-
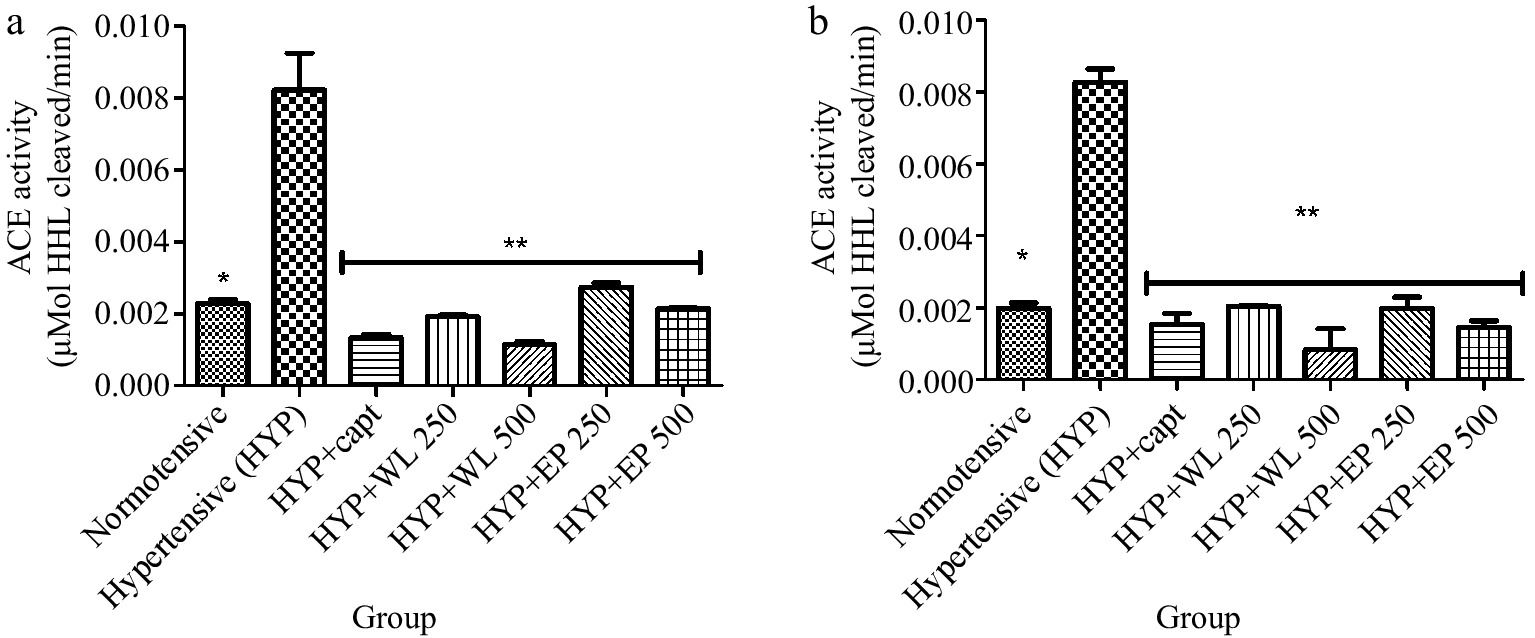
Figure 1.
Effect of wild lettuce and African eggplant leaves extract on (a) lungs and (b) kidney ACE activity in L-NAME induced hypertension in rats. Values represent mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). * Significantly different when compared normotensive with hypertensive (p < 0.05). ** Significantly different when compared wild lettuce and African eggplant leaves extract-treated hypertensive with hypertensive (p < 0.05).
