-
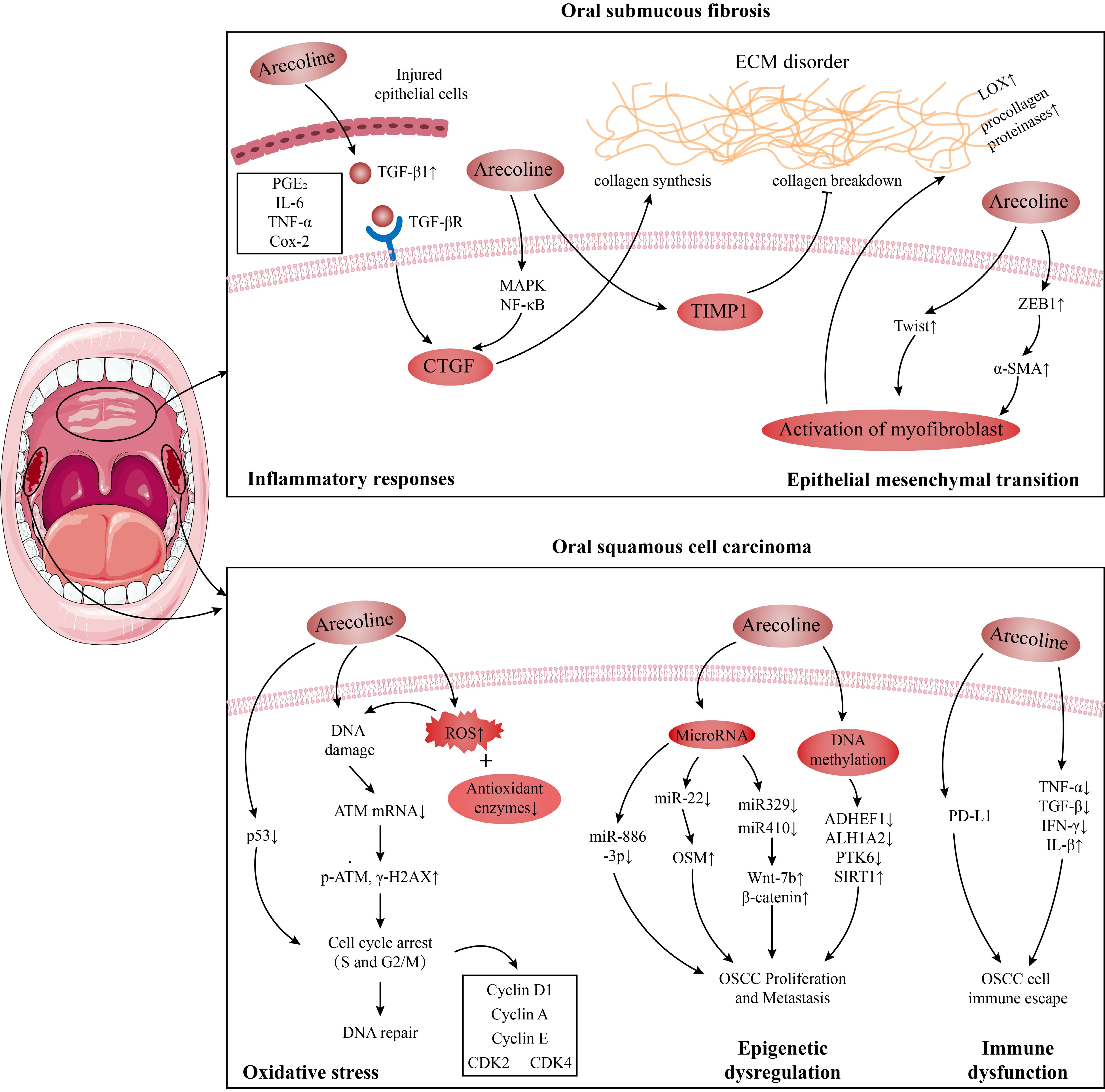
Figure 1.
Possible mechanisms of oral submucous fibrosis (OSF) and oral oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) induced by arecoline.
