-
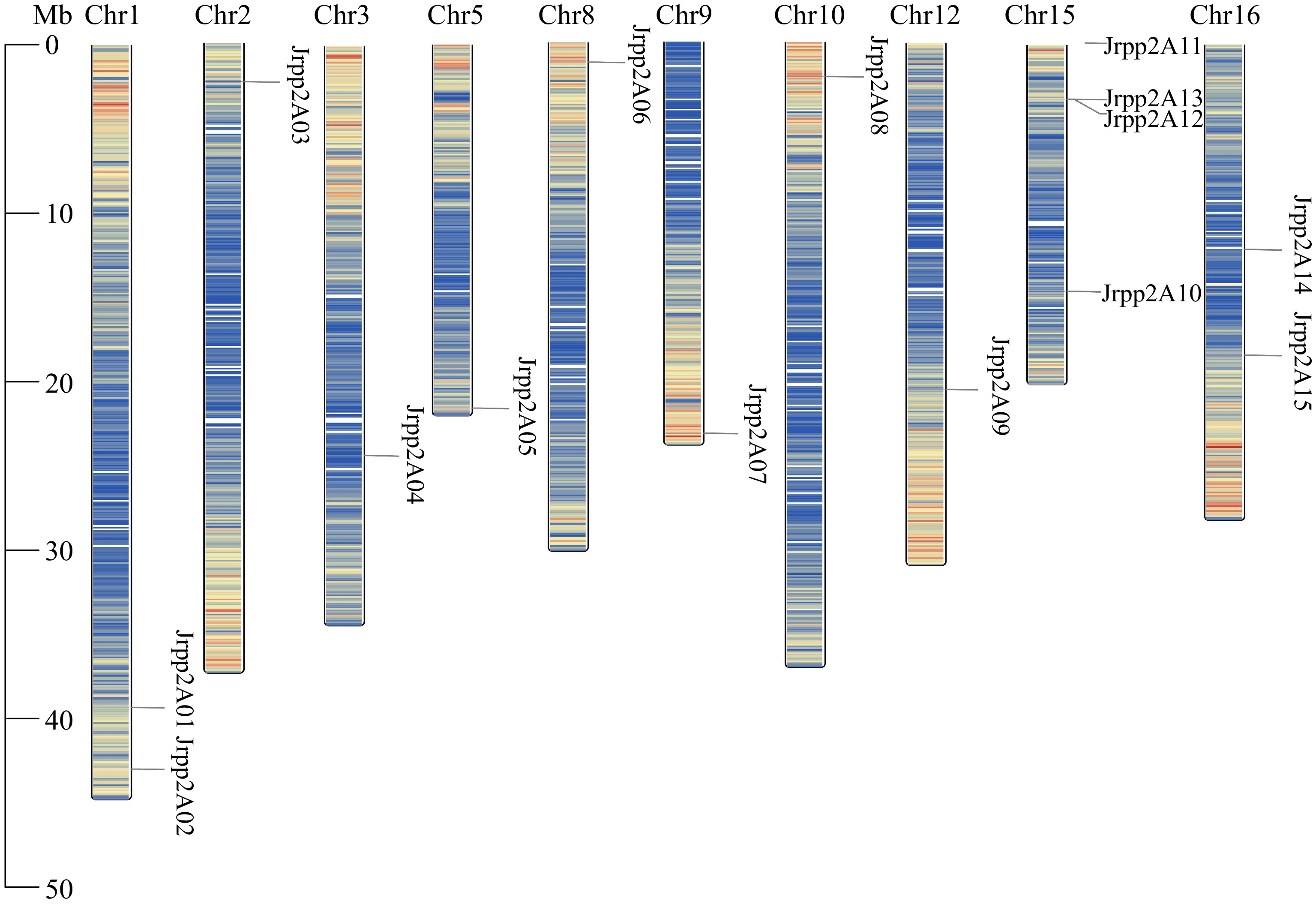
Figure 1.