-
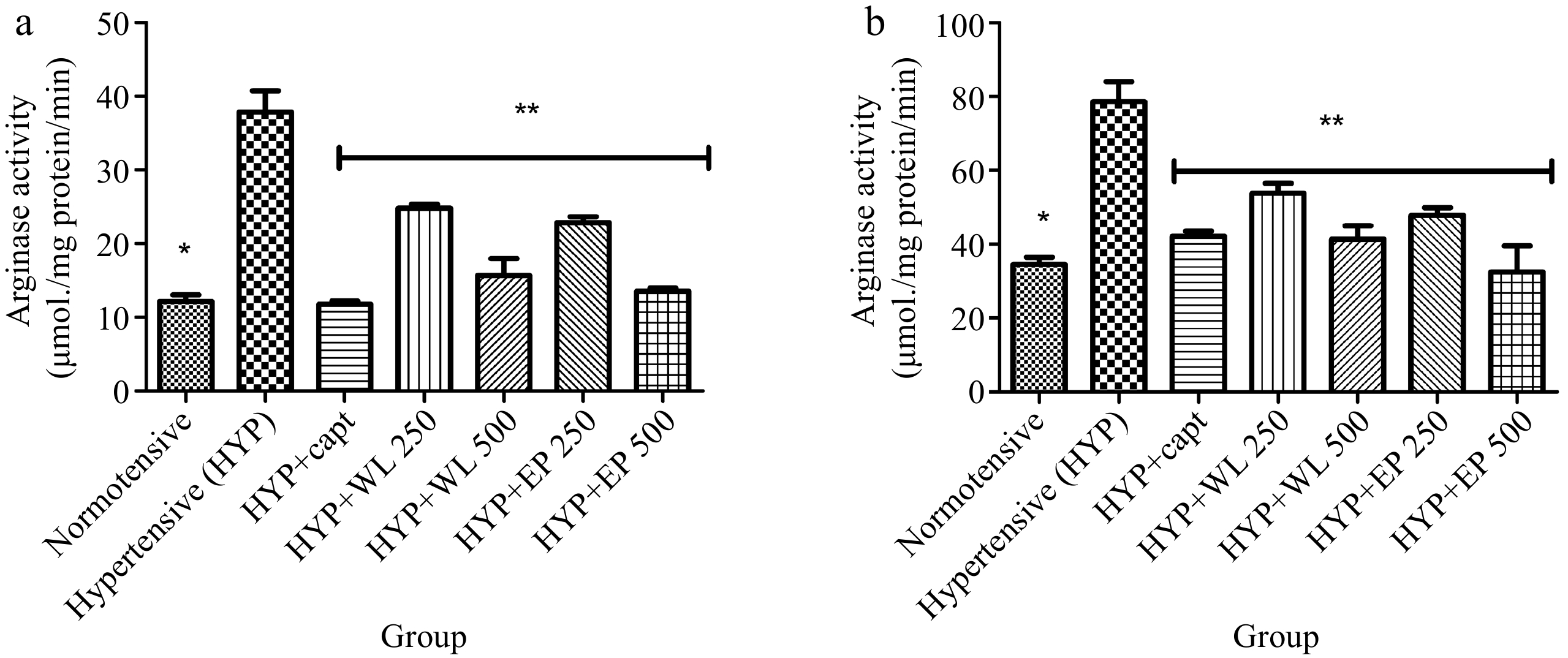
Figure 2.
Effect of wild lettuce and Africa eggplant leaves extract on the (a) heart and (b) kidney arginase activity in L-NAME induced hypertension in rats. Values represent mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). * Significantly different when compared normotensive with hypertensive (p < 0.05). ** Significantly different when compared wild lettuce and African eggplant leaves extract-treated hypertensive with hypertensive (p < 0.05).
