-
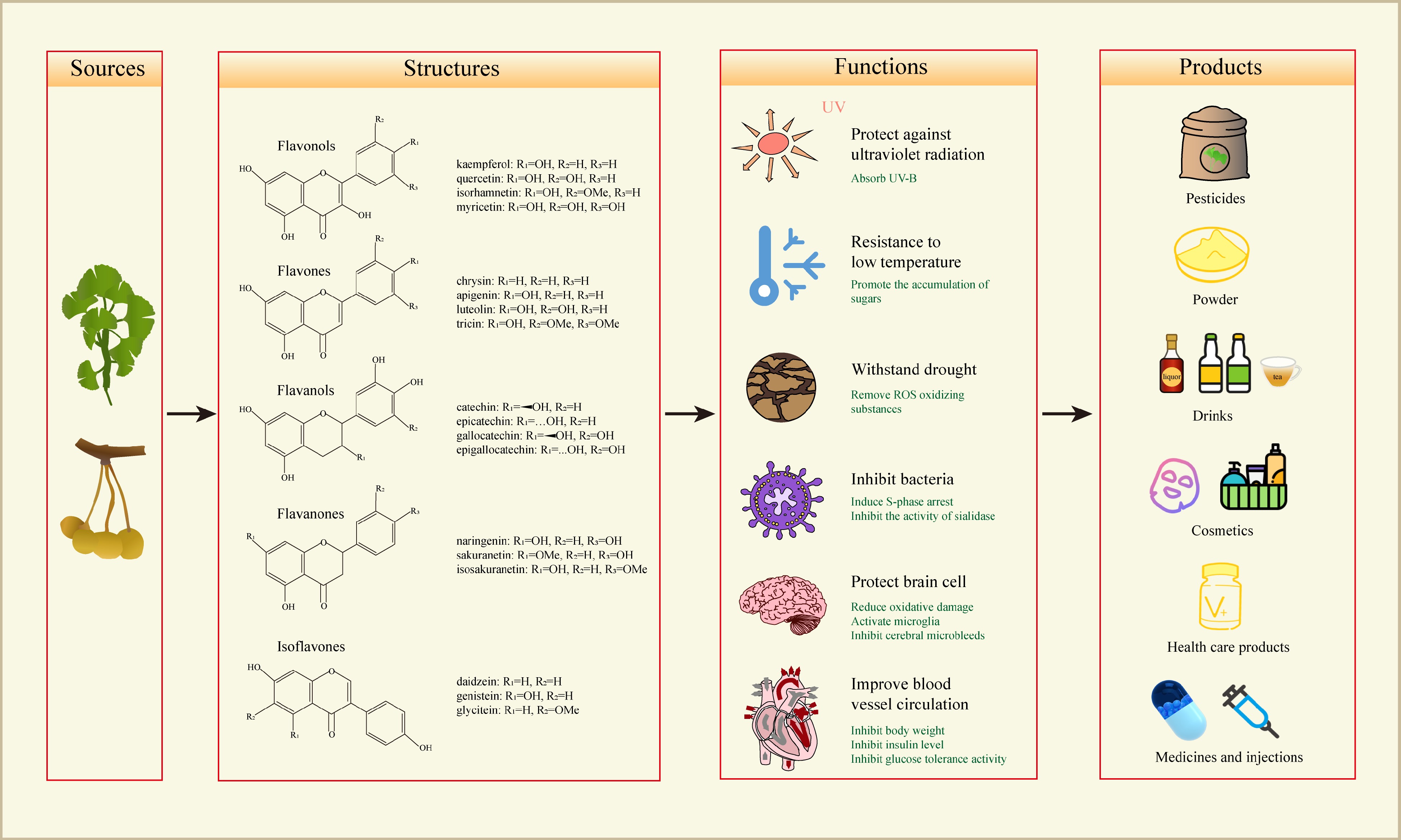
Figure 1.
The structures, functions and products of the flavonoids in G. biloba. Flavonoids in G. biloba are mainly divided into these categories, including flavones, flavonols, flavanols, flavanones and isoflavones. The flavonoids have the functions of inhibiting bacteria, withstanding drought, resisting low temperatures and protecting against ultraviolet radiation, as well as human health benefits for protecting brain cells and improving blood vessel circulation. In production, G. biloba flavonoid can be made into pesticides, powder, drinks, cosmetics, health care products, medicines and injections.
