-
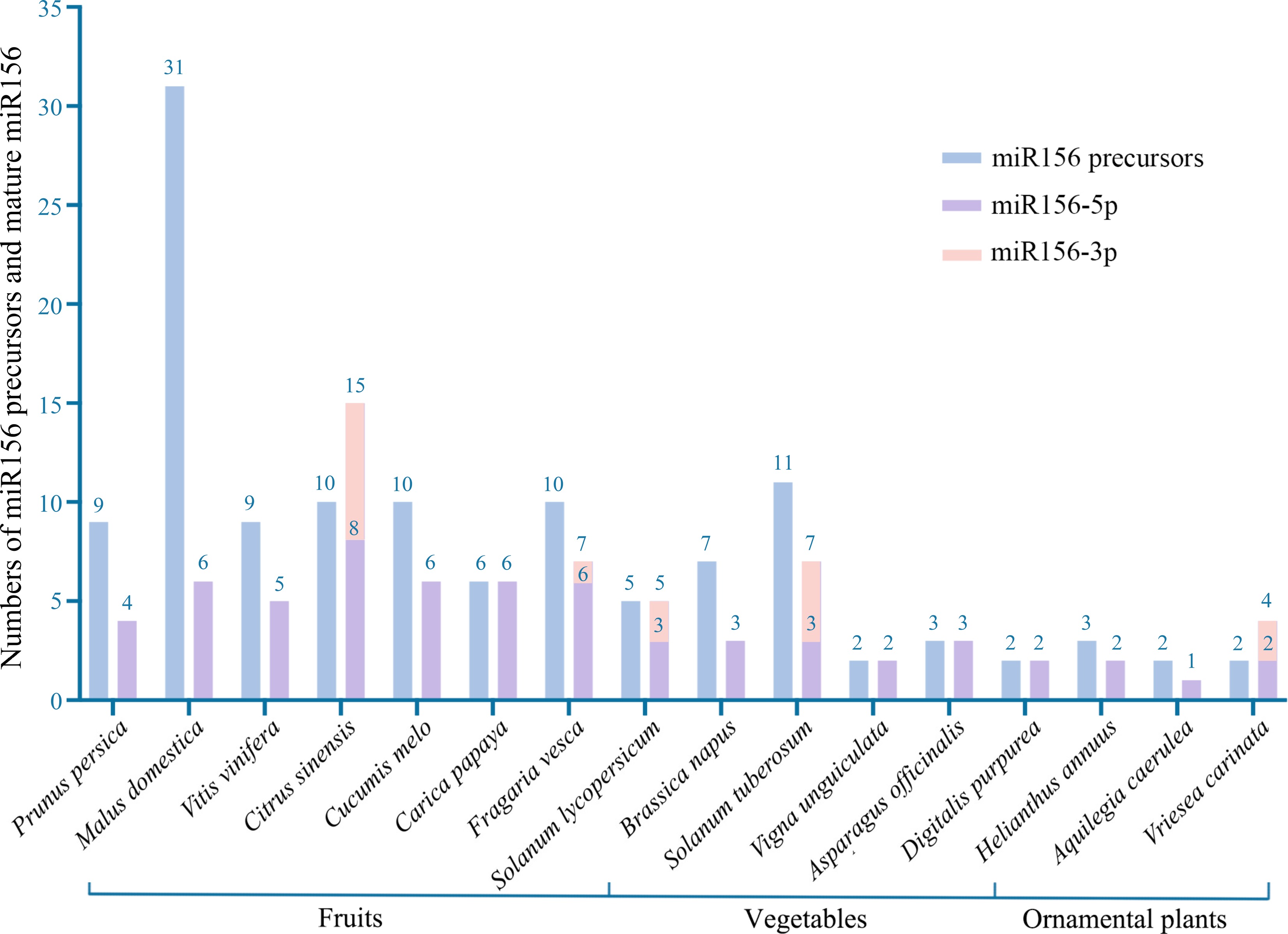
Figure 1.