Distribution of the JrPP2As on chromosomes of the J. regia genome. The chromosome number is shown on the top side of each chromosome.
-
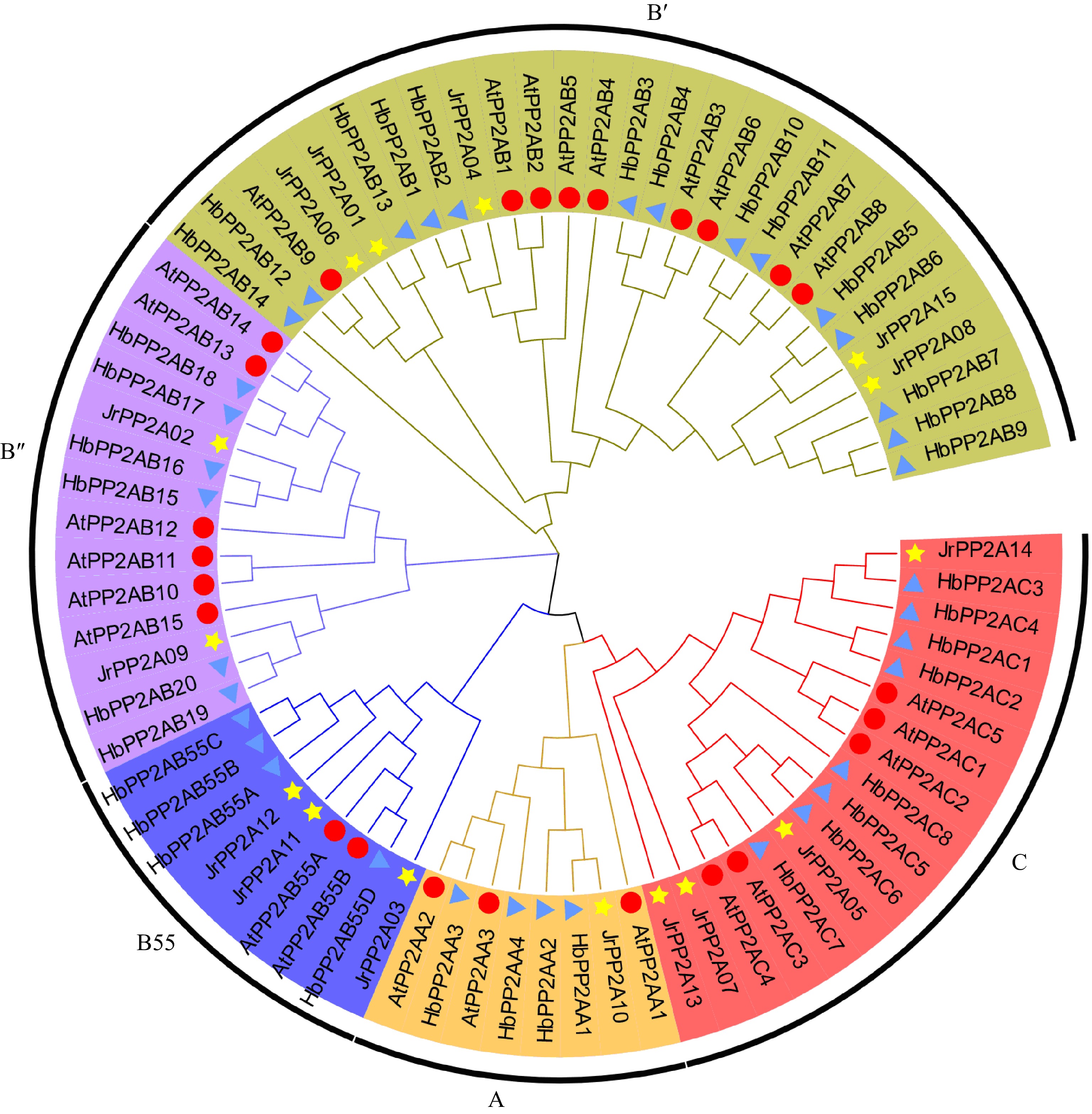
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic relationship of PP2A proteins from J. regia, A. thaliana and H. brasiliensis. A, C, B55, B', B" means five sub-family of PP2As, respectively, which are displayed in different colors. A total of 15 walnut PP2As are represented by yellow five-pointed stars, 25 Arabidopsis PP2As are represented by red circles, 36 H. brasiliensis PP2As are represented by blue triangles.
