-
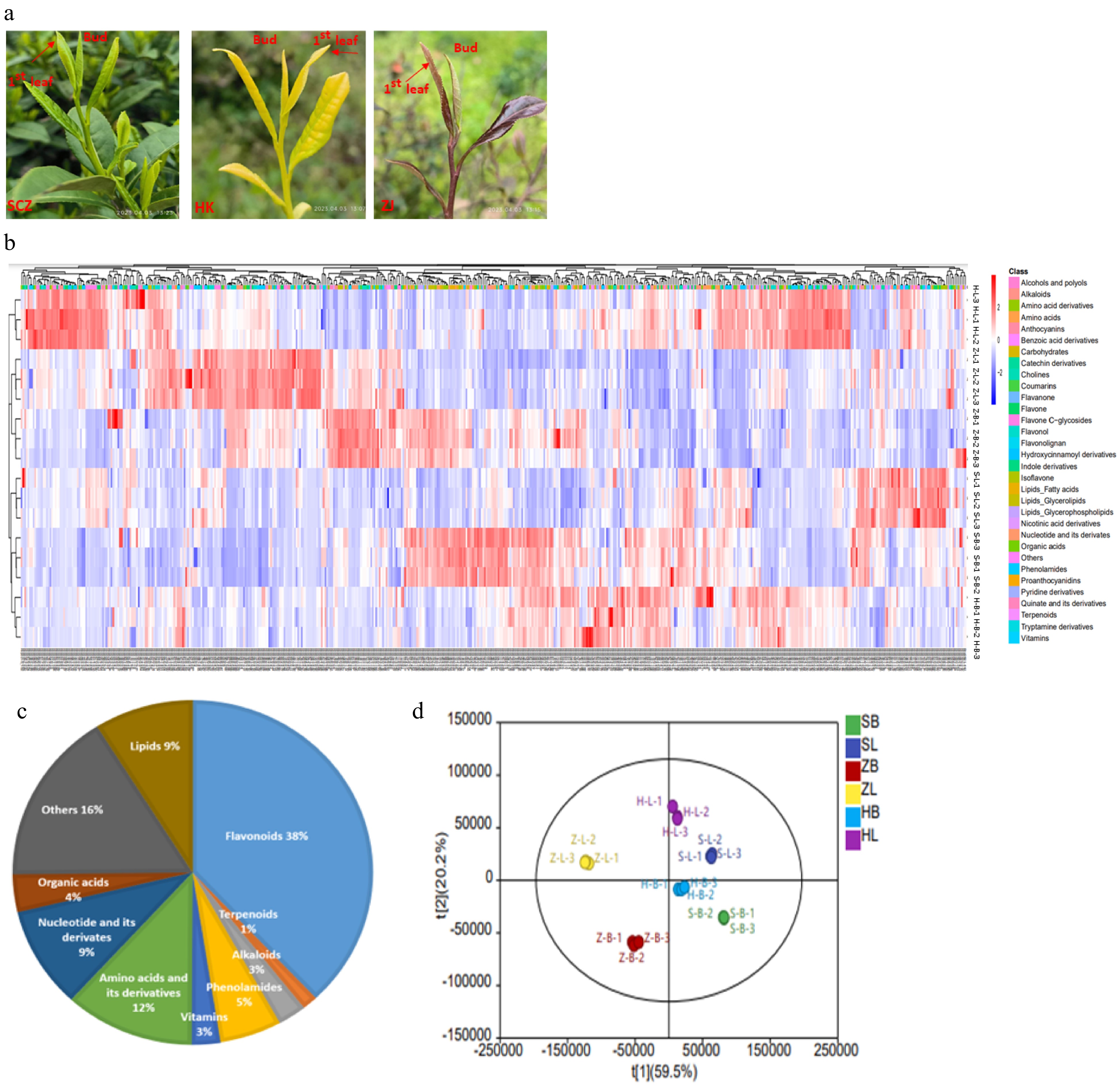
Figure 1.
Detection and identification of specialized metabolites. (a) The phenotypes of two tissues of the three cultivars. 'Shuchazao' (SCZ), 'Huangkui' (HK) and 'Zijuan' (ZJ). (b) Clustering heatmap tree of total metabolites of two tissues of the three cultivars. Z-scores normalize the value. Red indicates a high abundance, and blue indicates a low relative abundance of metabolites. (c) Composition and proportion of different metabolites in different tea cultivars. (d) PCA of the metabolites in different tissues of tea plants. SB: SCZ-bud; ZB: ZJ-bud; HB: HK-bud; SL: SCZ-leaf; ZL: ZJ-leaf; HL: HL-leaf.