-
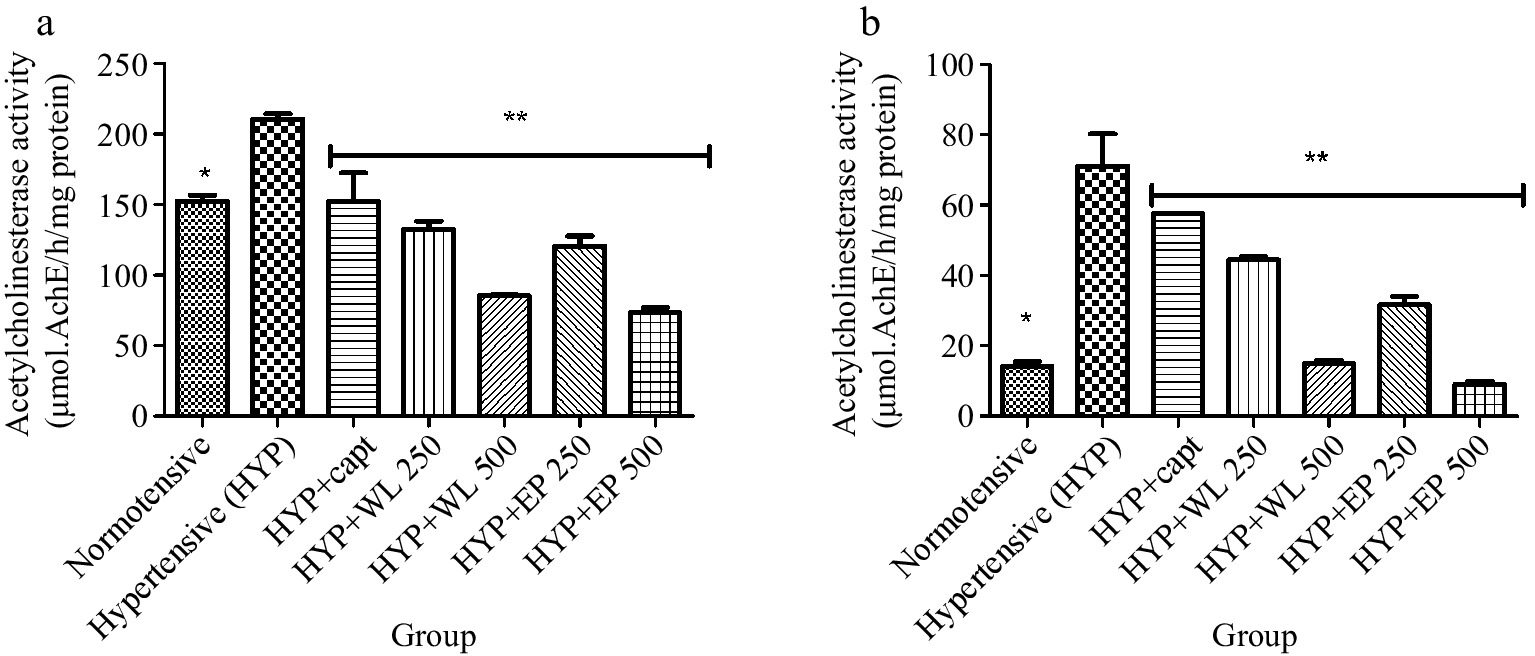
Figure 3.
Effect of wild lettuce and Africa eggplant leaves extract on the (a) heart and (b) kidney acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity in L-NAME induced hypertension in rats. Values represent mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). * Significantly different when compared normotensive with hypertensive (p < 0.05). ** Significantly different when compared wild lettuce and African eggplant leaves extract-treated hypertensive with hypertensive (p < 0.05).
