-
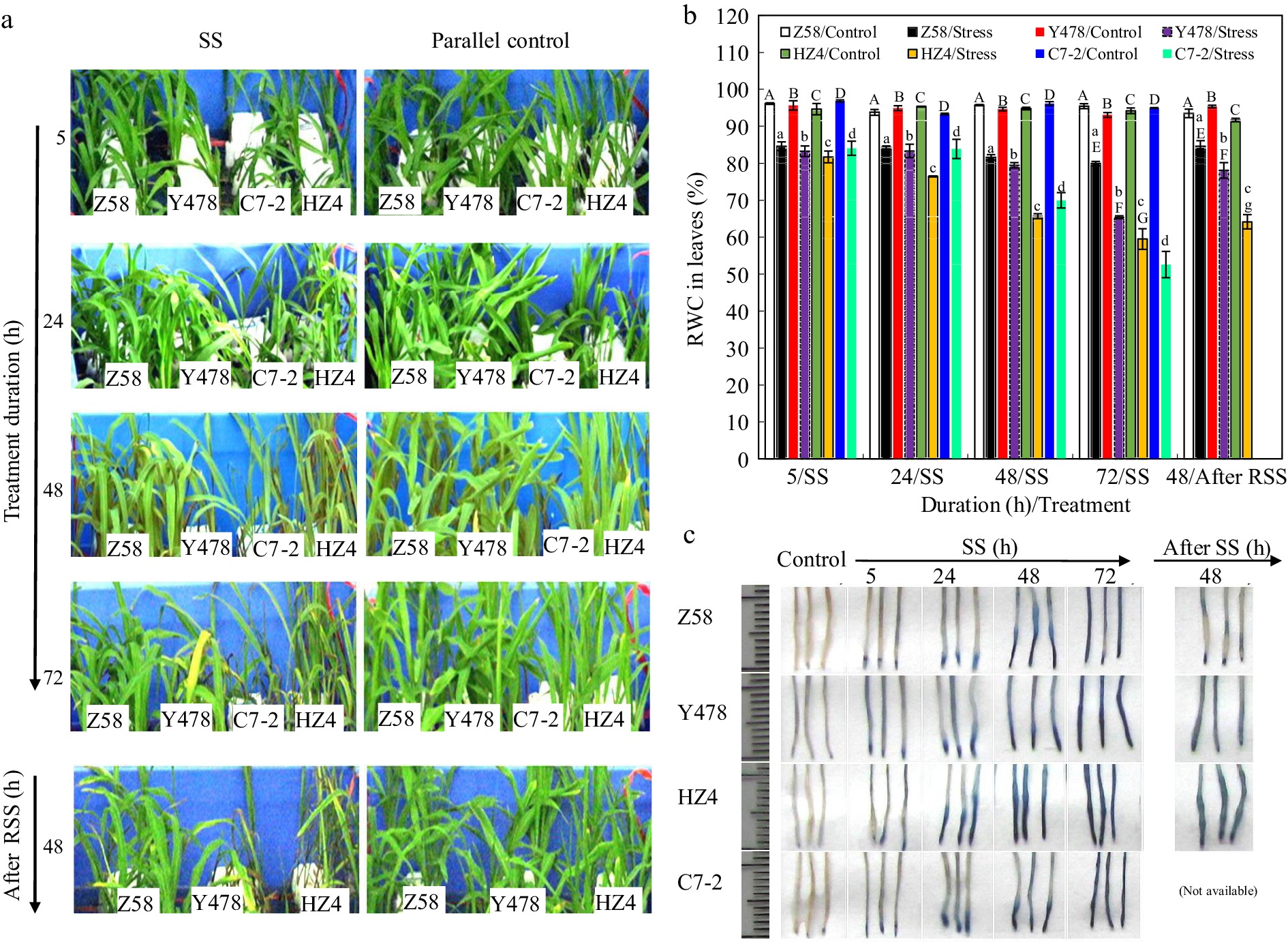
Figure 1.
(a) Phenotype, (b) leaf RWC, and (c) root staining of maize inbred lines under SS and after RSS. The SS stress was conducted with 150 mM NaCl. The RSS treatment was performed on maize plants stressed by SS for 72 h. In (b), the data were the means ± standard deviation (SD) of the fully expanded 2nd leaves of 5-leaf-old seedlings (n = 5−10) for each maize line under each treatment, and statistical analysis comparison was conducted between the same maize lines under control and the same SS stress, and between the same maize lines after SS of 72 h and after RSS. In (b), upper and lower cases of the same letter indicated a statistical significance at p < 0.05. In (c), fresh nodal roots (1 cm behind the root tip) from 5-leaf-old seedlings (n = 5−10) of each maize line were stained with Evans blue solution. The data of maize inbred line C7-2 after RSS were not available because of no surviving seedlings. C7-2, Maize inbred line Chang7-2. HZ4, Maize inbred line Huangzao4. RSS, Removal of SS. RWC, Relative water content. SS, Salt shock. Y478, Maize inbred line Ye478. Z58, Maize inbred line Zheng58.
