-
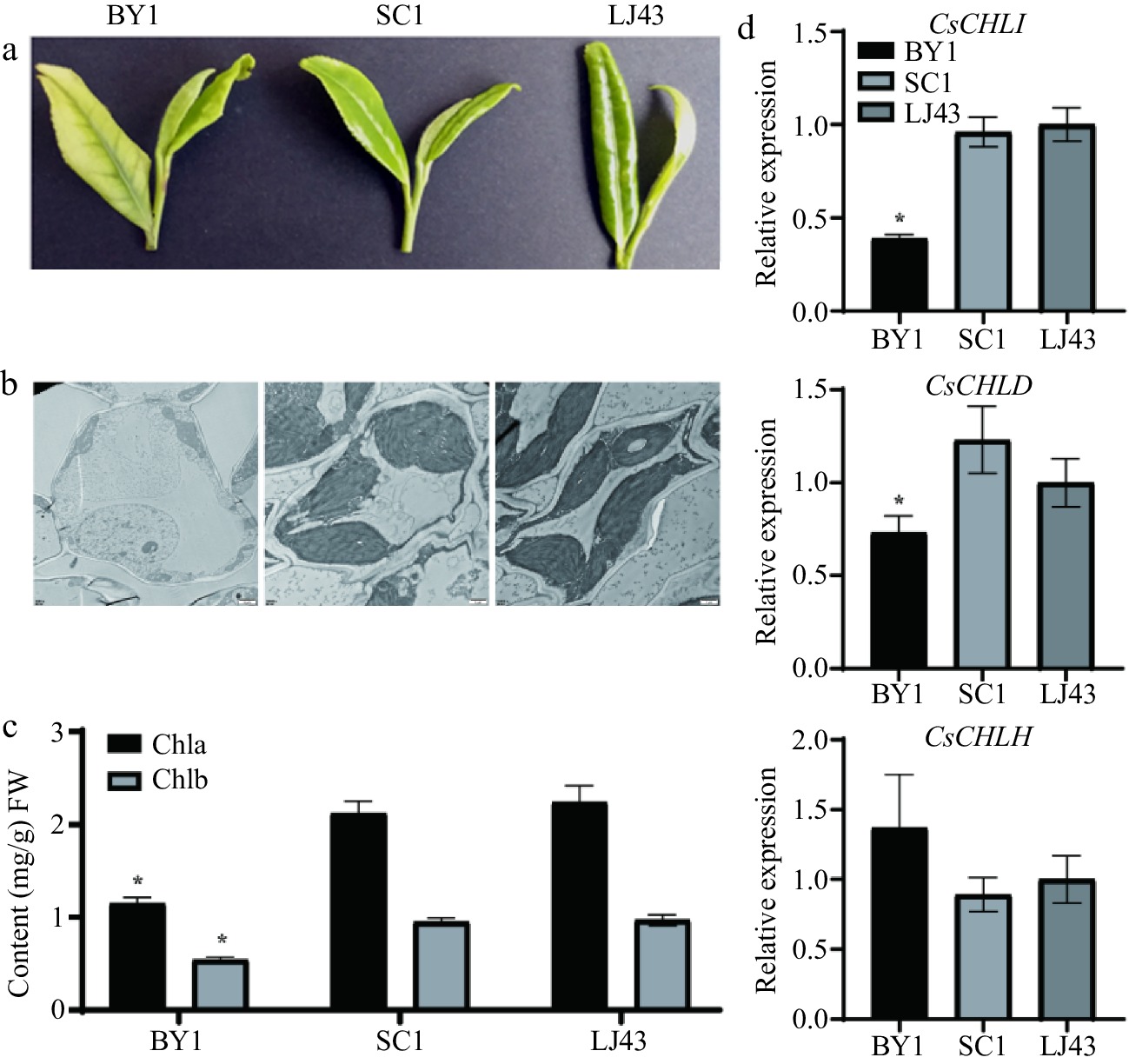
Figure 1.
