-
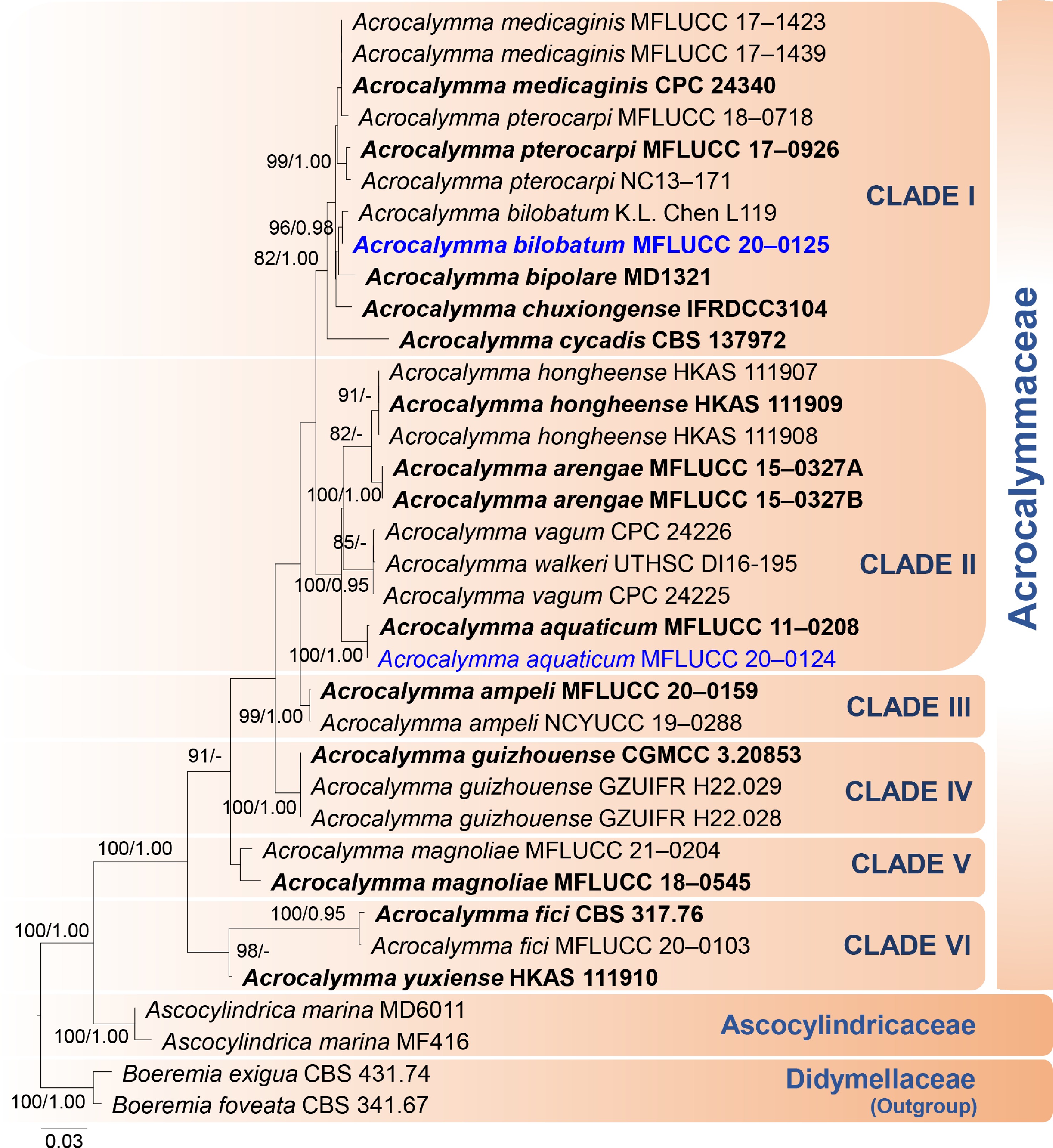
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree based on RAxML analyses of combined SSU, LSU, ITS, and TEF1-α sequence data. Bootstrap support values for maximum likelihood (ML) higher than 75% and Bayesian posterior probabilities (BYPP) greater than 0.95 are indicated above the nodes as ML/BYPP. The new species are represented in blue bold and type species are in bold. The tree is rooted to Boeremia foveata (CBS 