-
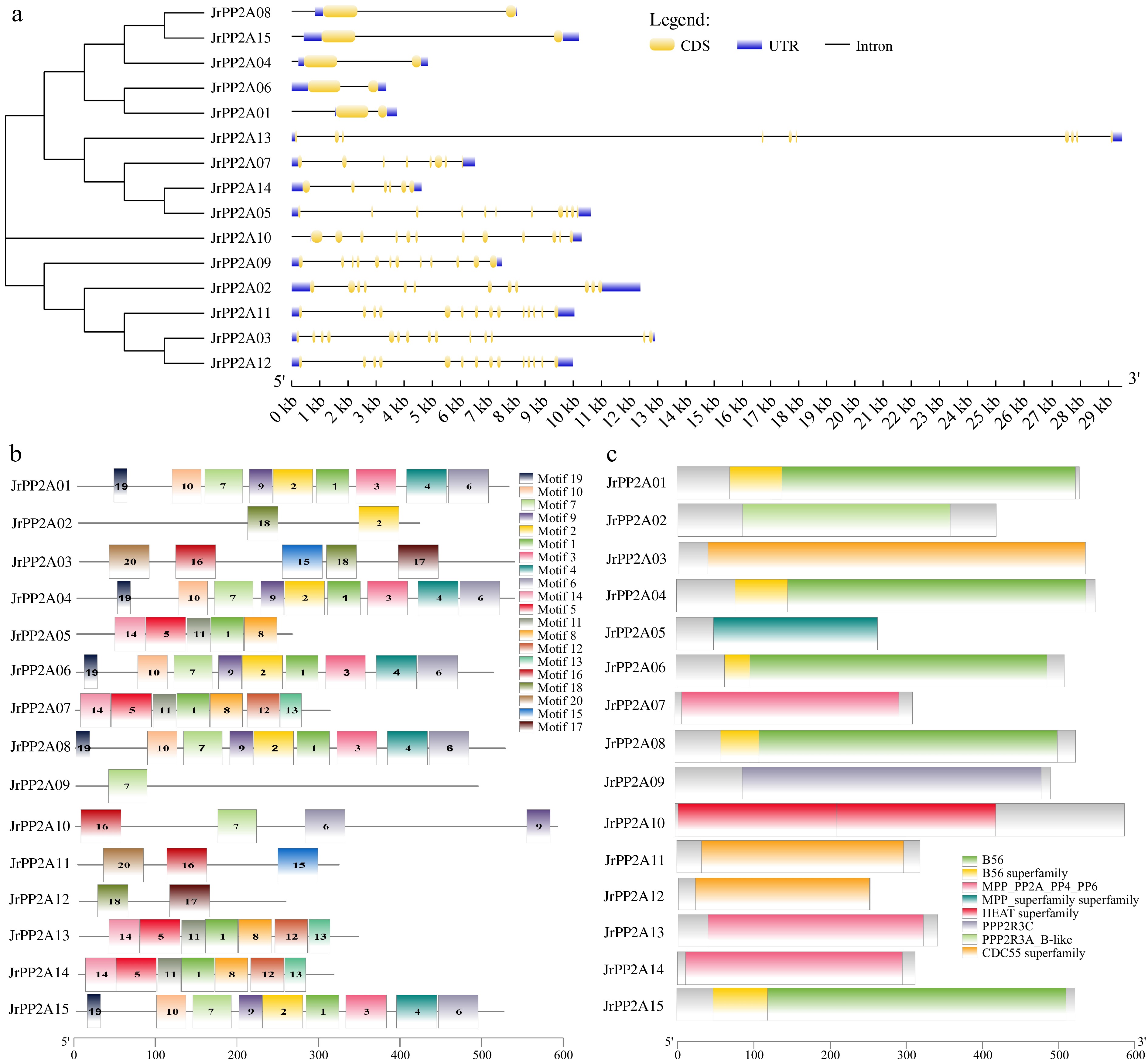
Figure 3.
