-
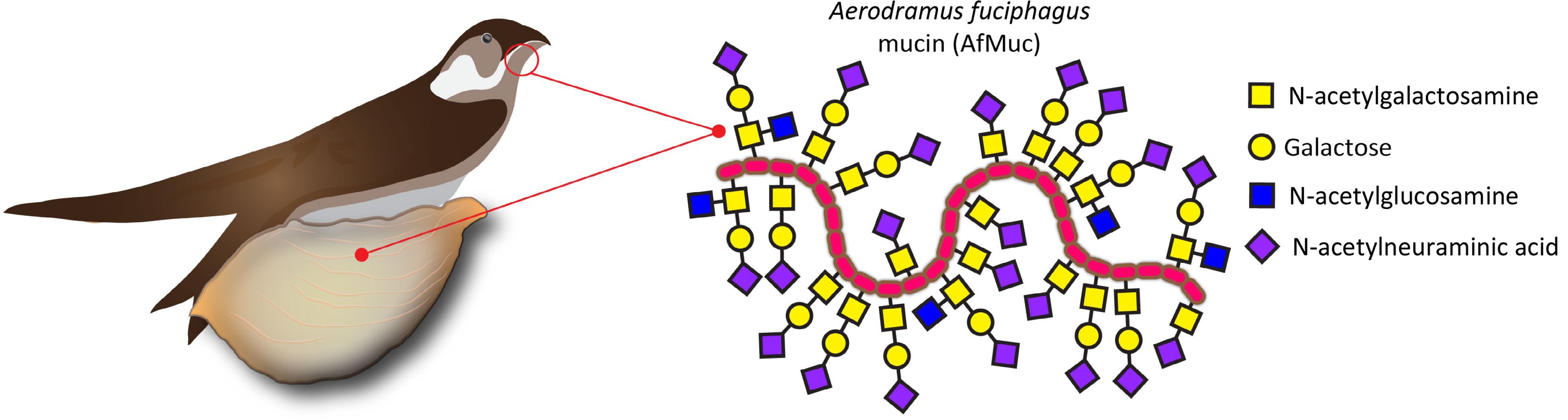
Figure 1.
EBN is produced by male swiftlets' salivary glands. The largest portion of this dried saliva consists of mucins, which are proteins heavily decorated with complex carbohydrates linked via N-acetylgalactosamine to the AfMuc protein backbone.
-
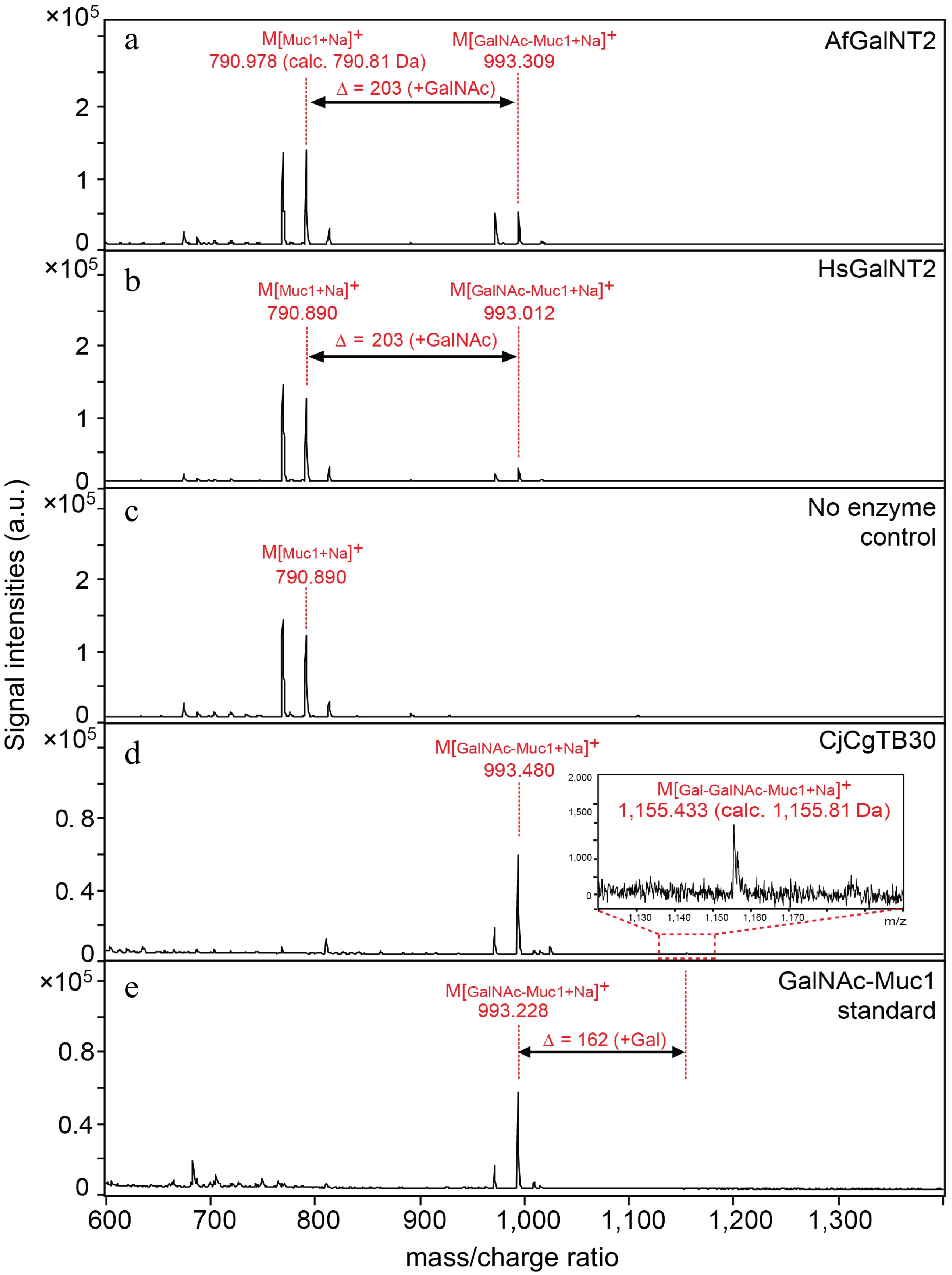
Figure 2.
