-
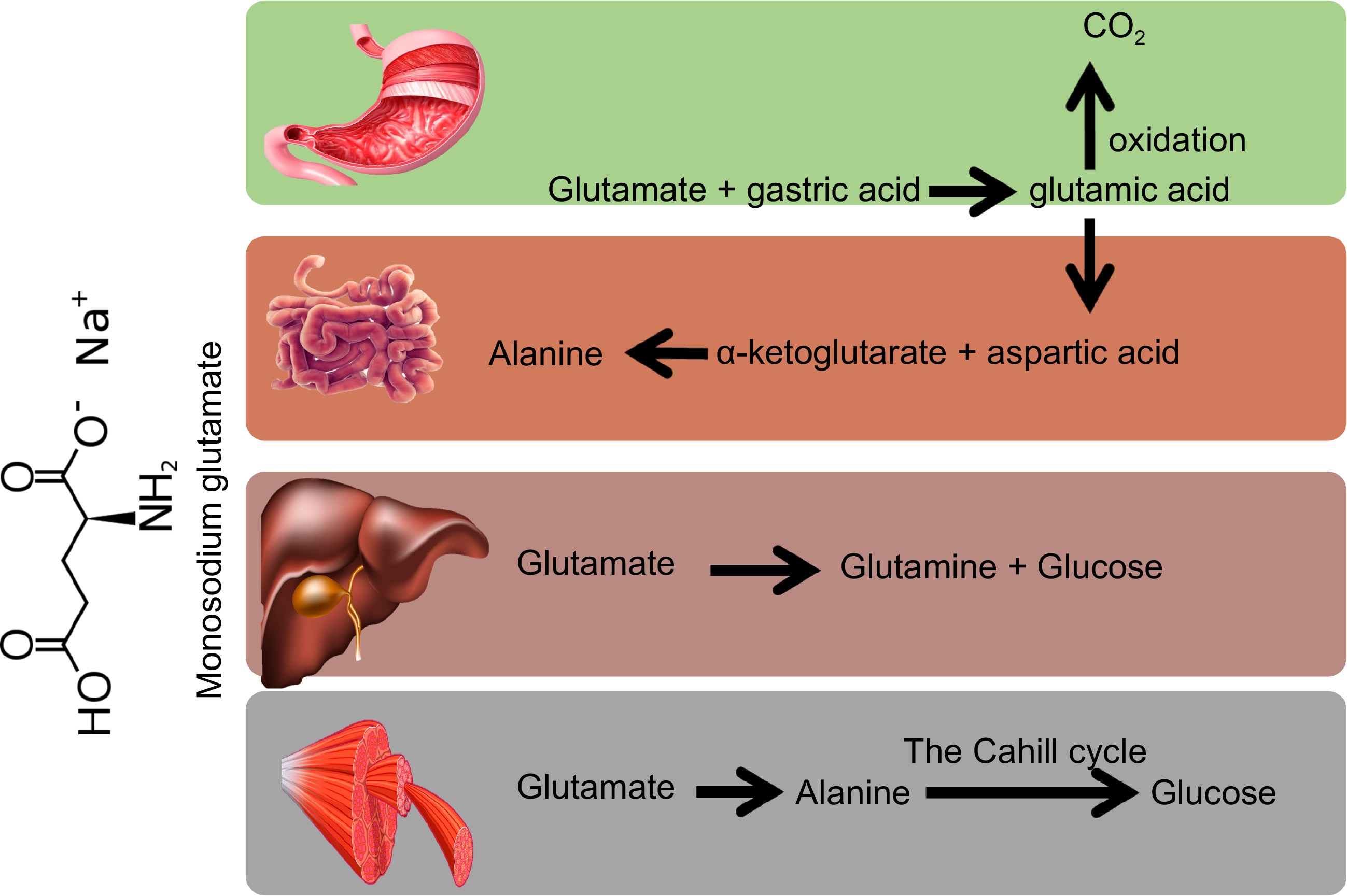
Figure 1.
Metabolic reactions for the biotransformation of monosodium glutamate (MSG) in different body organs.
