-
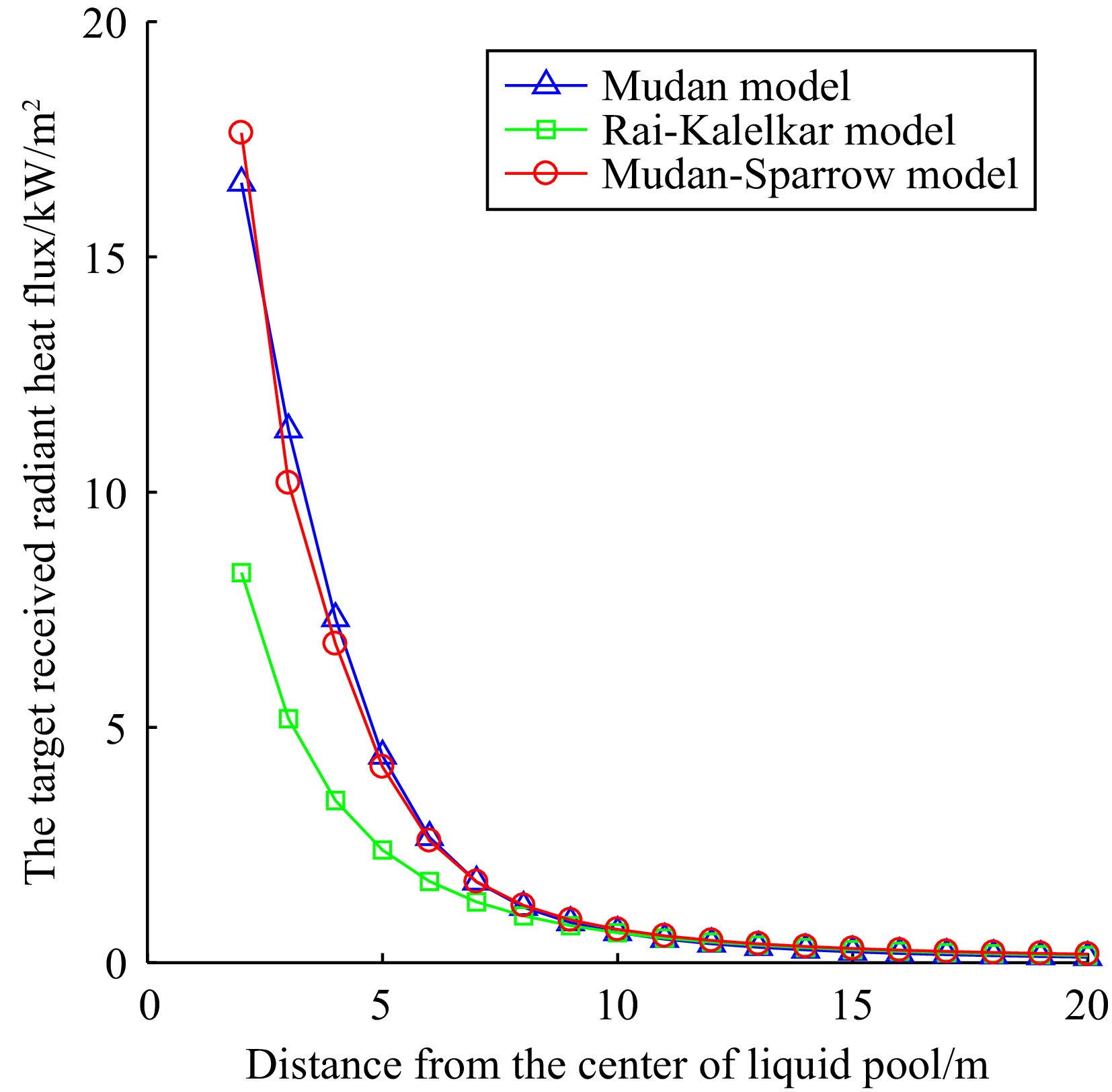
Figure 1.
The target received radiant heat flux with a small hole leak.