-
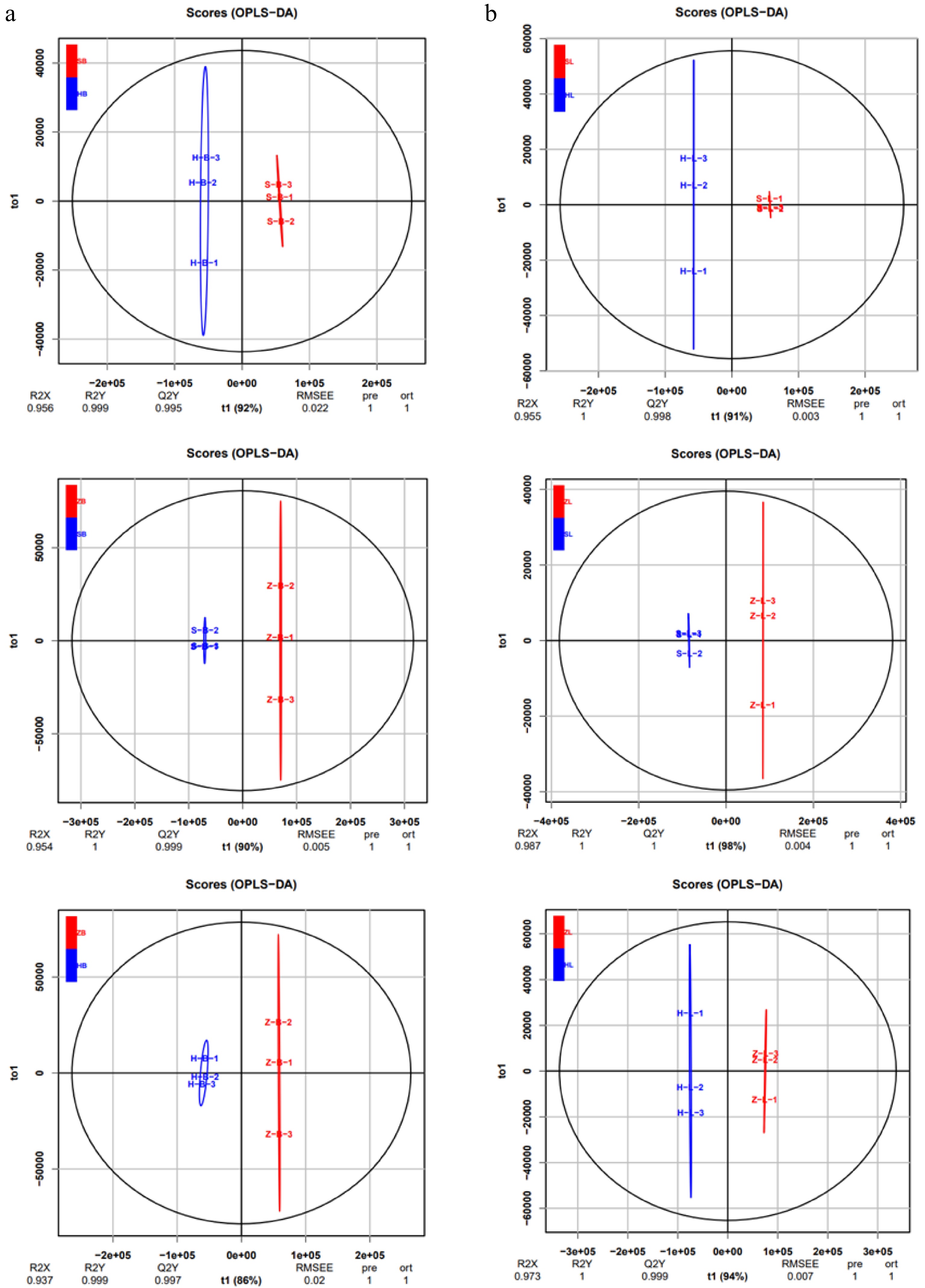
Figure 2.
Differential metabolite analysis by OPLS-DA.