Gene structure of walnut PP2As. (a) Exon-intron distribution map. The vertical phylogenetic tree and gene structure of JrPP2As was constructed by GSDS online software. Yellow boxes indicate exons; blue boxes indicate upstream or downstream; black lines indicate introns. (b) Conserved motif analysis: 20 separate patterns were identified with the MEME suite and each pattern was depicted with different colors. (c) Distribution of conserved domains.
-
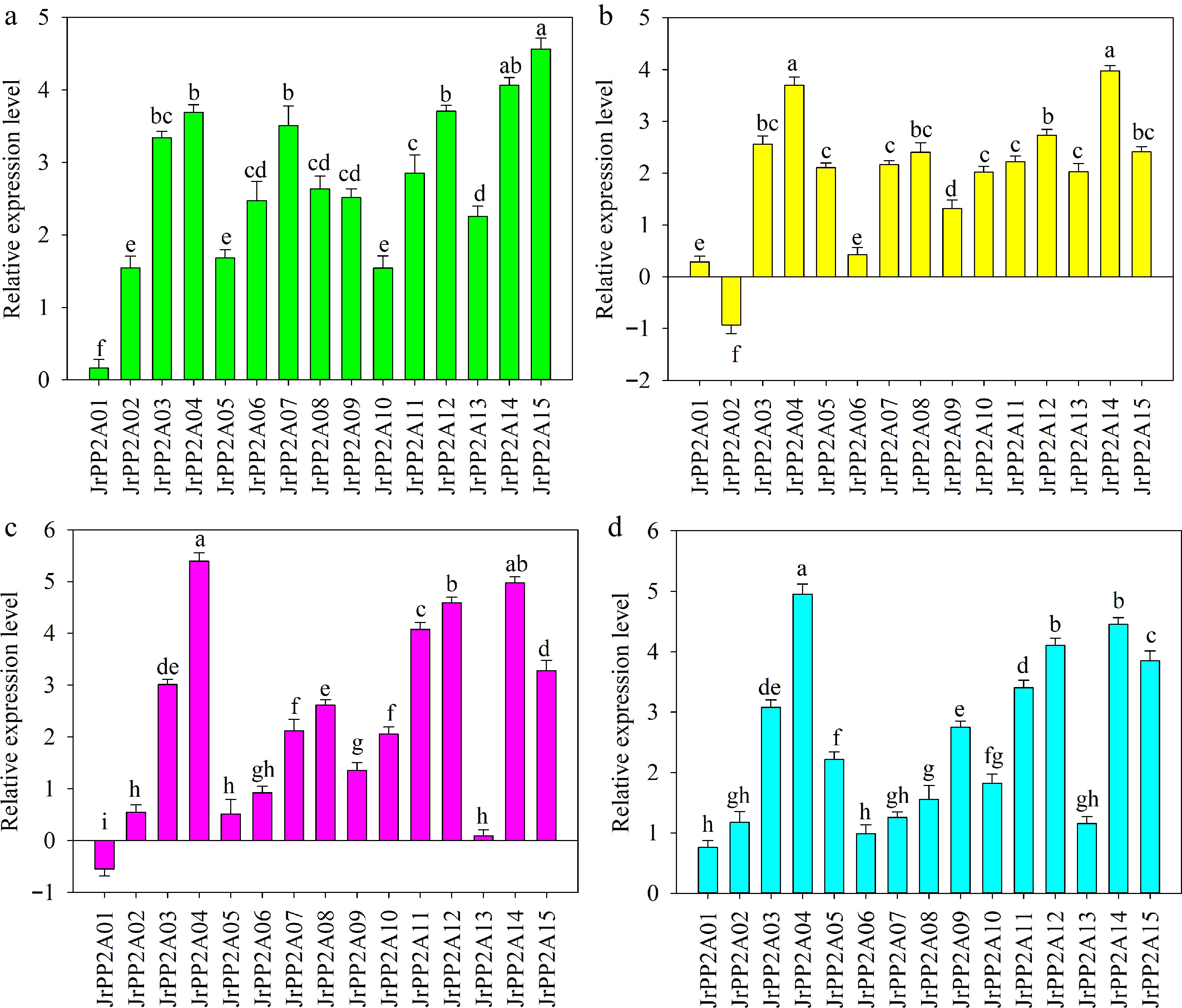
Figure 4.