-
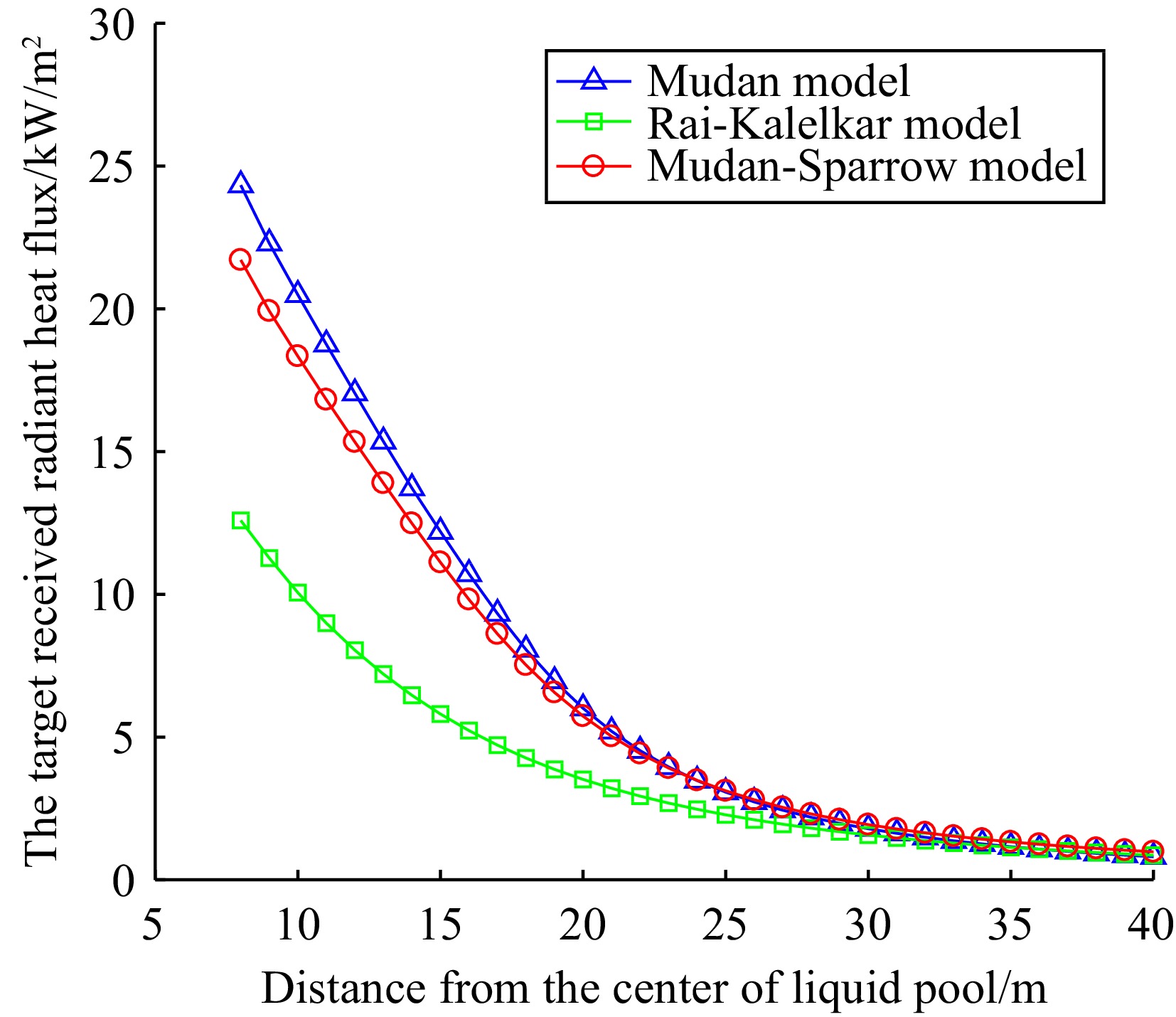
Figure 2.
The target received radiant heat flux with a medium hole leak.