-
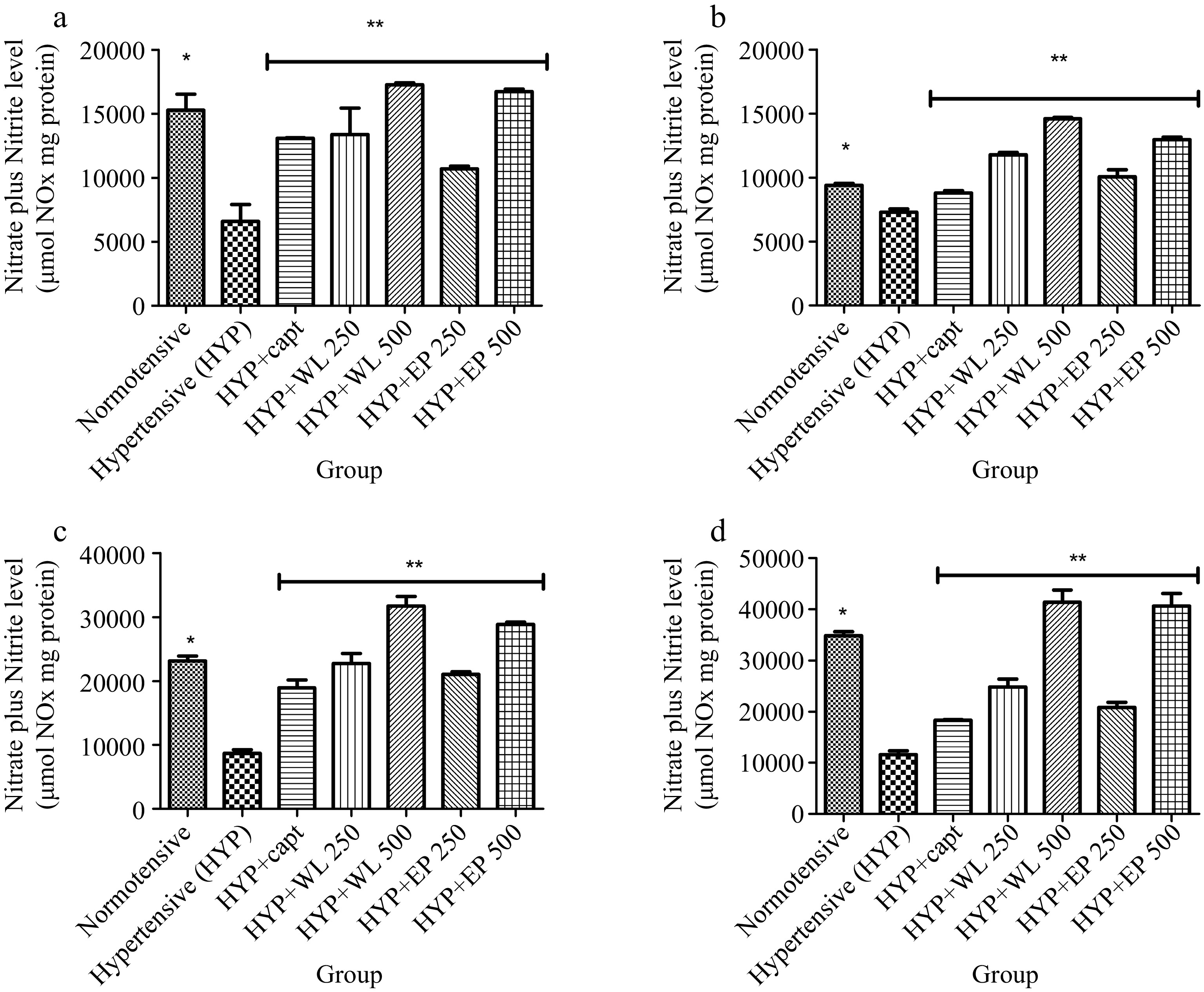
Figure 4.
Effect of wild lettuce and Africa eggplant leaves extract on (a) plasma, (b) heart, (c) kidney and (d) lungs Nitric oxide level in L-NAME induced hypertension in rats. Values represent mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). * Significantly different when compared normotensive with hypertensive (p < 0.05). ** Significantly different when compared wild lettuce and African eggplant leaves extract treated hypertensive with hypertensive (p < 0.05).
