-
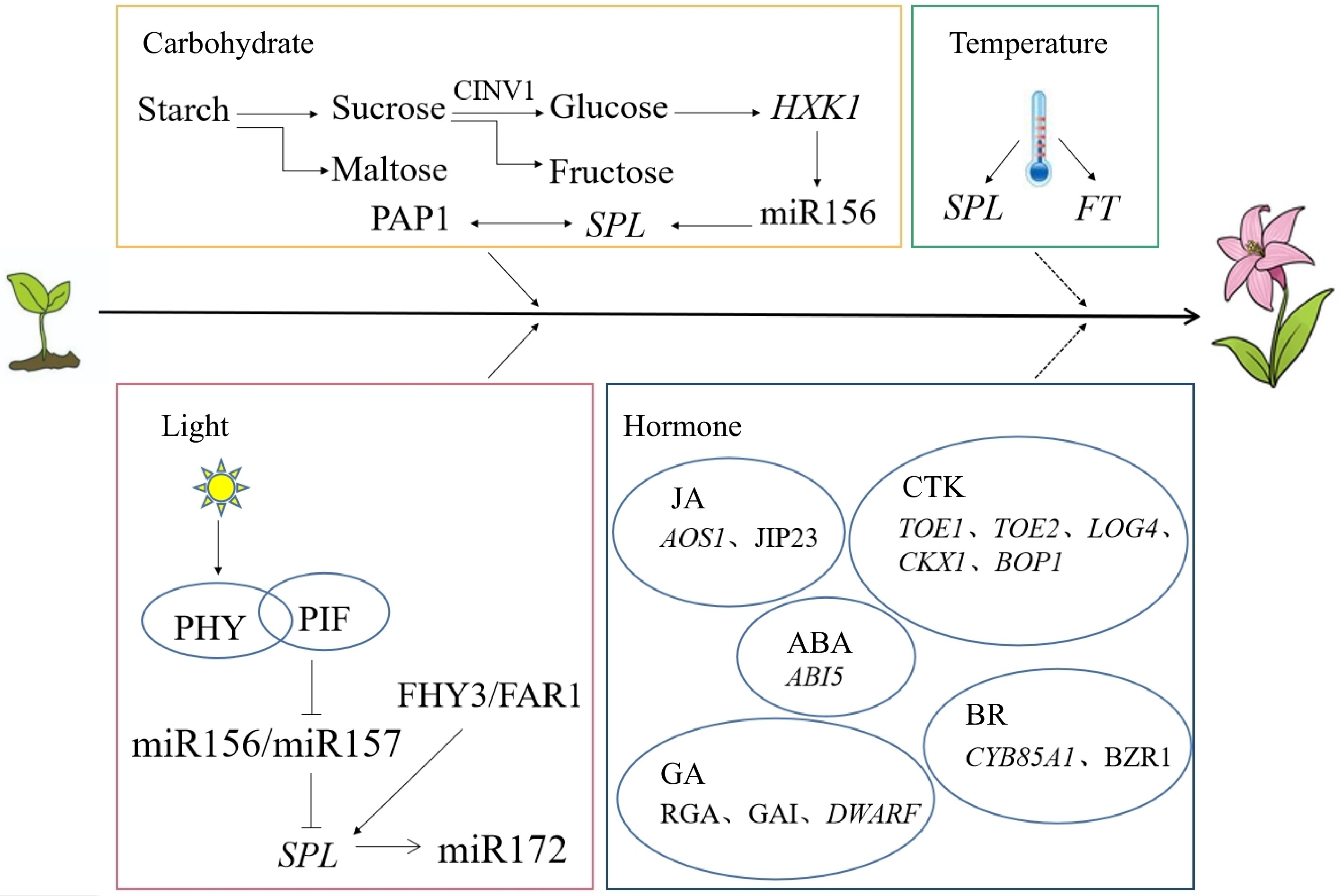
Figure 1.
Working mechanism of multiple factors regulating the juvenile phase in plants (according to the references). Solid arrows indicate positive interactions, dotted arrows indicate uncertain interactions, and flat lines indicate negative interactions[54,55,68−72,76,79,83,84,86,90,91,93−95,98,99].