-
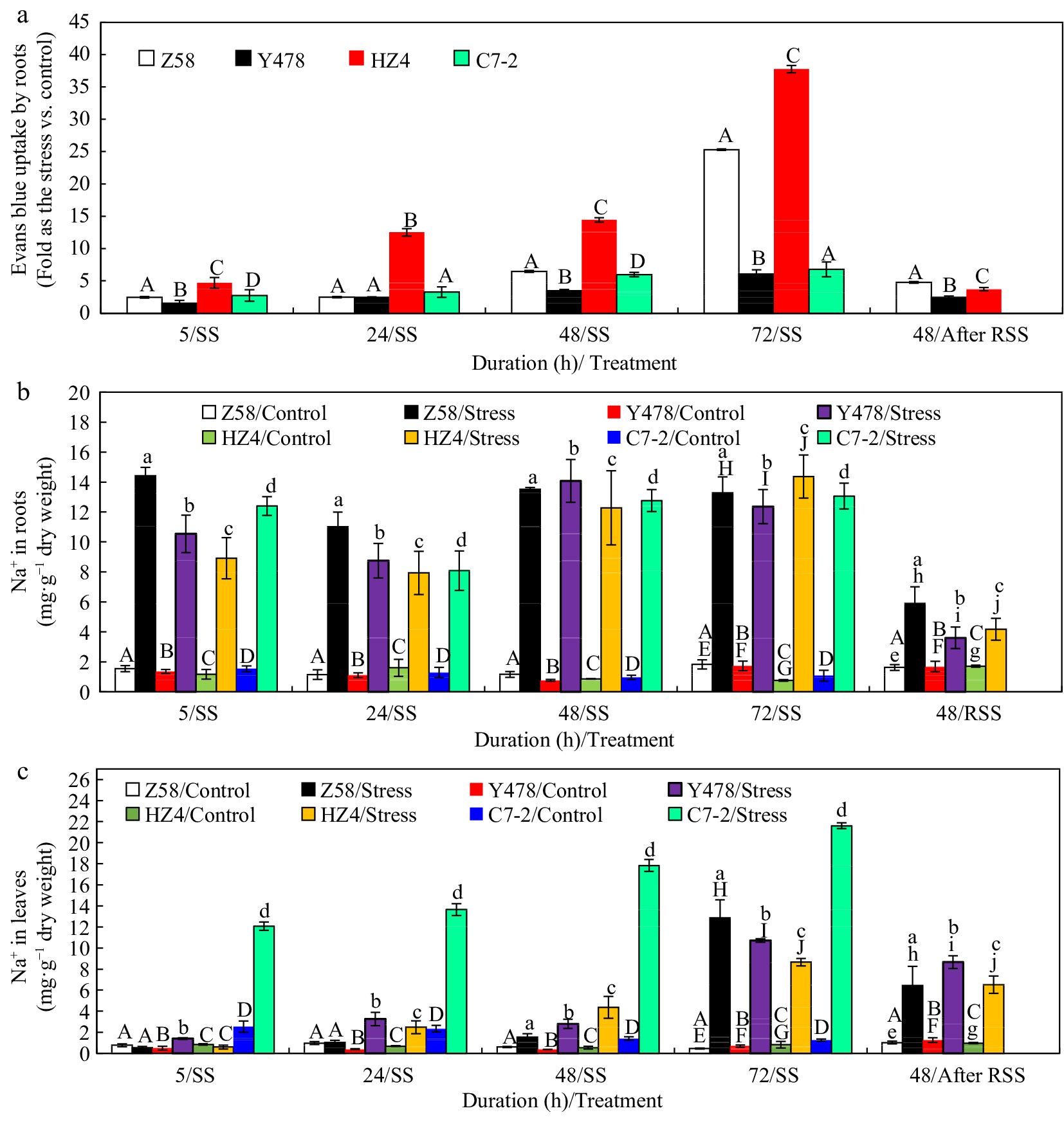
Figure 2.
Evans blue content in (a) fresh nodal roots, and Na+ content in (b) roots and (c) leaves of maize inbred lines under SS and after RSS. The SS was conducted with 150 mM NaCl. The RSS treatment was performed on maize plants stressed by SS for 72 h. In (a), Evans blue content analysis was based on the Evans blue-stained fresh nodal roots (1 cm behind the root tip), where each datum was the mean ± SD from 5-leaf-old seedlings (n = 3−5) for each maize line under each treatment. In (b), each datum was the mean ± SD from a collection of roots of 5-leaf-old seedlings (n = 5−10). In (c), each datum was the mean ± SD from the fully expanded 2nd leaves of 5-leaf-old seedlings (n = 5−10). The statistical analysis comparison was conducted between the same maize line under control and the same SS stress, and between the same maize line after SS of 72 h and after RSS. The upper and lower cases of the same letter indicated a statistical significance at p < 0.05. The data of maize inbred line C7-2 after RSS were not available because of no surviving seedlings. C7-2, Maize inbred line Chang7-2. HZ4, Maize inbred line Huangzao4. RSS, Removal of SS. SD, Standard deviation. SS, Salt shock. Y478, Maize inbred line Ye478. Z58, Maize inbred line Zheng58.