-
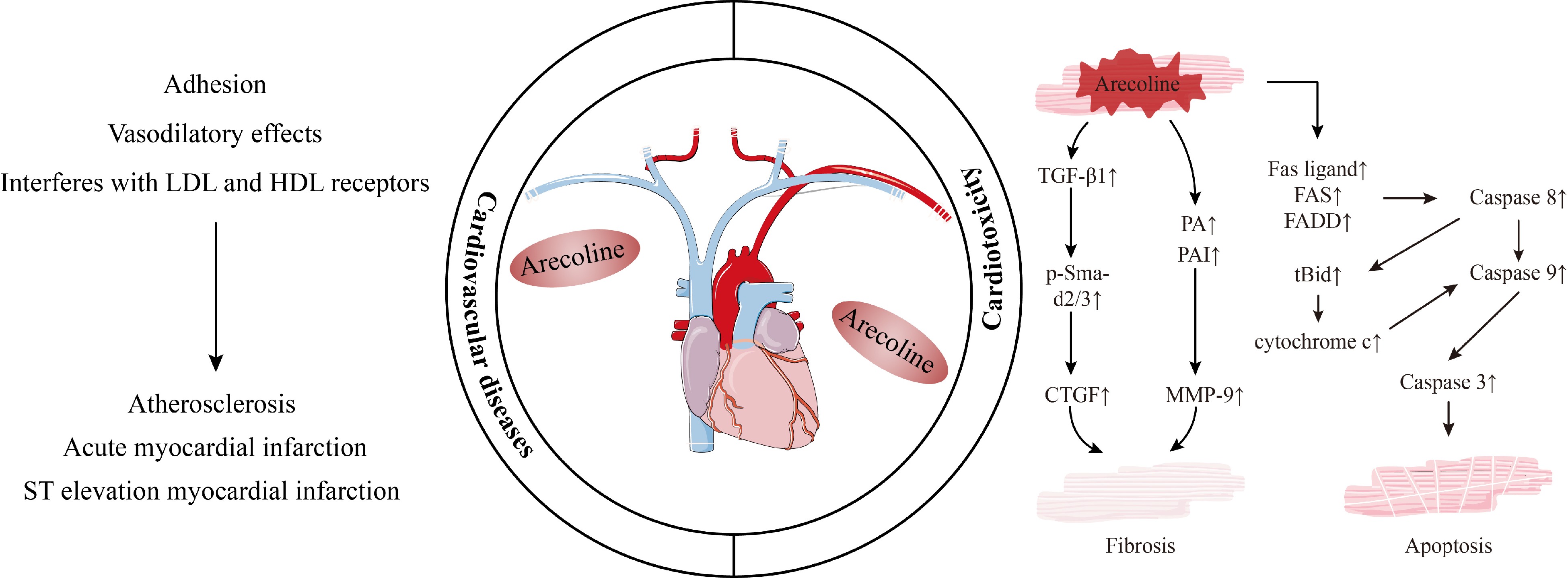
Figure 2.
Possible mechanisms of cardiovascular diseases and cardiotoxicity.
-
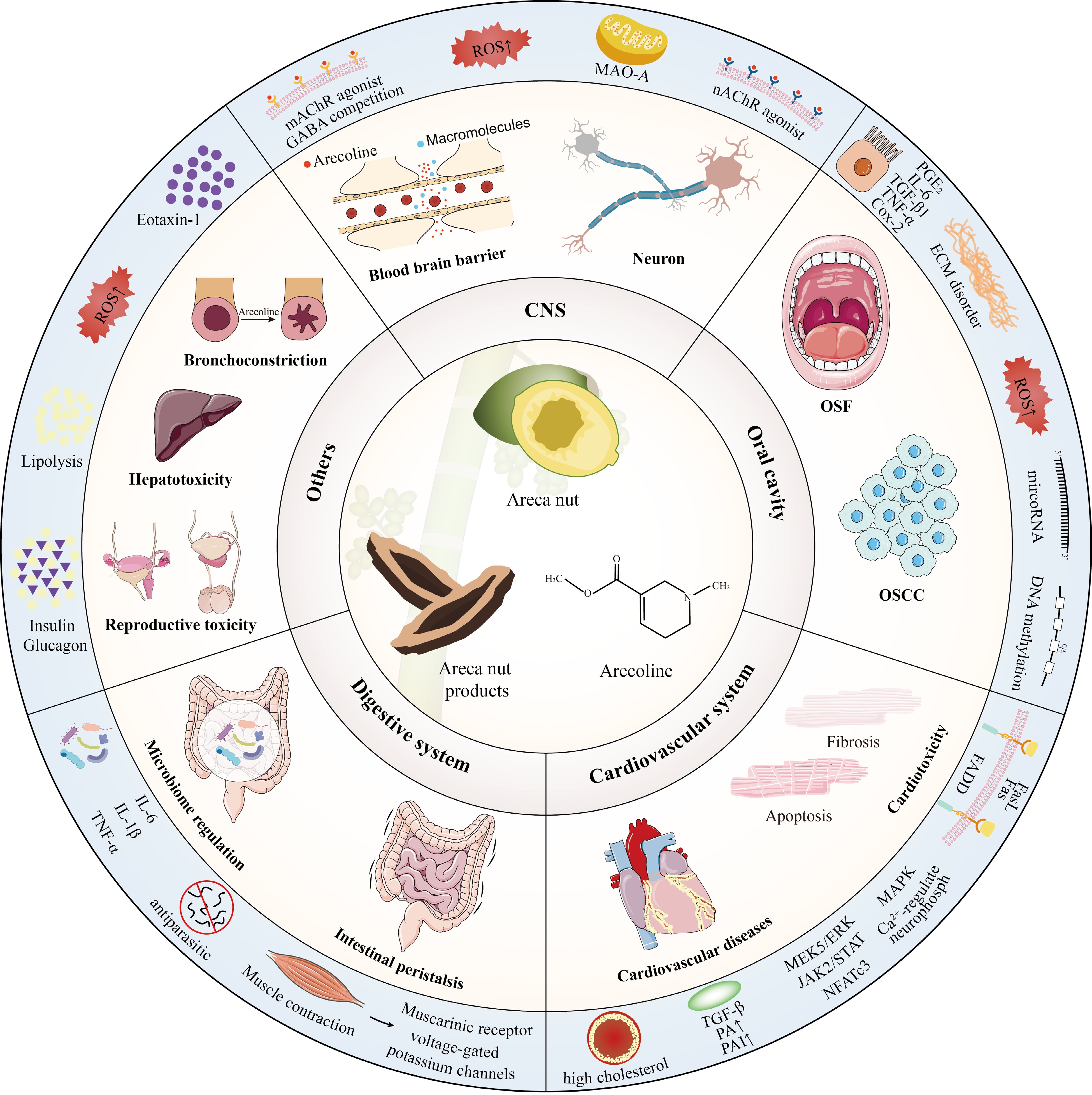
Figure 3.
Effects and mechanisms of arecoline on different organs and systems.
-
Effect Animal/cell Specific effect Pathway/mediators Dose Ref. Beneficial effects Xenopus laevis oocytes Anti-inflammatory activity As a silent agonist of α7 nAChR, targeting and regulating intracellular signaling against inflammation and pain / [61] Glioblastoma cell lines (U373 and U87MG) Interfere with the aggressiveness of malignant gliomas Inhibition of intermediate conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels 10 and 30 μM [62] Zebrafish Cluster disruption and increased social interaction Increased norepinephrine, serotonin, and DOPAC levels decreased 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid/serotonin level, and homovanillic acid/dopamine ratios 10 mg/L [55] Zebrafish Motor hyperactivity Binds with multiple mAChRs (M1−M4) to induce hyperactivity 0.001, 0.01, 0.1,
and 1 ppm[49] Male Swiss albino mice Antinociception By activation of central muscarinic receptors 0.3−1 mg/kg ip [53] Rat Attenuated a time perception impairment induced by daily scheduled feeding By modulating central cholinergic 10 mg/kg/d [52] Rat Anti-phenobarbital sodium-induced sleep time Not mentioned 0.5 mg [51] Male ICR mice Shortened the duration of
ethanol-induced sleepActs as a muscarinic agonist to relieve ethanol-induced central depression and intoxication 0.125−1.0 mg/kg, s.c. [50] CPZ mice Attenuating memory impairment and demyelination Acts as a muscarinic receptor 1 cholinergic agonist to improve cognition and promote myelination processes in the frontal cortex 2.5 or 5 mg/kg/d [8] Female BALB/c mice Increased the activity of preactivated NK cells By stimulating the secretion of