-
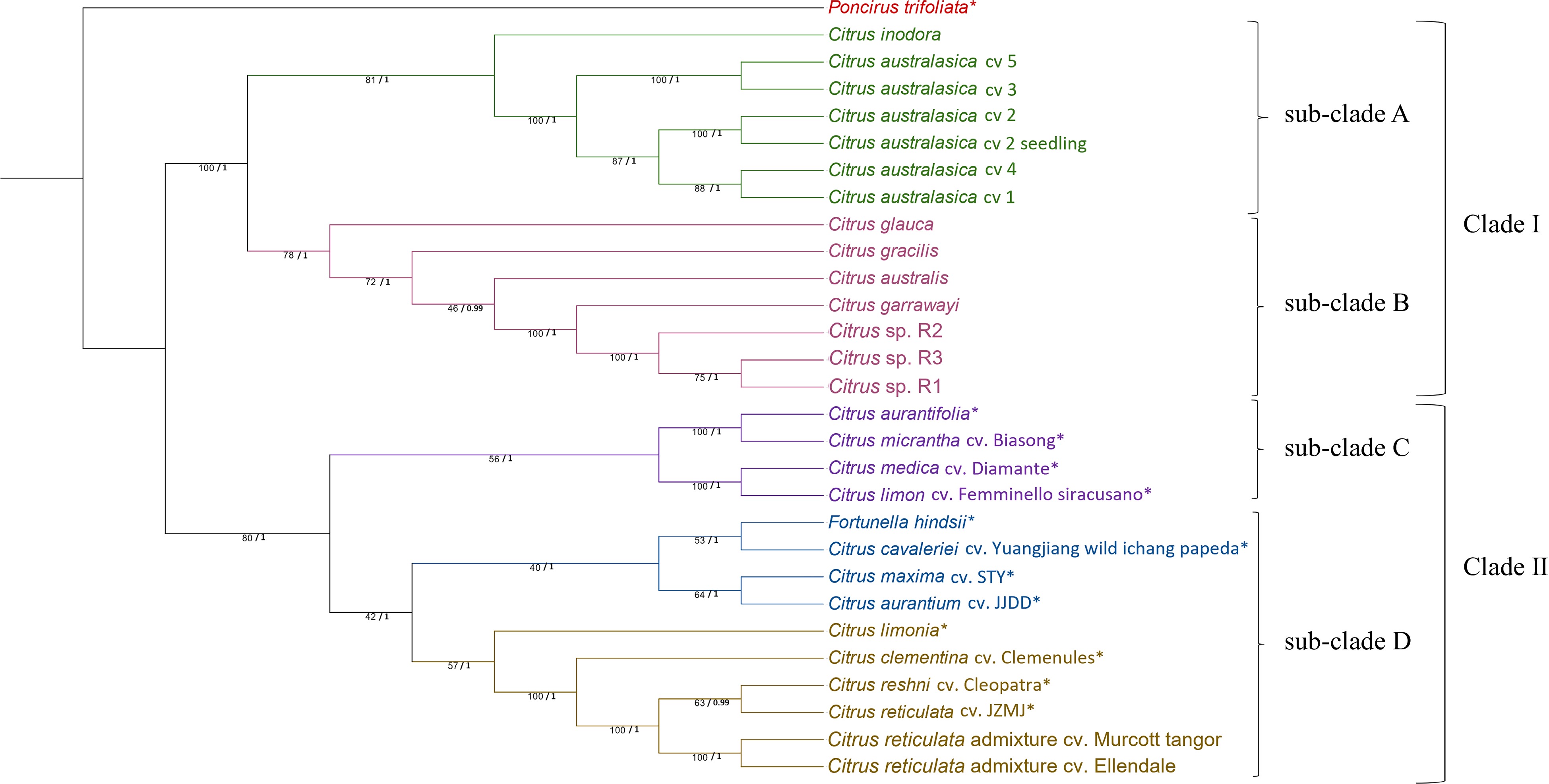
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree generated from 86 nuclear genes sequences of 29 citrus samples (species/cultivars) with Poncirus trifoliata as the outgroup. The tree was generated using Maximum Likelihood (ML) method in RAxML with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. ML bootstrap values from 1,000 replicates (/100) and posterior probability values are indicated on each node respectively. * SRA data obtained from National Centre for Biotechnology Information for nuclear genes assembly. Citrus sp. R1, R2 and R3 refers to three different seedlings of the Citrus sp.
