-
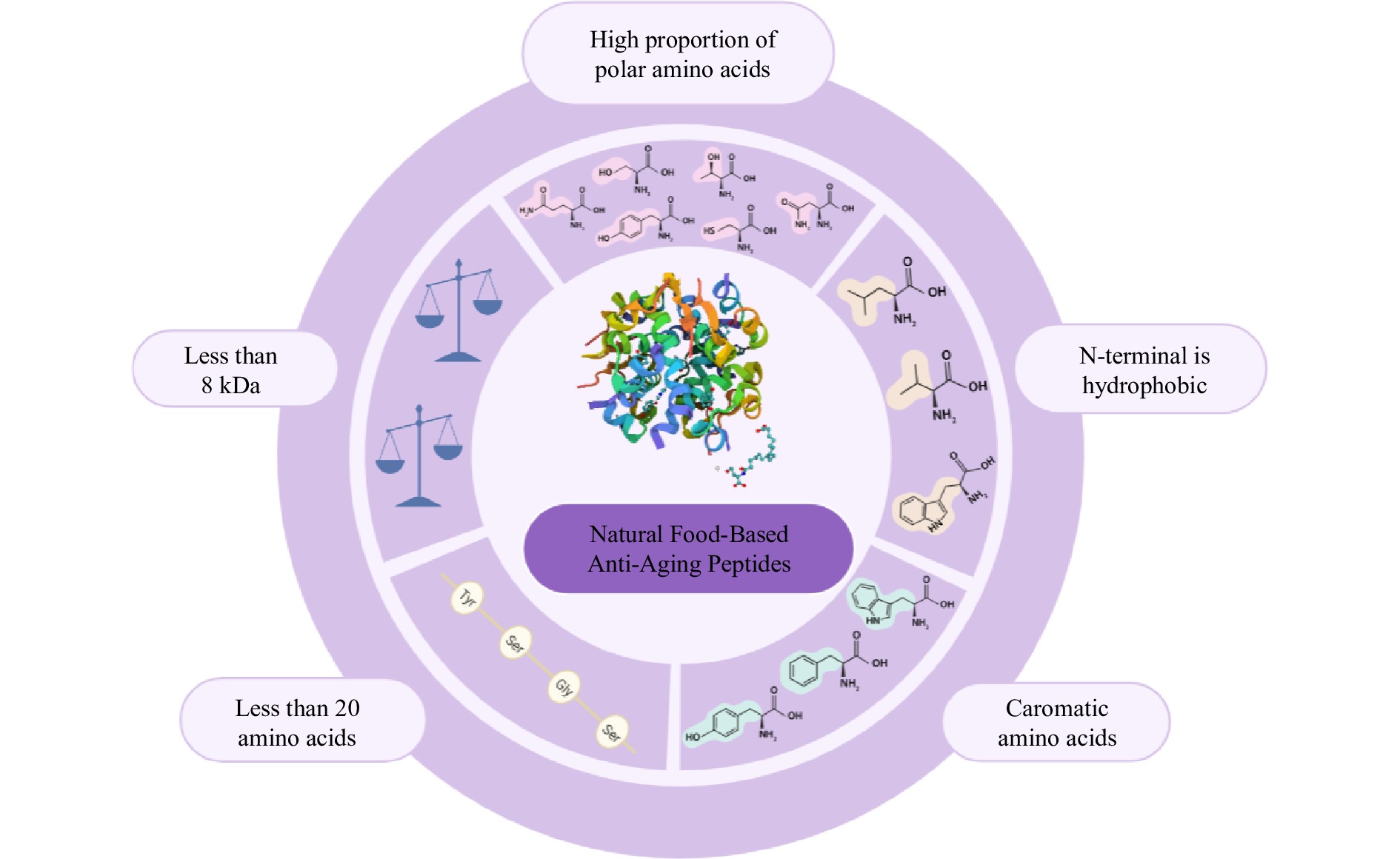
Figure 1.
Composition and structural characteristics of natural food-derived anti-aging peptides.
-
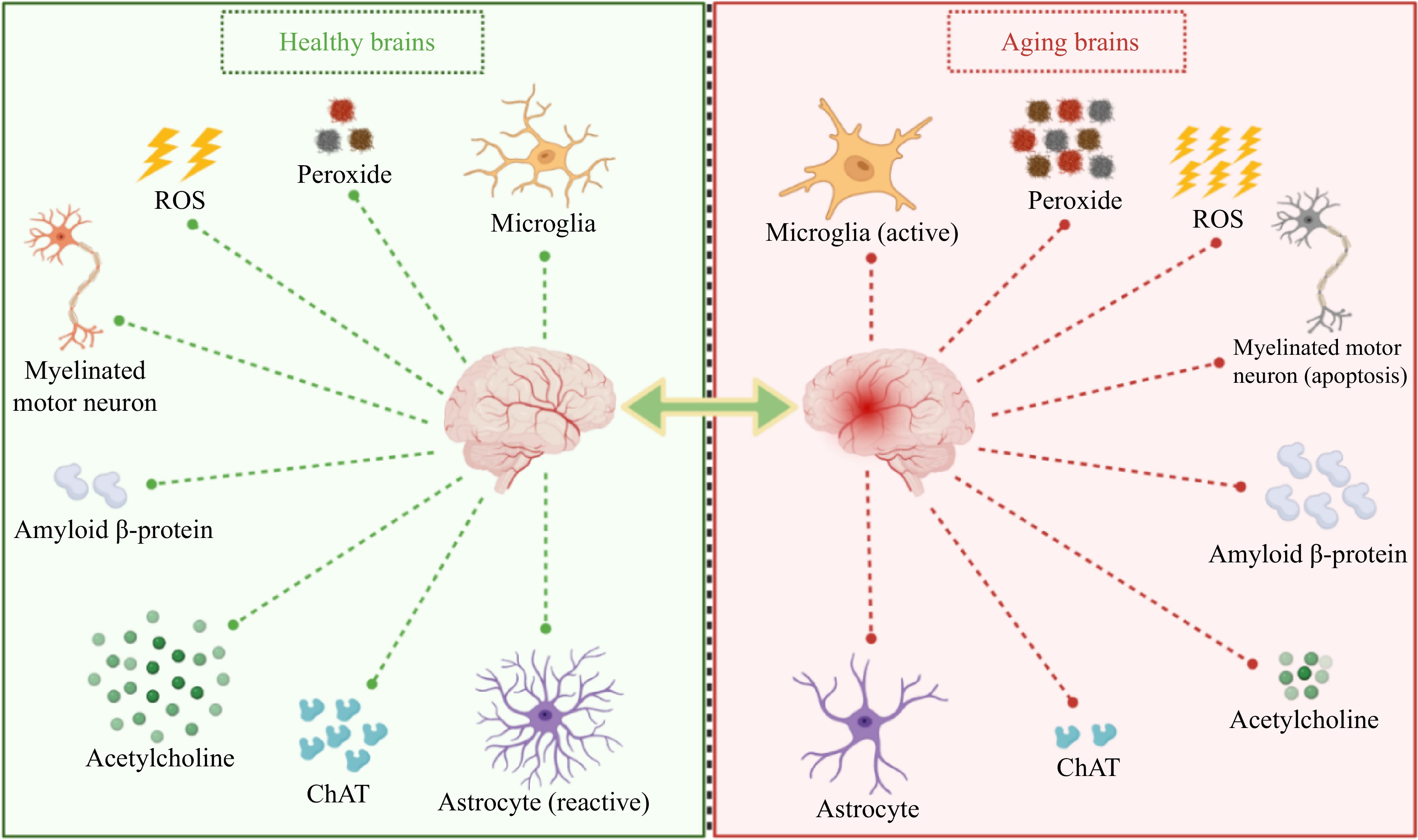
Figure 2.
