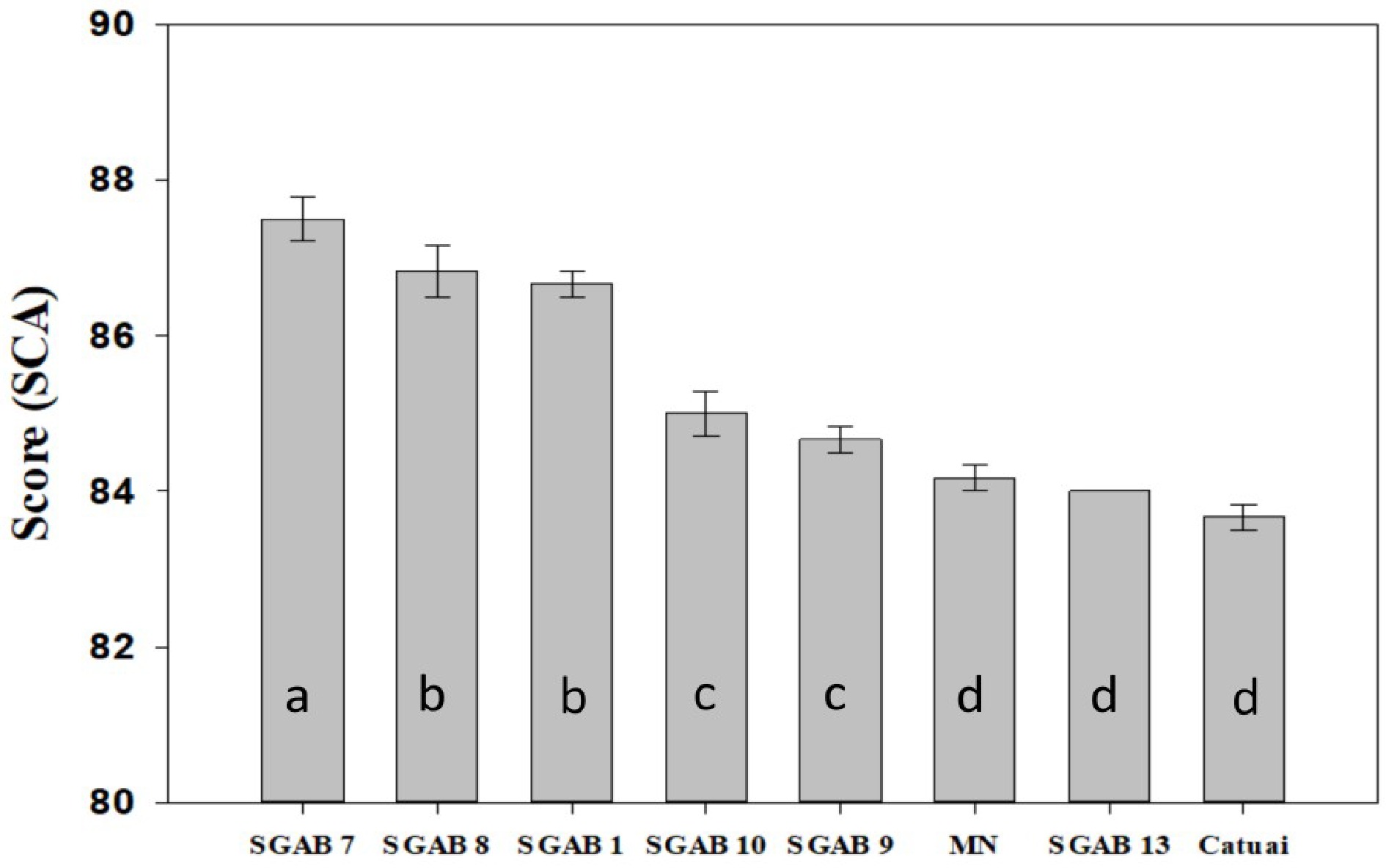
Figure 1.