-
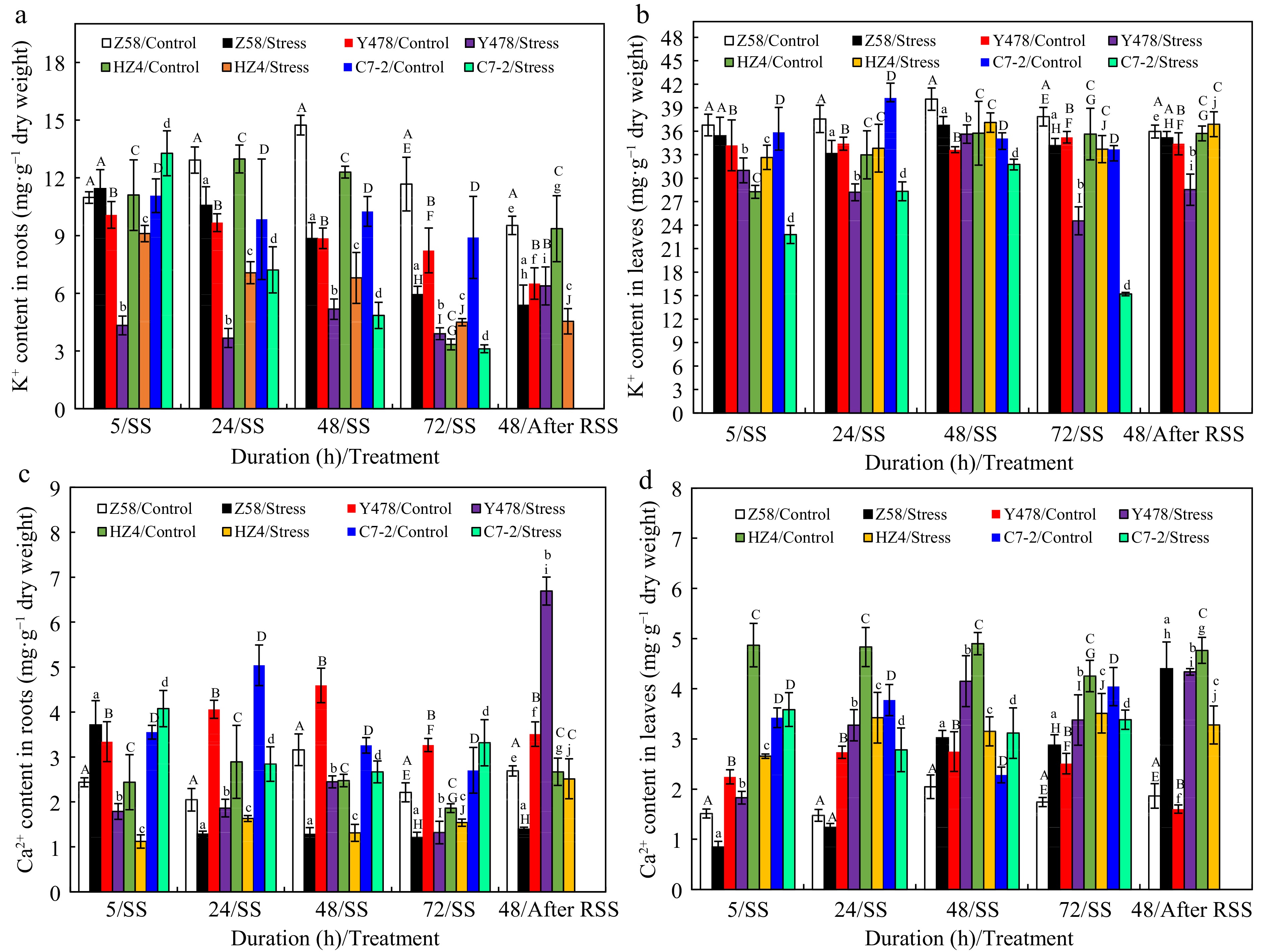
Figure 3.
K+ content in (a) roots and (b) leaves, and Ca2+ content in (c) roots and (d) leaves of maize inbred lines under SS and after RSS. The SS was conducted with 150 mM NaCl. The RSS treatment was performed on maize plants stressed by SS for 72 h. Each datum was the mean ± SD from the fully expanded 2nd leaves or a collection of roots of 5-leaf-old seedlings (n = 3−5) for each maize line under each treatment. The statistical analysis comparison was conducted between the same maize line under control and the same SS stress, and between the same maize line after SS of 72 h and after RSS. The upper and lower cases of the same letter indicated a statistical significance at p < 0.05. The data of maize inbred line C7-2 after RSS were not available because of no surviving seedlings. C7-2, Maize inbred line Chang7-2. HZ4, Maize inbred line Huangzao4. RSS, Removal of SS. SD, Standard deviation. SS, Salt shock. Y478, Maize inbred line Ye478. Z58, Maize inbred line Zheng58.