341.67) and B. exigua (CBS 431.74) (Didymellaceae). Bar = 0.03 estimated number of nucleotide substitutions per site per branch
-
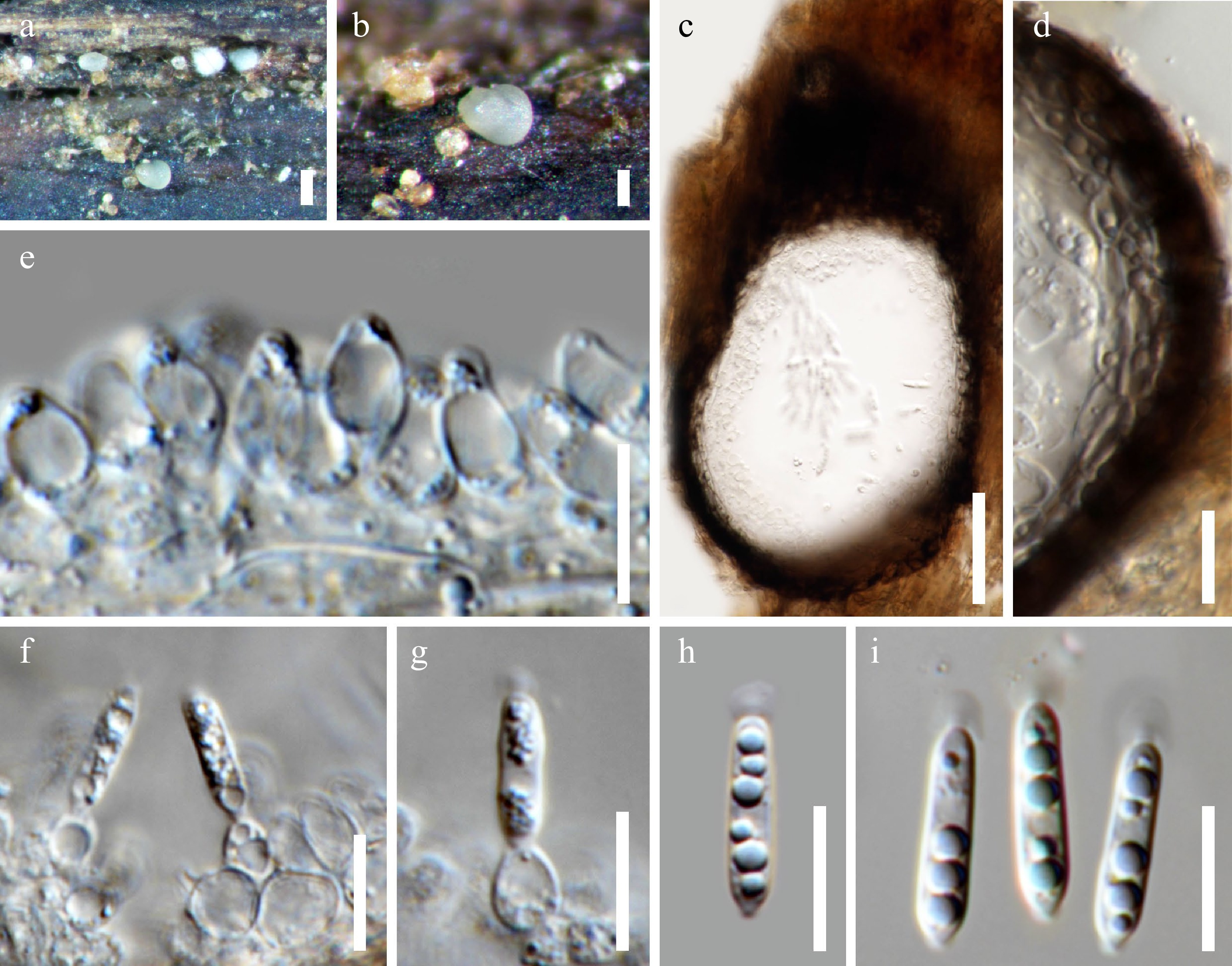
Figure 2.
Acrocalymma aquatica (MFLU 22–0114). (a), (b) Erumpent conidiomata on wood surface. (c) Vertical sections of a conidioma. (d) Section through the peridium. (e)–(g) Conidiogenous cells. (h), (i) Conidia with apical appendages. Scale bars: (a) = 200 μm, (b) = 100 μm, (c) = 50 μm, (d)–(i) = 10 μm.