QRT-PCR analysis of the expression of JrPP2A genes under drought, NaCl, CaCl2, and ABA treatments. The relative expression level is expressed as relative to the internal reference gene and at 0 h. Error bars represent the SD (n = 3). Lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different JrPP2A genes under each treatment according to the Student's t-test (p < 0.05). (a) PEG6000 stress. (b) NaCl stress. (c) CaCl2 treatment. (d) ABA treatment.
-
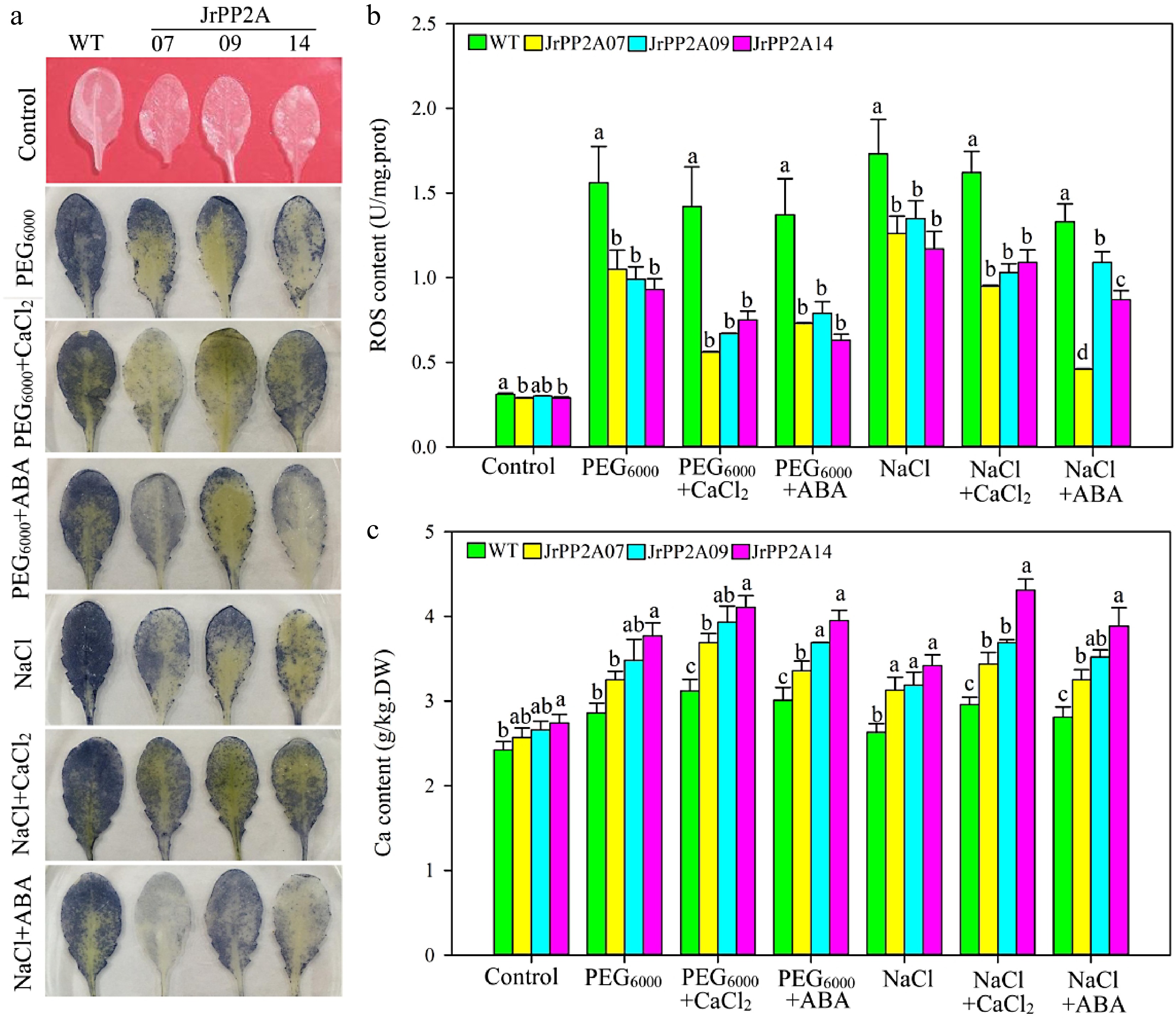
Figure 5.
Osmotic stress response function of JrPP2As. WT, wild type. JrPP2A07, 09, 14, the transgenic lines overexpression of