Leaf phenotypes, leaf ultrastructure, chlorophyll content, and expression levels of CsCHLI, CsCHLD, and CsCHLH genes in albino BY1 and green SC1 and LJ43 tea leaves. (a) Leaf phenotypes of BY1, SC1, and LJ43 plants. (b) Transmission electron microscope images of leaf ultrastructures. (c) Chlorophyll content in the BY1, SC1, and LJ43 leaves. (d) Expression patterns of CsCHLI, CsCHLD, and CsCHLH genes in BY1, SC1, and LJ43 leaves. BY1, Baiye 1; SC1, Shaancha1; LJ43, Longjing43. * means p ≤ 0.05.
-
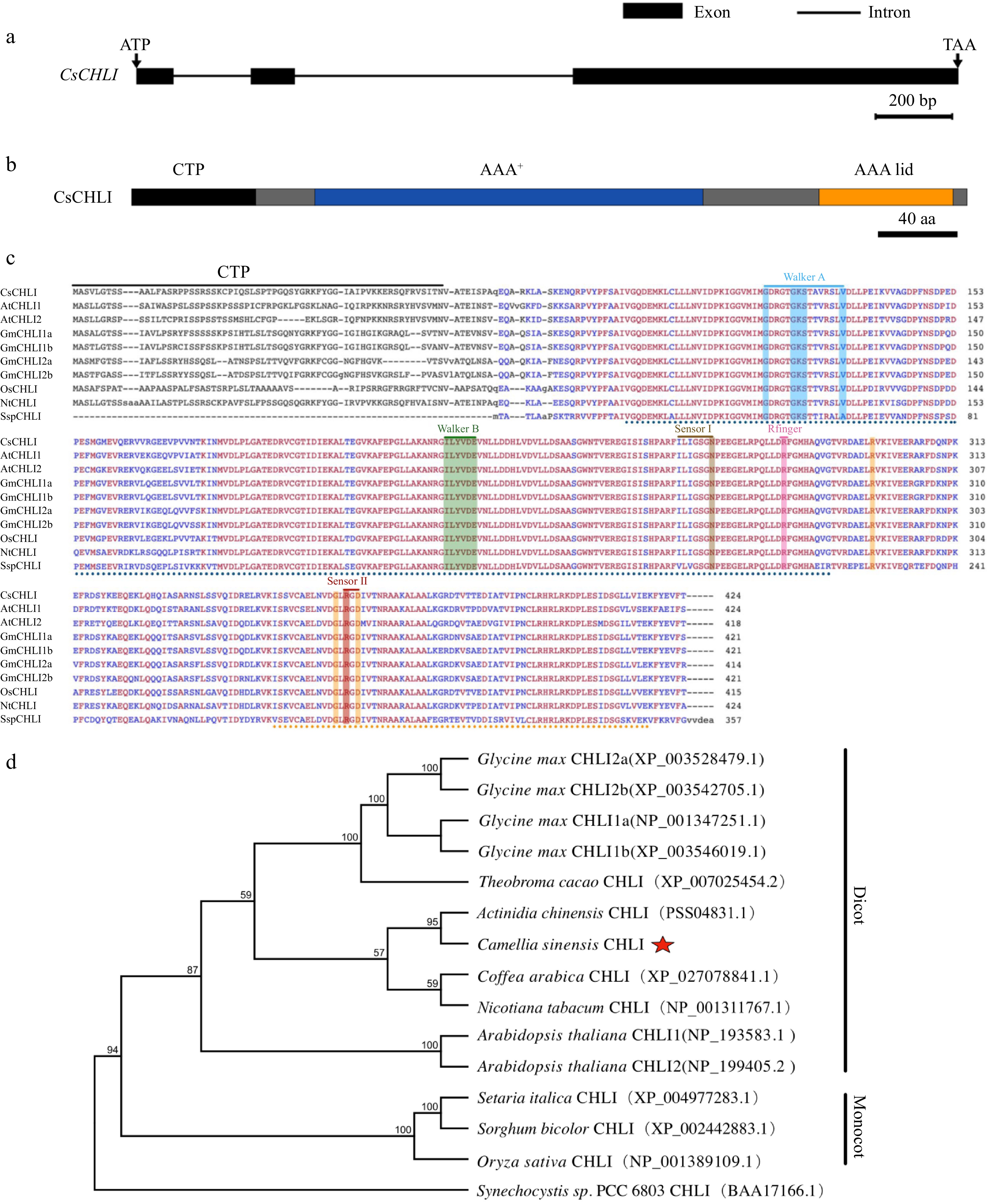
Figure 2.