-
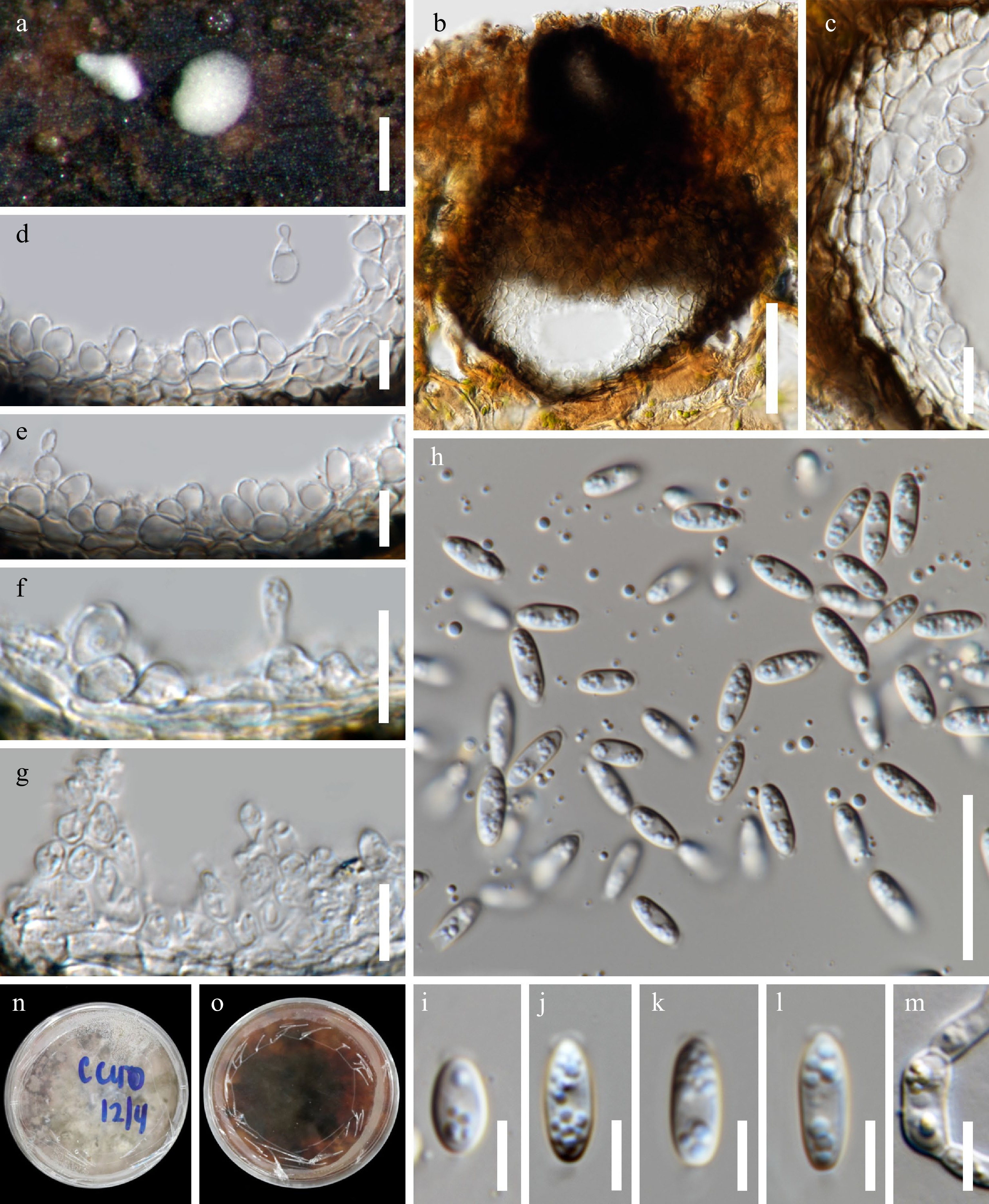
Figure 3.
Acrocalymma bilobatum (MFLU 22–0115, holotype). (a) Appearance of erumpent dark brown conidiomata on wood surface. (b) Vertical section of conidioma. (c) Section through the peridium. (d)–(g) Conidiogenous cells. (h)–(l) Conidia with appendages. (m) Germinated conidium. Colony on MEA: (n) obverse. Scale bars: (a) = 200 μm, (b) = 50 μm, (c)–(g) = 10 μm, (h) = 20 μm, (i)–(l) = 5 μm.
