-
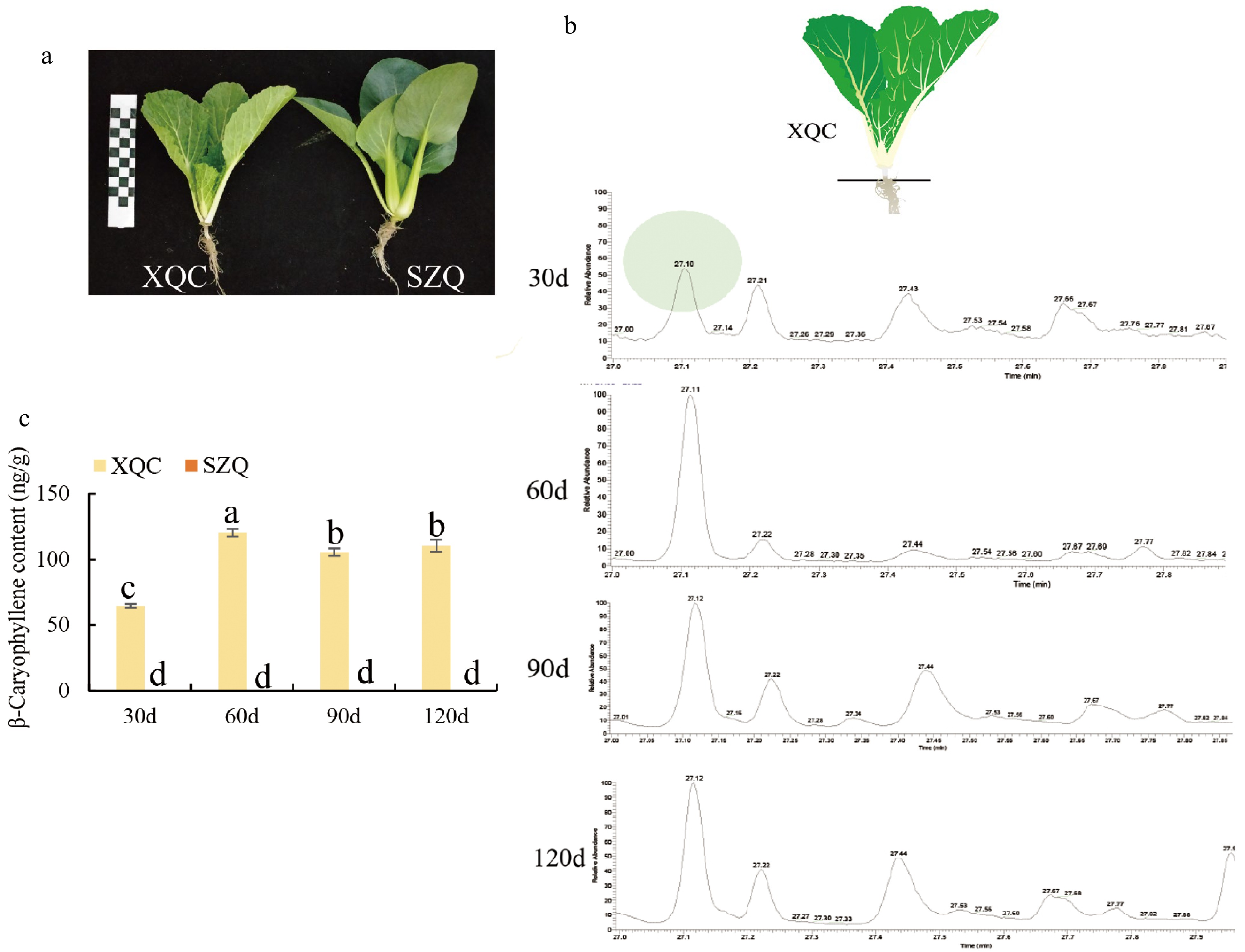
Figure 1.
β-Caryophyllene content in pak-choi cultivars 'XQC' and 'SZQ'. (a) Phenotypes of two pak-choi cultivars, 'XQC' and 'SZQ', at the 30 d stage. (b) Retention time of β-caryophyllene volatiles in GC-MS at 30, 60, 90, and 120 d. (c) β-caryophyllene content at 30, 60, 90, and 120 d in 'XQC' and 'SZQ'.