Schematic structure, multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree of CsCHL. (a) Gene structure of CsCHLI. Dark gray boxes represent coding exons, black lines represent introns, length of nucleotide sequence is represented in the scale. (b) Schematic representation of conserved motifs in CsCHLI. Different coloured rectangles represent different protein domains, length of amino acid sequence is represented in the scale. (c) Multiple sequence alignment of CHLI. The amino acid sequences for analysis include CsCHLI, from Camellia sinensis, GmCHLI1a, GmCHLI1b, GmCHLI2a and GmCHLI2b from Glycine max, OsCHLI from Oryza sativa, NtCHLI from Nicotiana tabacum, AtCHLI1 and AtCHLI2 from Arabidopsis thaliana, and SspCHLI from cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Red and blue highlight the sequences with 100% and 80% identity, respectively. (d) Phylogenetic analysis of CHLI.
-
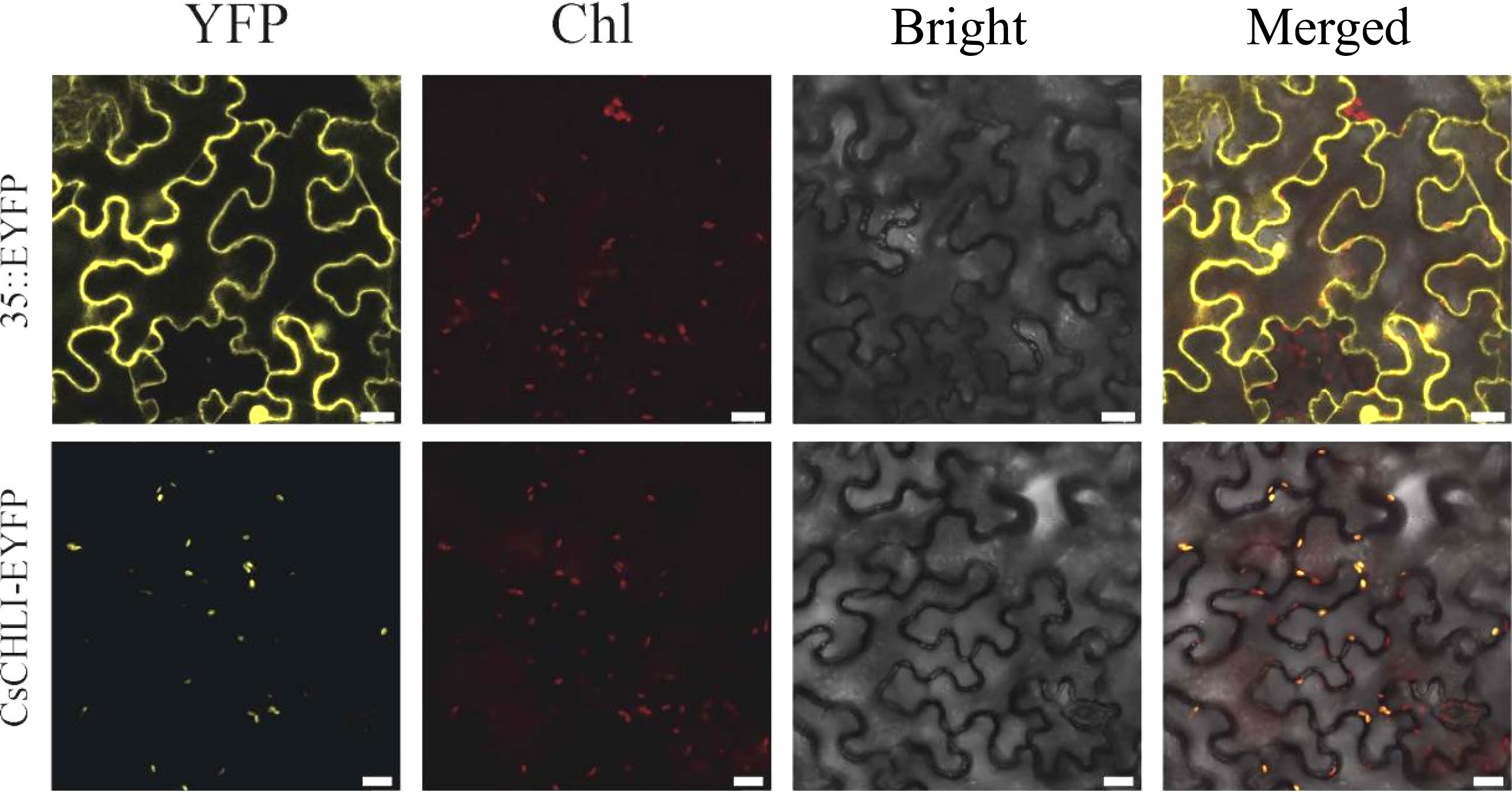
Figure 3.