-
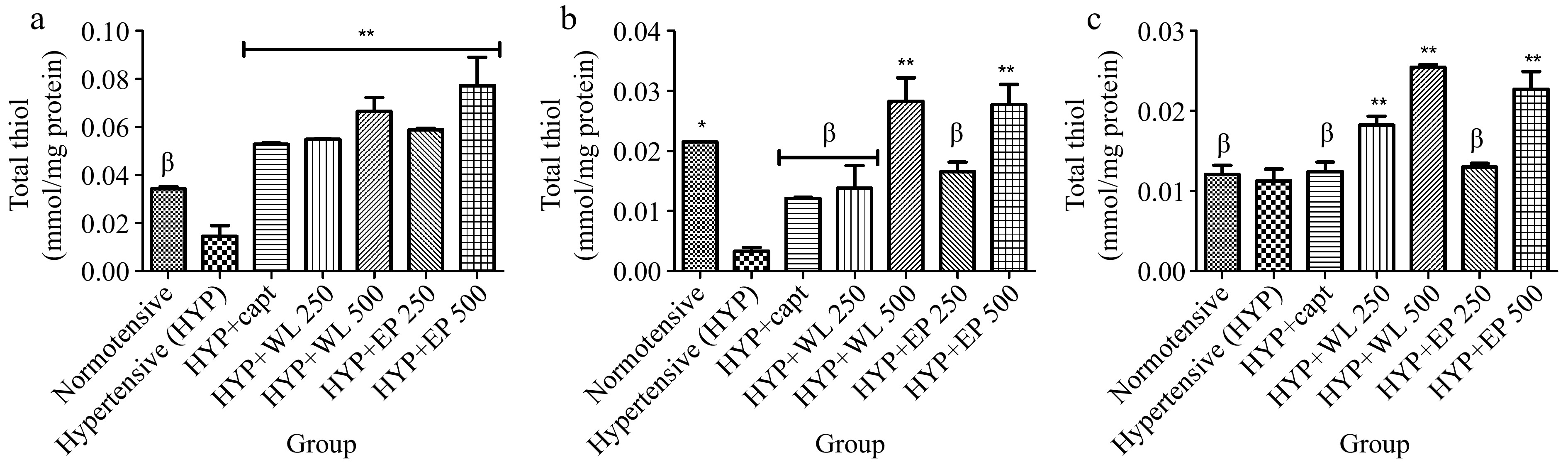
Figure 5.
Effect of wild lettuce and Africa eggplant leaves extract on the (a) heart, (b) kidney and (c) lungs total thiol level in L-NAME induced hypertension in rats. Values represent mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). * Significantly different when compared normotensive with hypertensive (p < 0.05). ** Significantly different when compared wild lettuce and African eggplant leaves extract-treated hypertensive with hypertensive (p < 0.05). β Not significantly different when compared wild lettuce and African eggplant leaves extract-treated hypertensive with hypertensive.
-
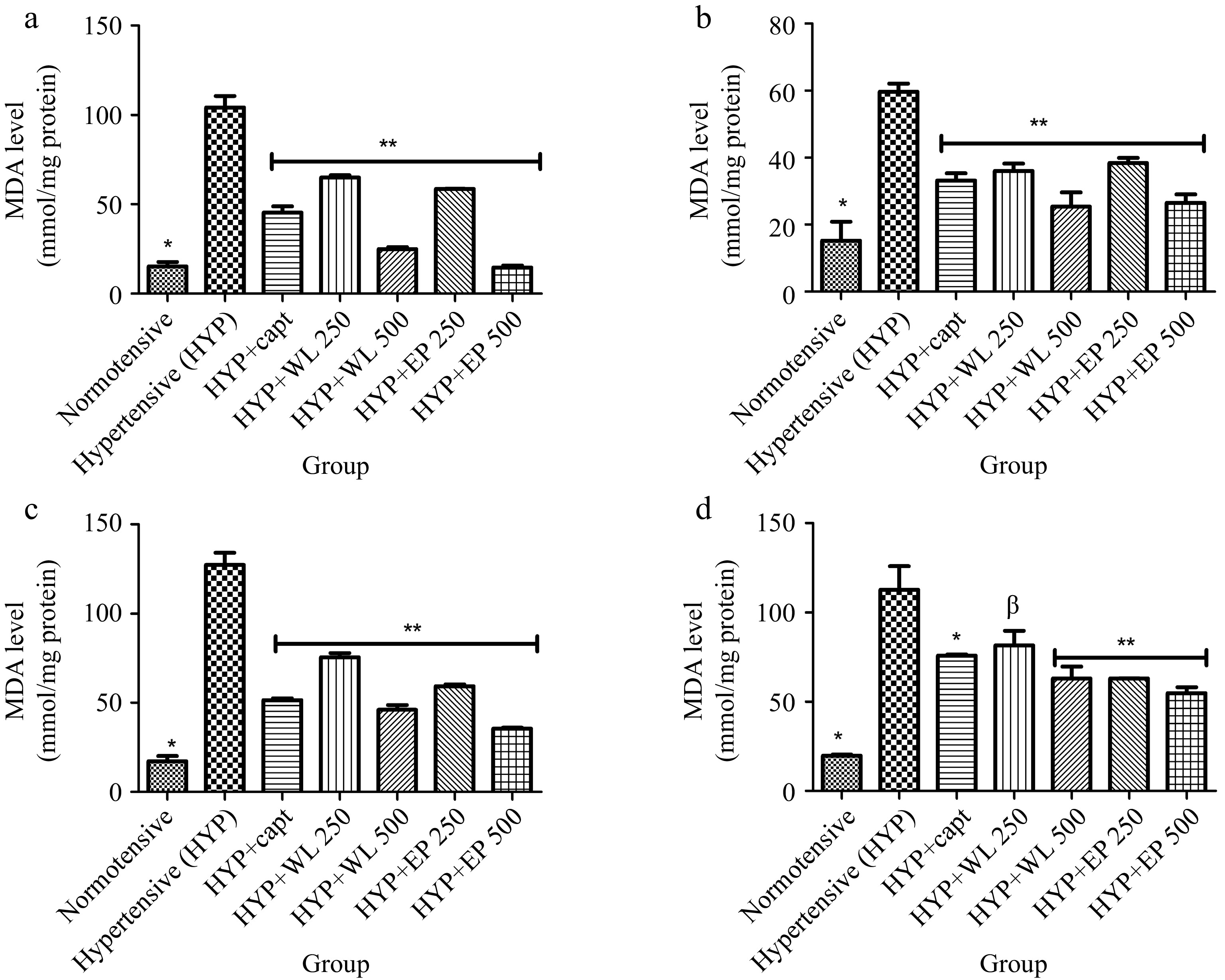
Figure 6.