-
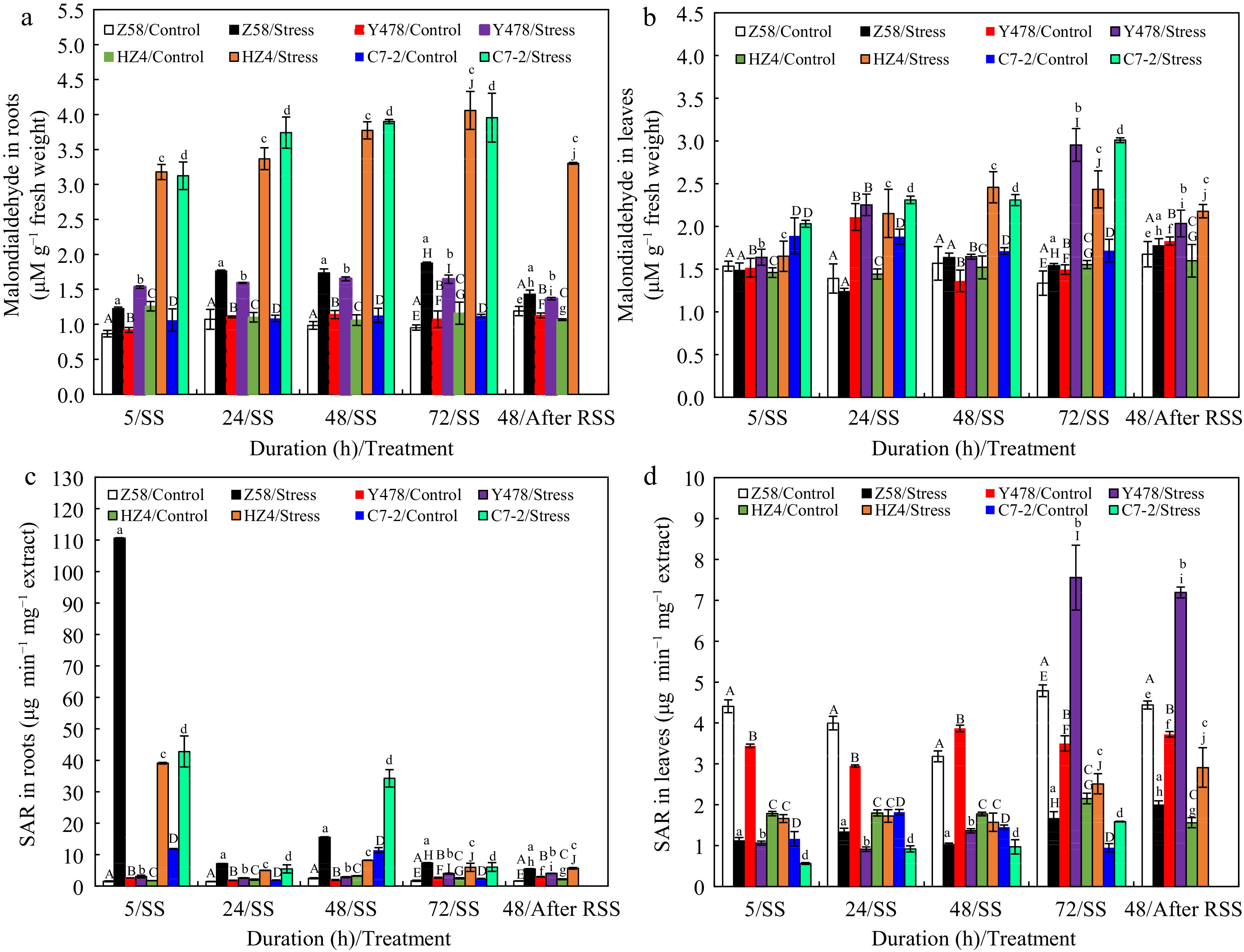
Figure 4.
Malondialdehyde content in (a) roots and (b) leaves, and SAR content in (c) roots and (d) leaves of maize inbred lines under SS and after RSS. The SS was conducted with 150 mM NaCl. The RSS treatment was performed on maize plants stressed by SS for 72 h. Each datum was the mean ± SD from the fully expanded 2nd leaves or a collection of the roots of 5-leaf-old seedlings (n = 3−5) for each maize line. The statistical analysis comparison was conducted between the same maize line under control and the same SS stress, and between the same maize line after SS of 72 h and after RSS. The upper and lower cases of the same letter indicated a statistical significance at p < 0.05. The data of maize inbred line C7-2 after RSS were not available because of no surviving seedlings. C7-2, Maize inbred line Chang7-2. HZ4, Maize inbred line Huangzao4. RSS, Removal of SS. SAR, Superoxide anion radical. SD, Standard deviation. SS, Salt shock. Y478, Maize inbred line Ye478. Z58, Maize inbred line Zheng58.