-
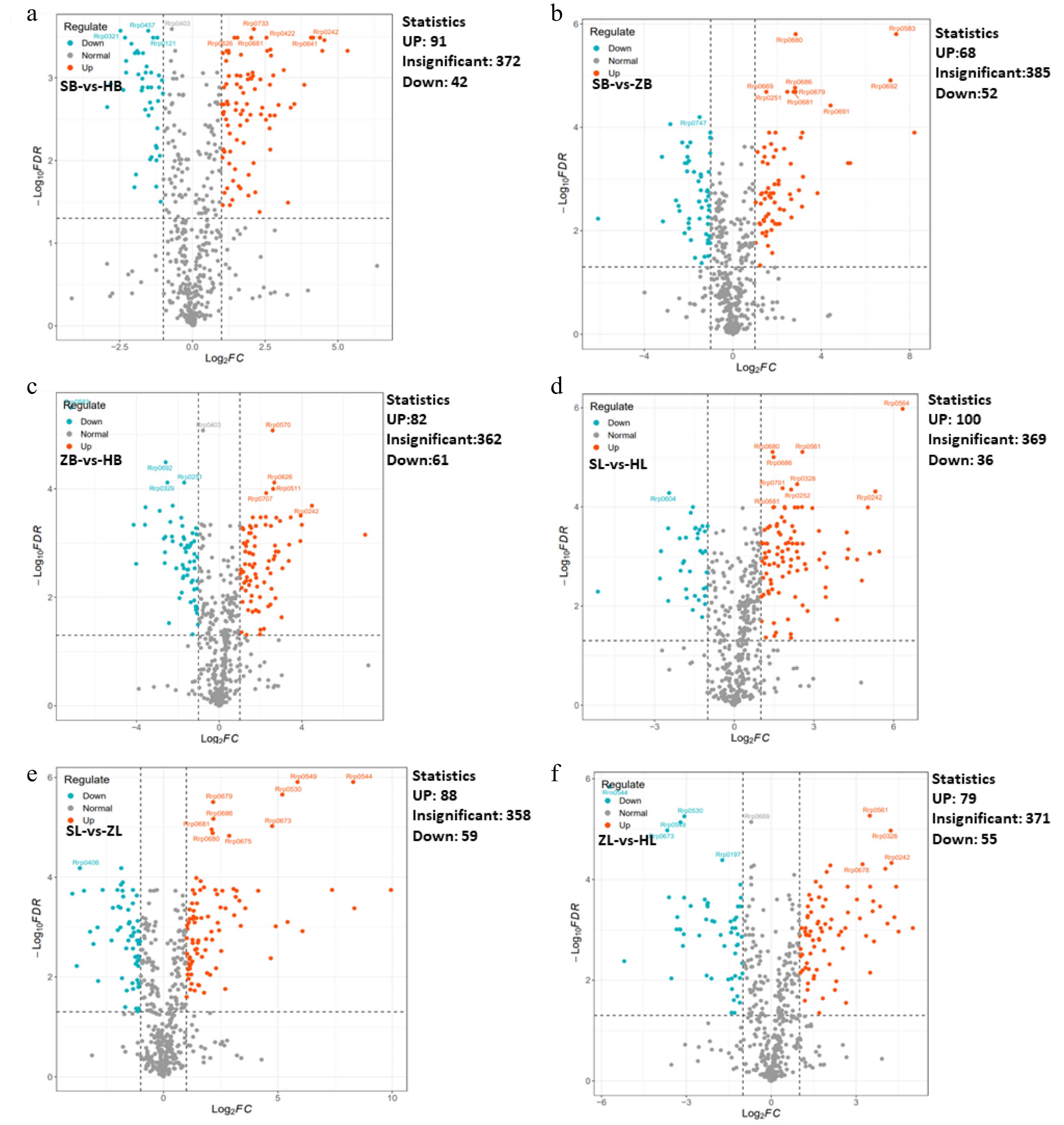
Figure 3.
Volcano plots showing the differential metabolite expression levels.