-
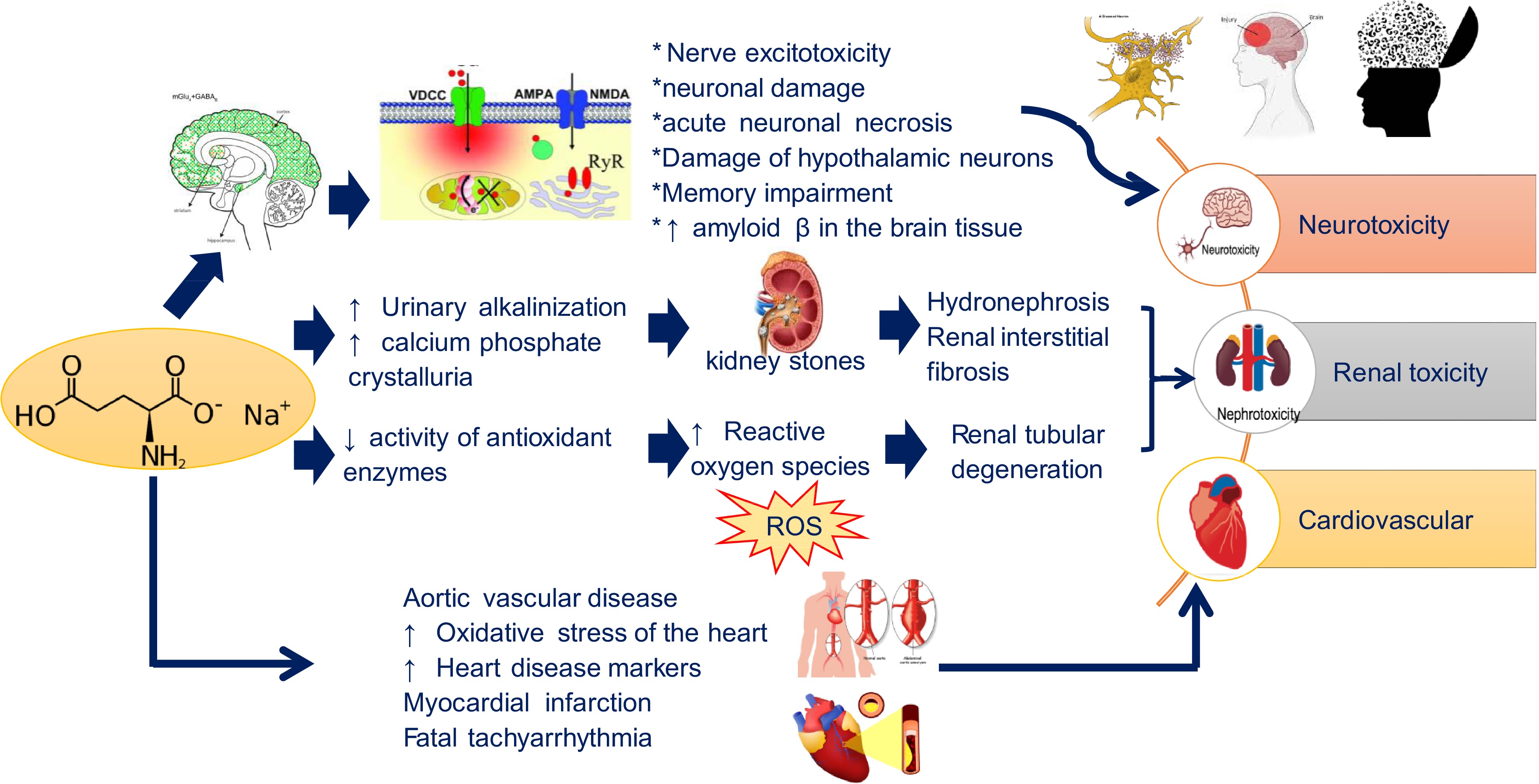
Figure 2.
MSG toxic effects on human functions.
