-
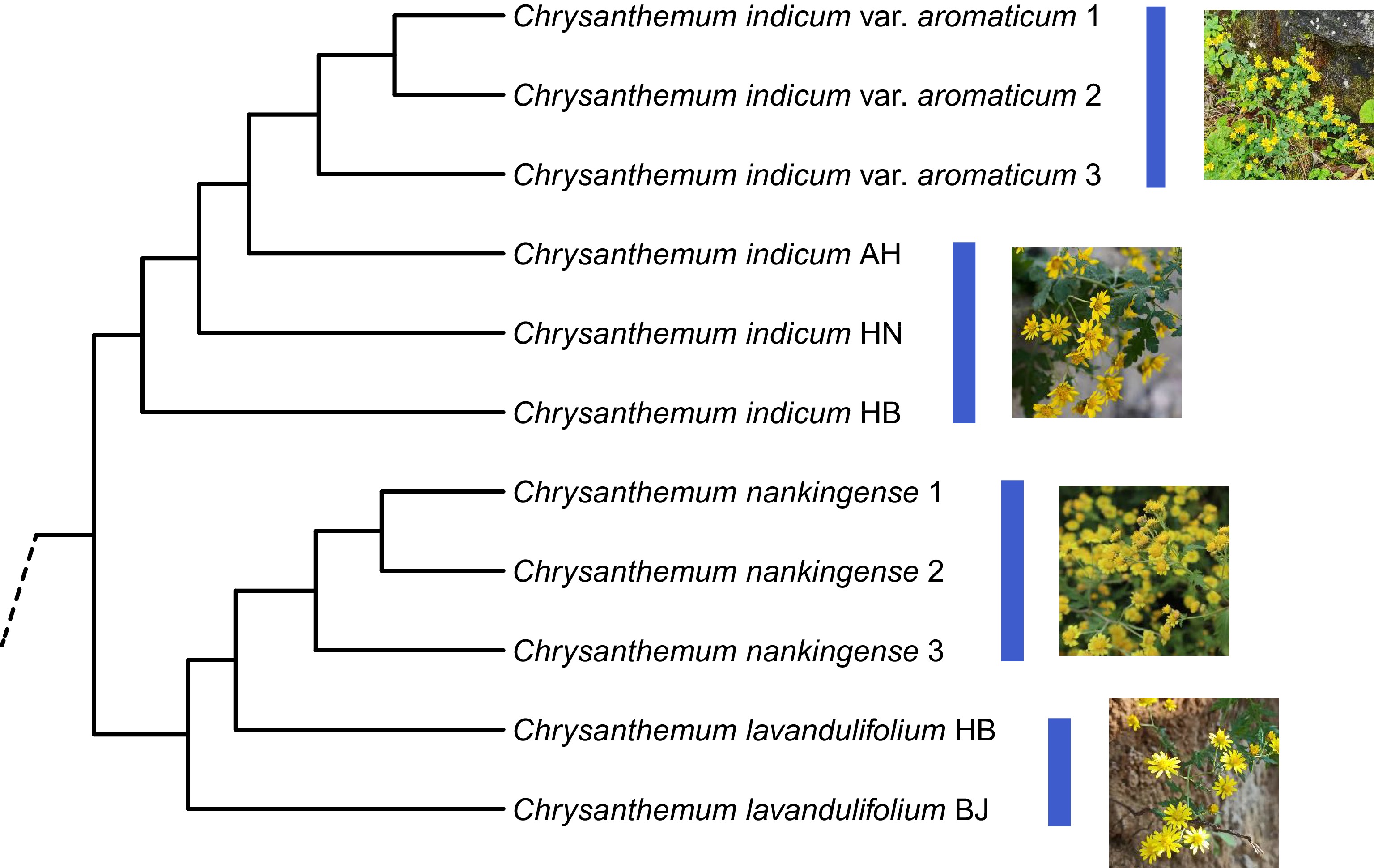
Figure 1.
The transcriptome data-based species relationship of the Chrysanthemum indicum complex. The C. indicum var. aromaticum samples were collected from the Shennongjia Forest region (China), and the C. nankingense samples from Nanjing, Jiangsu (China). AH, Anhui; HN, Hunan; HB, Hubei; BJ, Beijing. The specimens of these samples (HBTCM18101704-HBTCM18101714) were preserved in the Herbarium of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine (China).