-
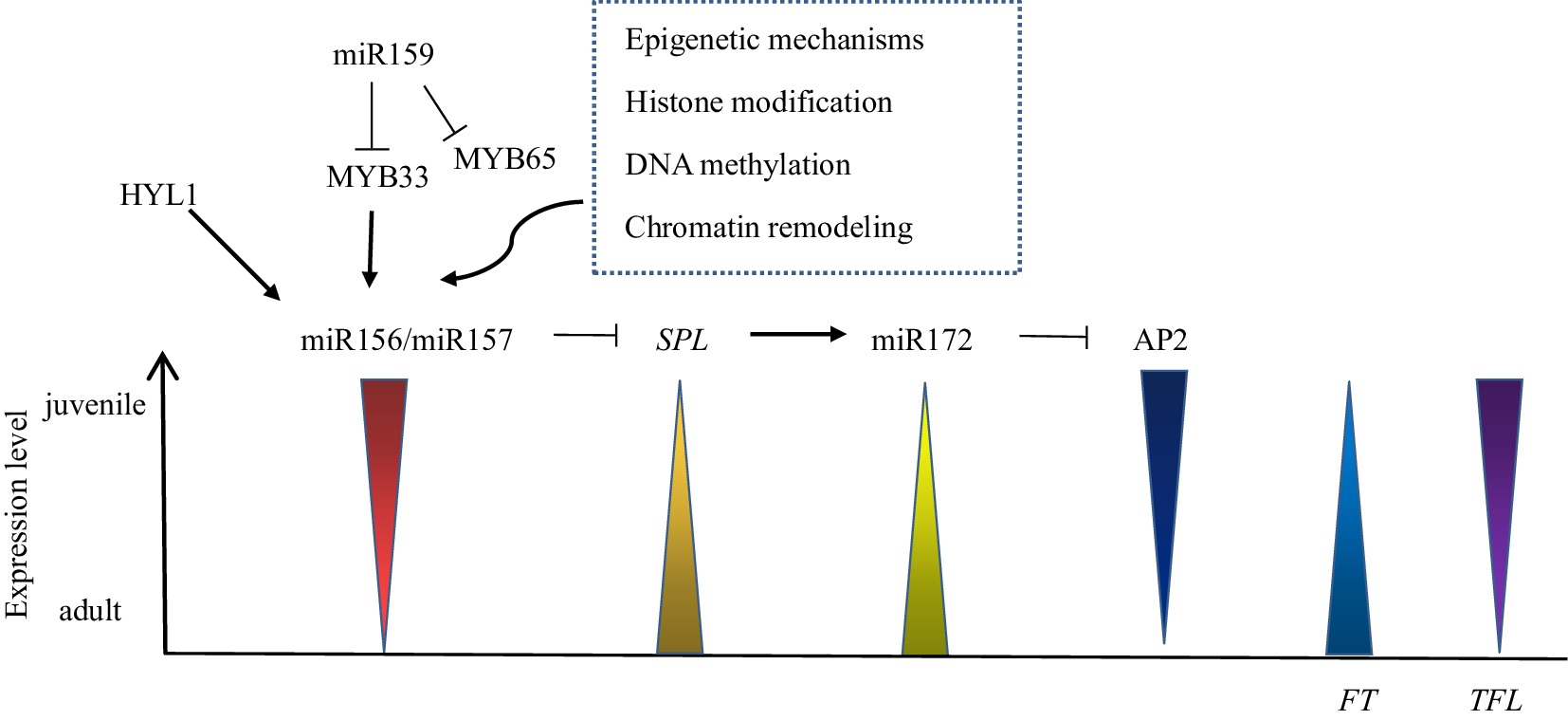
-
Species Juvenile phase (years) Reference Lilium spp. 2−3 [21] Piper nigrum 3−4 [22] Malus domestica 4−8 [23] Camellia nitidissima 8 [24] Citrus spp. 5 [25] Eucalyptus globulus 2−5 [26] Jatropha curcas 5 [27] Liriodendron chinense 8−10 [28] Populus spp. 7−10 [29] Pinus tabuliformis 5−7 [30] Ginkgo biloba 15−20 [31] Ziziphus jujuba 1−2 [32] Table 1.
Statistics of time of the juvenile phase in some species (according to the literature).
Figures
(2)
Tables
(1)