-
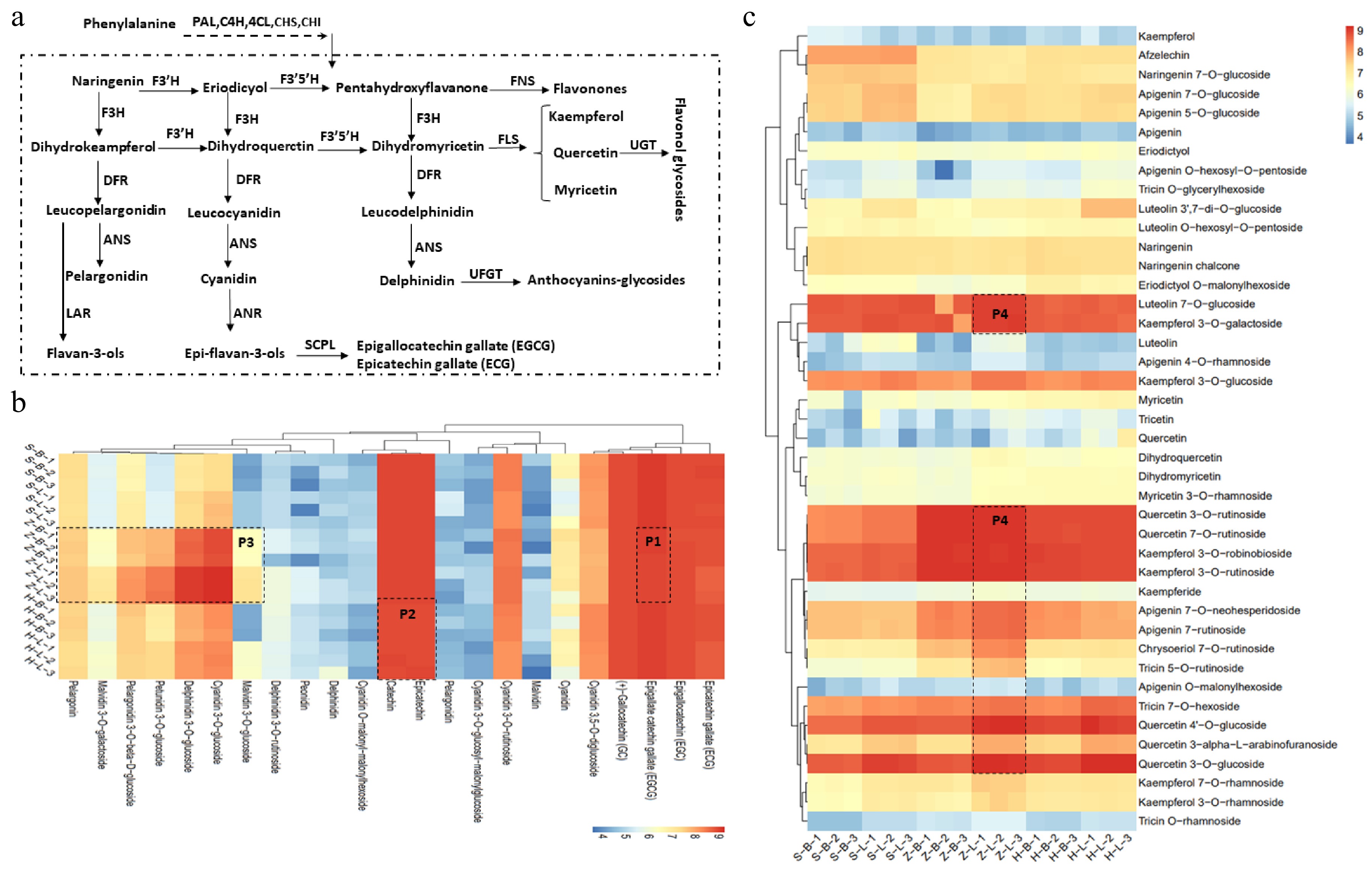
Figure 4.
Phenylpropanoid pathways toward the biosynthesis of flavonoids in tea plants. (a) Flavonoid biosynthesis pathways in tea plant. (b), (c) Catechins, flavonoids and anthocyanin relative content in different tissues of SCZ, HK and ZJ plants. CHS: Chalcone synthase; CHI: Chalcone isomerase; C4H: Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; DFR: Dihydroflavonol reductase; EGC: Epigallocatechin; ECG: Epicatechin-3-gallate; F3H: flavonoid 3-hydroxylase; F3'H: Flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase; F3'5'H: Flavonoid 3'5'-hydroxylase; FNS: flavone synthase; FLS: Flavonol synthase; LAR: Leuacoanthocyanidin reductase; PAL: Phenylalanine ammonialyase; 4CL: 4-Coumarate:CoA ligase; HCT: Hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA: shikimate hydroxycinnamoyl transferase1; SCPL: Serine carboxypeptidase-like Clade 1A; UGT: UDP-Glucose flavonoid 3-O-glucosyl transferase; C: Catechin; EC: Epicatechin; EGCG: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate.