-
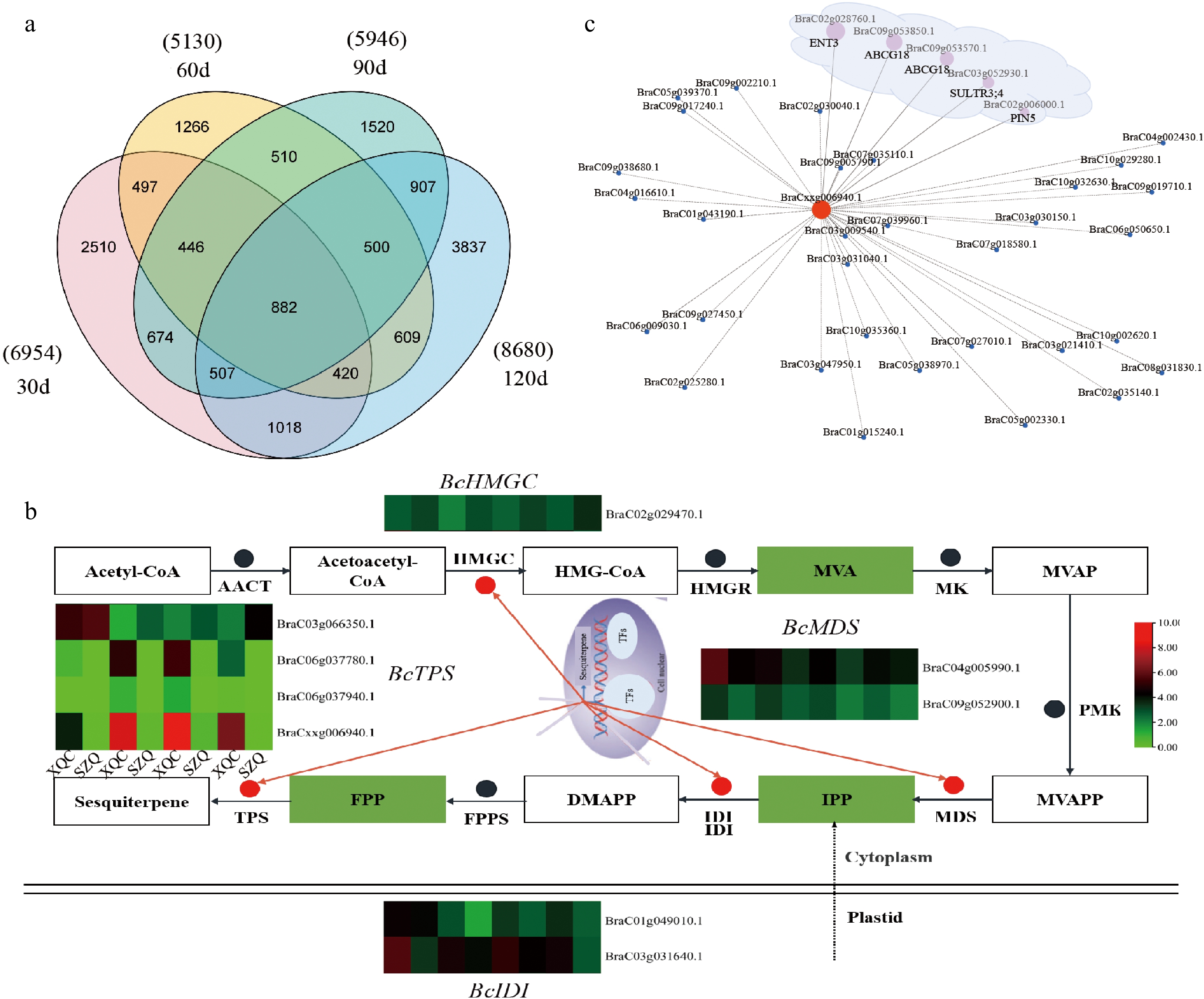
Figure 2.
Transcriptomic analysis of 'XQC' and 'SZQ' at 30, 60, 90, and 120 d. (a) Venn diagram showing the number of DEGs identified between 'XQC' and 'SZQ' at 30, 60, 90, and 120 d. (b) DEG heatmap of the RNA-Seq expression involved in the sesquiterpene pathway. (c) Network between TPS21 and the differential transporters. Circle size indicates Person correlation.