-
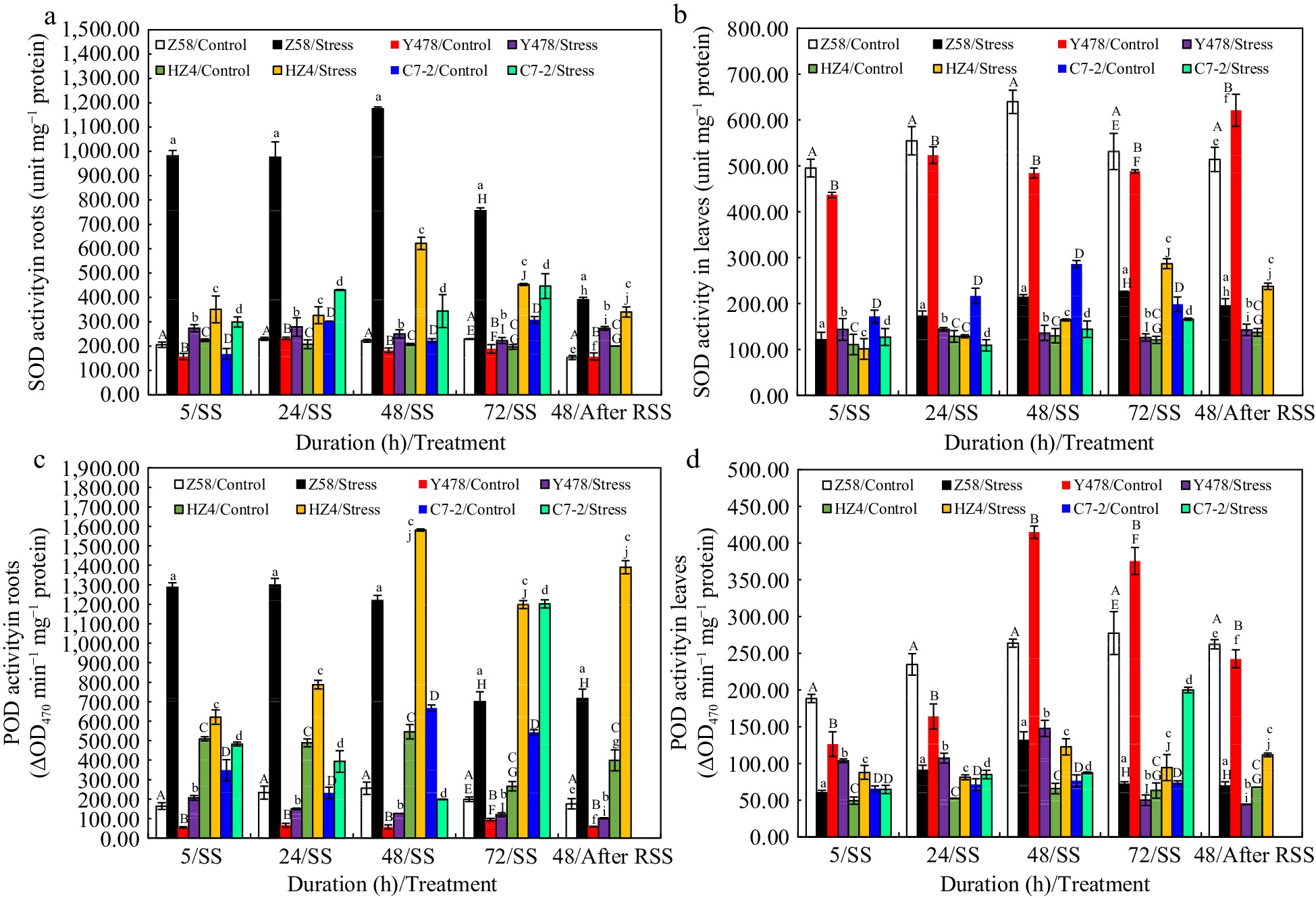
Figure 5.
SOD activity in (a) roots and (b) leaves, and POD activity in (c) roots and (d) leaves of maize inbred lines under SS and after RSS. The SS was conducted with 150 mM NaCl. The RSS treatment was performed on maize plants stressed by SS for 72 h. Each datum was the mean ± SD from the fully expanded 2nd leaves or a collection of the roots of 5-leaf-old seedlings (n = 3−5) for each maize line under each treatment. The statistical analysis comparison was conducted between the same maize line under control and the same SS stress, and between the same maize line after SS of 72 h and after RSS. The upper and lower cases of the same letter indicated a statistical significance at p < 0.05. The data of maize inbred line C7-2 after RSS were not available because of no surviving seedlings. C7-2, Maize inbred line Chang7-2. HZ4, Maize inbred line Huangzao4. POD, Peroxidase. RSS, Removal of SS. SD, Standard deviation. SOD, Superoxide dismutase. SS, Salt shock. Y478, Maize inbred line Ye478. Z58, Maize inbred line Zheng58.