Changes in related indicators of the brain during aging. ChAT, Acetylcholine transferase; ROS, Reactive oxygen species.
-
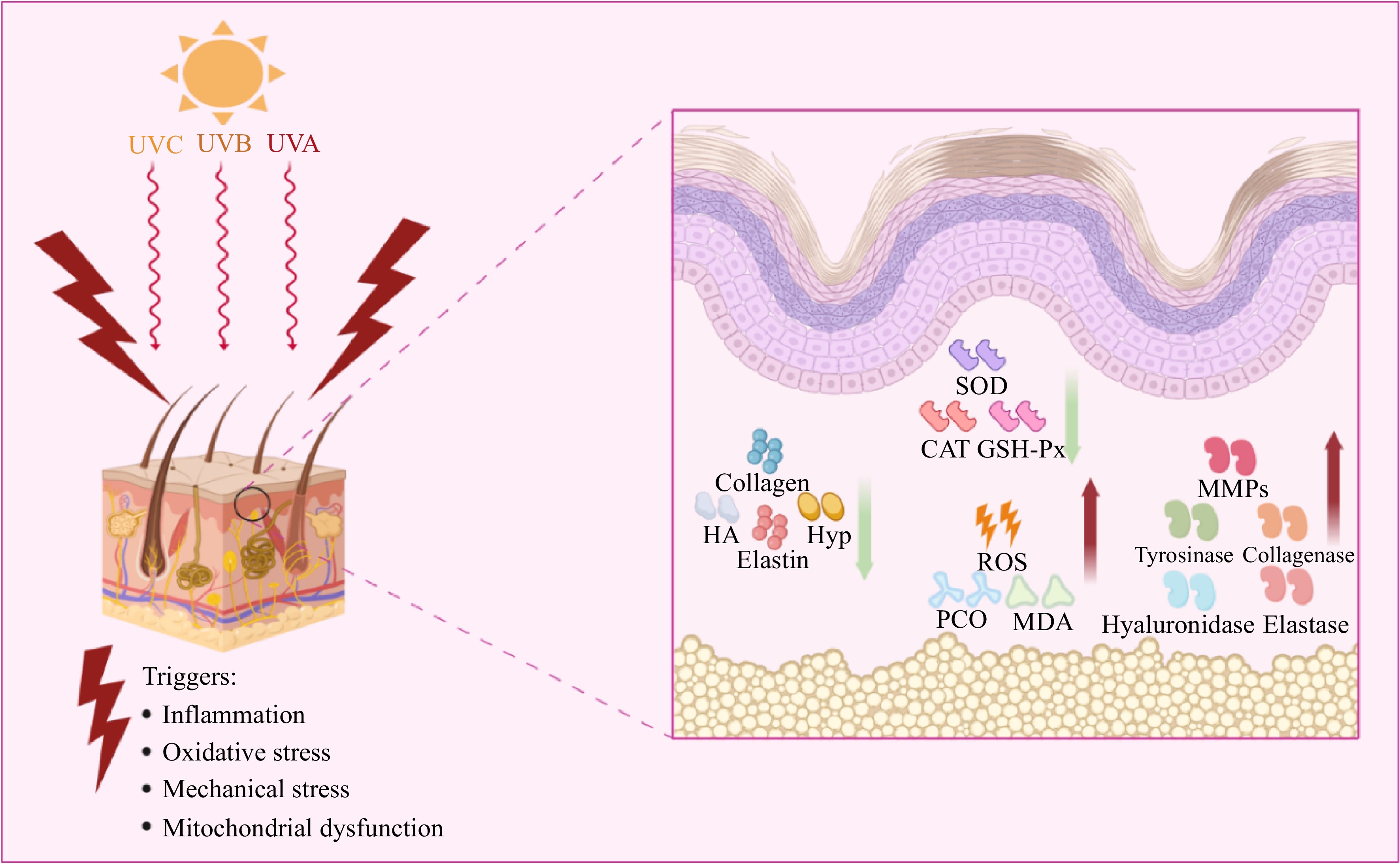
Figure 3.
Main causes of skin aging and related mechanisms. HA, Hydrated acid; Hyp, Hydroxyproline; SOD, Superoxide dismutase; CAT, Catalase; GSH-Px, Catalase; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; MDA, Malondialdehyde; MMPs, Matrix metalloproteinases; PCO, Pest Console Operation.