-
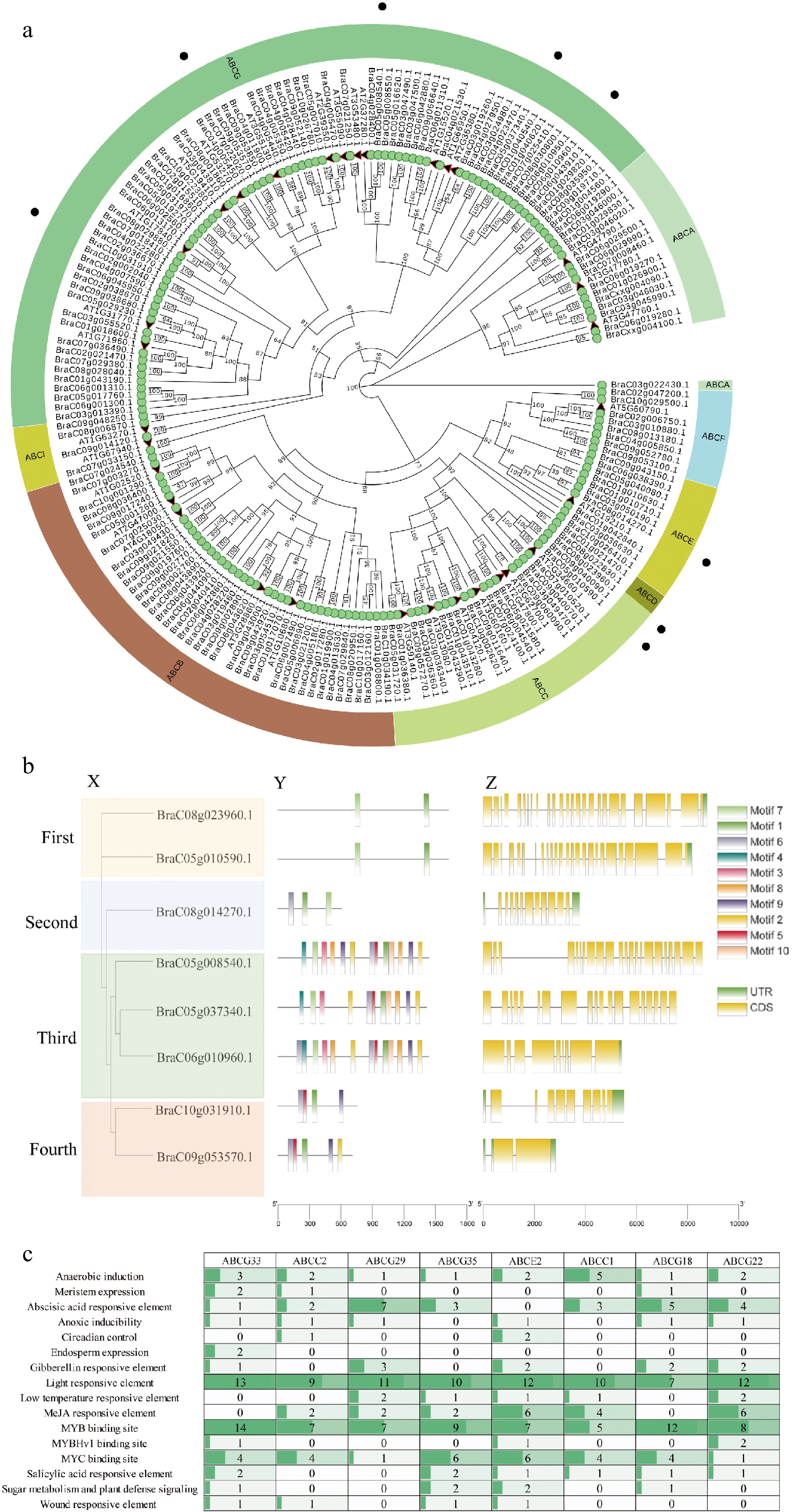
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis, gene structure, conserved domains, and cis-acting elements of ABC proteins from Brassica campestris and Arabidopsis. (a) Phylogenic relationship of the identified ABC genes in the Brassica campestris genome. (b) Eight ABC transporter motif distributions and exon-intron distribution in Brassica campestris. The motifs identified in the BcABC proteins are indicated by different colored boxes and named motifs 1–10. The closed yellow boxes and black lines represent exons and introns, respectively. (c) The number and type of existing putative cis-acting elements in two kb upstream regions of the eight ABC genes.