JrPP2A07, JrPP2A09, JrPP2A14. Fourty two-day old seedlings were treated with PEG6000, PEG6000 + CaCl2, PEG6000 + ABA, NaCl, NaCl + CaCl2, NaCl + ABA for 5 d. Control was normally watered. The significant differences among WT, JrPP2A07, JrPP2A09, and JrPP2A14 were marked with lowercase (p < 0.05). (a) NBT staining. (b) Total ROS content. (c) Total Ca content.
-
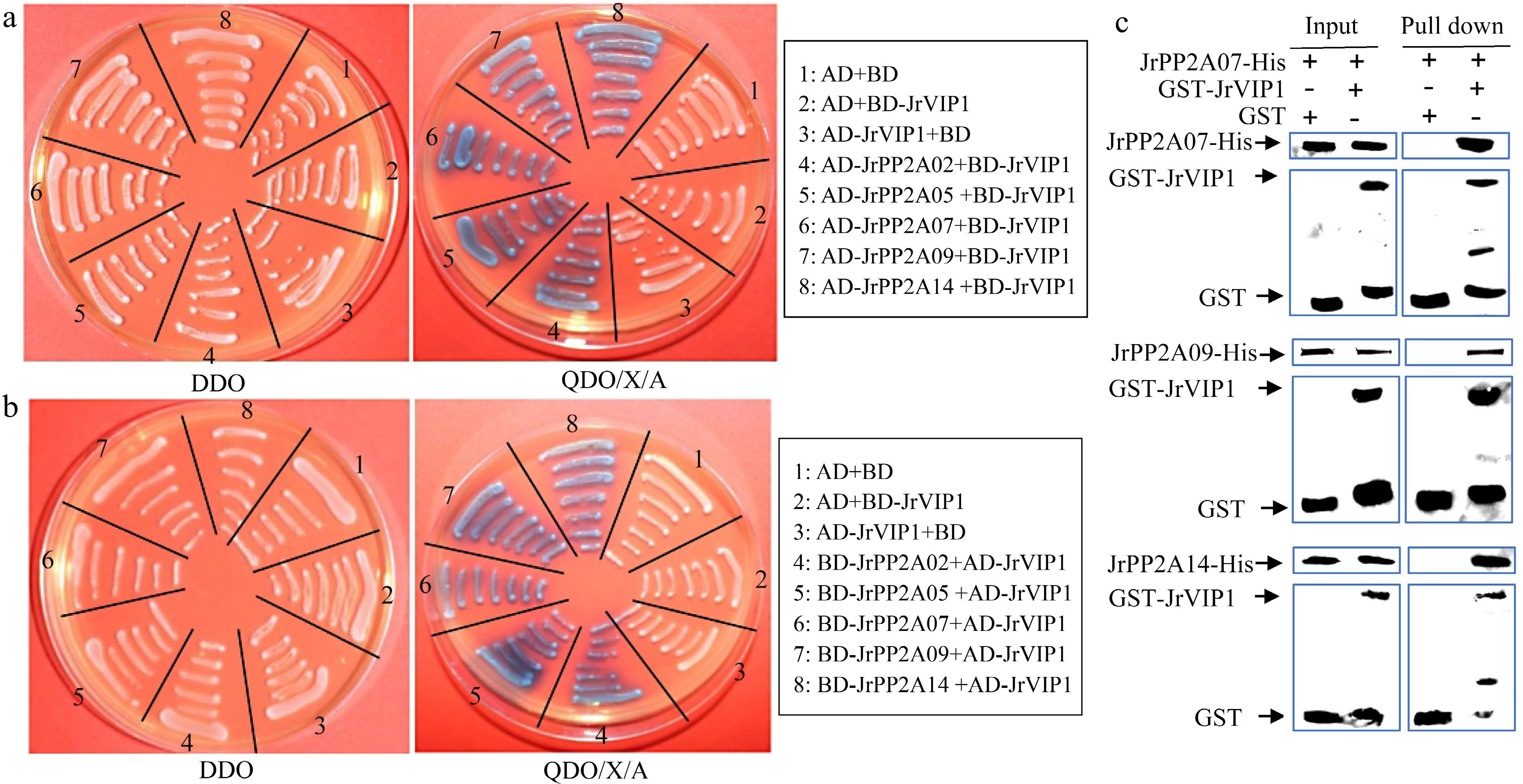
Figure 6.
Interaction analysis of JrVIP1 and JrPP2A proteins using yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) and in vitro pull-down assay. AD+BD, AD+BD-JrVIP1, AD-JrVIP1+BD, negative control. The DDO plate was used as