-
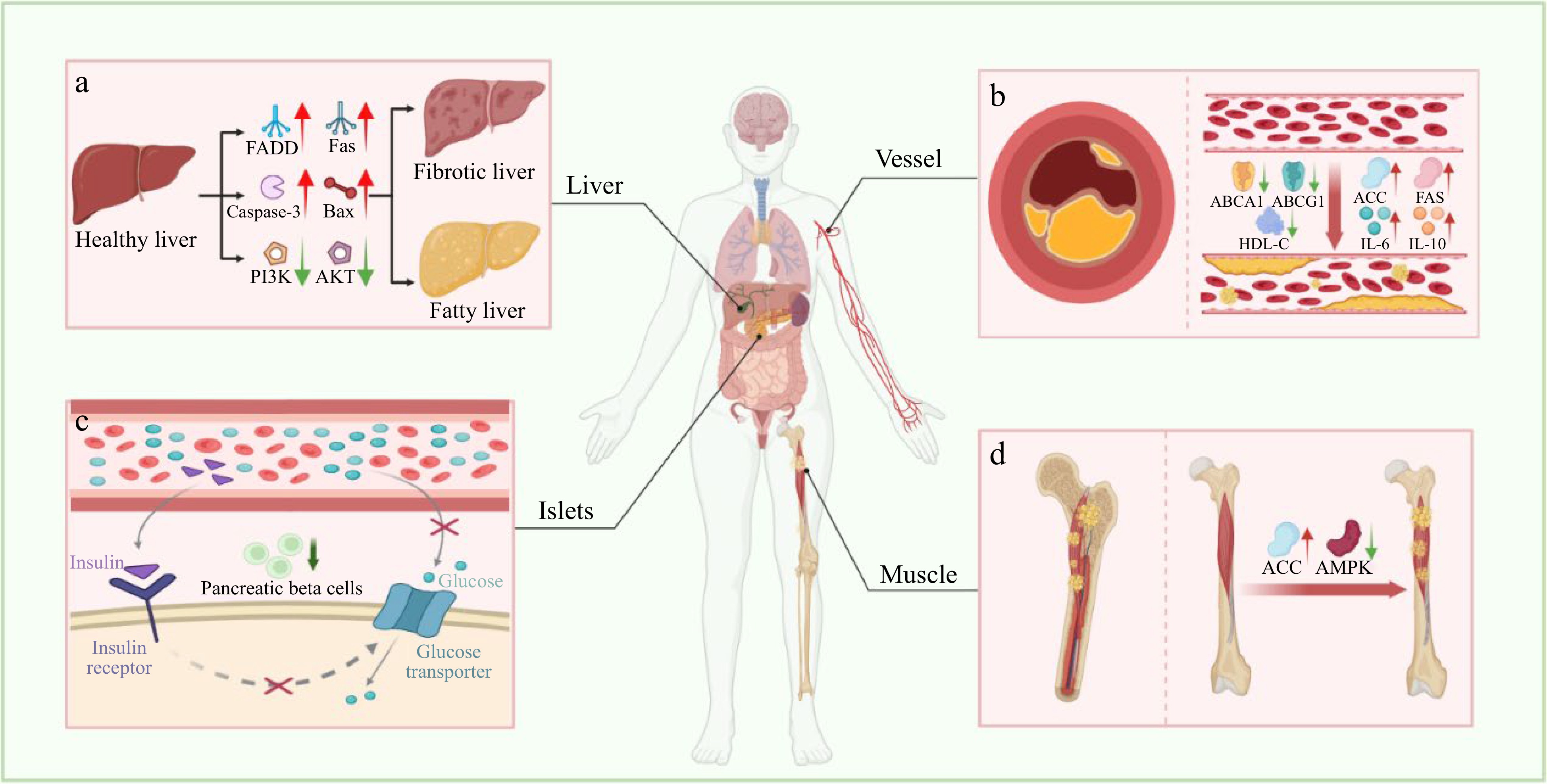
Figure 4.
Metabolic-related diseases caused by aging. (a) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. (b) Atherosclerosis. (c) Type 2 diabetes mellitus. (d) Fat deposition in skeletal muscle. FADD, Fas-associating protein with a novel death domain; Fas, Factor associated suicide; Bax, Bcl2-Associated X; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT, Protein kinase B; ABCA1, ATP-Binding cassette transporter A1; ABCG1, ATP-Binding cassette transporter G1; HDL-C, High-Density lipoprotein-cholesterol; IL-6, Interleukin-6; IL-10, Interleukin-10; ACC, Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; FAS, Fatty acid synthase; AMPK, AMP-Activated protein kinase.
-
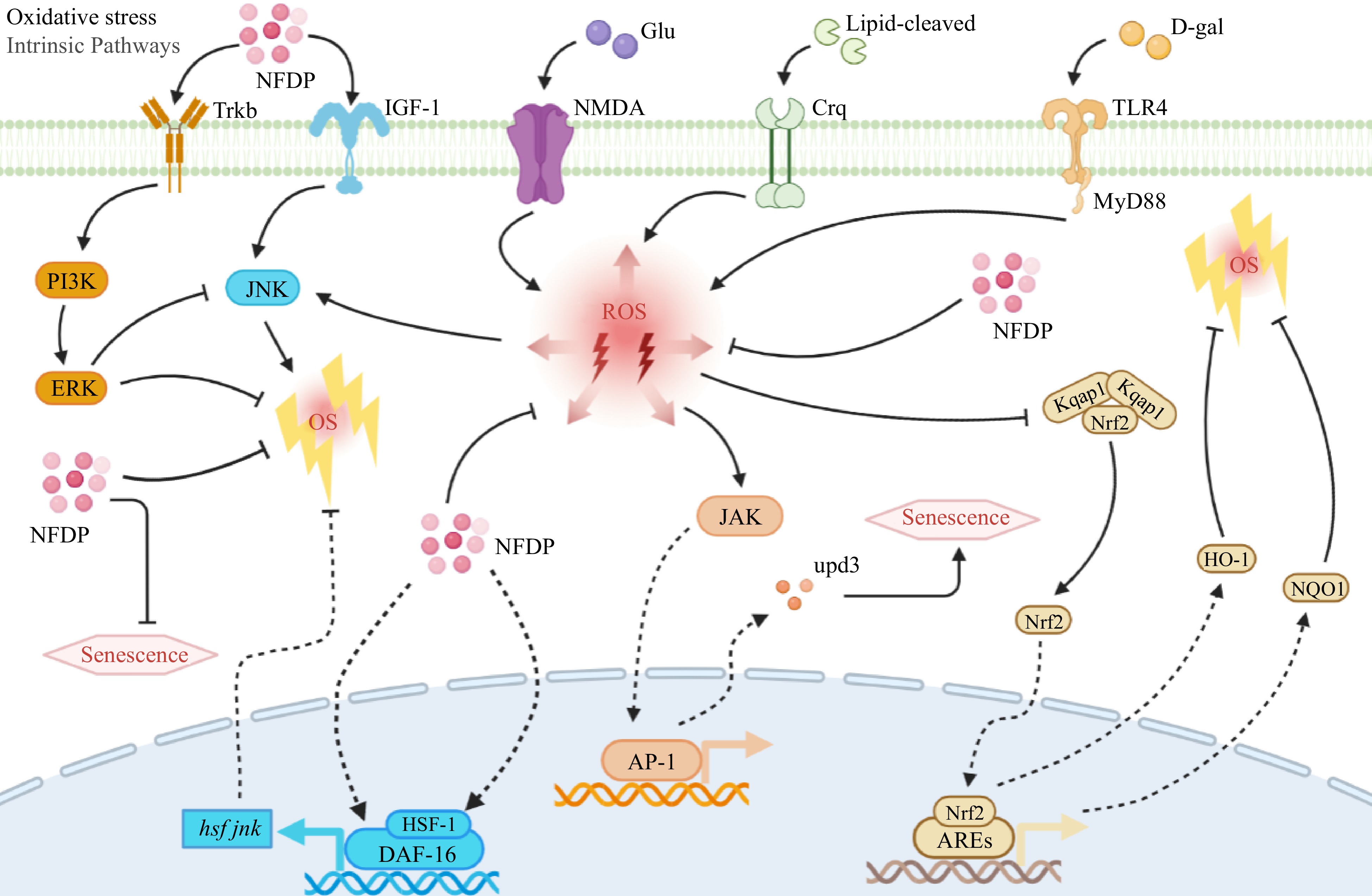
Figure 5.