-
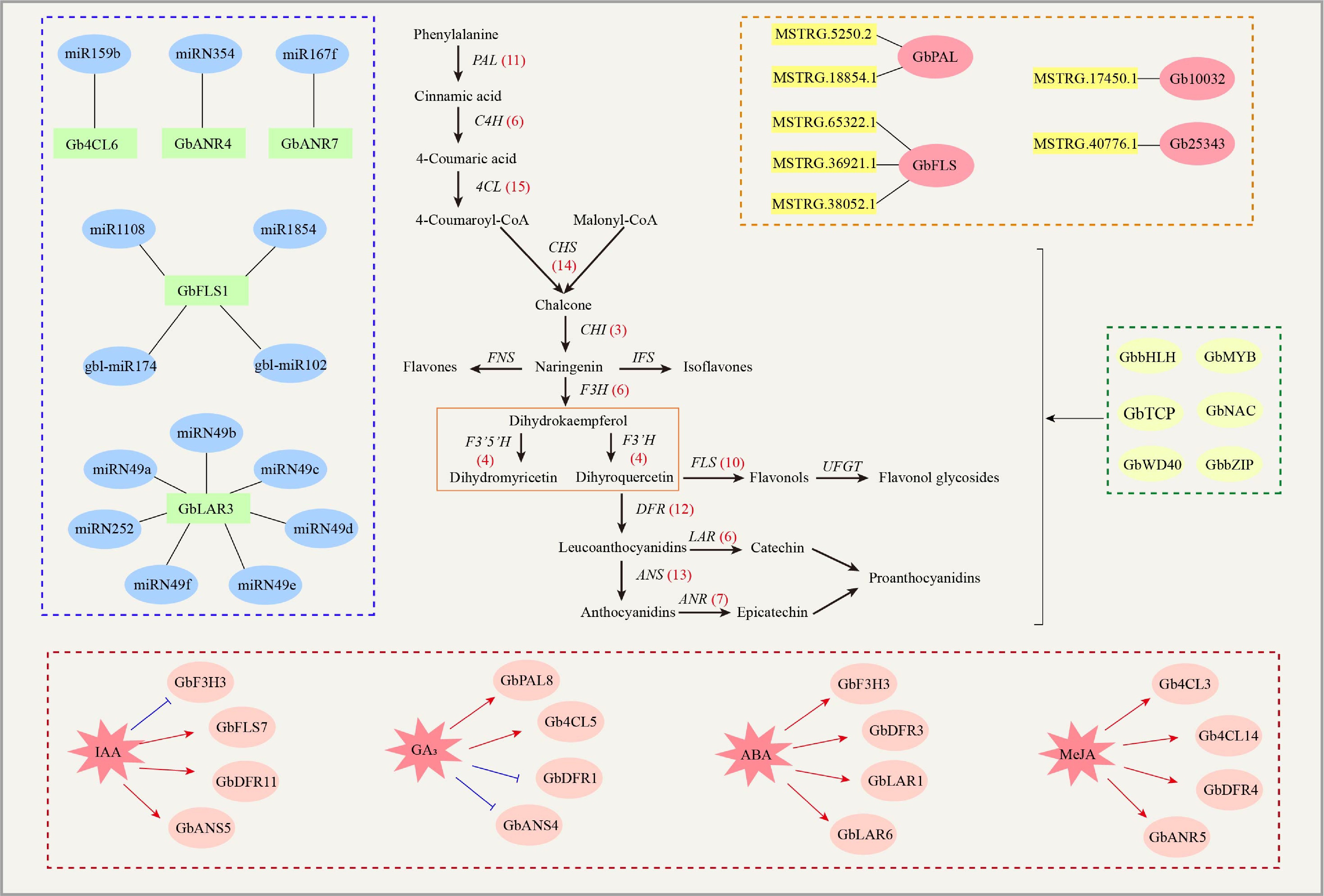
Figure 2.
The regulation network of flavonoids in G. biloba. The synthesis of flavonoids in G. biloba is regulated by several transcription factors including MYB, bZIP, bHLH, WD40, NAC and TCP. In addition, hormones, miRNAs and lncRNAs can also regulate the synthesis of flavonoids in G. biloba by regulating key enzyme genes. The numbers in brackets indicate the number of genes in G. biloba. ANR: Anthocyanidin reductase; ANS: Anthocyanin synthetase; C4H: Cinnamate-4-hydroxylase; CHS: Chalcone synthase; CHI: Chalcone isomerase; 4CL: 4-coumarate: coenzyme A ligase; DFR: Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase; FNS: Flavone synthase; F3H: Flavanone 3-hydroxylase; F3’H: Flavanone 3'-hydroxylase; F3’5’H: Flavanone 3'5'-hydroxylase; FLS: Flavonol synthase; IFS: Isoflavone synthase; LAR: Leucoanthocyanidin reductase; PAL: Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase; UFGT: UDP glucose: flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase.
Figures
(2)
Tables
(0)