-
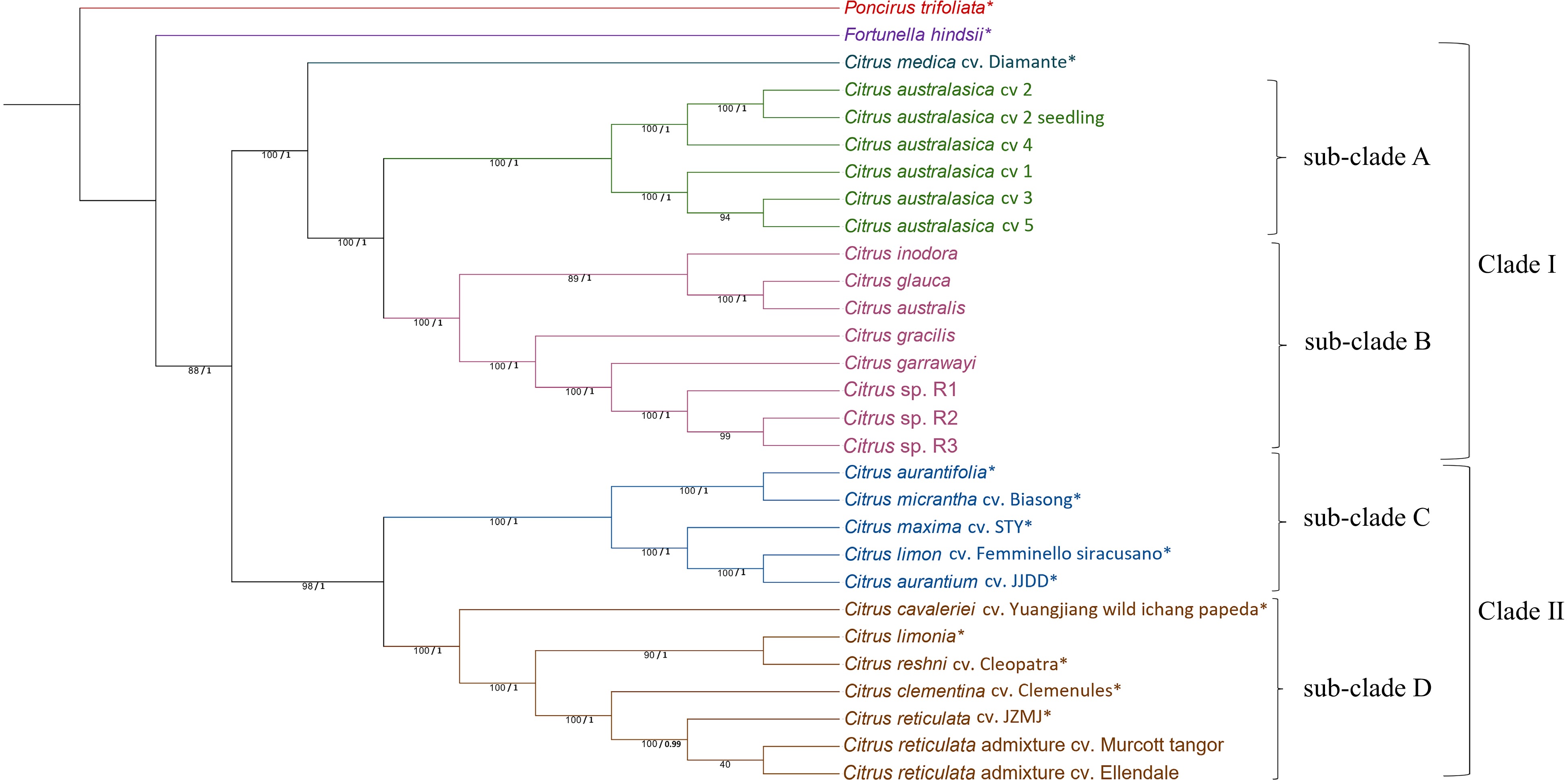
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree generated from complete chloroplast genome sequences of 29 citrus samples (species/cultivars) with Poncirus trifoliata as the outgroup. The tree was generated using Maximum Likelihood (ML) method in RAxML with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. ML bootstrap values from 1,000 replicates (/100) and posterior probability values are indicated on each node respectively. * SRA data obtained from National Centre for Biotechnology Information for chloroplast genome assembly. Chloroplast genome for P. trifoliata which was assembled by GetOrganelle toolkit was obtained from[34]. Citrus sp. R1, R2 and R3 refers to three different seedlings of the Citrus sp.
-
Species Cultivar Genome size (bp) LSC (bp) SSC (bp) IR (bp) Genes CDS tRNA genes rRNA genes C. australasica cv 1 160,400 87,686 18,757 26,952 113 78 31 4 C. australasica cv 2 160,400 87,723 18,759 26,959 113 78 31 4 C. australasica cv 3 160,335 87,677 18,754 26,952 113 78 31 4 C. australasica cv 4 160,365 87,692 18,755 26,959 113 78 31 4 C. australasica cv 5 160,335 87,677 18,754 26,952 113 78 31 4 C. australis N/A 160,530 87,882 18,760 26,944 114 78 32 4 C. garrawayi N/A 160,495 87,780 18,769 26,973 115 79 32 4 C. glauca N/A 160,570 87,849 18,763 26,979 