Oxidative stress-related signaling pathways in which natural food-derived peptides exert anti-aging activity. Italics indicate genes. NFDP, Natural food-derived peptides; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; OS, Oxidative stress; Glu, Glusate; D-gal, D-galactose; Trkb, Tyrosine kinase receptor B; IGF-1, Insulin-like growth factor 1; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor; Crq, Stimulating scavenger-receptor; TLR4, Toll-like receptors 4; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; ERK, Extracellular signal-related kinases; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; JAK, Janus kinase; upd3, Cytokine; Kqap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; Nrf2, Nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; HO-1, Heme oxygenase-1; NQO1, NADPH quinone dehydrogenase 1; HSF-1, Heat-shock transcription factor-1; DAF-16, Transcription factors; AP-1, Activator protein-1; AREs, Advanced glycation end products.
-
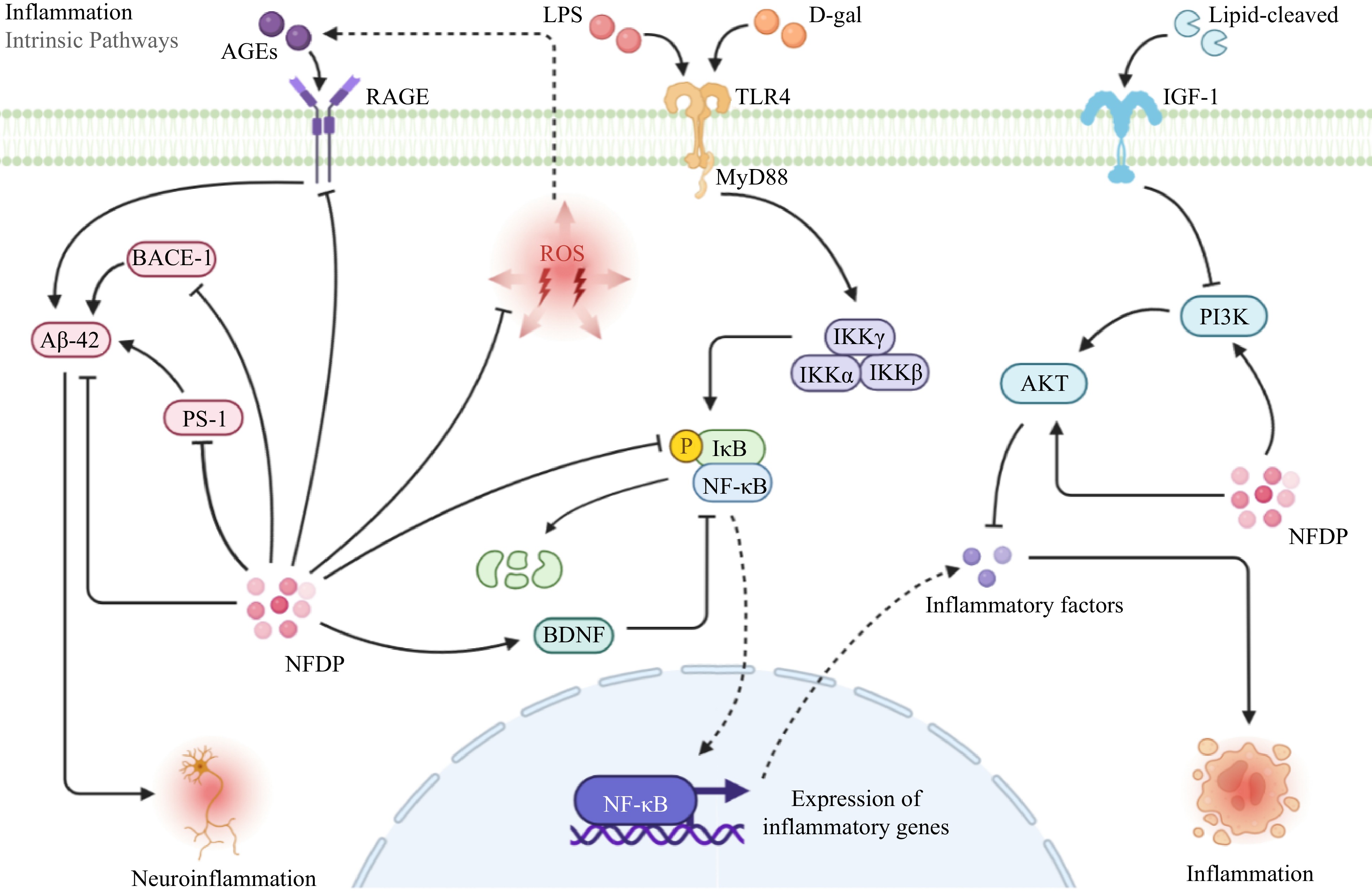
Figure 6.