Number of miR156 precursors and unique mature sequences in horticultural plants published in the miRbase database. Identical mature sequences from different precursors were considered as one sequence.
-
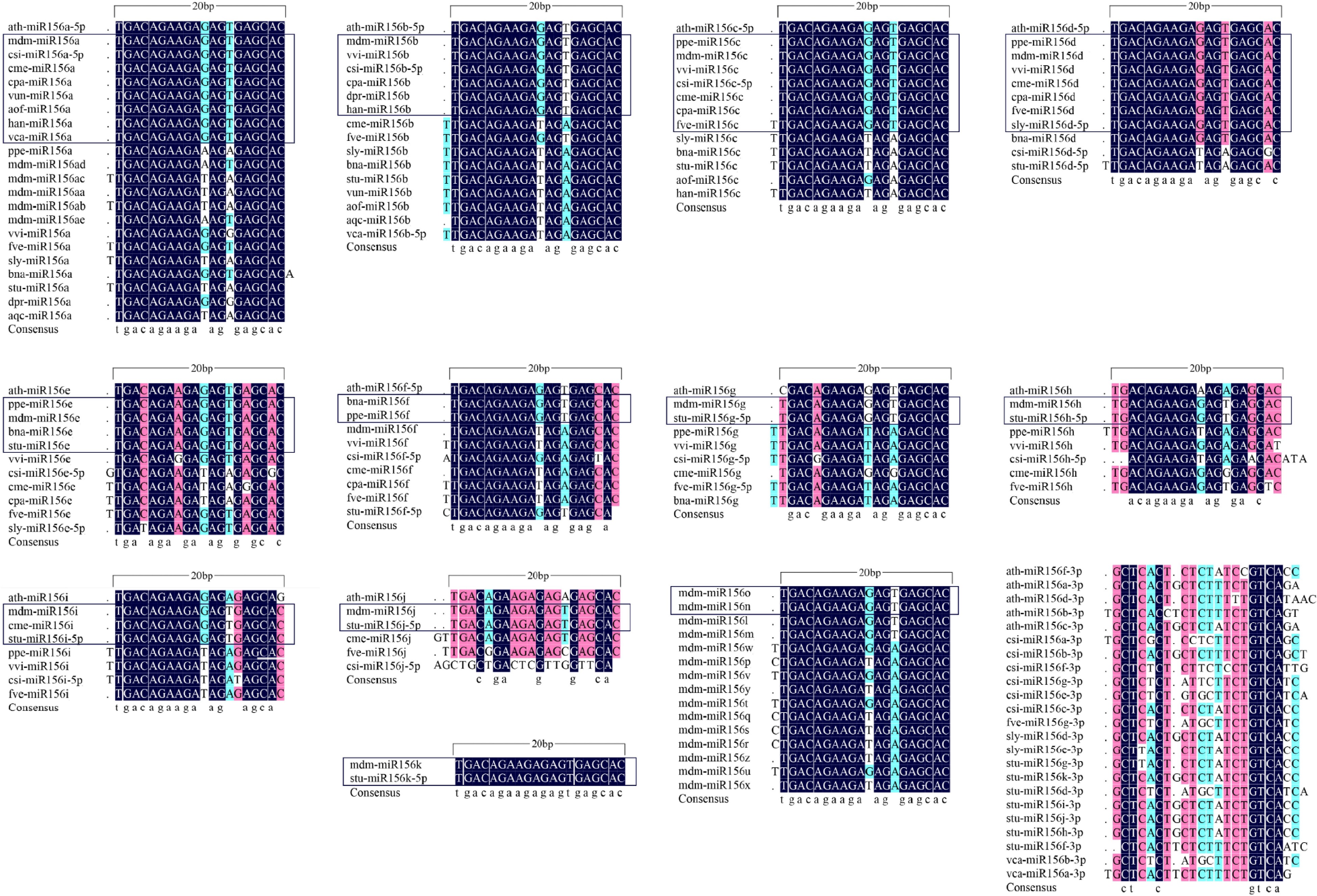
Figure 2.