-
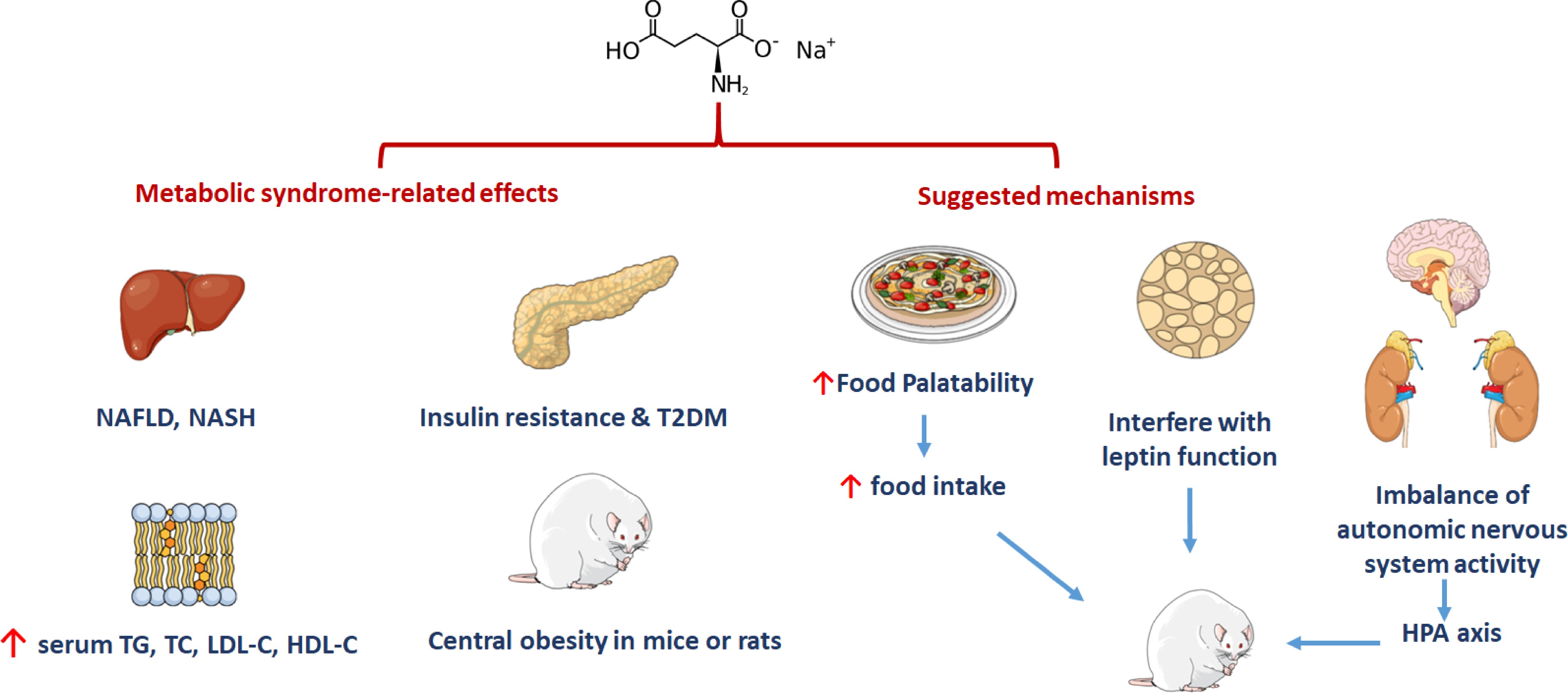
Figure 3.
MSG could lead to metabolic syndrome.