Inflammation-related signaling pathways in which natural food-derived peptides exert anti-aging activity. NFDP, Natural food-derived peptides; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; AGEs, Advanced glycation end products; LPS, Lipopolysaccharide; D-gal, D-galactose; RAGE, Receptor for advanced glycation end products; MyD88, Myeloiddifferentiationfactor 88; IGF-1, Insulin-like growth factor 1; BACE-1, Beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1; Aβ-42, Amyloid β-protein; PS-1, Presenilin-1; IKK α/β/γ, IκBkinase α/β/γ; IκB, inhibitor of NF-κB; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa-B; BDNF, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT, Protein kinase B; TLR4, Toll-like receptors 4.
-
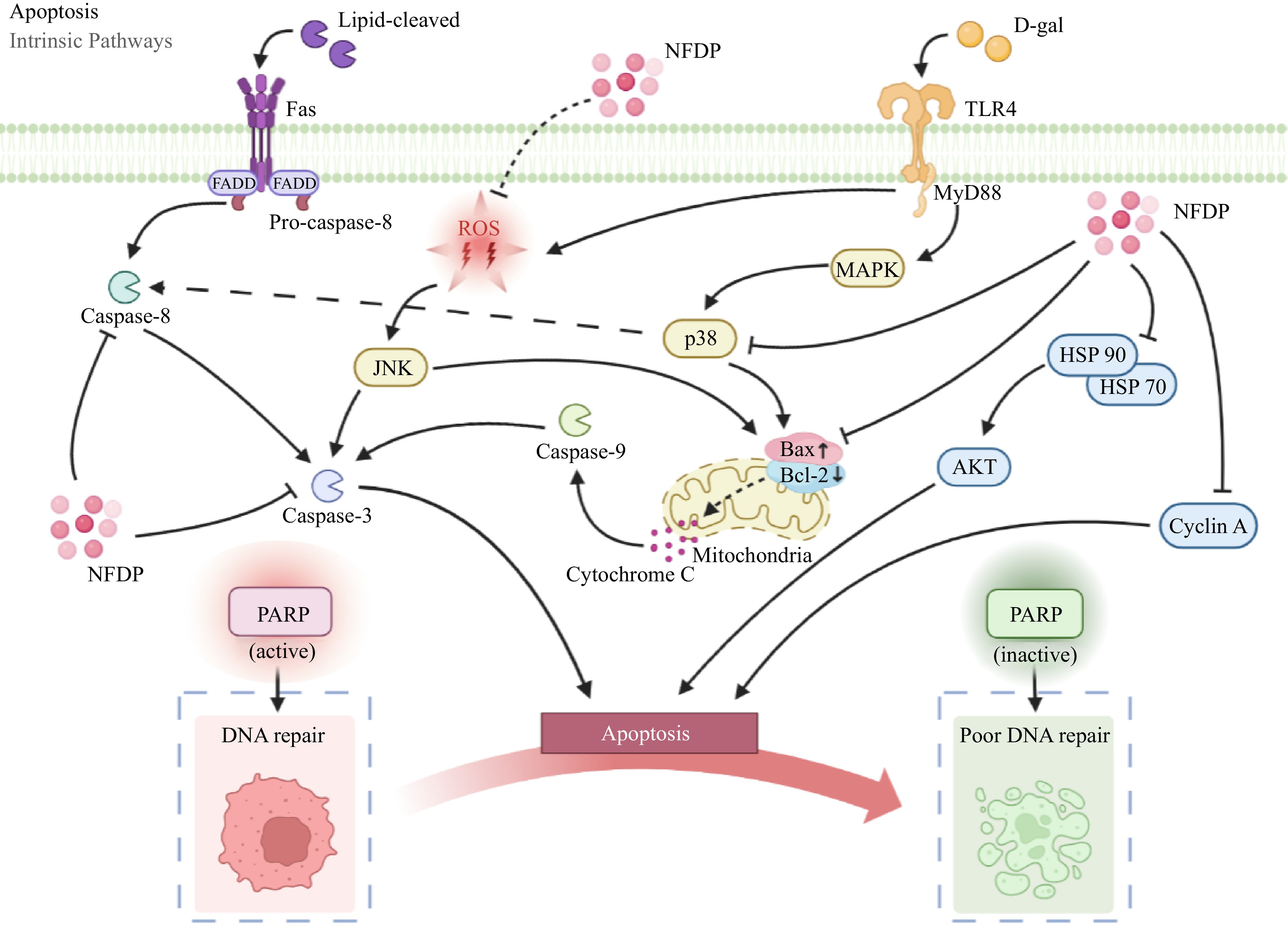
Figure 7.
Apoptosis-related signaling pathways in which natural food-derived peptides exert anti-aging activity. NFDP, Natural food-derived peptides; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; D-gal, D-galactose; Fas, Factor associated suicide; FADD, Fas-associating protein with a novel death domain; TLR4, Toll-like receptors 4; MyD88, Myeloid differentiation factor 88; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinases; Bax, Bcl2-Associated X; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma-2; HSP 70/90, Heat shock protein 70/90; AKT, Protein kinase B; PARP, Poly ADP-ribose polymerase.