Total score according to the SCA methodology, obtained in univariate sensory analysis for six genotypes and two control cultivars ('Catuaí Vermelho IAC 99' and 'Mundo Novo IAC 376/4' - MN) referring to the 2018/2019 crop year. Means followed by the same letter do not differ by the Scott Knott test (1974) (P < 0.05).
-
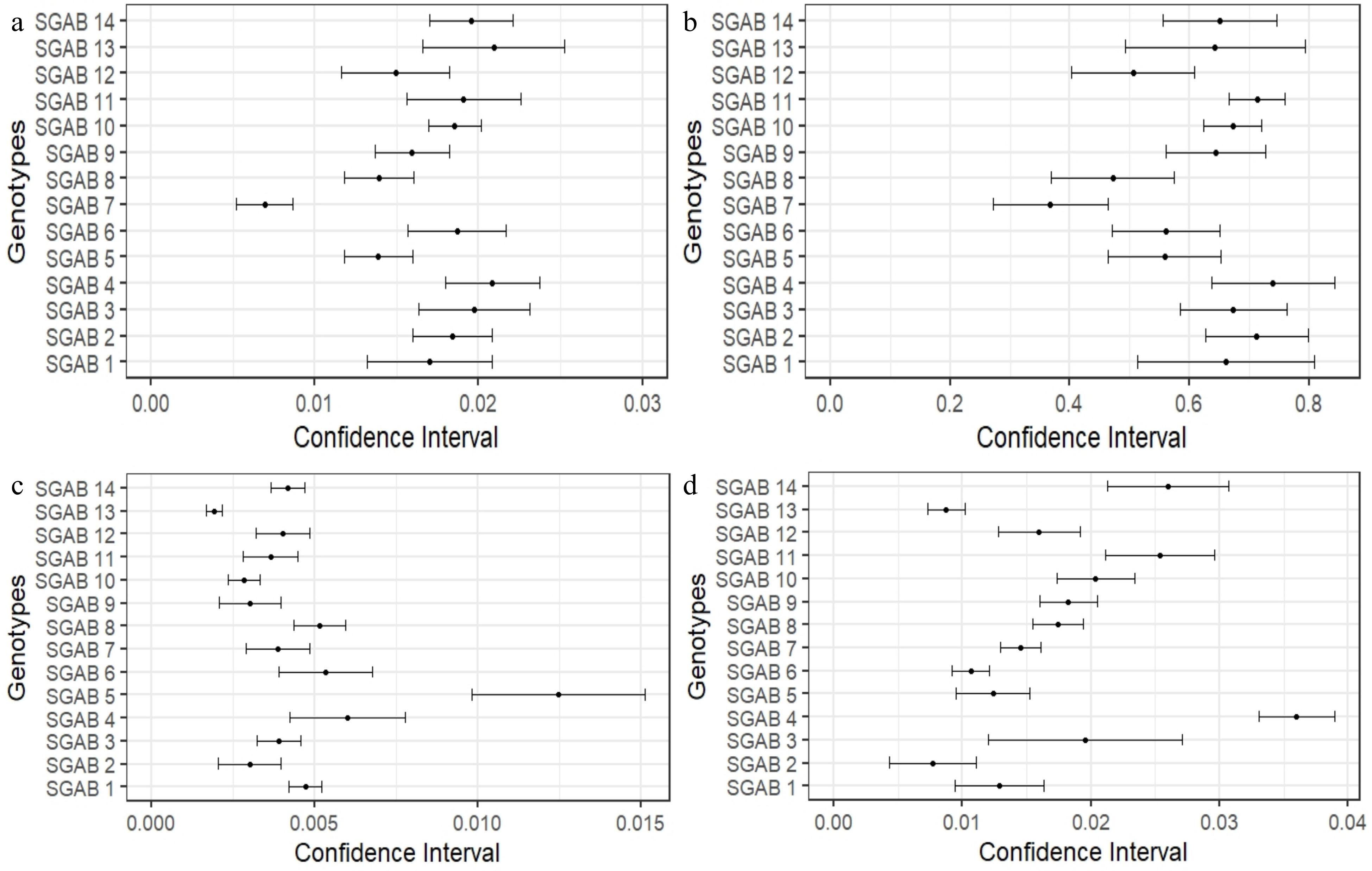
Figure 2.