Subcellular localization of CsCHLI. 35S::EYFP, control vector with 35S promoter; CsCHLI-EYFP, CsCHLI-EYFP fusion protein under 35S promoter; YFP, YFP Fluorescence; Chl, Chlorophyll autofluorescence; Bright, bright field; Merged, Merged images. The scale bar is 20 μm.
-
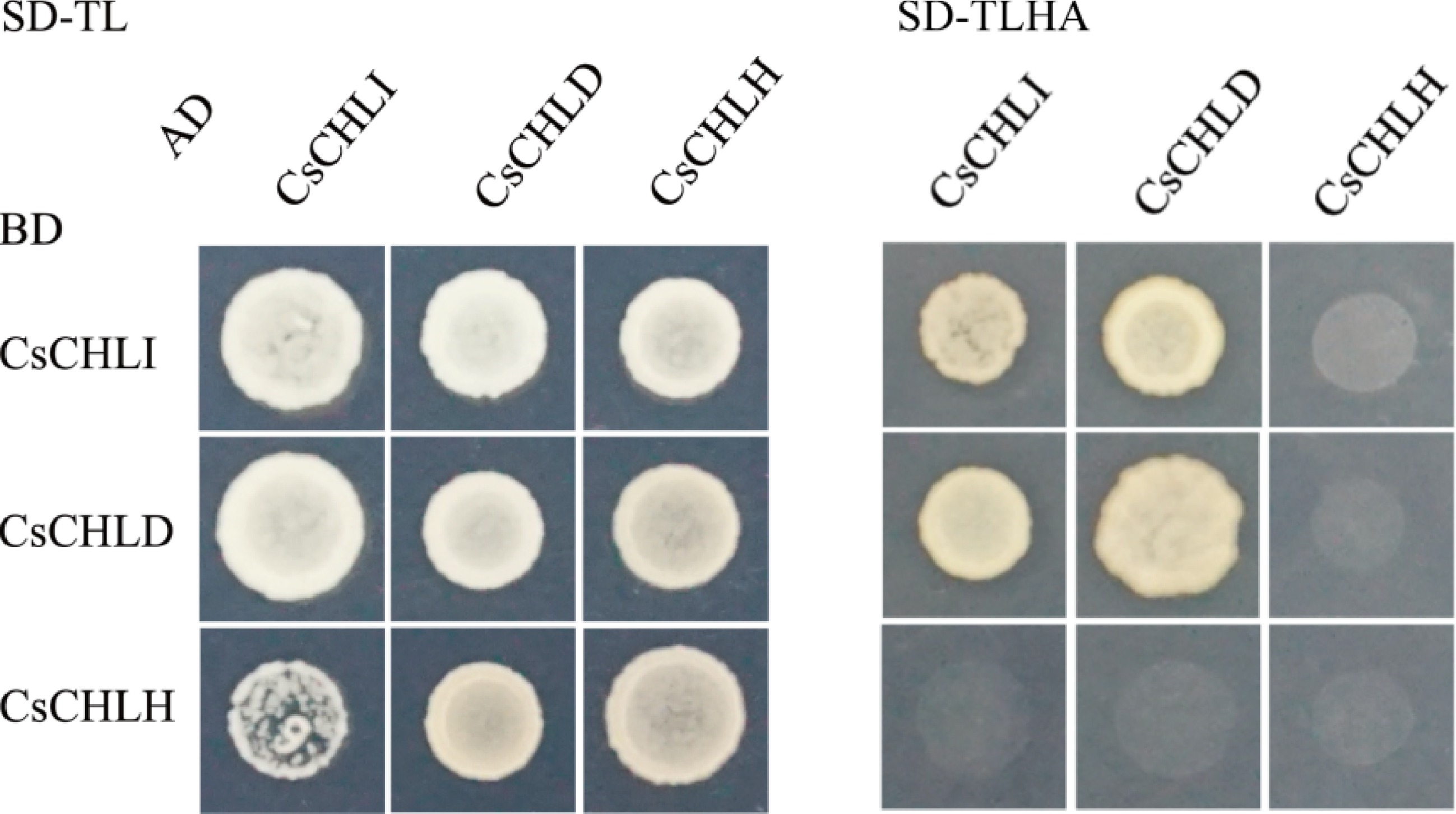
Figure 4.
Yeast two hybrid assay between CsCHLI, CsCHLD, and CsCHLH. pGBKT7 vectors expressing BD-fused CsCHLI, CsCHLD, and CsCHLH were co-transformed with pGADT7 ones expressing