-
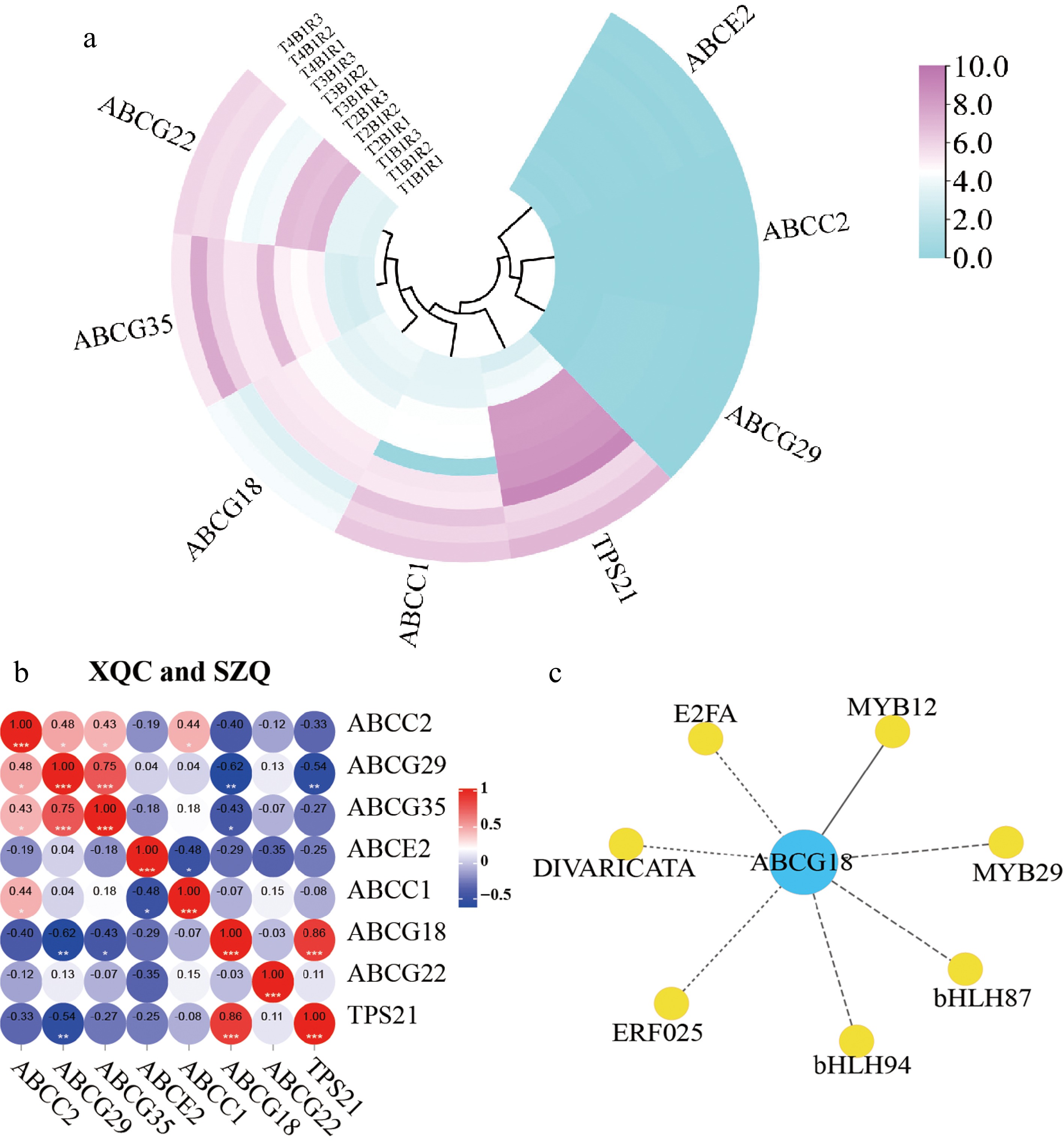
Figure 4.
Pearson analysis of 'XQC' and 'SZQ' at 30, 60, 90, and 120 d. (a) Heatmap of RNA-Seq expression of seven ABC differential transporters. (b) Correlation among the ABC proteins in 'XQC' and 'SZQ'. (c) The correlation between transcription factors and ABCG18 of 'XQC' and 'SZQ' transcriptome data, solid line -> 0.8.