-
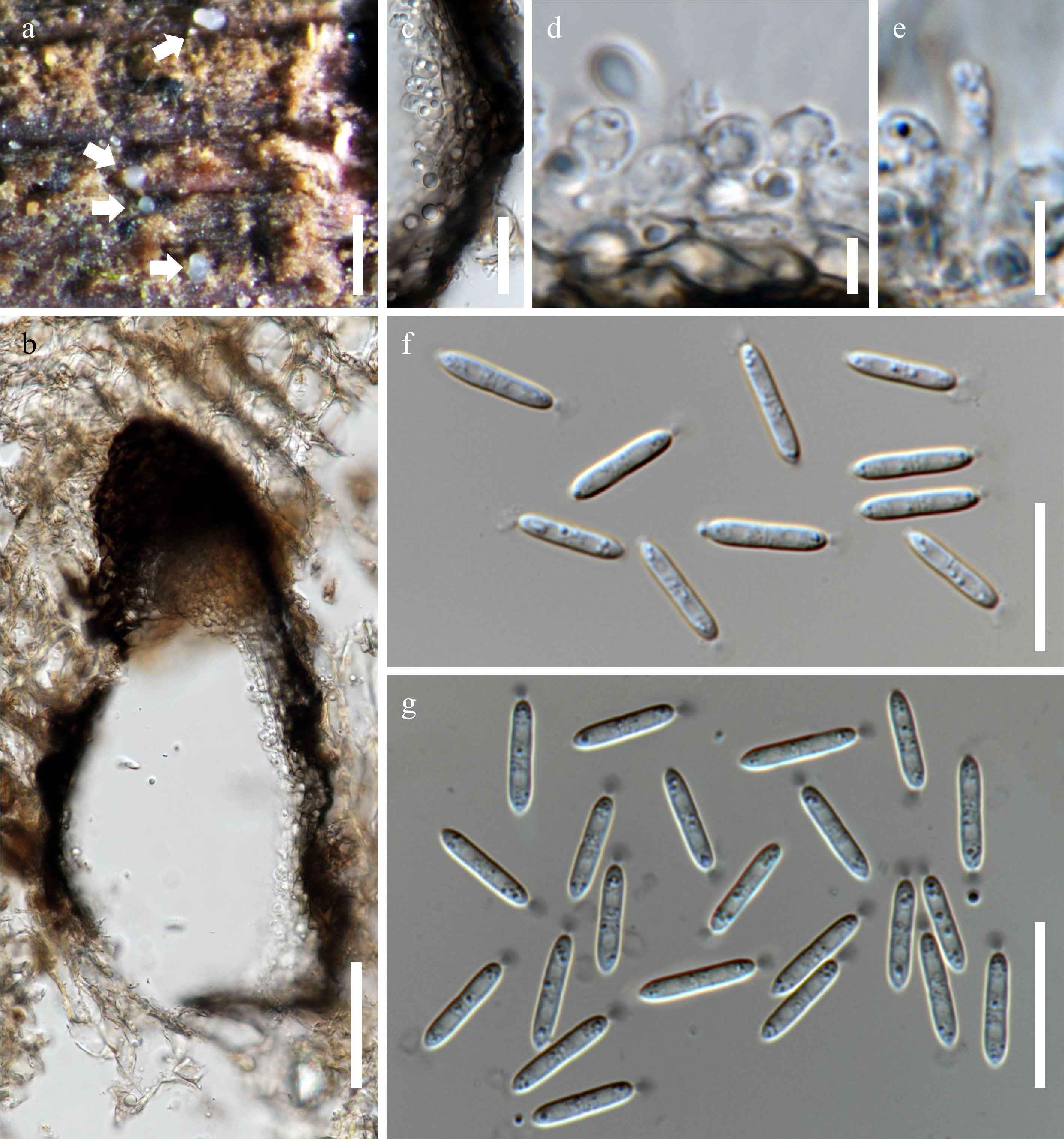
Figure 4.
Acrocalymma fici (MFLU 21–0124). (a) Appearance of conidiomata on wood surface. (b) Vertical section of conidioma. (c) Section through the peridium. (d), (e) Conidiogenous cells. (f), (g) Conidia with apical appendages. (g) Conidia stained with nigrosin. Scale bars: (a) = 500 μm, (b) = 50 μm, (c), (f), (g) = 20 μm, (d), (e) = 5 μm.