114 78 32 4 C. gracilis N/A 160,372 87,652 18,752 26,984 115 79 32 4 C. inodora N/A 160,669 87,945 18,728 26,998 114 78 32 4 C. sp. R1 N/A 160,585 87,866 18,787 26,966 115 79 32 4 C. sp. R2 N/A 160,572 87,853 18,787 26,966 115 79 32 4 C. sp. R3 N/A 160,572 87,853 18,787 26,966 115 79 32 4 C. aurantifolia − 159,882 87,137 18,763 26,991 115 79 32 4 C. aurantium JJDD 160,140 87,755 18,385 27,000 115 79 32 4 C. cavaleriei Yuangjiang wild
ichang papeda160,997 87,634 18,763 27,300 115 79 32 4 C. clementina Clemenules 160,722 87,941 18,801 26,990 115 79 32 4 C. limon Femminello
siracusano160,141 87,754 18,385 27,001 115 79 32 4 C. limonia − 160,715 87,910 18,789 27,008 115 79 32 4 C. maxima STY 160,186 87,791 18,395 27,000 115 79 32 4 C. medica Diamante 160,048 87,490 18,576 26,991 115 79 32 4 C. micrantha Biasong 159,923 87,178 18,763 26,991 115 79 32 4 C. reshni Cleopatra 160,666 87,866 18,784 27,008 115 79 32 4 C. reticulata JZMJ 160,699 87,918 18,801 26,990 115 79 32 4 C. reticulata admixture Murcott 160,699 87,918 18,801 26,990 115 79 32 4 C. reticulata admixture Ellendale 160,699 87,918 18,801 26,990 115 79 32 4 F. hindsii − 160,265 87,587 18,734 26,972 115 79 32 4 P. trifoliata − 160,260 87,442 18,760 27,029 115 79 32 4 Table 1.
Characteristics of the chloroplast genomes of 28 citrus samples.
Figures
(2)
Tables
(1)