corticotropin-releasing hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone 1.5 mg/kg [63] Male albino rats Improved retrieval and memory storage in the stair maze Not mentioned 0.5 mg/kg [64] Human (Alzheimer) Low-dose arecoline improved cognitive performance, highest-dose impaired psychomotor activation By modulating central cholinergic 1, 2, or 4 mg/h infusions 2 h [9] Human (Alzheimer) Improved memory As a cholinergic agonist, maintaining patients’ cholinergic steady-state 0.042−1.7 mg/h Infusion for 11−16 d [65] Human (Alzheimer) Improved cognition As a muscarinic receptor agonist, regulating patients’ cholinergic system 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 22,
28, 34, and 40 mg/d[66] Neurotoxicity Primary cortical neuron Induction of neuronal cell death By attenuating antioxidant defense and enhancing oxidative stress 50−200 μM [16] PC12 Cells Apoptosis By inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress, attenuating H2S levels, CBS and 3-MST protein expression 0.5−2 mM [58] Drosophila melanogaster Neurotoxic agent and affected the life cycle parameters By reducing acetylcholinesterase and MAO, increasing caspase-3, caspase-9 activity, and oxidative stress 20, 40 and 80 μM [67] Zebrafish Dyskinesia By increasing ROS, endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptotic p53 signaling pathway. 10 μM [68] Male albino rats Decreased correct responses and accelerated spontaneous decay of memory Not mentioned 3.5 and 8 mg/kg [64] Addiction-related Xenopus laevis oocytes Habitual use By activating addiction-related nAChR activity, receptors containing α4, β2, α6 and β3 subunits / [61] Xenopus laevis oocytes Addiction By activating α4 nAChR 100 μM [62] Zebrafish Withdrawal syndrome-like responses Not mentioned 1 mg/L [55] Pregnant women Exceptional adverse birth outcome Not mentioned Not mentioned [69] Table 1.