Alignment of orthologous miR156 subfamilies from Arabidopsis and horticultural plants. A total of 138 miR156 mature sequences from 16 different horticultural plants were aligned. The sequences boxed in black are miR156 seed sequences. ath: Arabidopsis thaliana; mdm: Malus domestica; csi: Citrus sinensis; cme: Cucumis melo; cpa: Carica papaya; vun: Vigna unguiculata; aof: Asparagus officinalis; han: Helianthus annuus; vca: Vriesea carinata; ppe: Prunus persica; vvi: Vitis vinifera; fve: Fragaria vesca; sly: Solanum lycopersicum; bna: Brassica napus; stu: Solanum tuberosum; dpr: Digitalis purpurea; aqc: Aquilegia caerulea. The miR156 sequences were downloaded from the miRbase database. Sequences are listed in Supplemental Table S1.
-
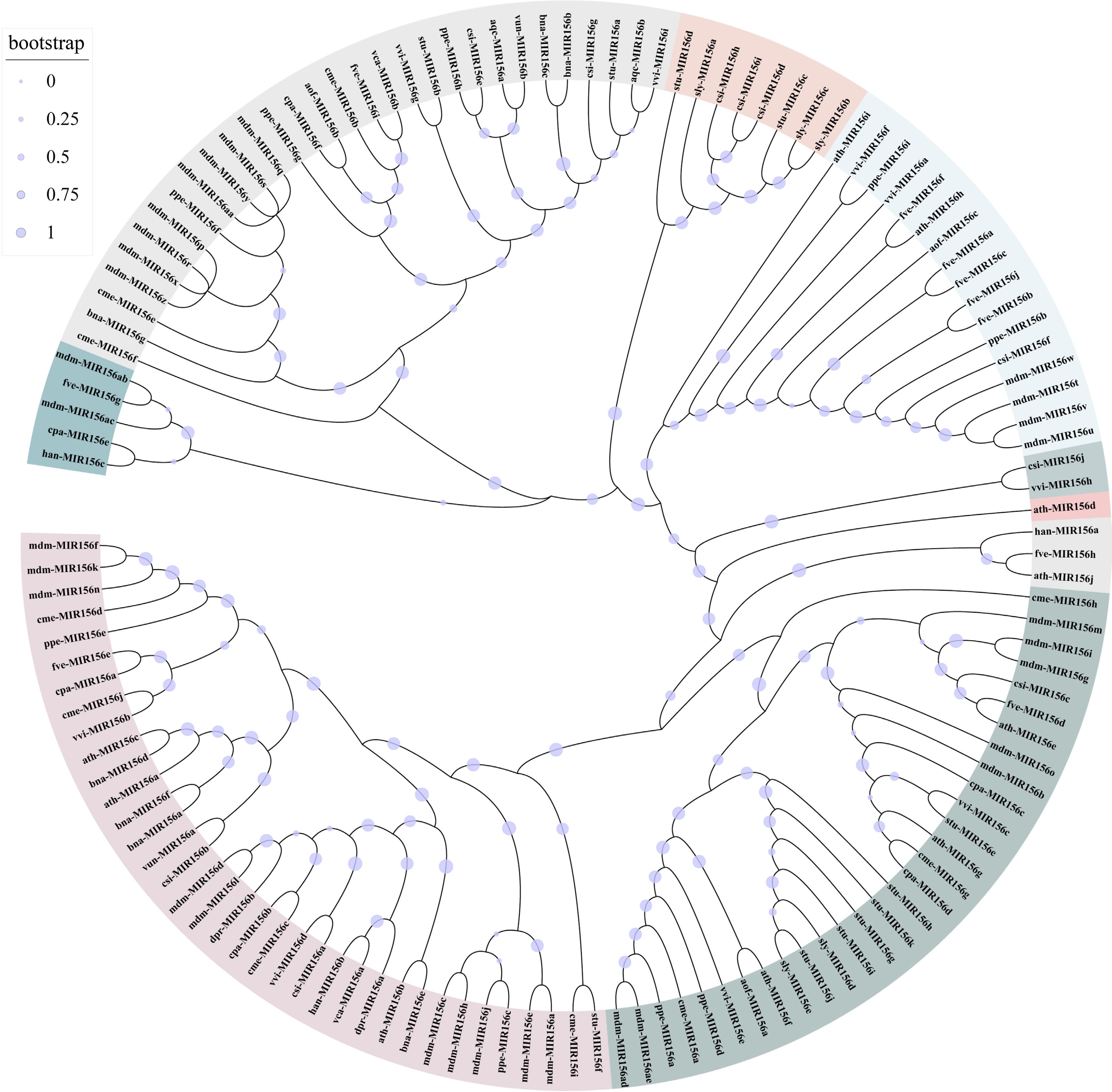