-
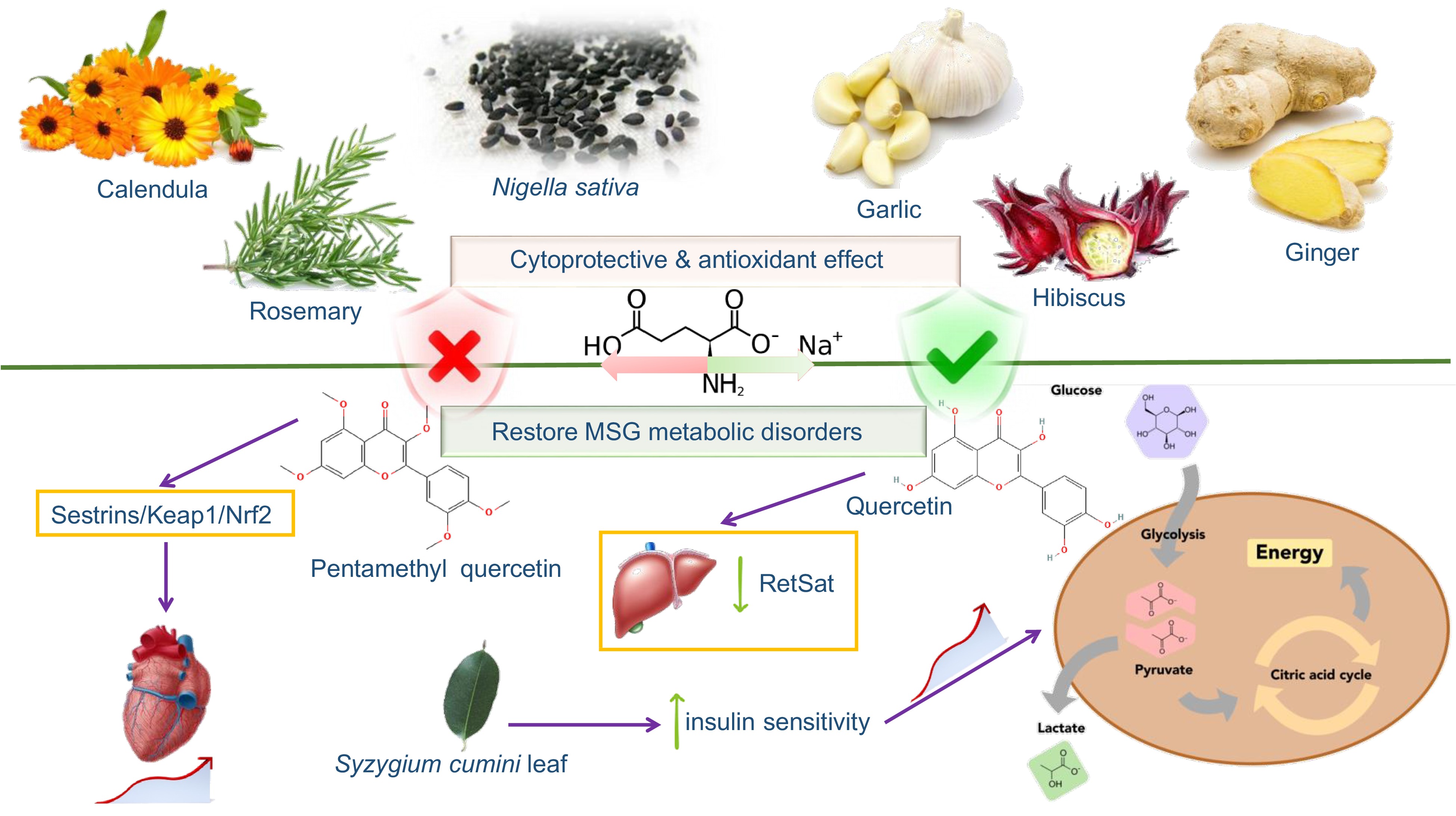
Figure 4.
Nutraceuticals and natural products protective effect against MSG toxic actions in human functions.
-
Separation
and extractionChemical synthesis Fermentation Materials Wheat
glutenAcrylonitrile Selected
microorganism,
carbohydrates
and ammoniaYield ↑ × √ √ Time ↓ × √ √ Purity ↑ × √ √ Cost ↓ × √ √ Environmentally friendly ↑ × × √ Table 1.
The advantages or disadvantages of various methods for producing MSG.