Effect of arecoline on the CNS.
-
Effect Animal/cell Specific effect Pathway/mediators Dose Ref. Respiratory system Human and dermal and gingival fibroblast Causing lung function impairment In pro-inflammatory conditions (IL-4 and
TNF-α), arecoline can induce eotaxin-1 release and alter the disease process in asthma25 and 100 μg/mL [18] Human Asthma Possibly related to arecoline-induced bronchoconstriction / [89] Hepatotoxicity Human liver microsome and Male Wistar rats Hepatotoxicity By increasing the hepatic CYP2E1 and CYP2B activity, induced oxidative damage, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma 4, 20, and 100 mg/kg/d [90] HA22T/VGH hepatoma cells Inducing anoikis By inhibiting STAT3 and SHP2 phosphorylation, decreasing the levels of anti-apoptotic factors, as well as by promoting the activity of pro-apoptotic factors 0−100 μg/mL [91] Human and C57BL/6 mice’s organ of Corti and spiral ganglions Sensorineural hearing impairment Reducing cochlear explant cell activity, inducing cell death and ROS production by causing disruption of hair cells in the organ
of Corti0.2, 0.8, 2, and 10 mM [92] Mice Fatty degeneration and inflammatory infiltration By increasing serum alkaline phosphatase, glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase, glutamate-pyruvate transaminase, and decreasing levels of reduced glutathione, glutathione-S-transferase, SOD, and catalase 10 mg/kg body weight [19] Mice Decreasing nuclear size; the rough endoplasmic reticulum with profusely inflated cisternae and abundance of lipid droplets By Upregulating SGOT and SGPT (hepatotoxicity marker enzymes) in serum 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg body weight [87] Reproduction Zebrafish embryos Reducing survival of embryos with growth retardation and lower heart rate General cytotoxic effects mainly due to intracellular thiol depletion 0.01%−0.04% (wt/vol) [93] Oocyte Apoptosis By disrupting actin filament dynamics, spindle assembly, and kinetochore-microtubule attachment stability, mitochondrial distribution, and increasing oxidative stress levels 180 μg/mL [94] ICR mice and blastocysts Reduction of early embryos and inhibition of blastocyst growth and expansion By inducing DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, or apoptosis 0−8.47 × 10−2 M [88] Male rats Stimulation of testosterone secretion By activating L-type calcium channels, increasing 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity and StAR expression, thereby stimulating testosterone production 1 μg/kg [95] Immunity and endocrine Swiss albino mice Lymphocyte depletion of the thymic cortex and the B and T lymphocyte areas in the spleen and MLN, Elevated corticosterone, SGOT, and SGPT levels, and decreased white and red blood cell counts Not mentioned 20 mg/kg [96] Adult male mice The orientation of nuclei was irregular, follicle degeneration, a decrease in the T3, T4, number, and size of thyroid follicles, and an increase in the TSH level MAChRs mediate the effect of arecoline on thyroid 10 mg/kg [97] BALB/c mice Reducing the spleen index, hemolysin, IL-2 production, and splenocyte proliferation induced by concanavalin A or lipopolysaccharide Mediated via mAChRs 2 mg/kg [98] Fat Mouse 3T3-L1 cells and human Adipocyte dysfunction Inhibiting adipogenic differentiation, inducing adenylate cyclase-dependent lipolysis, and interfering with insulin-induced glucose uptake ≥ 300 µM [99] 3T3-L1 cells Regulating the growth of preadipocytes Inhibiting the CDK family and the CKI pathway by inactivating AMPK activity as
well as the intracellular ROS pathway0−1,000 μM [100] Table 2.
Other toxicological and pharmacological effects of arecoline.
Figures
(3)
Tables
(2)