-
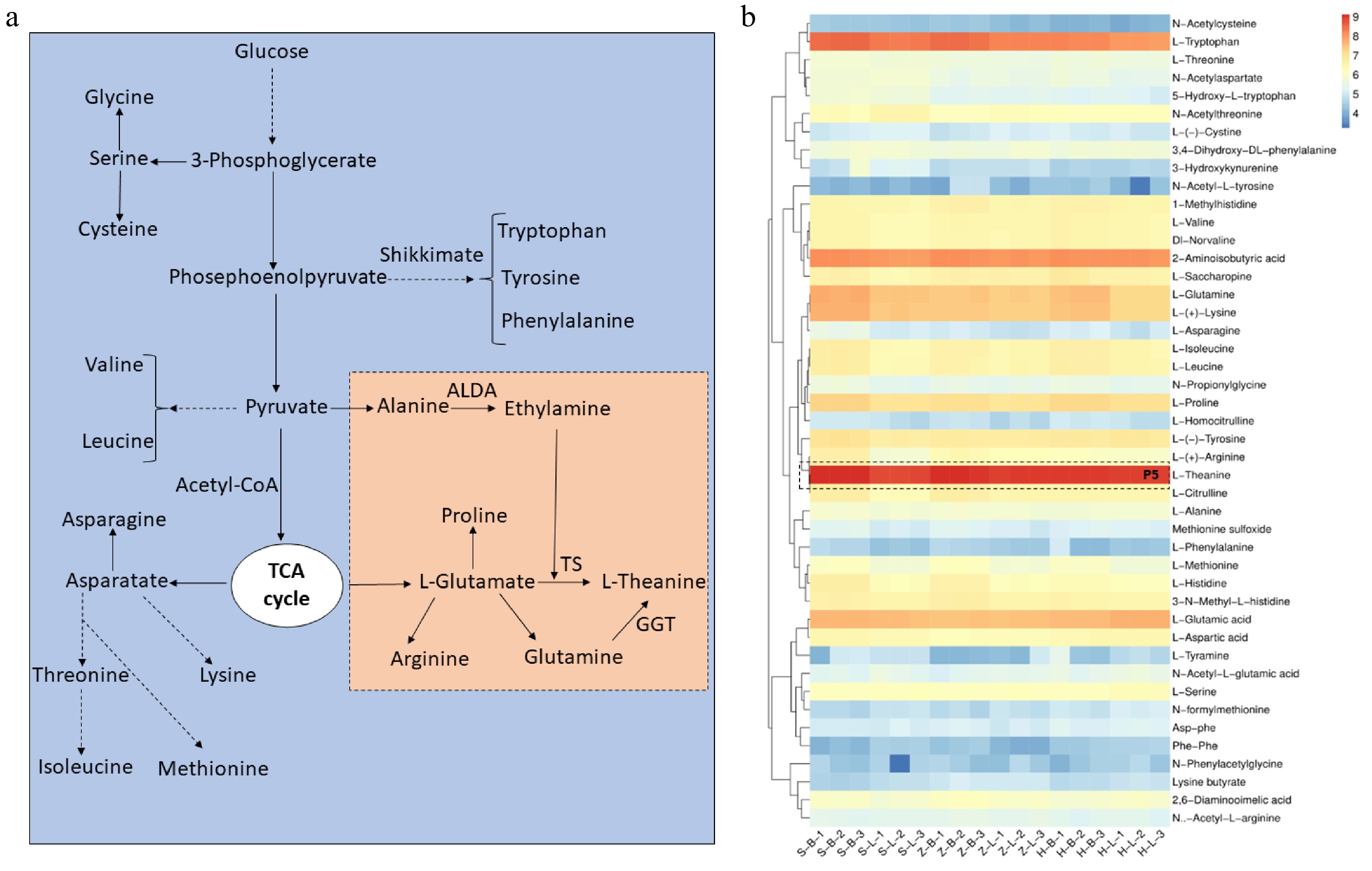
Figure 5.
L-theanine and other free amino acid metabolism pathways in tea plants. (a) L-theanine biosynthesis pathways in tea plant. (b) Other free amino acid and L-theanine relative content in different tissues of SCZ, HK and ZJ plants. OGAT: Glutamate synthase; ALDA: Alanine decarboxylase; GGT: γ-glutamyltranspeptidase; TS: Theanine synthetase.