-
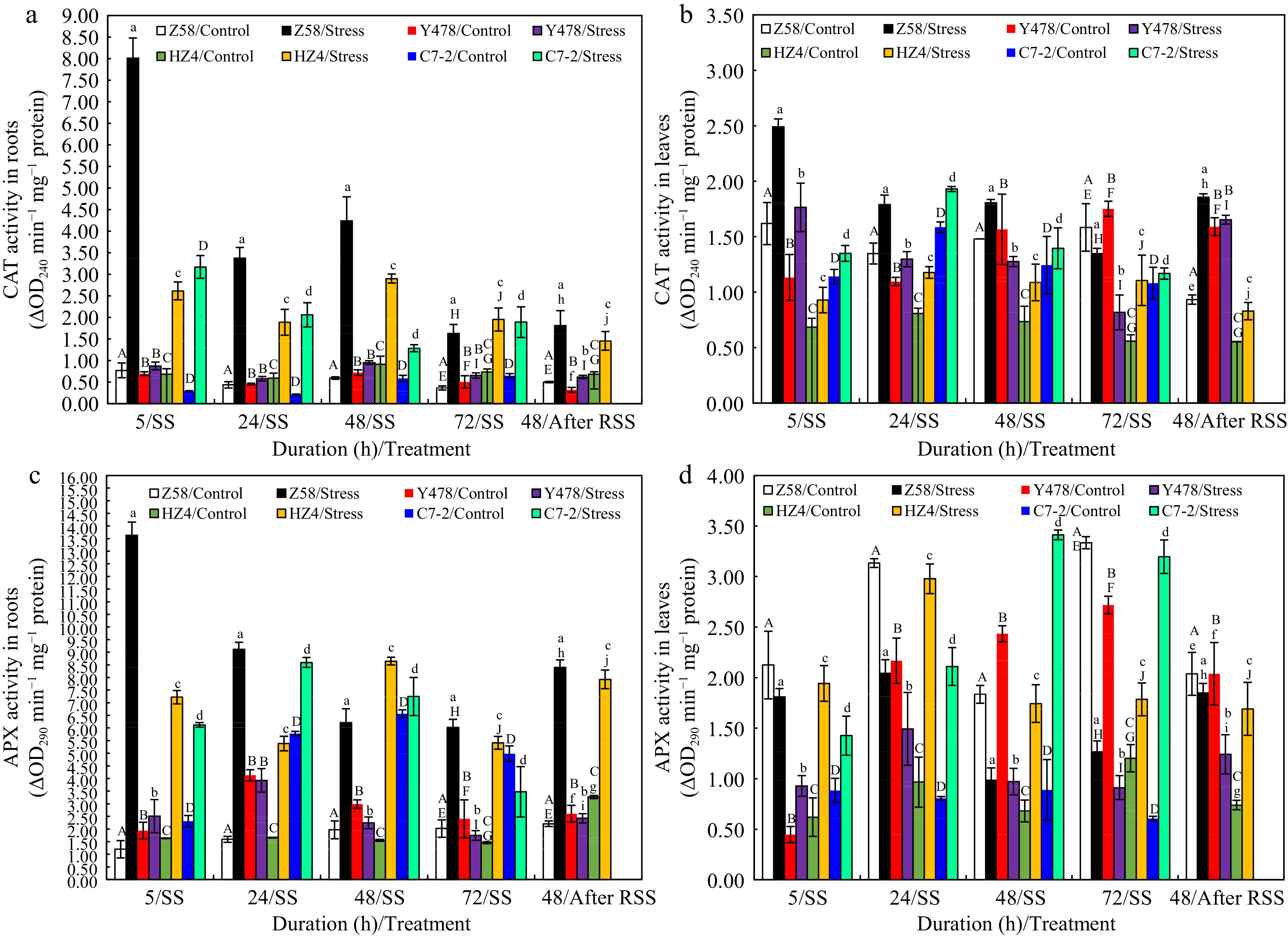
Figure 6.
CAT activity in (a) roots and (b) leaves, and APX activity in (c) roots and (d) leaves of maize inbred lines under SS and after RSS. The SS was conducted with 150 mM NaCl. The RSS treatment was performed on maize plants stressed by SS for 72 h. Each datum was the mean ± SD from the fully expanded 2nd leaves or a collection of the roots of 5-leaf-old seedlings (n = 3−5) for each maize line under each treatment. The statistical analysis comparison was conducted between the same maize line under control and the same SS stress, and between the same maize line after SS of 72 h and after RSS. The upper and lower cases of the same letter indicated a statistical significance at p < 0.05. The data were not available for maize inbred line C7-2 after RSS because of no surviving seedlings. APX, Ascorbate peroxidase; CAT, Catalase. C7-2, Maize inbred line Chang7-2. HZ4, Maize inbred line Huangzao4. RSS, Removal of SS. SD, Standard deviation. SS, Salt shock. Y478, Maize inbred line Ye478. Z58, Maize inbred line Zheng58.