Effect of wild lettuce and African eggplant leaves extract on malondialdehyde level in (a) plasma, (b) heart, (c) kidney and (d) lungs of L-NAME induced hypertensive rats. Values represent mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). * Significantly different when compared normotensive with hypertensive (p < 0.05). ** Significantly different when compared wild lettuce and African eggplant leaves extract-treated hypertensive with hypertensive (p < 0.05). β Not significantly different when compared wild lettuce and African eggplant leaves extract-treated hypertensive with hypertensive.
-
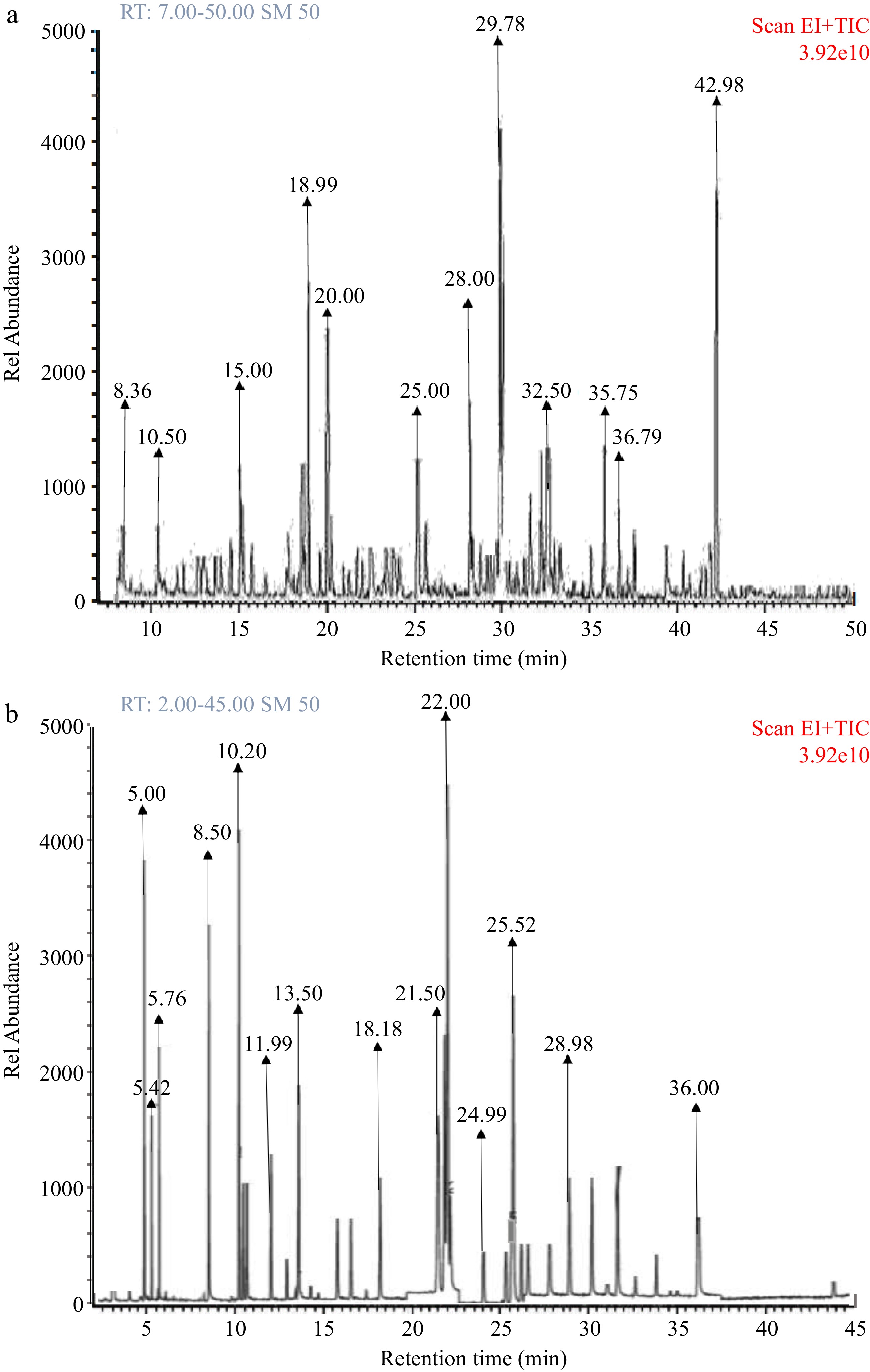
Figure 7.
(a) GC-MS fingerprint of wild lettuce (Launaea Taraxacifolia) leaves bioactive constituents. (b) GC-MS fingerprint of African eggplant (Solanum macrocarpon) leaves bioactive constituents.
-
S/N Compounds detected Molecular formula Phenolic content (mg/g) Wild
lettuceAfrican eggplant 1 1,2,3-Benzenetriol C6H6O3 0.04 0.02 2 Gentisic acid C5H11NO2 0.03 0.02 3 Benzoic acid, 4-hydroxy- C7H6O3 0.36 0.38 4 Cinnamic acid C12H16O2Si 1.22 1.31 5 Syringic acid C15H26O5Si2 1.07 1.03 6 Protocathecolic acid C16H30O4Si3 0.32 0.49 7 Kaempferol C27H44O6Si4 0.91 0.62 8 Quercetin C15H10O7 1.18 1.14 9 3-Caffeoyl quinic acid C34H66O9Si6 0.41 0.54 10 Cathecol C12H22O2Si2 0.44 0.54 11 Tyrosol C14H26O2Si2 0.01 0.02 12 P-coumaric acid C9H8O3 1.31 1.41 Table 1.
Bioactive compound constituent of wild lettuce and African eggplant leaves.
Figures
(7)
Tables
(1)