-
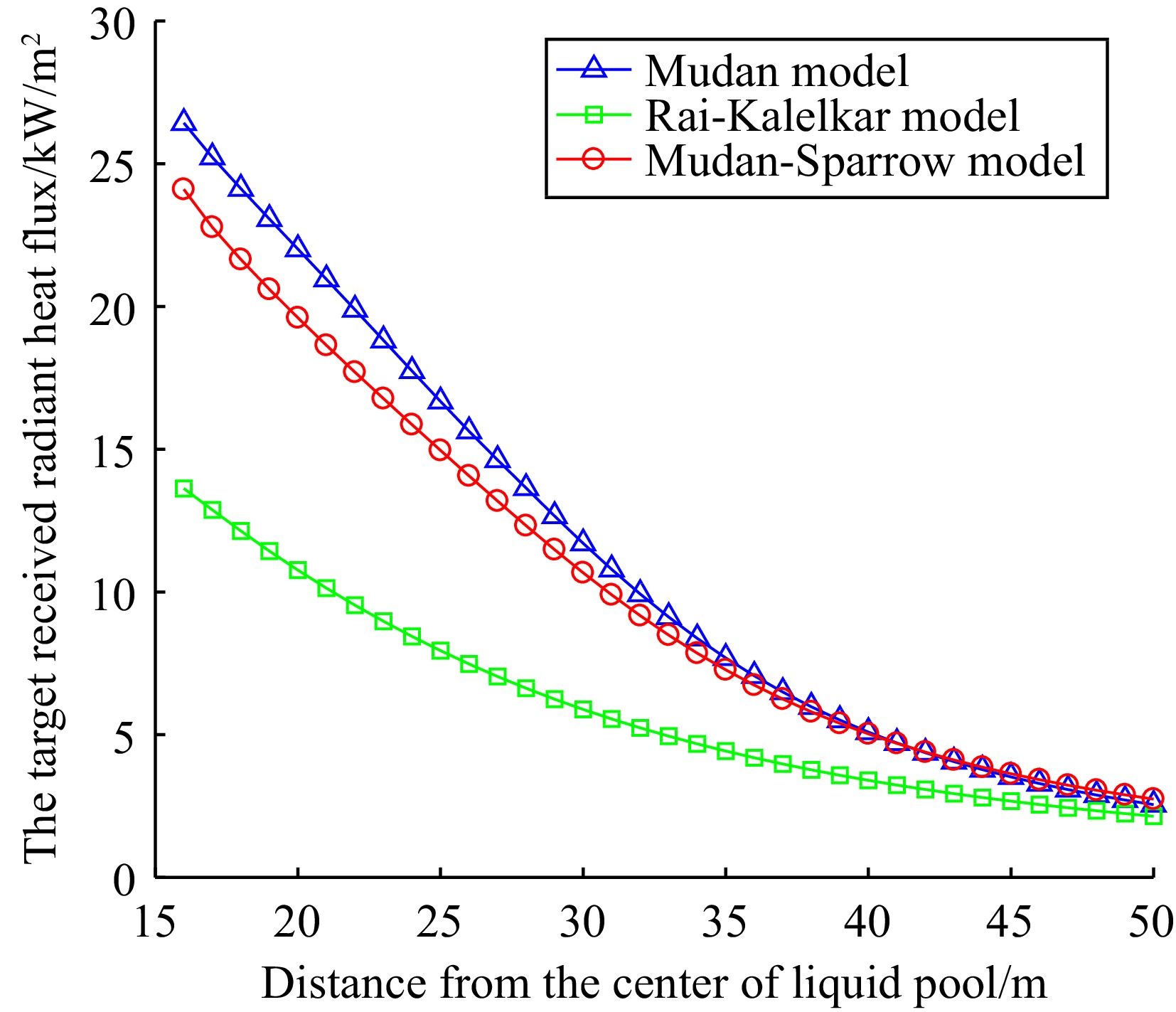
Figure 3.
The target received radiant heat flux with a large hole leak.