Confidence interval (95%) of β1's estimates (linear regression coefficients - slope) for the variables (a) branch length, (b) number of nodes, (c) stem diameter and (d) plant height in 14 genotypes of C. arabica. Confidence interval values that are not overlapped indicate that estimates differ statistically from each other (Supplemental Table S3).
-
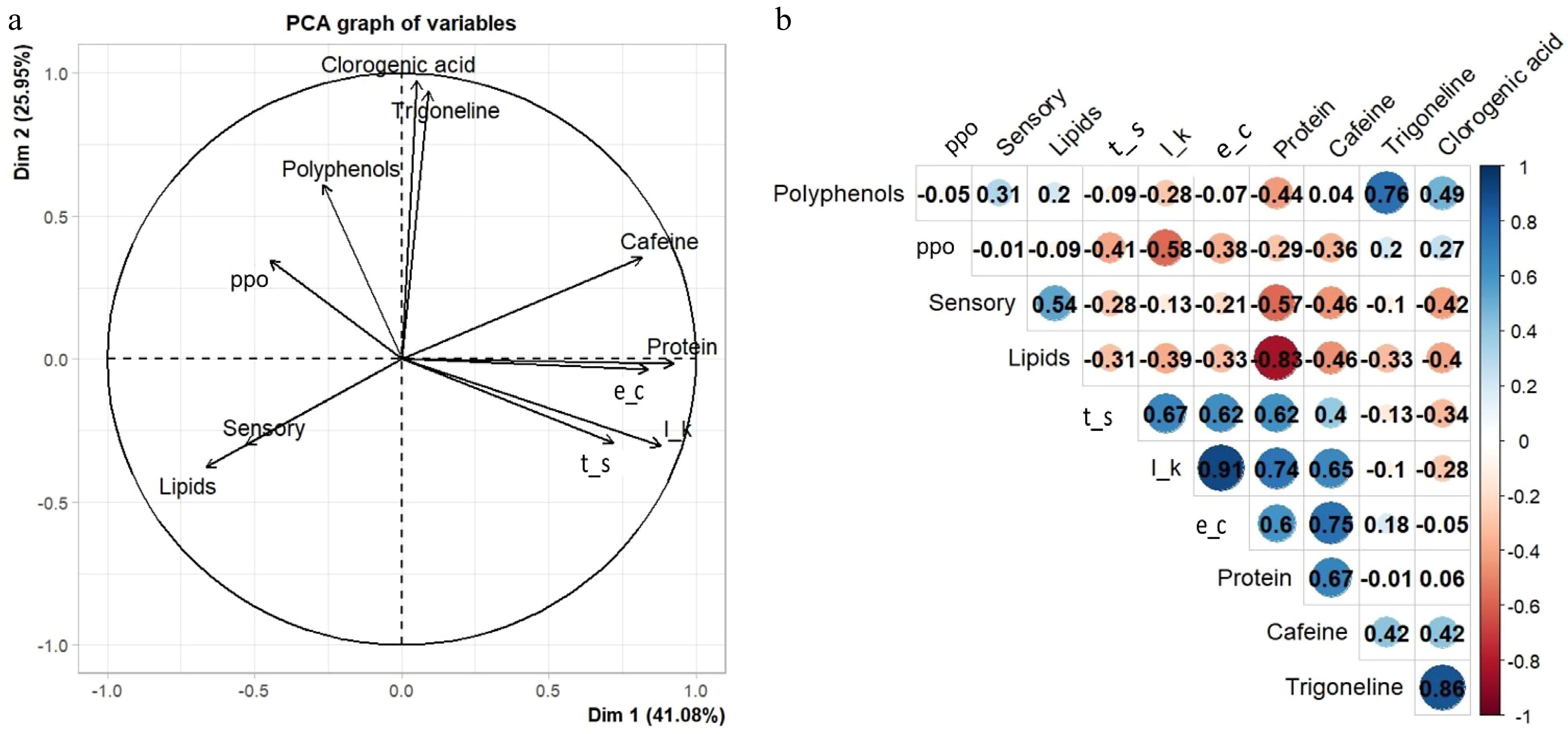
Figure 3.