-
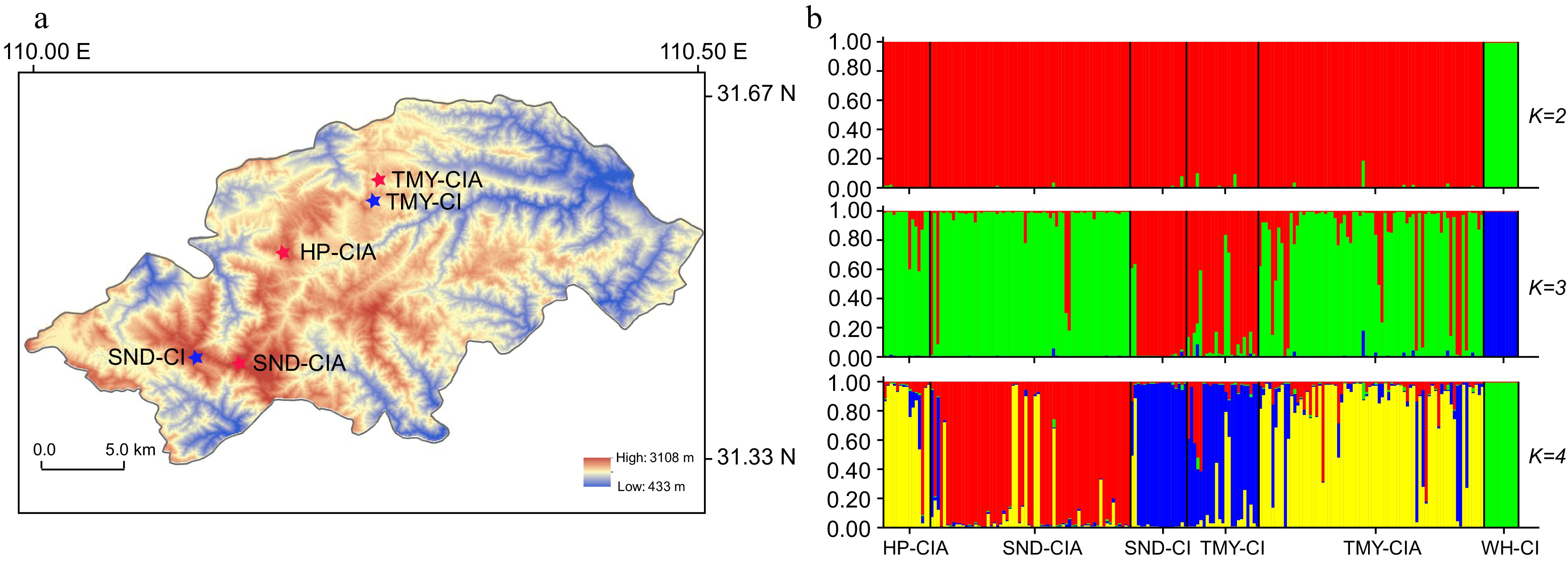
Figure 2.
Genetic structure for Chrysanthemum indicum and C. indicum var. aromaticum populations. (a) Geographical distribution of the populations sampled from the Shennongjia Forest region. (b) STRUCTURE analysis of the sampled populations. CI, C. indicum; CIA, C. indicum var. aromaticum; WH, Wuhan; HP, Hongping, Shennongjia; SND, Shennongding, Shennongjia; TMY, Tianmenya, Shennongjia. When K = 2, the C. indicum samples from Wuhan can be distinguished from those samples in Shennongjia. When K = 3, the C. indicum samples in Shennongjia further showed genetic differentiation from those of the C. indicum var. aromaticum populations in Shennongjia. When K = 4, subdivision was observed within the C. indicum var. aromaticum populations.