-
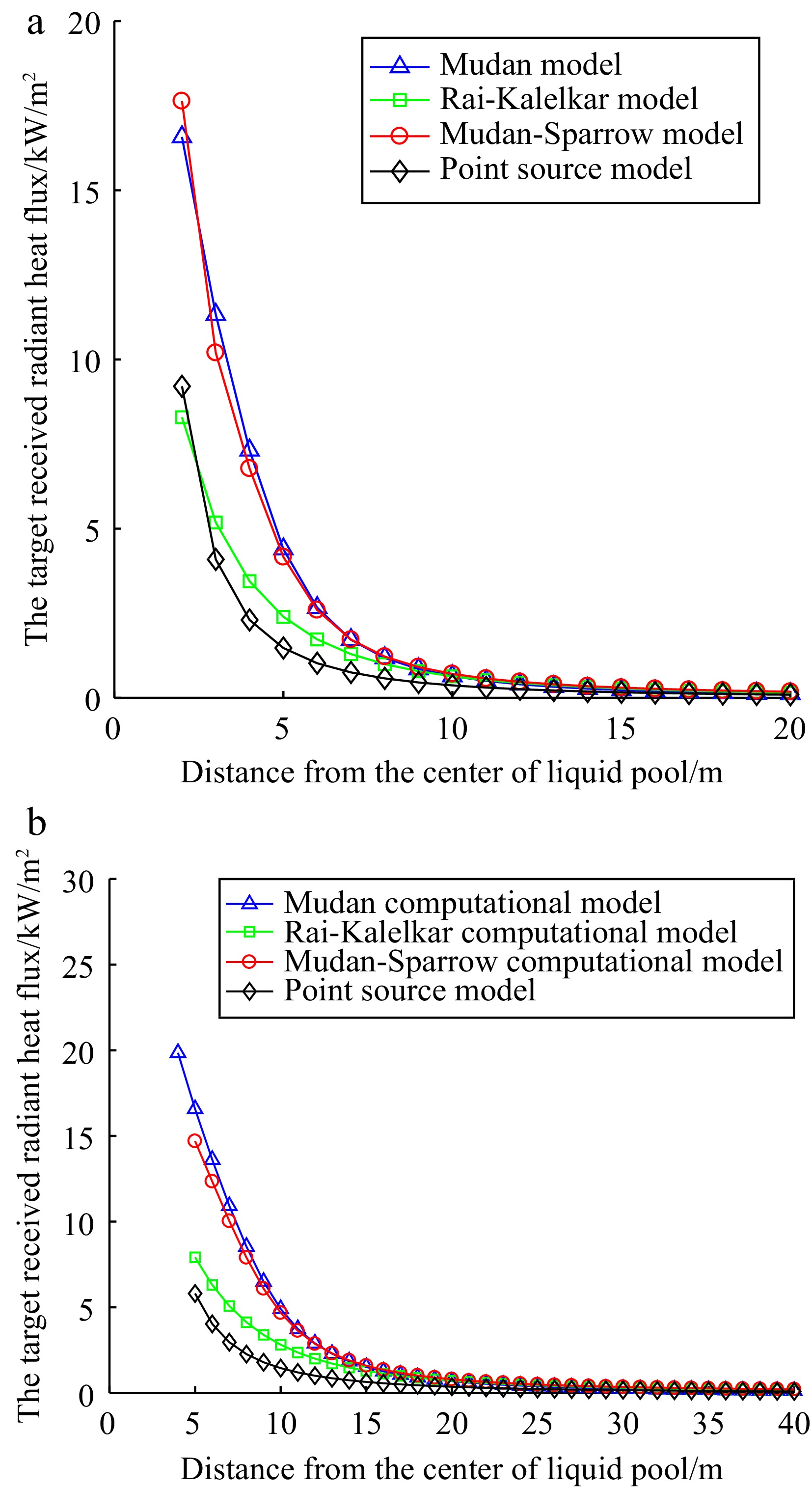
Figure 4.
The target received radiant heat flux: (a) small hole leak, (b) medium hole leak.
-
Serial number Perforation diameter
(mm)Perforation area
(A/m2)Leakage rate
Qm1/(kg/s)Leakage time (s) Leakage quantity
(kg)Exceeds the storage
capacity?1 5 1.9635 × 10−5 0.1398 330 46.1219 No 2 25 4.9087 × 10−4 3.4941 1,153.0486 No 3 50 1.9635 × 10−3 13.9763 4,612.1943 No Table 1.