AD-fused CsCHLI, CsCHLD, and CsCHLH into the yeast strain Y2H Gold. The transformants were grown on the synthetic dextrose medium (SD) lacking Trp and Leu (SD-TL) or on the SD medium without Trp, Leu, His, and Ade (SD-TLHA).
-
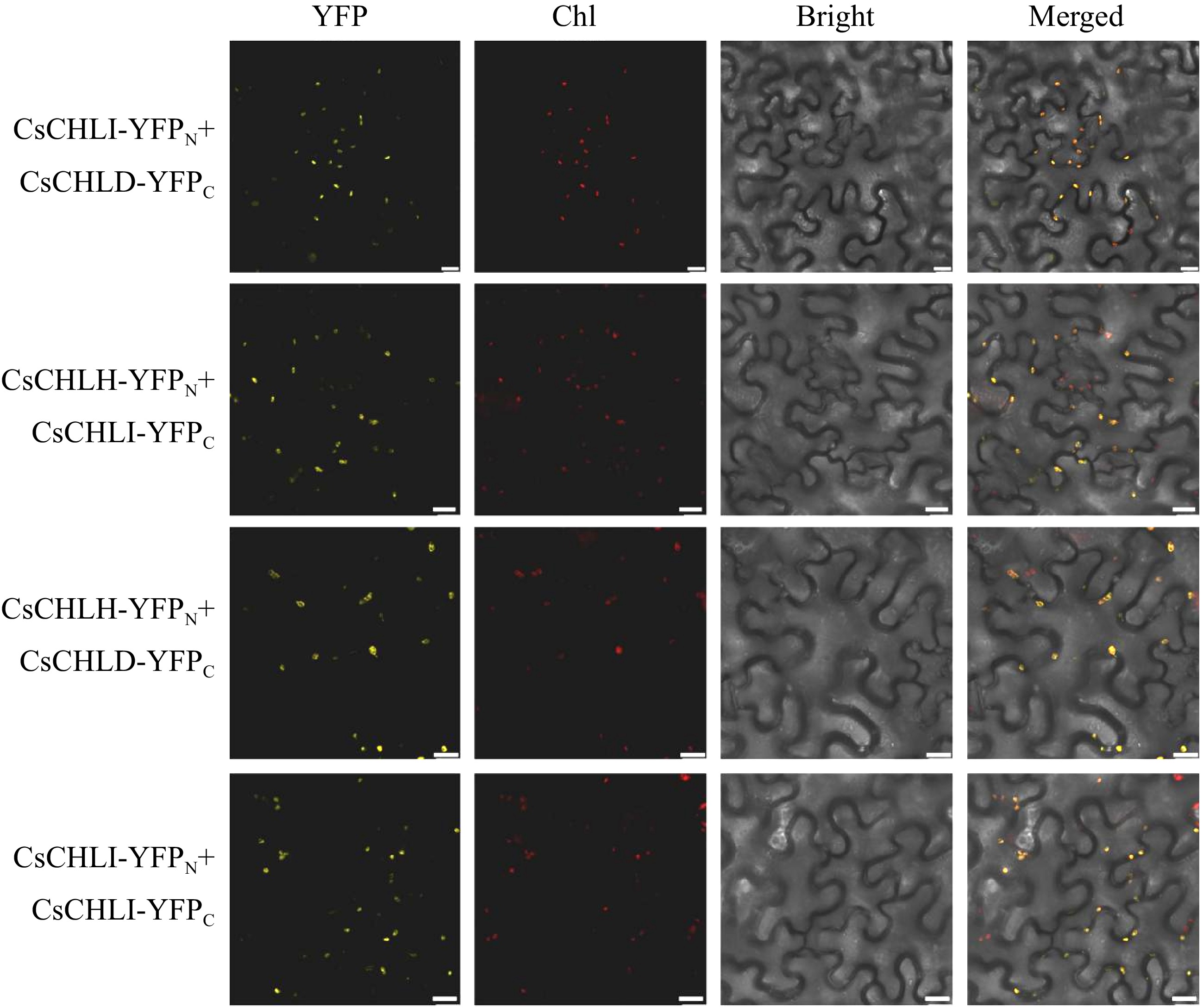
Figure 5.
BiFC assay for examining the interactions of CsCHLI, CsCHLD, and CsCHLH. YFP Fluorescence (YFP), Chlorophyll autofluoresence (Chl), bright-filed (Bright), and Merged images (Merged). The scale bar is 20 μm.