-
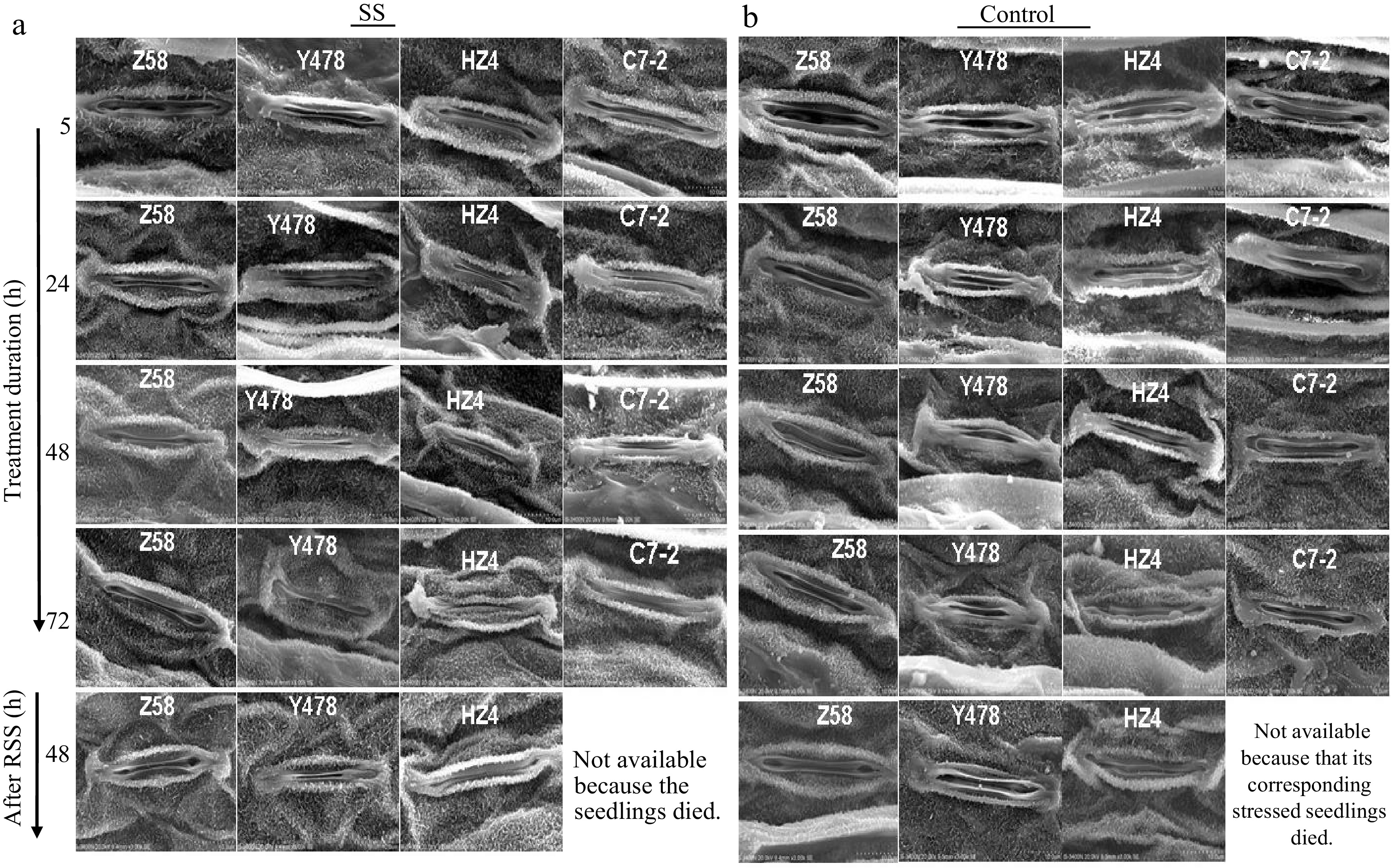
Figure 7.
Stomatal behaviour in leaves of maize inbred lines under SS and after RSS. The SS was conducted with 150 mM NaCl. The RSS treatment was performed on maize plants stressed by SS for 72 h. The photos of the leaf stomata were taken by SEM from the central region of the front surface of the fully expanded 2nd leaves of 3-leaf-old seedlings (n = 5) for each maize line under each treatment. The data of maize inbred line C7-2 after RSS were not available because of no surviving seedlings. C7-2, Maize inbred line Chang7-2. HZ4, Maize inbred line Huangzao4. RSS, Removal of SS. SEM, Scanning electron microscopy. SS, Salt shock. Y478, Maize inbred line Ye478. Z58, Maize inbred line Zheng58.