-
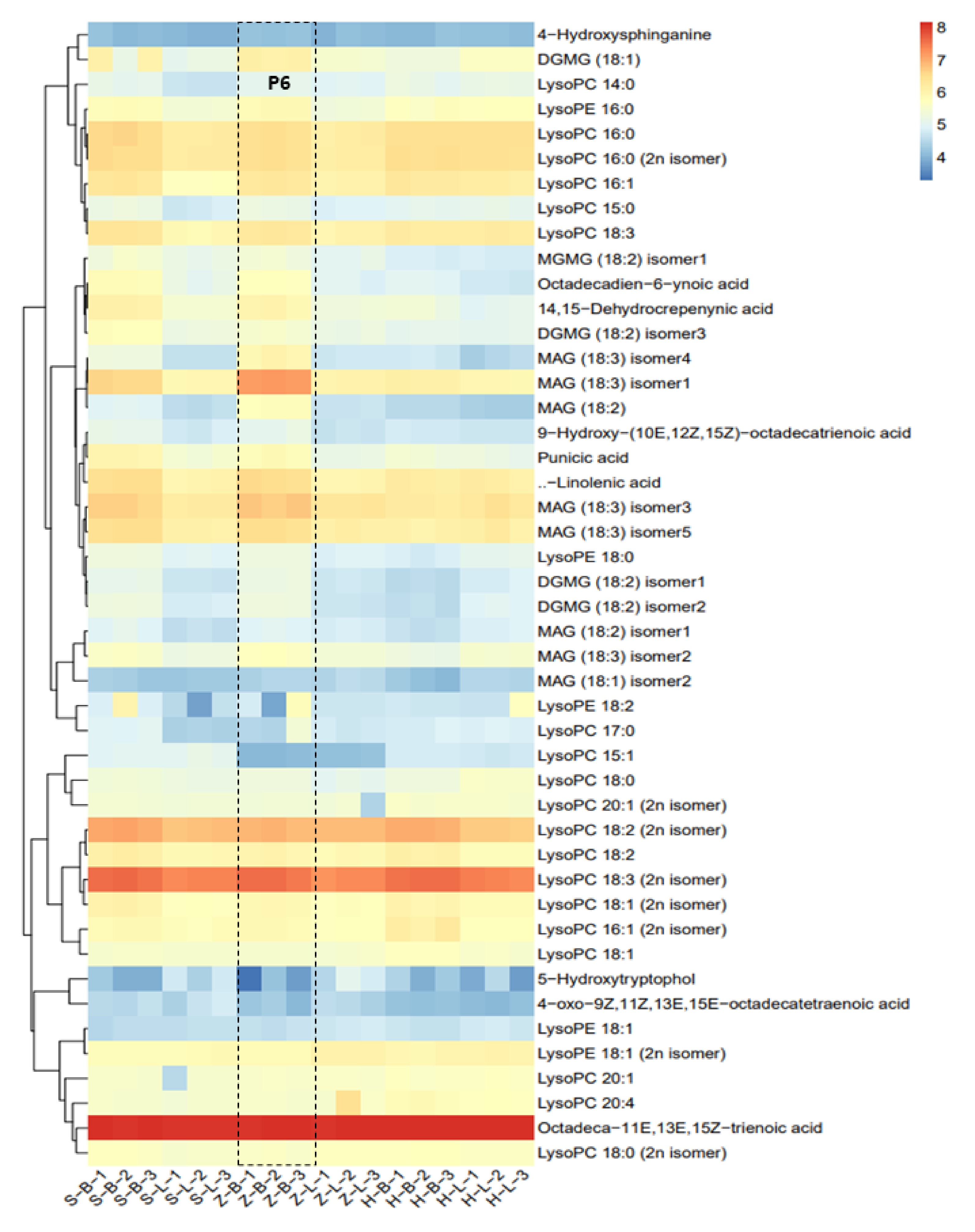
Figure 6.
Differential analysis of lipid metabolites. (MGDG - monogalactosyldiacylglycerol, GDG - digalactosyldiacylglycerol, C12:0 - lauric acid, C14:0 - myristic acid, C16:0 - palmitic acid, C16:1 - palmitoleic acid, C18:0 - stearic acid, C18:1 - oleic acid, C18:2 - linoleic acid, C18:3 - linolenic acid, C20:0 - arachidic acid, C20:1 - eicosenoic acid, C20:2 - eicosadienoic acid, C20:3 - eicosatrienoic acid, C20:4 - eicosatetraenoic acid, C22:0 - docosanoic acid, C24:0 - tetracosanoic acid, C24:1 - tetracosenoic acid, C26:0 - hexacosanoic acid, C28:0 - octacosanoic acid; DG - diacylglycerol, TG - triacylglycerol; PC - phosphatidylcholine; LPC - lysophosphatidylcholine, PE - phosphatidylethanolamine, PA - phosphatidic acid).
Figures
(6)
Tables
(0)