-
Diseases Dosage/day Species Effects References Obesity Inject MSG (4 mg/g) Mice Induced obesity [18] Mixed with 3, 6 and 9 g of MSG Wistar rats Increased in body weight gain [88] S.c. 4 mg/g Adult Wistar rats Induced obesity [23] 2.2 ± 1.6 g/d Healthy Chinese adults Induced overweight [26] 250 g of MSG for food preparation
for 10 dFamilies from rural area of Thailand Overweight [27] NAFLD S.c. 2 mg/g ICR mice Induced obesity and diabetes with steatosis and steatohepatitis resembling human NAFLD and NASH with pre-neoplastic lesions [33] Drinking water containing
0.64 g/L MSGFemale C57BL/6J mice Induced dyslipidemia and markers of insulin resistance [19] Insulin resistant S.c. 4 g/kg Newborn Wistar rats Developed glucose intolerance [20] T2DM S.c. 4 mg/g Male DIAR mice Obesity, diabetes and macrovesicular steatohepatitis [21] Table 2.
List of the effect of MSG on metabolic syndrome.
-
Diseases Dosage/d Species Effects References Nervous system S.c 4 mg/g Male Wistar rats Increased brain extracellular Glu level and produced hyperexcitability and motor behavior alterations [30] 3,200 mg/kg/d − Induced neurodevelopmental toxicity [9] 2 mg/g or 4 mg/g Mice and rats Caused acute neuronal necrosis [31] I.p.500 mg/kg Adult male Fischer-344 rats Altered the dopamine content in adult rats [32] I. p. 2 g/kg Male Wistar rats Lead to long-term memory impairment [34] − Mice and rats Exhibited peripheral insulin resistance, cognitive deficits, and a reduction in the total hippocampal volume with decreased neuron count in the DG, CA3, and CA1 subfields. [35] Kidneys 4 mg/g Adult albino Wistar rats The cortex of the kidneys developed variable pathological changes [37] 3 g/kg Male Wistar rats Produced hyperfiltration with increased tubular reabsorption of Na, K and water [38] 2 mg/g Wistar male rats The renal handling and toxicity mainly related to oxidative stress and metabolism [39] 3 g/kg Male Wistar rats Occurred the renal pathologic changes, intrarenal oxidative stress and reduction of nitric oxide excretion [40] Table 3.
The effect of MSG on nervous system and kidneys.
-
Diseases Dosage/day Species Effects References Cardiovascular diseases 4 mg/g Newborn rats Resulted in typical adult life MetS and oxidative stress with significant increase in ET-1 and MMP-1 with aortic vasculopathy [41] 4 g/kg Neonatal Wistar rats Induced dyslipidemia and oxidative stress [42] I.v 1.5 g/kg Wistar rats Induced bradycardia [43] Fertility and fetal development 60 and 120 mg/kg Adult male rats Significant damage to the reproductive system [45] 6, 17.5 and 60 mg/kg Mature male Wistar rats Induced testicular toxicity and reduce the oxidative stress on testis tissues [46] S.c. 4 g/kg Male and female Wistar rats Male rats were more susceptible to induce metabolic alterations [47] 0.8, 1.6 and 2.4 mg/kg BW/day Female virgin albino rats Suppressed the female reproductive function by impairing the functions of ovary and uterus [48] S.c 4 g/kg Pregnant Wistar rats Decrease in oocyte count and increase the total primordial and atretic follicles [49] 0.2 g/kg Female Wistar rats Decrease in primary follicle count and increased in atretic follicle count [50] Cancer S.c 400 mg/kg Newborn male Wistar rats Increased tumor growth [51] S.c 2 mg/g The pregnant ICR mice Highly susceptible to AOM-induced colorectal carcinogenesis [52] Immune system Human lymphocytes 250, 500, 1,000, 2,000, 4,000 and 8,000 μg/mL Showed genotoxic to the human peripheral blood lymphocytes [55] 1−100 mM B cells Induced apoptosis in naïve and memory human B cells [56] I.p. 4 mg/g Adult male and female Sprague-Dawley rats Induced immune derangements [57] 2 mg/g C57BL/6J male mice Impaired the defense mechanism against