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic relationships between MIR156 from different plants. A total of 122 MIR156 sequences were phylogenetically analyzed. ath: Arabidopsis thaliana; mdm: Malus domestica; csi: Citrus sinensis; cme: Cucumis melo; cpa: Carica papaya; vun: Vigna unguiculata; aof: Asparagus officinalis; han: Helianthus annuus; vca: Vriesea carinata; ppe: Prunus persica; vvi: Vitis vinifera; fve: Fragaria vesca; sly: Solanum lycopersicum; bna: Brassica napus; stu: Solanum tuberosum; dpr: Digitalis purpurea; aqc: Aquilegia caerulea. The MIR156 sequences were downloaded from the miRbase database. Sequences are listed in Supplemental Table S2.
-
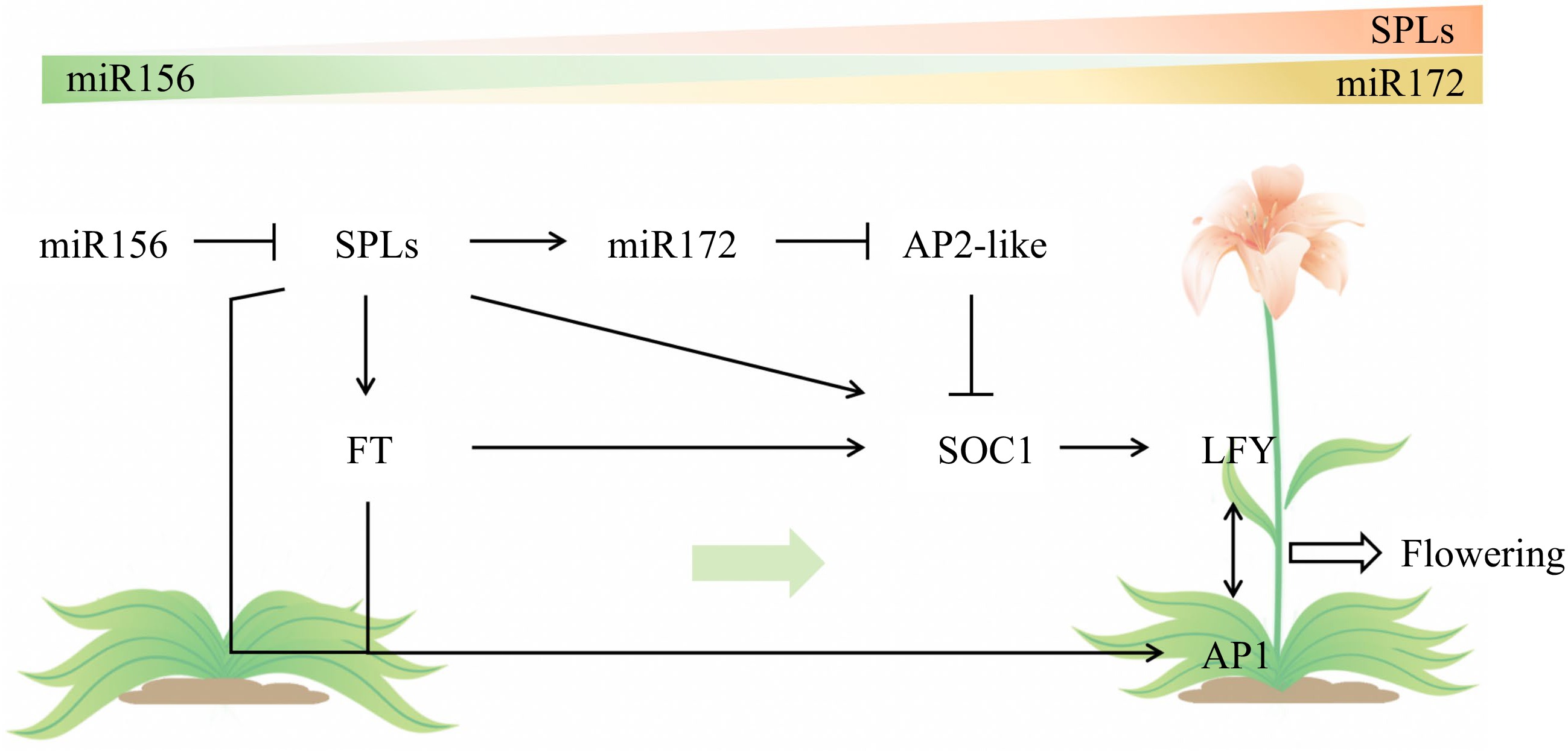
Figure 4.
Age pathway for flowering defined by the miR156-SPL module.
-
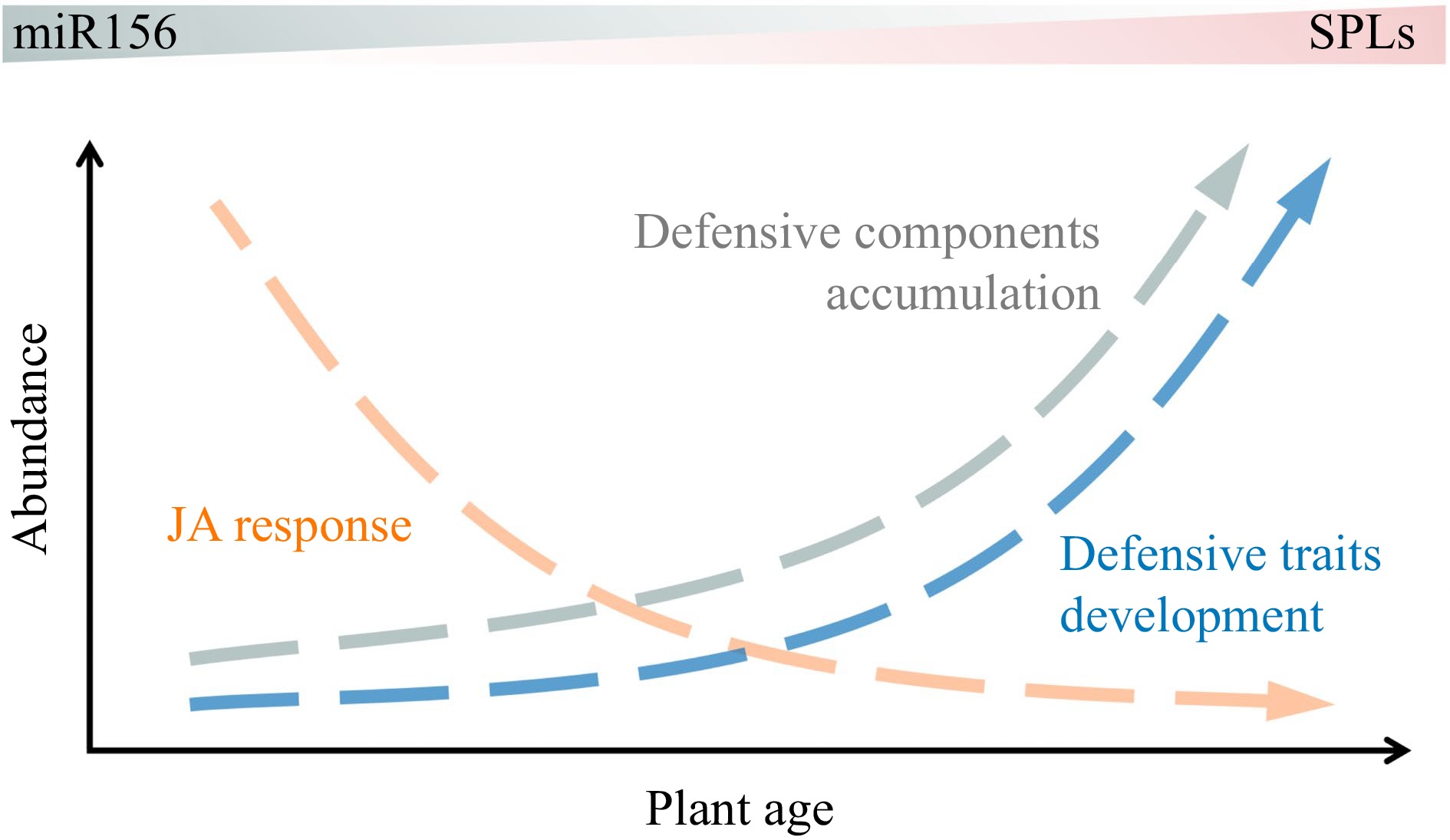
Figure 5.
Age-dependent change in plant resistance to biotic stress.
-
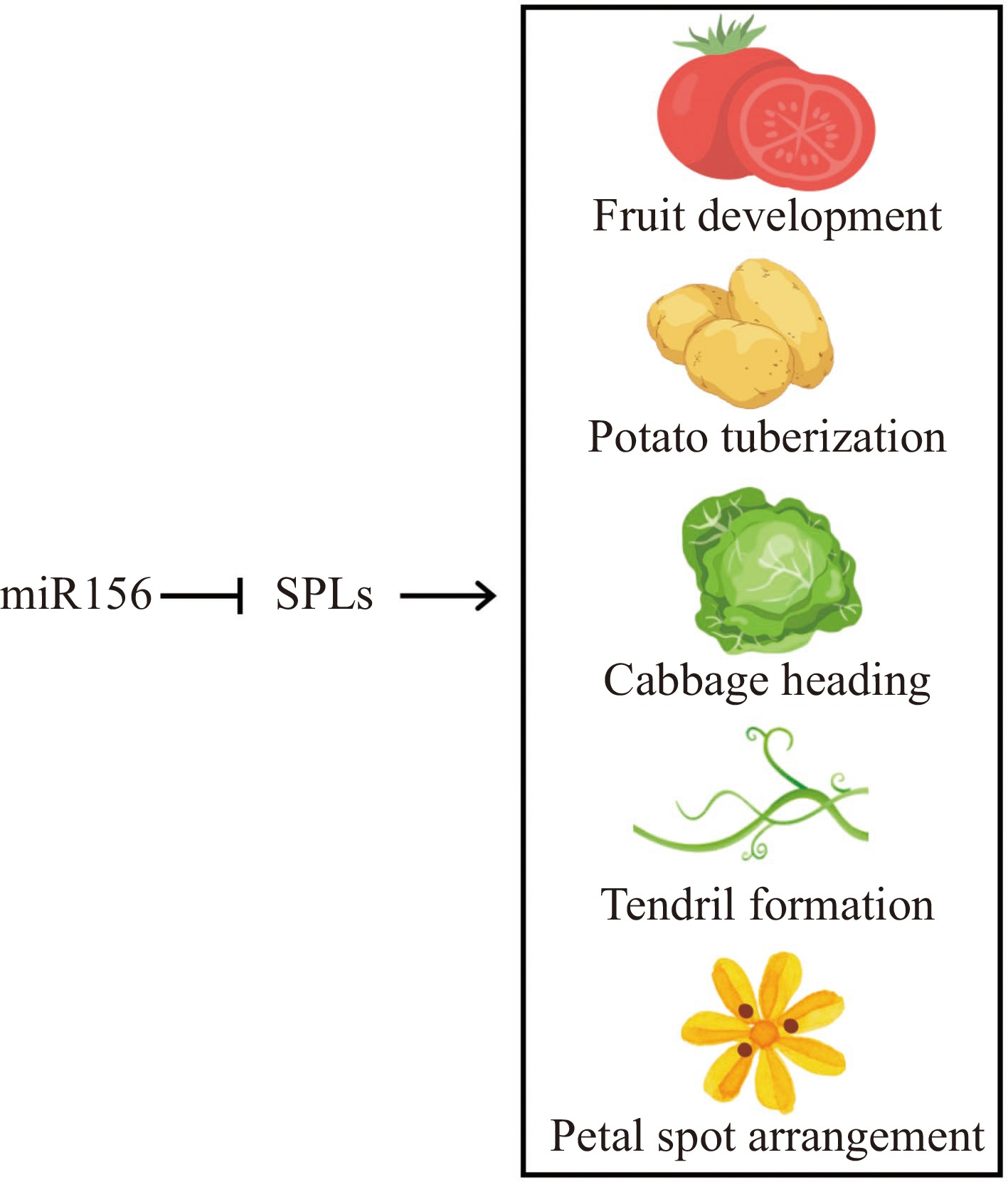
Figure 6.