-
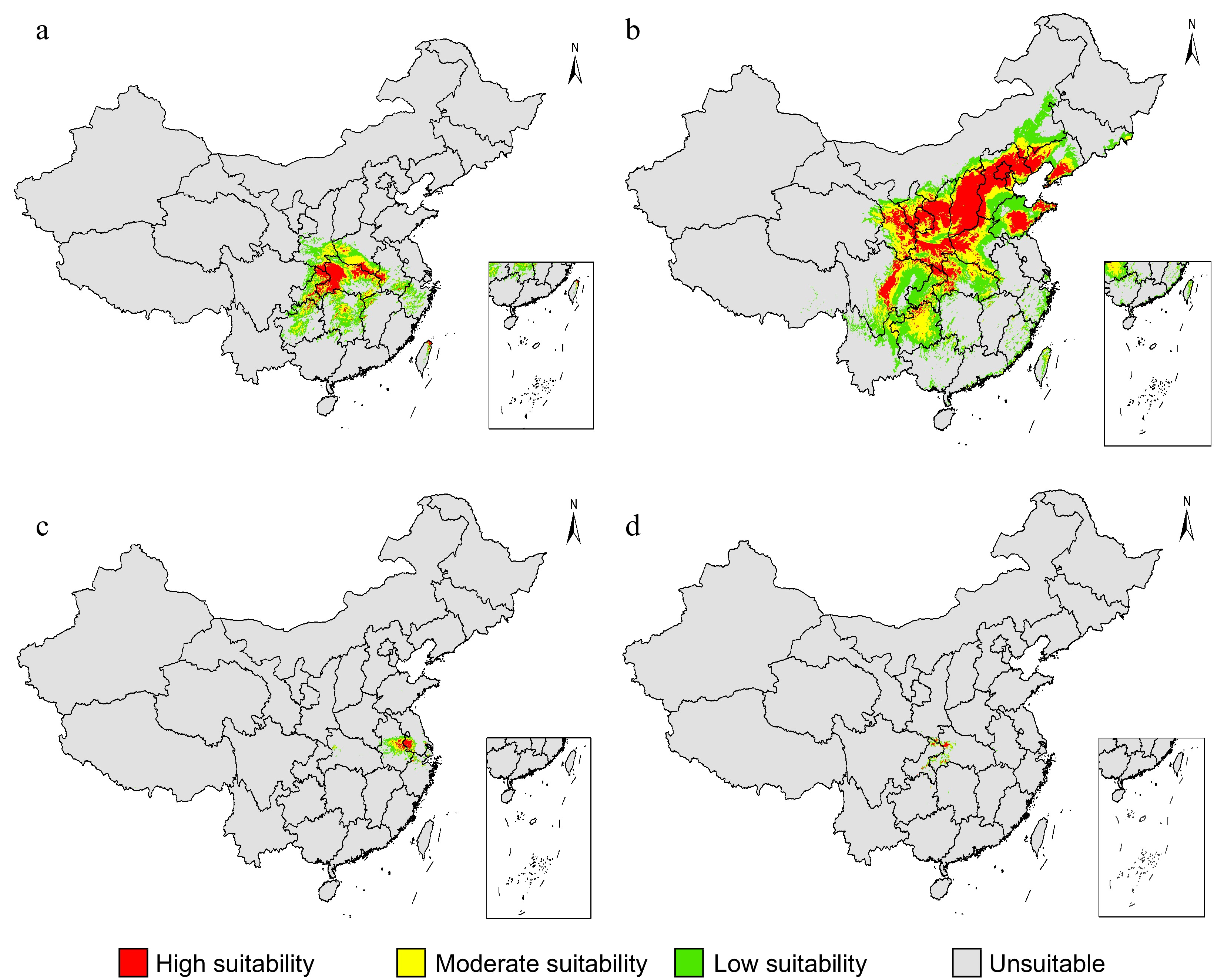
Figure 3.
The predicted suitable areas of the Chrysanthemum indicum complex under current bioclimatic conditions. The respective prediction for each taxon of the C. indicum including (a) both diploids and tetraploids, (b) C. lavandulifolium, (c) C. nankingense and (d) C. indicum var. aromaticum were showed. The predictions were conducted using the MaxEnt model based on 27 bioclimatic variables retrieved from the Worldclim website.