(a) Principal components and (b) Pearson correlation analysis of chemical variables of six coffee genotypes evaluated. Polyphenol oxydase (ppo); Total Sugars (t_s); Potassium Leaching (l_k), Electrical Conductivity (e_c).
-
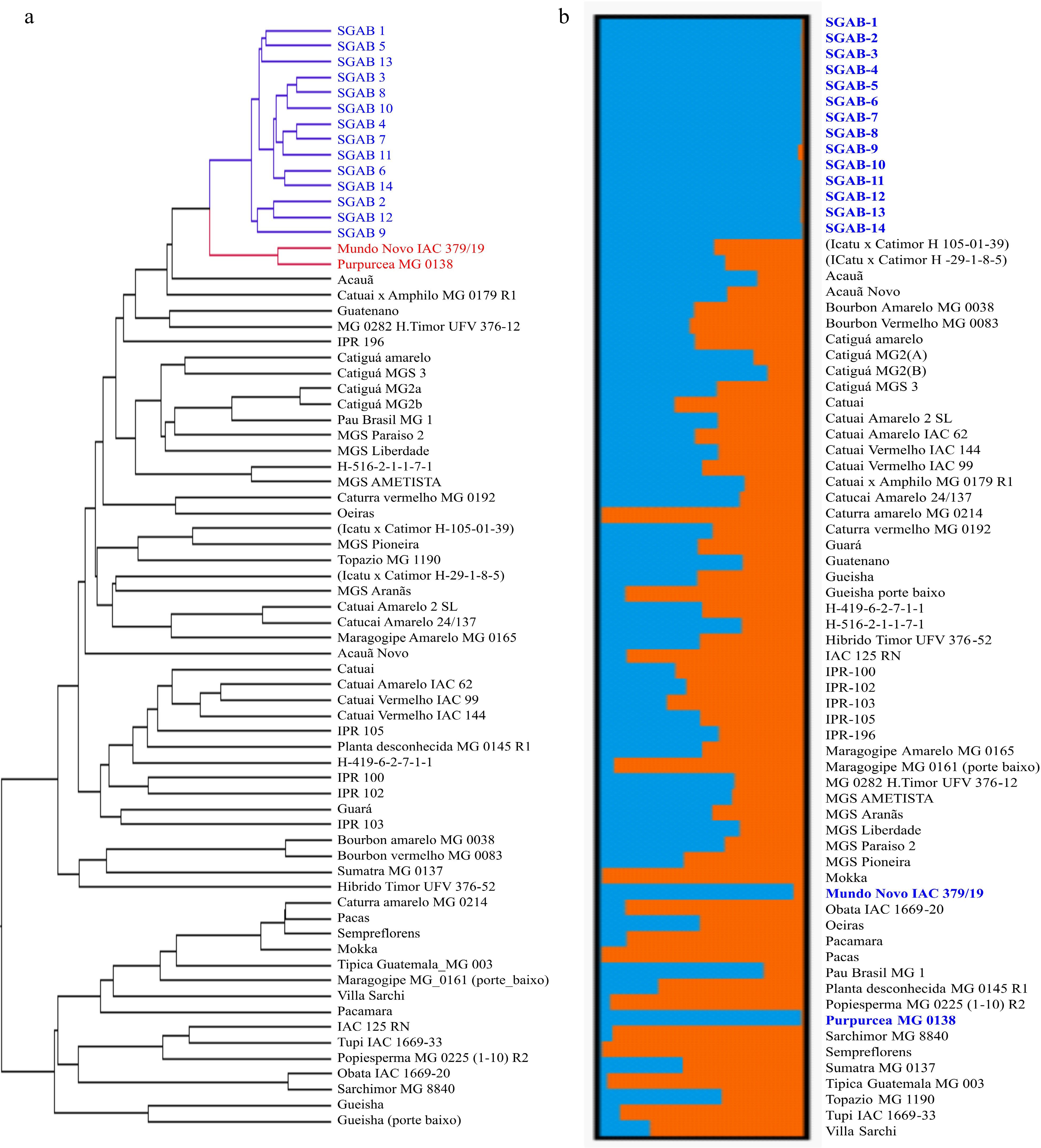
Figure 4.