-
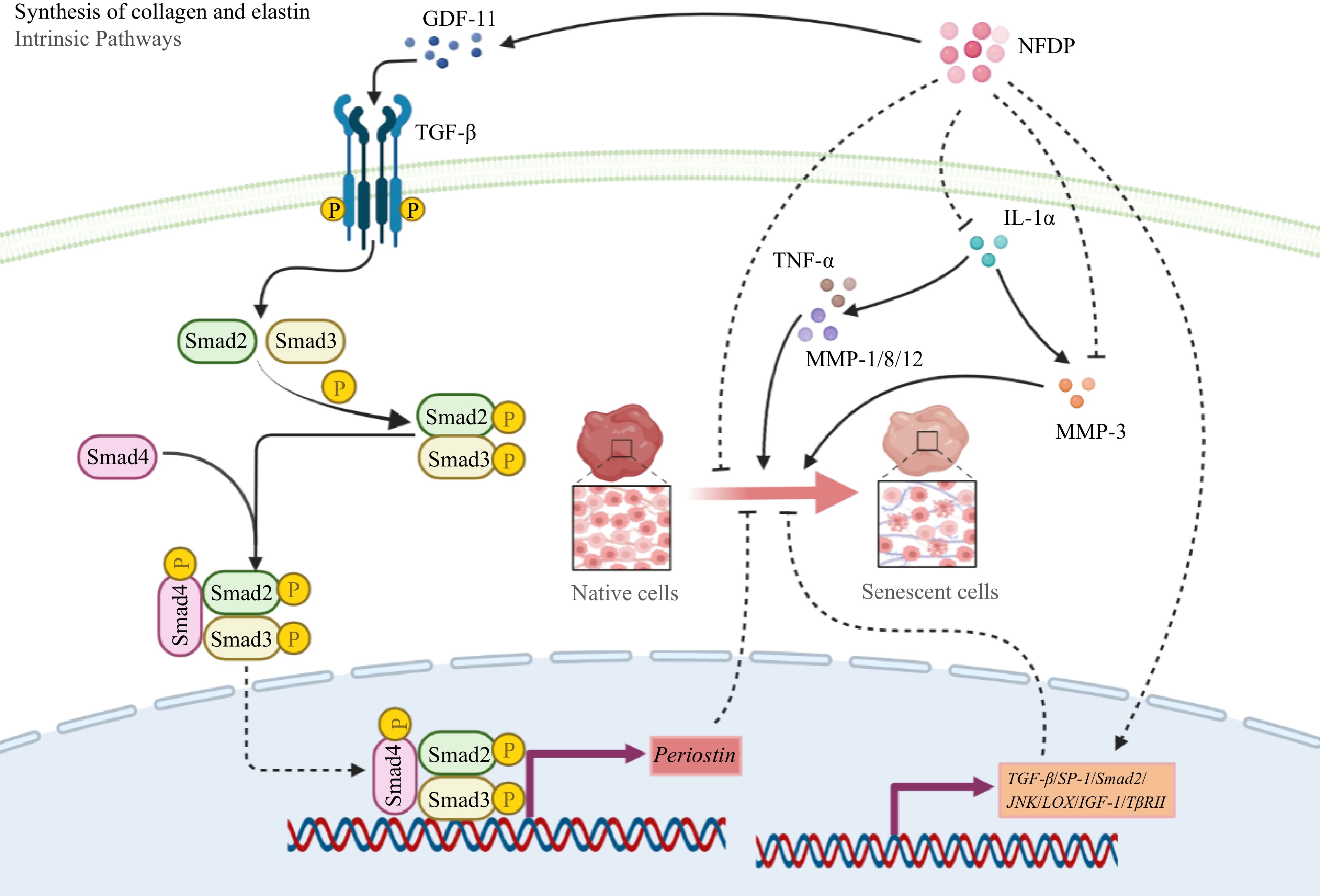
Figure 8.
Collagen synthesis-related signaling pathways in which natural food-derived peptides exert anti-aging activity. Italics indicate genes. NFDP, Natural food-derived peptides; GDF-11, Growth differentiation factor-11; TGF-β, Transforming growth factor-β; Smad, Small mothers against decapentaplegic; TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-1α, Interleukin-1α; MMP, Matrix metalloproteinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; LOX, Ysyloxidase; IGF-1, Insulin-like growth factor 1; TβRII, Transforming growth factor-β receptor II; SP-1, Transcription factor SP-1.
-
Species Sources Peptides Amino acid composition Molecular weight Extraction preparation Separation and purification Identification References Fungus Isaria japonica Naturido (DOPA)VLE 566.3 Da Solvent extraction (Water) RP-FCC, RP-HILIC-HPLC NMR, MS [41] Pyropia yezoensis PYP None None Enzymatic hydrolysis (Trypsin) CS MS [40] Pleurotus abalonus PPC None None Solvent extraction (Water) CS, GFC None [39] Plant Soybean WPK; AYLH WPK; AYLH 334.9 Da; 376.9 Da Enzymatic hydrolysis (Alkaline protease, Flavorzyme) AEC, GFC LC-MS/MS [75] Pea (Pisum sativum) Pep_RTE626 None 1,819.1 Da None None LC-MS/MS [37] Cardamine violifolia CSP None < 8 kDa Enzymatic hydrolysis (Alkaline protease, Neutral protease) CF None [33] Rice bran KF-8 KHNRGDEF 1,002.6 Da None HPLC HPLC, MS [34] Chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.) CSPs None < 3 kDa Enzymatic hydrolysis (Alkaline protease, Flavourzyme) UVAF HPLC, LC-MS/MS [35] Lotus japonicus somatic embryo LjSEC-EP PDLGSAVTRFIYKCMHEC(Taurine) < 0.8 kDa Enzymatic hydrolysis (Protease) CF MS, NMR, AAA [38] Rapeseed meal RP-1 EPLVKFGDIRTHMSYC < 3 kDa Fermentation (Bacillus subtilis) CF, UF, IEC None [54] Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) APPH None 5% > 6 kDa, 95% < 6 kDa Enzymatic hydrolysis (Alkaline protease) UF, RP-HPLC MS/MS [31] Potato PHP None None Fermentation (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) None None [53] Angelica sinensis AsiPeps None < 3 kDa Enzymatic hydrolysis (Trypsin, Papain) CF, UF, GFC LC-MS/MS [32] Black soybean (Glycine max) BSPs GSTHDERACMKVLPFYI None Enzymatic hydrolysis (Alkaline protease, Neutrase, Flavourzyme) UF, MARC AAA [30] Animal Whey WHP EDLKTIPVASFYRCMWGH(Hyp) None Enzymatic hydrolysis None None [26] Whey WHP None None None None None [83] Whey WHP None 356 Da None None None [75] Whey BWW None < 1.2 kDa None CF, UF,
RP-HPLCMS/MS [28] Collagen PCP None None None None None [25] Collagen CP; EP KWFMTILVHDEGAYRPCS; KWFMTILVHDEGAYRPCS None None None AAA [62] Collagen CP DESGHTAPRYVMCILFK 70% < 1 kDa Enzymatic hydrolysis (Alkaline protease) None HPLC, RP-HPLC [22] Gadus morhua SWPI; SWPII DECSGHRTAPYVMWILFK 4976 Da; 1,960 Da Enzymatic hydrolysis (Protamex) VC, GFC FT-IR, UV, RP-HPLC [42] Crimson snapper CSSPs DESHGTRAYCVMFILKP 99% < 3 kDa Enzymatic hydrolysis (Papain) None AAA, HPLC [43] Fish FHS None < 1 kDa None None None [67] Fish CPNS GP; P(Hyp) 800 Da Enzymatic hydrolysis (Multiple fungal proteases) HPLC GPC, LC-MS/MS [23] Oncorhynchus keta MCP GEP(Hyp)DARKLSVITFHMY < 0.86 kDa Enzymatic hydrolysis (Trypsin, Papain, Alkaline proteinase) RP-HPLC RP-HPLC, MS, AAA [27] Apostichopus japonicus AJPH None < 3 kDa Enzymatic hydrolysis (Typsin, Papain) UF, GFC RP-LC-MS/MS [47] Stichopus variegates SVPF None < 3 kDa Enzymatic hydrolysis (Protamex) UF UPLC-MS/MS [48] Royal jelly and Carcharhinus falciformis ERJ-CP GEDAPRKYLSVMLFHTC 95.8% < 1 kDa Enzymatic hydrolysis (Alkaline protease, Flavourzyme) CF AAA, HPLC [29] Locusta migratoria manilensis LP-1 TFKHG 589.3 Da Solvent extraction (Isopropyl alcohol) UF, HC,
AEC, GFC,
RP-HPLCAAA, LC-MS [24] Mytilus edulis MP None None None None None [21] Bombyx mori SP-NN; SP-PN None 962.9 Da Enzymatic hydrolysis (Neutrase, Protease N, Protease P) None None [20] The abbreviations in Table 1 are all listed in Supplemental Tables S1 & S2. Table 1.