-
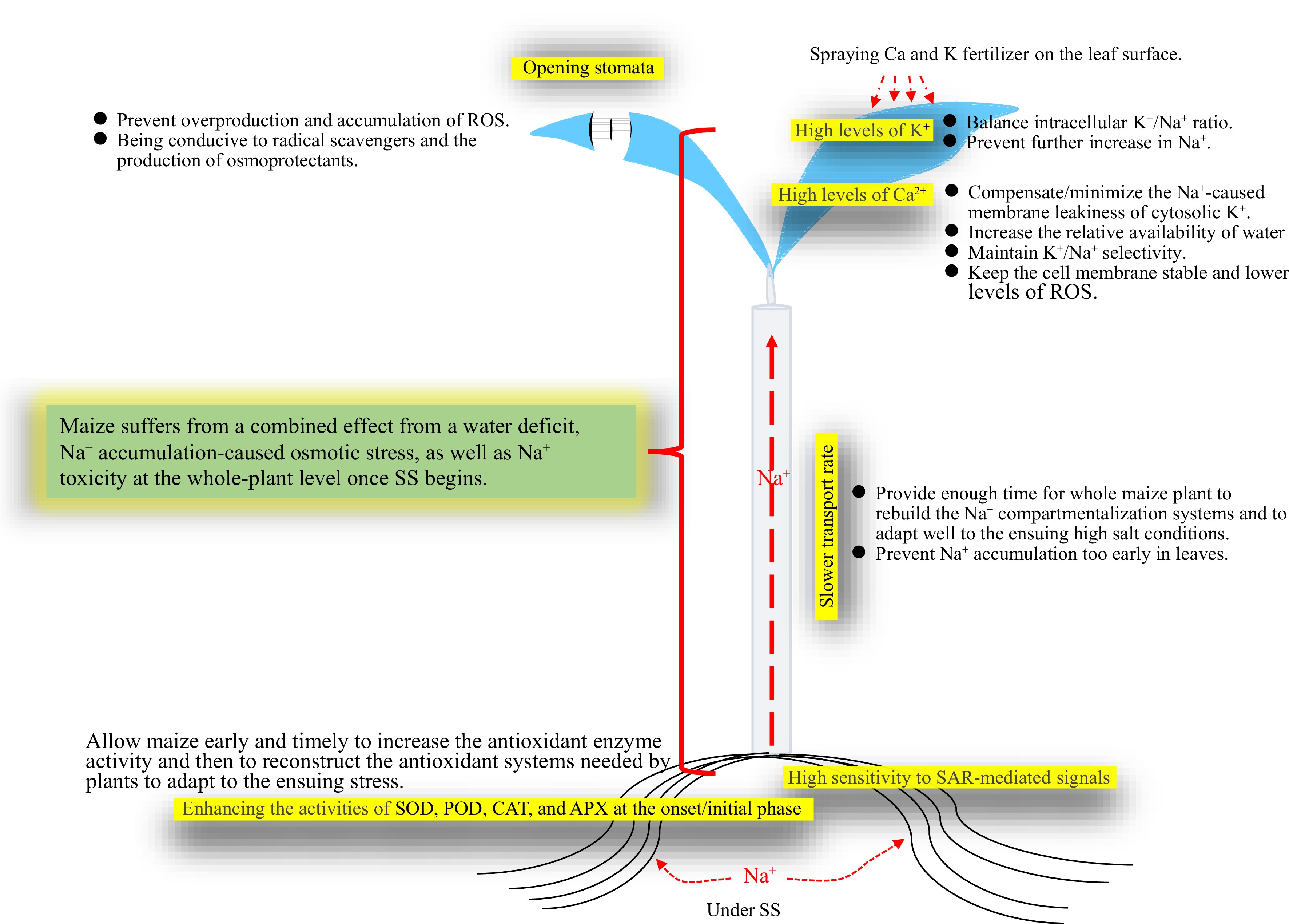
Figure 8.
Schematic mechanisms of maize tolerance to SS, and a possible measure to improve tolerance to SS. A possible measure to improve maize tolerance to SS by spraying Ca and K fertilizer onto leaf surfaces was suggested and shown. APX, Ascorbate peroxidase; CAT, Catalase; POD, Peroxidase; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; SAR, Superoxide anion radical; SOD, Superoxide dismutase; SS, Salt shock.
-
Maize line Yellowing of leaves Death rate (%) of seedlings under SS for After RSS 5 h 24 h 48 h 72 h Surviving seedlings (%) Z58 Slightly; The edge of about 10% of leaves after SS of 72 h 0 0 0 0 100 Y478 Obviously; About 15% of leaves began turning yellow after SS of 48 h 0 0 1.2 2.1 50.5 C7-2 Obviously; About 15% of the leaves began turning yellow after SS of 24 h 0 0 40.5 95 0 HZ4 Somewhat like C7-2 0 0 23.5 80 48.65 The SS stress was conducted with 150 mM NaCl. The RSS treatment was performed on maize plants stressed by SS for 72 h. Leaves were observed and counted from leaves of 15−20 seedlings for each maize line. Survival rate after RSS referred to the percentag of surviving seedlings compared to seedlings stressed after SS of 72 h. C7-2, Maize inbred line Chang 7-2. HZ4, Maize inbred line Huangzao4. RSS, Removal of SS. SS, Salt shock. Y478, Maize inbred line Ye478. Z58, Maize inbred line Zheng58. Table 1.
Phenotypes of seedlings of maize inbred lines under SS and after RSS.
Figures
(8)
Tables
(1)