-
Taxon Strain / voucher number SSU LSU ITS TEF1-α Acrocalymma ampeli MFLUCC 20-0159 MW079341 MW063211 MW063150 – Acrocalymma ampeli NCYUCC 19-0288 MW079342 MW063212 MW063151 – Acrocalymma aquaticum MFLUCC 11-0208 JX276953 NG_042698 NR_121544 – Acrocalymma aquaticum MFLUCC 20-0124 – MT875393 MT875395 MT897894 Acrocalymma arengae MFLUCC 15–0327A ON650177 ON650673 ON650154 – Acrocalymma arengae MFLUCC 15–0327B ON650178 ON650674 ON650155 – Acrocalymma bilobatum K.L. Chen L119 – – KX034339 – Acrocalymma bilobatum* MFLUCC 20-0125 – MT875394 MT875396 MT897895 Acrocalymma bipolare MD1321 – NG_075326 – – Acrocalymma chuxiongense IFRDCC3104 – ON596248 ON595715 – Acrocalymma cycadis CBS 137972 – NG_057046 NR_137884 – Acrocalymma fici CBS 317.76 – NG_057056 NR_137953 KP170663 Acrocalymma fici MFLUCC 21-0103 – MT860429 MT864351 – Acrocalymma guizhouense CGMCC 3.20853 OM838471 OM838474 OM838410 – Acrocalymma guizhouense GZUIFR H22.028 OM838472 OM838475 OM838411 – Acrocalymma guizhouense GZUIFR H22.029 OM838473 OM838476 OM838412 – Acrocalymma hongheense HKAS 111907 MW424792 MW424777 MW424763 – Acrocalymma hongheense HKAS 111908 MW424791 MW424776 MW424762 – Acrocalymma hongheense HKAS 111909 MW424790 MW424775 MW424761 – Acrocalymma magnoliae MFLUCC 18–0545 OL331094 OK655819 OL413439 – Acrocalymma magnoliae MFLUCC 21–0204 OL331095 OK655820 OL413440 – Acrocalymma medicaginis CPC 24340 – KP170713 KP170620 – Acrocalymma medicaginis MFLUCC 17-1423 MT214387 MT214432 MT214338 – Acrocalymma medicaginis MFLUCC 17-1439 MT214388 MT214433 MT214339 – Acrocalymma pterocarpi MFLUCC 17-0926 MK347840 NG_066306 MK347732 MK360040 Acrocalymma pterocarpi MFLUCC 18–0718 OL331093 OK655818 OL413438 – Acrocalymma pterocarpi NC13-171 – LC517881 LC517880 – Acrocalymma vagum CPC 24225 – – KP170635 – Acrocalymma vagum CPC 24226 – – KP170636 – Acrocalymma walkeri UTHSC DI16-195 – LN907338 LT796832 LT797072 Acrocalymma yuxiense HKAS 111910 MW424793 MW424778 – – Ascocylindrica marina MD6011 KT252907 KT252905 – – Ascocylindrica marina MF416 MK007124 MK007123 – – Boeremia exigua CBS 431.74 EU754084 EU754183 FJ427001 KY484687 Boeremia foveata CBS 341.67 GU238203 GU237947 GU237834 KY484716 Table 1.
Taxa used in this study for the analysis of combined SSU, LSU, and ITS rDNA sequence data and their GenBank accession numbers. The newly generated sequences are indicated with * and the ex-type strains are indicated in bold.
-
Step Features Species 1a Sexual morph 2 1b Asexual morph 6 2a Asci, <100 μm 3 2a Asci, >100 μm 4 3a Ascospores, 17–21 × 3–5 μm A. pterocarpi 3b Ascospores, 19–22 × 4.5–5.5 μm A. walkeri 4a Ascospores, 1-septate 5 4b Ascospores, 1–3-septate A. arengae 5a Ascospores, 35–45 × 18–20 μm A. chuxiongense 5b Ascospores, 20–35 × 7–9 μm A. hongheense 6a Conidia lacks mucoid cap 7 6b Conidia with mucoid caps 8 7a Conidia, (16–)18–25(– 28) × (4.0–)4.5–6.0(–6.9) μm A. vagum 7b Conidia, 15–21 × 4–5 μm A. yuxiense 8a Conidia, mucoid caps in apex 9 8b Conidia, mucoid caps in both ends 13 9a Conidia, <20 µm 10 9b Conidia, >20 µm 12 10a Conidia <10 A. guizhouense 10b Conidia >10 11 11a Conidia, 12–17 × 3–4 µm A. cycadis 11b Conidia, 12–16 × 2.5–3 µm A. magnoliae 12a Conidia, 22–30 × 5–7 μm A. aquatica 12b Conidia, (25–)28–32(–35) × (4–)5 μm A. fici 13a Conidia <15 14 13b Conidia >15 15 14a Conidia, 7–12 × 2.5–4 µm A. bilobatum 14b Conidia, 9–12 × 3–5 µm A. bipolare 15a Conidia, 17–19 × 5.5–6.5 μm A. ampeli 15b Conidia, 11–21 × 3.5–5.0 µm A. medicaginis Table 2.
Key to species of Acrocalymma
Figures
(4)
Tables
(2)