Leak source strength calculation.
-
Serial
numberPerforation diameter (mm) Mass burning rate/kg/(m2·s) Equipped with fire dike? Liquid pool radius (m) Flame height (m) Total radiant heat flux (kW) Surface average radiant
heat flux (m2)Wind-free Wind-affected Wind-free Wind-affected 1 5 0.0283 No 1.5265 4.6112 3.0975 479.5543 15.1637 21.1090 2 25 0.0283 7.6327 14.1125 10.1102 7,998.7043 22.7281 29.2598 3 50 0.0283 15.2654 22.8464 16.8273 27,196.7423 26.7388 33.3186 4 5 0.0283 Yes 1.5265 4.6112 3.0975 479.5543 15.1637 21.1090 5 25 0.0283 3.3500 7.9625 5.5195 1,887.1085 18.5574 24.8589 6 50 0.0283 3.3500 7.9625 5.5195 1,887.1085 18.5574 24.8589 Table 2.
The characteristic parameter table of pool fire model.
-
Distance from the
center of liquid
pool (m)Small hole leak Medium hole leak Large hole leak 2 3 4 5 6 8 10 12 14 16 16 20 24 28 32 Mudan model View factor 0.8181 0.5731 0.3769 0.2296 0.1408 0.9456 0.8082 0.6805 0.5537 0.4362 0.9452 0.7995 0.6528 0.5075 0.3730 The target received radiant heat flux q/kW/m2 16.5750 11.3269 7.3157 4.3946 2.6642 24.3302 20.4908 17.0419 13.7205 10.7118 26.4286 22.0097 17.7406 13.6406 9.9288 Mudan-Sparrow model View factor 0.8704 0.5160 0.3492 0.2175 0.1371 0.8437 0.7234 0.6124 0.5038 0.3998 0.8620 0.7121 0.5836 0.4584 0.3445 The target received radiant heat flux q/kW/m2 17.6353 10.1972 6.7778 4.1621 2.5934 21.7100 18.3397 15.3364 12.4843 9.8176 24.1031 19.6036 15.8612 12.3222 9.1710 Rai-Kalelkar model View factor 0.4092 0.2623 0.1776 0.1251 0.0914 0.4892 0.3968 0.3212 0.2608 0.2129 0.4873 0.3910 0.3107 0.2466 0.1969 The target received radiant heat flux q/kW/m2 8.2912 5.1836 3.4472 2.3934 1.7280 12.5867 10.0593 8.0426 6.4630 5.2275 13.6247 10.7653 8.4438 6.6281 5.2404 Table 3.
The view factor and target received radiant heat flux.
-
Incident flux I (kW/m2) Damage to equipment Injury to personnel 37.5 Total damage to operating equipment 1% dead/10 s; 100% dead/min 25.0 The minimum energy required for wood combustion under
the absence of flame and long-time radiationSignificant injury/10 s; 100% death/1 min 12.5 The minimum energy required for wood combustion and
plastic melting under the presence of flameFirst-degree burns/10 s; 10% death/1 min 4.0 Glass breaks after 30 min of exposure More than 20 s feeling pain, may not be blistering Table 4.
Thermal radiation damage/injury criteria.
-
Serial number Model Distance from the center of liquid pool (m) The target received radiant heat flux (q/kW/m2) 1 Point source model 13.35 0.8142 2 Mudan model 2.1215 3 Mudan-Sparrow model 2.1548 4 Rai-Kalelkar model 1.6273 Table 5.
The target received radiant heat flux at a distance of 13.35 m.
-
The target received
radiant heat flux
(q/kW/m2)Damage distance/m Point source model Mudan Rai-Kalelkar Mudan-Sparrow Liquid pool radius = 1.5256 m 37.5 — — — — 25 — — — — 12.5 1.7165 2.7515 1.5672 2.4835 4 3.0343 5.1796 3.618 5.0796 Liquid pool radius = 3.35 m 37.5 — — — — 25 — — — — 12.5 3.4661 6.4002 2.0926 5.9354 4 6.1272 10.7444 8.1554 10.6076 Table 6.
Thermal radiation hazard consequence.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(6)