(a) Genetic diversity and (b) structure population of SGAB coffee genotypes compared with EPAMIG coffee germplasm.
-
Genotypes Sensory description SGAB 7 Vivid acidity, creamy and soft body, floral, honey, Swiss lemonade, fruity, long and sweet finish. SGAB 8 Vivid and sweet acidity, creamy and soft body, yellow fruits, floral, honey, brown sugar, long and sweet finish. SGAB 1 Bright and lively acidity, creamy and velvety body, floral flavor, yellow fruits, honey, molasses, brown, long and pleasant finish. SGAB 10 Sweet acidity, creamy body, brown, caramel, long finish. SGAB 9 Vivid acidity, creamy body, high sweetness, honey, caramel, milk chocolate, long and pleasant finish. Mundo Novo IAC 376/4 Sweet acidity, creamy body, high sweetness, yellow fruit, caramel, brown, milk chocolate, long finish. SGAB13 Medium acidity, creamy body, caramel, milk chocolate, brown, long and sweet finish. Catuaí Vermelho IAC 99 Medium acidity, creamy body, clean, caramel, milk chocolate, brown, long finish. Source: adapted from Nadaleti[56]. Table 1.
Nuances identified by three tasters based on the methodology described by SCA using the six coffee genotypes provided and two control cultivars.
-
Genotype EC LK TS PPO POL P L Trig CA C SGAB7 34.20 d 28.49 f 7.96 d 46.50 a 6.38 b 11.68 b 12.91 a 1.13 b 3.91 c 1.16 c SGAB8 41.09 b 46.02 b 8.51 c 44.08 a 6.31 b 12.29 a 10.62 b 1.15 b 3.84 c 1.17 c SGAB1 37.40 c 30.71 e 8.90 b 45.30 a 7.10 a 11.65 b 12.79 a 1.17 b 3.69 d 1.07 d SGAB10 39.68 b 43.06 c 9.40 a 44.43 a 6.15 b 12.56 a 10.61 b 1.09 b 3.74 d 1.25 b SGAB9 55.02 a 56.87 a 9.28 a 45.41 a 5.85 b 12.53 a 10.86 b 1.15 b 3.74 d 1.34 a Mundo Novo 376/4 43.08 b 36.17 d 8.55 c 45.54 a 7.32 a 12.24 a 10.44 b 1.42 a 5.23 a 1.36 a SGAB13 41.6 b 42.76 c 8.69 c 42.44 a 6.02 b 12.20 a 12.18 a 1.06 b 3.91 c 1.27 b Catuaí Vermelho IAC 99 32.18 e 25.73 g 8.30 c 47.92 a 5.70 b 12.16 a 10.64 b 1.12 b 4.27 b 1.11 d EC, Electrical Conductivity; LK, Potassium Leaching; TS, Total Sugars; PPO, Polyphenol oxydase; POL, Polyphenols, P, Proteins; L, Lipids; Trig, Trigonelin; CA, Chlorogenic Acid; C, Caffeine. Different letters represent statistical significance according to Scott-Knott test. Table 2.
Chemical characterization of six genotypes and two control cultivars ('Catuaí Vermelho IAC 99' and 'Mundo Novo IAC 376/4') related to the 2018/2019 crop year.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(2)