-
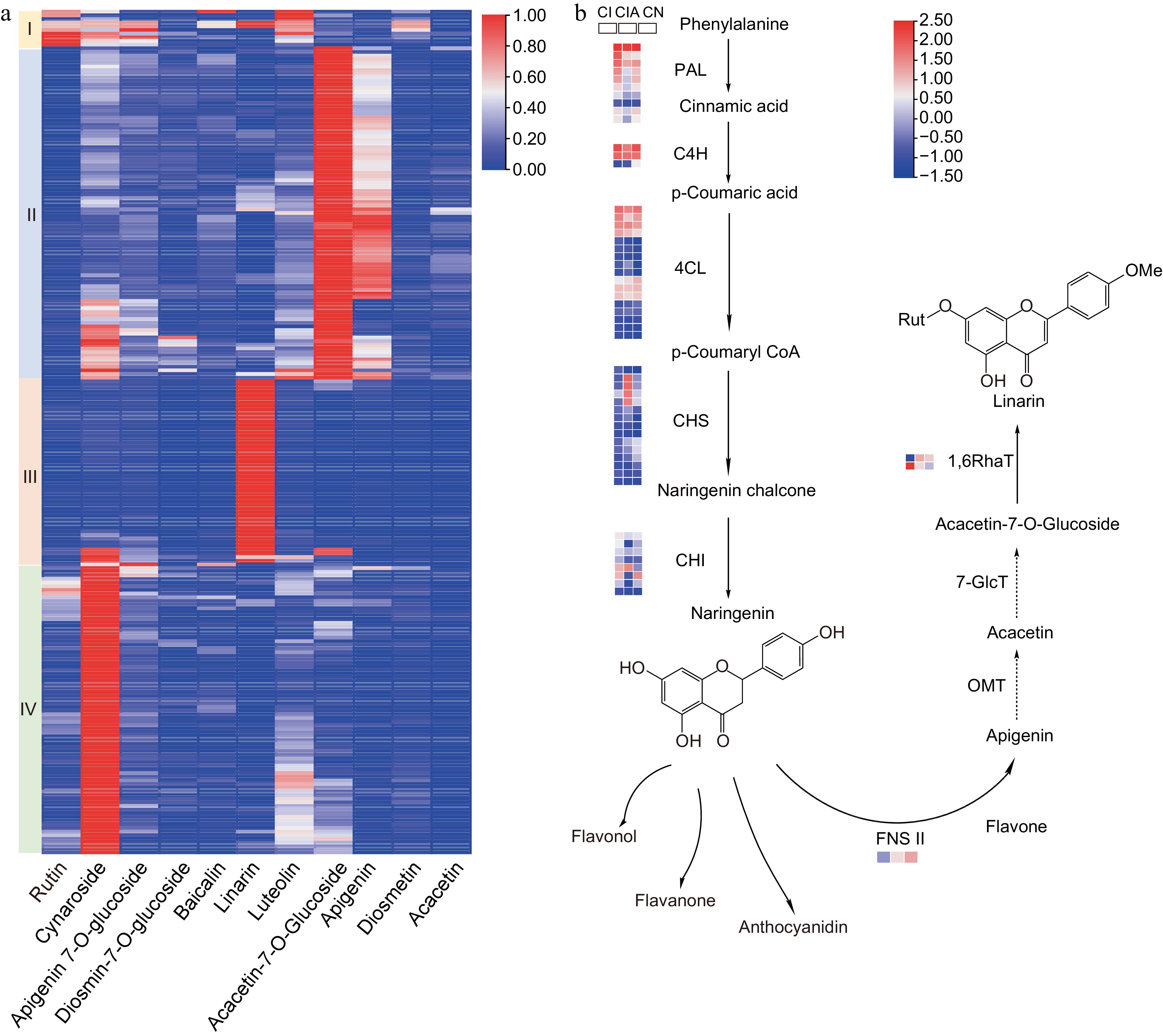
Figure 4.
The main flavonoids presented in the Chrysanthemum indicum complex populations and the speculated biosynthesis pathway of linarin. (a) The C. indicum populations revealed differential distribution of main flavonoids. (b) The possible biosynthesis pathway of linarin. The expressions of potential pathway genes from C. indicum (CI), C. indicum var. aromaticum (CIA) and C. nankingense (CN) were also revealed. PAL, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase; C4H, cinnamate-4-hydroxylase; 4CL, CoA ligase; CHS, chalcone synthase; CHI, chalcone isomerase; FNS II, flavonoid synthase II; OMT, O-methyltransferase; 7-GlcT, flavonoid-7-O-glucosyltransferase; 1,6RhaT, flavonoid-7-O-glucoside-1,6-rhamnosyltransferase.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(0)