-
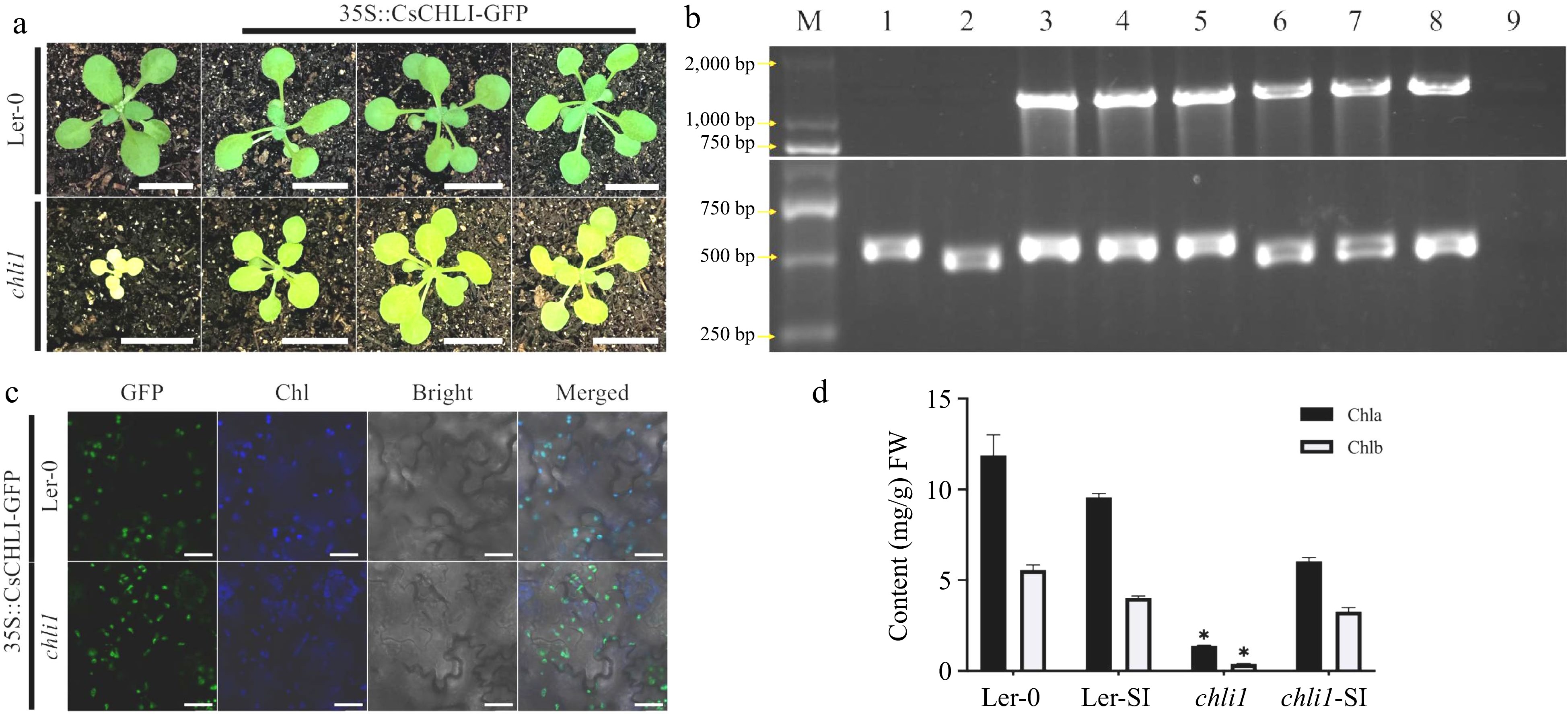
Figure 6.
CsCHLI could restore the yellow leaf phenotype in Arabidopsis. (a) The phenotype of 4-week old Arabidopsis in different lines. Ler-0 wild type background (Ler-0), atchli1 mutant in Ler-0 wild type background (atchli1) and transgenic atchli1 mutants or Ler-0 carrying 35S-driven fused CsCHLI. Scale bar is 1 cm. (b) The identification of different Arabidopsis lines. M: DNA marker, 1: Ler-0, 2: atchli1, 3-5: Ler-0 carrying CsCHLI, 6-8: atchli1 carrying 35::CsCHLI-GFP, 9: water. (c)The fluoresence of different Arabidopsis transgenic lines. YFP Fluorescence (YFP), Chlorophyll autofluoresence (Chl), bright-filled (Bright), and Merged images (Merged). Chlorophyll autofluoresence (Chl) changes to blue. The scale bar is 20 μm. (d) Content of Chlorophyll in different Arabidopsis lines. Ler-SI: Ler-0 carrying 35::CsCHLI-GFP, atchli1-SI: atchli1 carrying 35::CsCHLI-GFP. *: p ≤ 0.05.
Figures
(6)
Tables
(0)