Activity of AfGalNT2 and HsGalNT2 towards the Muc1 peptide substrate. Reaction mixtures containing the Muc1 peptide in the presence of UDP-GalNAc and (a) AfGalNT2; (b) HsGalNT2; (c) no enzyme; (d) Galactosylation reaction of the GalNAc-Muc1 glycopeptide substrate in the presence of CjCgTB30 enzyme and UDP-galactose; (e) reaction mixtures without CjCgTB30.
-
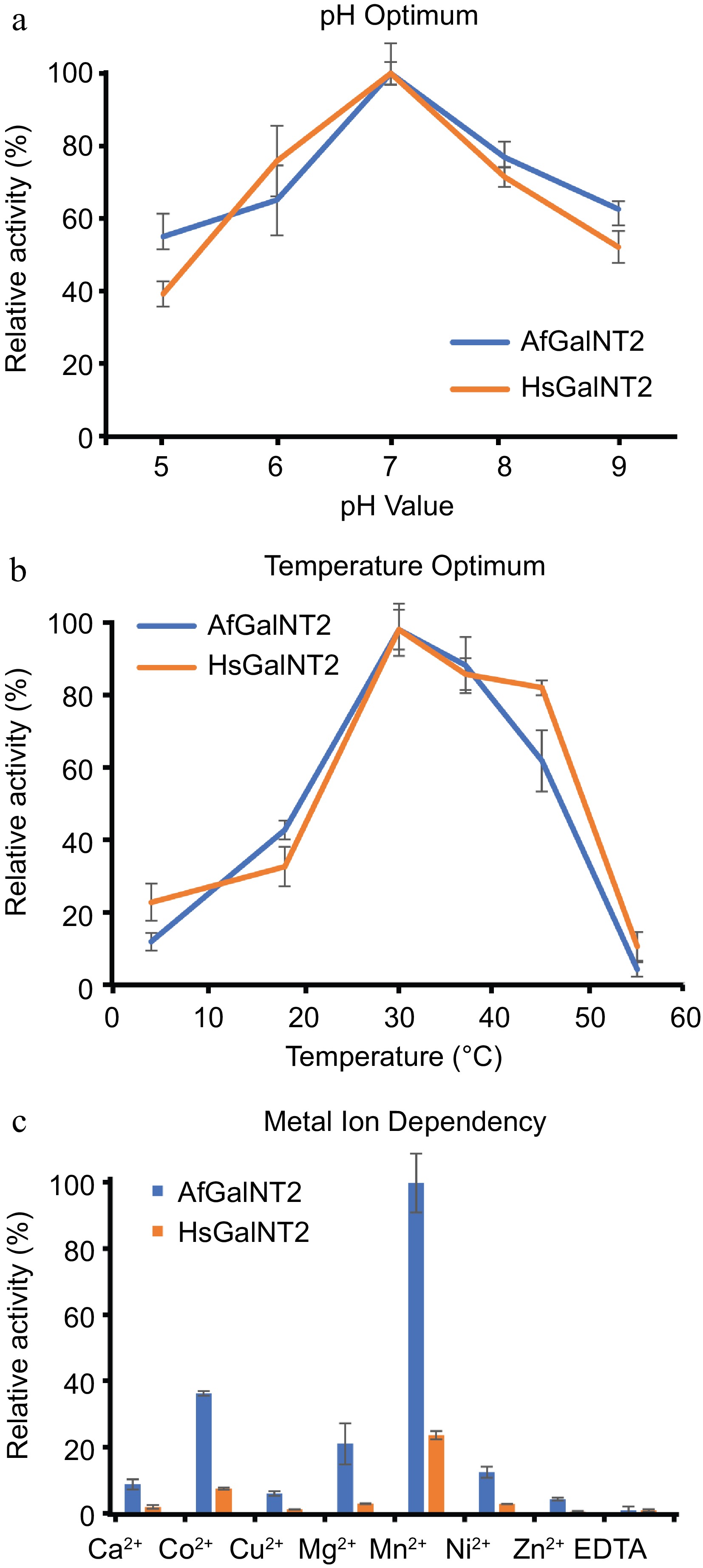
Figure 3.