invasion of pathogenic microbes [58] I.p.4 mg/g Male Wistar rats Triggered the thymocyte apoptosis [59] 4 mg/g − Induced thymocyte apoptosis [60] − Newborn mice Destructed the mouse arcuate nucleus [61] Miscellaneous ellaneous effects 300 mg/kg Male NMRI mice Induced hyperalgesia [63] 4 mg/g Newborn rats Affected the thyroid function [64] 2 mg/g Newborn mice Induced obesity and recognition memory deficits [65] − Mice Exhibited endocrine dysfunctions [66] 2 or 4 g/kg Male Wistar rat Influenced cortical excitability [67] − Rats Caused behavioral deficits [69] 4 mg/g Adult male Wistar rats Induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in thymocyte [60] 0.5% MSG and 1% MSG APPswe, PSEN1dE9-85Dbo/J transgenic mice and WT mice Accelerated AD-like pathophysiology in a
mouse model of AD[70] S.c 3 mg/g Pregnant Hannover-Wistar female rats Reduced locomotion [71] 1.0 g/L Wistar Albino rats Increased CNS excitability [72] 3.0 and 3.5 mg/g Wistar rats Decreased motor coordination and the estimated total number of Purkinje cell of rats [73] 0.05%, 0.1%, 0.2%
and 0.5%Male Wistar rats Induced pancreatic acinar cells injury [74] 250, 500, 1,000, 2,000, 4,000 and 8,000 μg/mL Human lymphocytes Induced genotoxicity [55] 100 μM, 250 μM, 2.5 mM and 25 mM 3T3-L1 preadipocytes cells Changes in cell proliferation and lipid accumulation [75] 2.5 g Two young women Induced asthma [76] − Subjects Induced asthma and make recognition difficult [77] 75 or 150 mg/kg 14 healthy men Induced headache and craniofacial pain [78] − − Induced chronic pain [79] − 1,227 Chinese subjects Increased the risk of SDB in Chinese adults [80] − 1,227 Chinese men and women Independent BP-increasing effects [81] Table 4.
MSG-induced miscellanious injuries.
-
Target MSG-induced diseases Compound Dose or concentration Experimental model Effects References Metabolic syndrome Vitamin D 0.2 mcg/kg Female rats Suppressed body weight [82] Probiotics 109 CFU/kg Newborn rats Recovery of lipid metabolism and prevention of the obesity development [83] Pentamethylquercetin 5, 10 and 20 mg/kg Obese mice Ameliorated obesity phenotypes and improved metabolic disorders [84] Quercetin 5 mg/kg C57BL/6J mice Reduced the hypothalamus damage and the expression of liver RetSat [85] n-6/n-3 PUFAs n-6/n-3 fatty acid ratio of 1.2: 1.0 Female mice Prevented metabolic dysfunction [86] Quercetin 75 mg/kg Male Wistar rats Normalized serum lipid and glucose profile [87] (p-CIPhSe)2 10 mg/kg Newborn Wistar rats Reduced hepatotoxicity [89] Berberine 150 mg/kg Newborn rats Alleviated postnatal metabolic disorders associated vascular endothelial dysfunction [41] Polyphenol-rich extract of Syzygium cumini leaf 500 mg/kg Obese rats Improved peripheral insulin sensitivity [90] Nervous system Allium sativum powder 200 mg/kg Male Wistar albino rats Anti-oxidative stress and apoptosis [91] Calendula officinalis L. flowers 100 and 200 mg/kg Adult female Wistar rats Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory [92] Rosemary extract and/
or fluoxetine50 mg/kg Male Sprague-Dawley rats Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory [93] Kidney Zinc oxide nanoparticles − − Reduced the level of intracellular peroxidation by enhancing antioxidant capacity [95] Nigella sativa seeds 30 g/kg Male adult albino rats Rebalanced LPO and TAC, antioxidant and cytoprotective activities [96] Others Hibiscus sabdariffa extract 180 mg/kg Adult rats Reduced oxidative stress and cellular apoptosis [97] N-Acetylcysteine 500 μM C6 cells Protected C6 stellate cells [98] Table 5.
Protective effects of some plants or natural products against various MSG negative health effects.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(5)