-
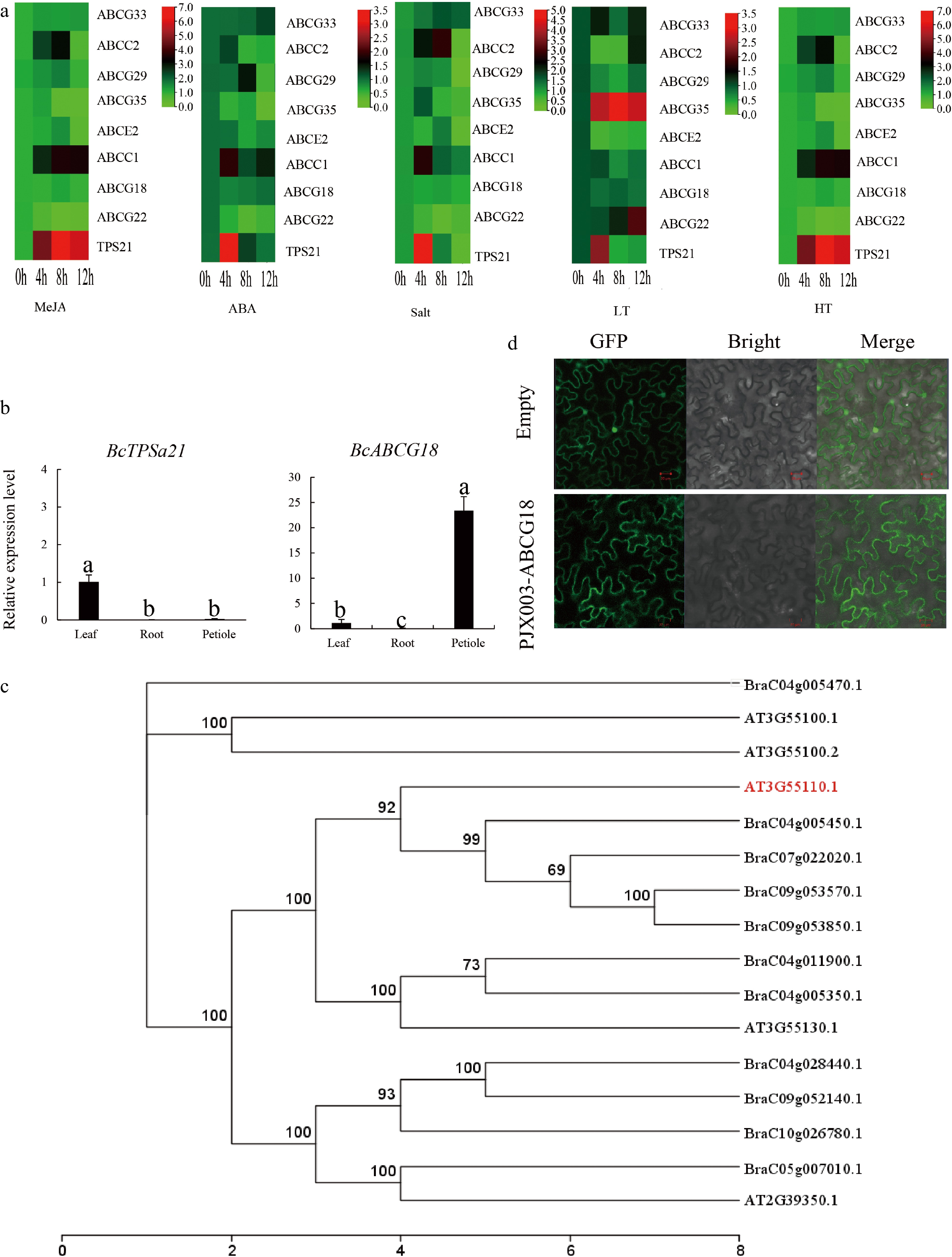
Figure 5.
Expression profiles of BcABC genes and subcellular localization. (a) Expression profiles of BcABC genes under different conditions (MeJA, ABA, salt, high temperature, low temperature). (b) Transcript levels of ABCG18 and TPS21 in leaf, stem, and root tissue. (c), (d) Finding the best homology of the ABCG18 gene and subcellular localization.
Figures
(5)
Tables
(0)