Biochemical characterization of AfGalNT2 and HsGalNT2. The following parameters were measured for both enzymes using the EA2 peptide: (a) pH optimum, (b) temperature optimum and (c) metal ion dependence.
-
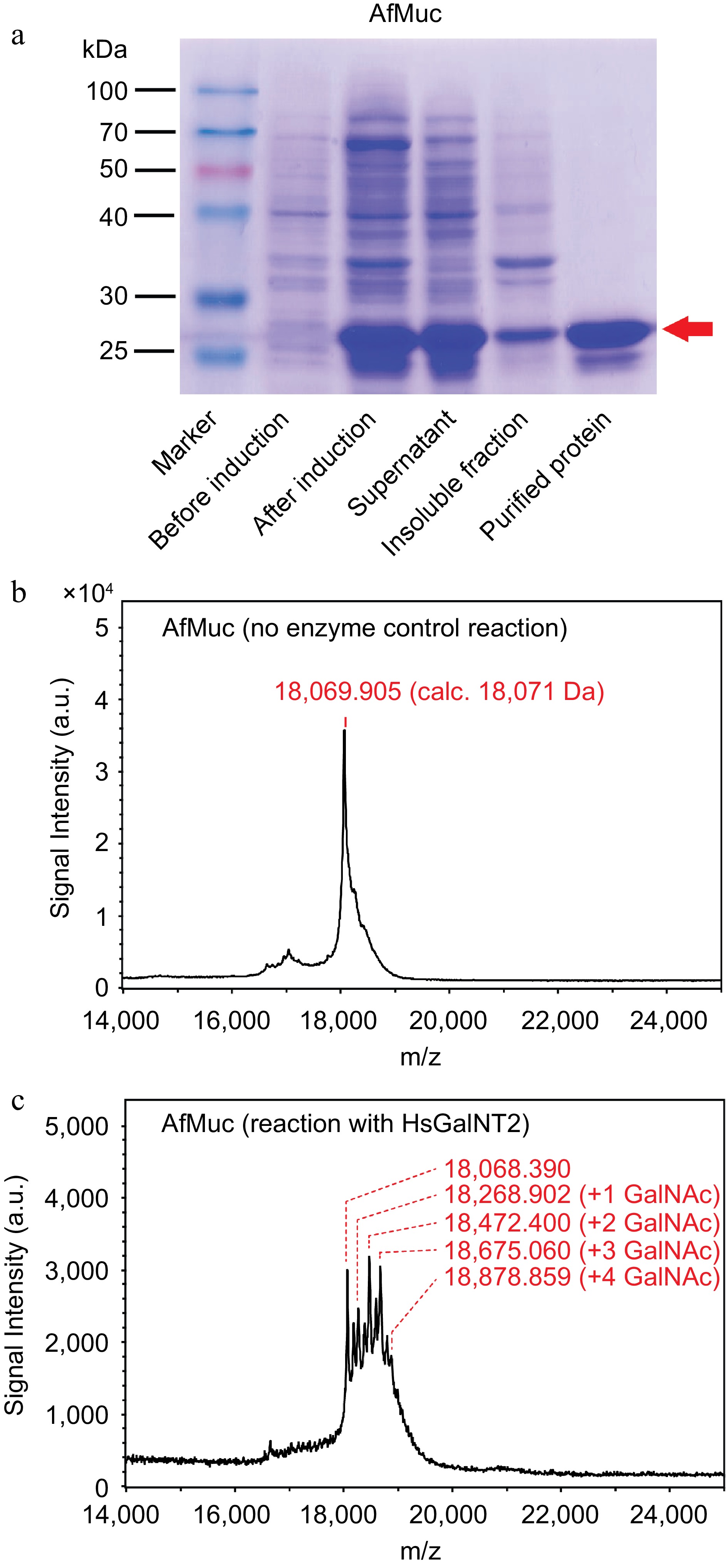
Figure 4.
Purification and in vitro glycosylation of AfMuc. (a) SDS-PAGE analysis of AfMuc during expression and purification. The red arrow indicates the position of the desired purified protein. (b) MALDI-ToF MS analysis of recombinant AfMuc without the presence of HsGalNT2. (c) MALDI-ToF MS analysis of recombinant AfMuc in the presence of HsGalNT2. The intermediate-mass peaks between discrete GalNAc units may be the result of terminal proteolysis of the recombinant AfMuc protein backbone.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(0)