miR156-SPL module regulates special horticultural traits.
-
Classification Species Growth and development Stress response Others Ref. Vegetables Solanum tuberosum Tuberization; development of leaves, trichomes, branches, lateral roots and inflorescences Cytokinin and strigolactone level [61, 101] Solanum lycopersicum Development of leaves, branches and trichomes; floral induction and flower development; ovary and fruit development Drought, cold; Botrytis cinerea infection [9, 20, 36, 48 ,
59, 60, 75, 86]Brassica campestris Vegetative phase change; heading Heat [29, 85] Cucumis sativus Tendril formation; vegetative phase change [15,16] Brassica alboglabra Seed development [102] Brassica oleracea Xanthomonas campestris infection [103] Lactuca sativa Seed dormancy [94] Fruits Malus spp. Vegetative phase change; adventitious root formation Salt, drought Browning inhibition [19, 92, 93,
104, 105]Citrus sinensis Vegetative phase change Somatic embryogenesis [99, 100] Vitis vinifera Vegetative phase change; flower development in winter; grape berry development and ripening [65, 106, 107] Citrus × paradise Vegetative phase change [108] Morus atropurpurea Vegetative phase change Silkworm herbivory [25, 81] Passiflora edulis Vegetative phase change [48] Saccharum officinarum Cold, drought and salt [83] Musa acuminata Fruit ripening Heat [58, 84] Pyrus spp. Red peel coloration Apple stem pitting virus infection Anthocyanin biosynthesis [63, 74] Vaccinium corymbosum Fruit coloration Anthocyanin biosynthesis and chlorophyll degradation [64] Litchi chinensis Flowering Anthocyanin biosynthesis [49, 66] Ornamental plants Paeonia lactiflora Flower coloration Anthocyanin biosynthesis [10, 53] Paeonia delavayi Vegetative phase change [26] Chrysanthemum morifolium Flowering time [42] Rosa chinensis Vegetative phase change; flowering time [109, 110] Vachellia cornigera Herbivore defense [82] Paulownia fortunei Paulownia witches' broom (PaWB) infection [111] Pogostemon cablin Sesquiterpene biosynthesis [70] Gorteria diffusa Petal spot placement [54] Lilium Oriental Trumpet Vegetative phase change [28] Viburnum macrocephalum Differentiation of fertile and sterile flowers [55] Cymbidium goeringii Reproductive organ development [56] Dendrobium catenatum Vegetative phase change [27] Petunia spp. Development of branches and internodes; flowering time [43] Tea plants Camellia sinensis Double flower domestication Colletotrichum gloeosporioides infection Taste compound (catechin, caffeine, and theanine) biosynthesis [51, 68,
69, 76, 77]Table 1.
Biological functions of miR156 in horticultural plants.
Figures
(6)
Tables
(1)