Summary of source, extraction, isolation, and identification of natural food-derived anti-aging peptides.
-
Species Sources Peptides Aging model Delivery ways Diseases Signaling pathway Indicators References Fungus Isaria japonica Naturido SAMR1; SAMP8; Cerebral astrocytes; Hippocampal neurons; Microglial 25 μg/kg/d, 5 weeks;
25 μM, 24 h; 0.1 μM, 3 d; 1 uM, 24 hNeurodegenerative disease Inflammation AChE↓, VGF↑, NGF↑ [41] Pyropia yezoensis PYP PHNs, Glutamate, 100 uM, 60 min 1 μg/mL, 24 h Neurodegenerative disease Oxidative stress TrkB↑, PI3K↑, ERK 1/2↑, JNK↓, GRP78↓, NMDA↓, SA-β-GAL↓ [40] Pleurotus abalonus PPC SAM 30 mg/kg Enhance stress resistance Oxidative stress SOD↑, GSH-Px↑, CAT↑, MDA↓ [39] Plant Soybean WPK; AYLH Kunming mice, D-galactose,
500 mg/kg/d, 28 d; PC12 cells, Hydrogen peroxide, 0.4 mM/3 h600 mg/kg/d, 28 d;
0.05 mM, 24 hNeurodegenerative disease Oxidative stress SOD↑, GSH-Px↑, MDA↓, ROS↓, DPPH↓, AGEs↓ [75] Pea (Pisum sativum) Pep_RTE626 HDFs; Keratinocytes, Cratch cells 0.5 μg/mL, 24 h; 0.5 μg/mL, 72 h Skin aging Collagen synthesis CP↑, EP↑ [37] Cardamine violifolia CSP SD rat, Intraperitoneal injection of D-galactose, 200 mg/kg, 8 weeks 14.2 mg/kg, 8 weeks Neurodegenerative disease, Metabolic abnormalities Oxidative stress, Inflammation, Apoptosis SOD↑, GSH-Px↑, CAT↑, MDA↓, TAOC↑, ROS↓, Nrf2↑, HO1↑, NQO1↑, TNF-α↓, IL-6↓, NFkβ p65↓, AChE↓, Na+/K+-ATPase↑, p-JNK↓, RAGE↓, BACE 1↓, PS1↓, Bax↓, Bcl2↑, Caspase-3↓ [33] Rice bran KF-8 ICR mice, D-galactose, 25 mg/kg, 12 weeks; NIH/3T3 cells, Hydrogen peroxide, 100 μg/mL, 48 h 30 mg/kg, 12 weeks; 30 μg/mL, 4 h Metabolic abnormalities Oxidative stress, Inflammation, Apoptosis SOD↑, GSH-Px↑, MDA↓, Nrf2↑, Keap1↓, 8-ODdG↓, ROS↓, NF-kB p65↓, TLR4↓, lkB↓, IKK↓, MyD88↓, TNF-α↓, RAGE↓, MAPK p38↓, Bax↓, Bcl-2↑, PARP↓, Caspase-8↓, Caspase-3↓ [34] Chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.) CSPs Elastase; Collagenase; Tyrosinase; Hyaluronidase None Skin aging None Elastase↓, Collagenase↓, Tyrosinase↓, Hyaluronidase↓ [35] Lotus japonicus somatic embryo LjSEC-EP HDFs, Hydrogen peroxide,
200 uM, 2 d2 μg/mL, 24 h Skin aging Collagen synthesis GDF-11↑, Smad2↑, Collagen I↑, Collagen III↑, Periostin↑ [38] Rapeseed meal RP-1 Kunming mice, Subcutaneous injection of D-galactose,
500 mg/kg/d, 28 d600 mg/kg/d, 28 d Neurodegenerative disease Oxidative stress SOD↑, GSH-Px↑, MDA↓, DPPH↓, Na+/K+-ATPase↑, Ca2+/Mg2+-ATPase↑ [54] Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) APPH SD rat, High fat diet, 60% equivalent, 8 weeks 15 mg/kg/d, 30 d Metabolic abnormalities Apoptosis, Inflammation Fas↓, FADD↓, Bax↑, PI3K↑, AKT↑, Caspase-3↓ [31] Potato PHP Keratinocytes 0.5% concentration,
48 hSkin aging None Cholesterol↑, Alpha-Hydroxy Fatty Acids↑, Fatty Acids↑ [53] Angelica sinensis AsiPeps Caenorhabditis elegans, Paraquat, 70 mM, 2 d 0.5 mg/mL, 24 h Skin aging Oxidative stress SOD↑, GSH-Px↑, CAT↑, MDA↓, Pigment↓ [32] Black soybean (Glycine max) BSPs Kunming mice, Intraperitoneal injection of D-galactose,
400 mg/kg, 6 weeks500 mg/kg/d, 3 weeks Enhance stress resistance Oxidative stress SOD↑, GSH-Px↑, MDA↓ [30] Animal Whey WHP C57BL/6N mice, Intraperitoneal injection of D-galactose,
100 mg/kg, 6 weeks1.5 g/kg, 30 d Neurodegenerative disease, Metabolic abnormalities Oxidative stress, Inflammation SOD↑, GSH-Px↑, MDA↓, PCO↓, TNF-α↓, IL-1β↓, AChE↓, ChAT↑, CREB↑, CaMKII↑, BDNF↑ [26] Whey WHP SAMP6 18.7% concentration, 28 weeks Metabolic abnormalities Inflammation AMPK↓, ACC↓ [83] Whey WHP HRM, Ultraviolet, 36-180 mJ/cm², 17 weeks 400 mg/kg, 17 weeks Skin aging Oxidative stress MMP2↓, MMP9↓, VGEF↓,
Ki-67↓, 8-OHdG↓, ROS↑,
ST↓, Elasticity↑, Pigment↓, Wrinkle↓[75] Whey BWW CaCo2 cells, Hydrogen peroxide, 50 mM, 30 min 0.08 mg/mL, 24 h Anti-cancer Apoptosis HSP-70↓, HSP-90↓, AKT↓, Cyclin A↓, MSA↓ [28] Collagen PCP PCFs and Keratinocytes Mitomycin C, 7.5 μg/mL, 2 h (isolated from
human)10 g, 24 h Skin aging Collagen synthesis Ki-67↑, Collagen↑ [25] Collagen CP; EP BALB/c-nude mice, Subcutaneous injection of D-galactose and Ultraviolet, 10% concentration 1g/kg and 50 mJ/cm²/30 min,
42 d and 42 d0.03 g/kg, 42 d Skin aging Collagen synthesis MMP-3↓, IL-1α↓, HYP↑, HA↑, IGF-1↑, LOX↑, Smad2↑, JNK↑, SP-1↑, TβRII↑, TGF-β↑ [62] Collagen CP Kunming mice, 2 and 13 months 400 mg/kg/d, 8 weeks Skin aging Oxidative stress, Collagen synthesis SOD↑, CAT↑, MDA↓ROS↓, ABTS↓, HA↑, Collagen I↑, Collagen III↑, DSL↓ [22] Gadus morhua SWPI; SWPII 2BS cells, Hydrogen peroxide,
0.2 mM, 2 h100 µg/mL, 24 h Enhance stress resistance Oxidative stress, Apoptosis SA-β-GAL↓, ROS↓,
Fe2+-chelating activity↑[42] Crimson snapper CSSPs Drosophila melanogaster, High fat diet, 10% (w/v), 7 d 6 mg/mL, 7 d Enhance stress resistance Oxidative stress SOD↑, CAT↑, MDA↓, PCO↓, ROS↓ [43] Fish FHS C57Bl/6J mice, 7 weeks and 12 months; BV2 cells, Lipopolysaccharide, 1 μg/mL, 6 h; HT22 cells, Lipopolysaccharide, 1 μg/mL, 6 h 5.5 mg/d, 3 months;
0.27 mg/mL, 16 h; 0.27 mg/mL, 16 hNeurodegenerative disease Inflammation NF-kB↓, IBA1↓, CD11b↓,
IL-6↓, IL-1β↓, TNF-α↓,
BDNF↑, NGF↑, Cort↑[67] Fish CPNS HRM, Ultraviolet, 55 mJ/cm2, increasing by 55mJ/cm2 every week to 220 mJ/cm2, 12 weeks; HDFs, Ultraviolet, 25 mJ/cm²/none; SD rat, 6 weeks 300 mg/kg/d, 12 weeks; 50 μg/mL, 24 h Skin aging Collagen synthesis MMP-1↓, Collagen I↑, Wrinkle↓, ET↓, SH↑, TSWL↓ [23] Oncorhynchus keta MCP C57BL/6J mice, 20 months 0.44% concentration,
3 monthsNeurodegenerative disease Oxidative stress SOD↑, GSH-Px↑, MAD↓, BDNF↑, PSD95↑ [27] Apostichopus japonicus AJPH Caenorhabditis elegans, Paraquat, 2 mM, 48 h; PC12 cells, Paraquat,
1 mM, 12 mg/mL, 10 d; 0.4 mg/mL, 24 h Enhance stress resistance Oxidative stress SOD↑, CAT↑, MDA↓, ROS↓, Pigment↓ [47] Stichopus variegates SVPF Kunming mice, Intraperitoneal injection of D-galactose,
100 mg/kg, 8 weeks; Drosophila melanogaster, D-galactose,
40 g/L, Until death1,000 mg/kg, 8 weeks;
4 g/L, Last until all
deathEnhance stress resistance Oxidative stress SOD↑, GSH-Px↑, MDA↓, PCO↓, Klotho↑ [48] Royal jelly and Carcharhinus falciformis ERJ-CP Drosophila melanogaster, Hydrogen peroxide, and Paraquat, 30% and 20 mM, 8 h and 3 d 3 mg/mL, 10 d Enhance stress resistance Oxidative stress SOD↑, GSH-Px↑, CAT↑, MDA↓, PCO↓, ROS↓ [29] Locusta migratoria manilensis LP-1 Caenorhabditis elegans, Paraquat and High temperature and Ultraviolet, 1 mM and 35 °C and 1,000 J/m², 4 h, 10.2 h and 30 s 2.5 mg/mL, 3 d Enhance stress resistance Oxidative stress ROS↓, DAF-16↑, HSF-1↑,
JNK-1↑[24] Mytilus edulis MP ICR mice, Subcutaneous injection of D-galactose, 200 mg/kg,
8 weeks1,000 mg/kg, 8 weeks Metabolic abnormalities Oxidative stress SOD↑, GSH-Px↑, MDA↓, PPARα↑, PPARγ↑, p21↓,
BS↓, Trig↓, FFA↓, HDL↑, LG↑[21] Bombyx mori SP-NN; SP-PN SD rat, Subcutaneous injection of D-galactose, 150 mg/kg, 4 weeks 50 mg/kg, 5 weeks Neurodegenerative disease, Metabolic abnormalities Oxidative stress ChAT↑, HGCP↓ [20] '↑' represents up-regulation, and '↓' represents down-regulation. The main abbreviations in Table 2 are listed in Supplemental Tables S1 & S3. SAMR: Senescence-accelerated mouse resistance; SAMP: Senescence-accelerated mouse prone; SAM: Senescence-accelerated mice; PHNs: Primary hippocampal neurons; HDFs: Human dermal fibroblasts; HRM: Hairless mice; PCFs: Primary cutaneous fibroblas. Table 2.
Summary of natural food-derived anti-aging peptides and aging-related diseases, models, and mechanisms.
Figures
(8)
Tables
(2)