positive control for growth. (a) JrVIP1 was used as the bait. (b) JrVIP1 was used as the pray. (c) An in vitro pull-down assay demonstrates the interaction between JrVIP1 with JrPP2A07, JrPP2A09, JrPP2A14. JrPP2A-His protein was incubated with immobilized GST or GST-JrVIP1 protein, and immunoprecipitated fractions were detected by anti-His antibody. The assay was performed three times with the same result.
-
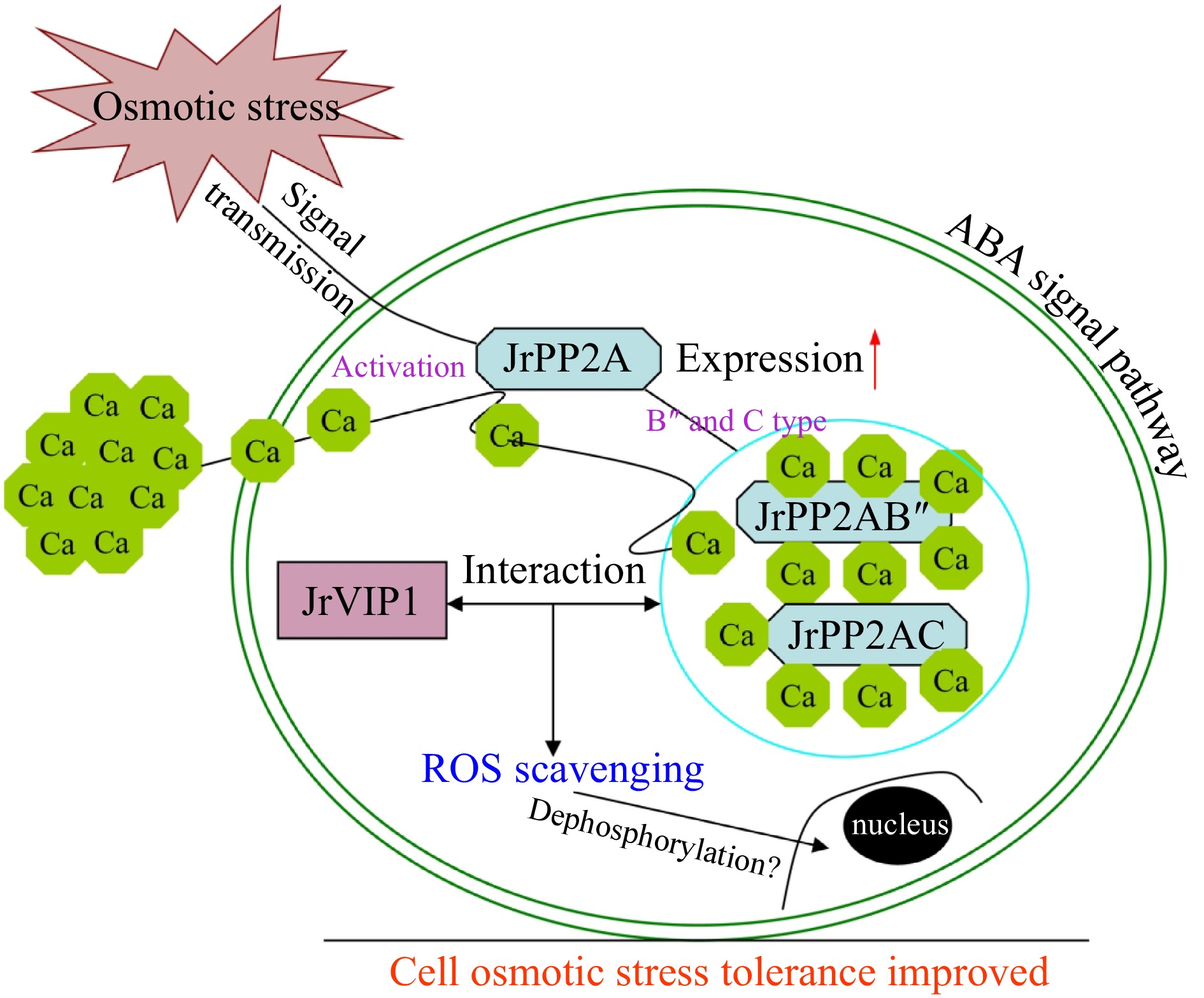
Figure 7.
The JrVIP1 and JrPP2As mediated osmotic stress responsive pathway in walnut trees.
-
Gene names Type Transcriptome No. Gene Bank accession No. Gene ID Chromosome ORF length (bp) Number of amino acids Molecular weight (kDa) pI JrPP2A01 B' comp30409_c0 XM_018967286.2 LOC108992675 ch1 1,452 483 55.13 8.37 JrPP2A02 B'' comp28147_c0 XM_018971752.2 LOC108996025 ch1 1,254 417 49.44 4.8 JrPP2A03 B55 comp26329_c0 XM_018982199.2 LOC109003870 ch2 1,506 501 56.72 6 JrPP2A04 B' comp20037_c0 XM_018993415.2 LOC109011996 ch3 1,503 500 57.52 6.24 JrPP2A05 C comp26715_c0 XM_018952439.2 LOC108981323 ch5 681 226 25.7 4.94 JrPP2A06 B' comp24655_c0 XM_018979195.2 LOC109001785 ch8 1,503 500 56.94 7.61 JrPP2A07 C comp32898_c0 XM_018969187.2 LOC108994090 ch9 918 305 34.78 5.24 JrPP2A08 B' comp25187_c0 XM_018958784.2 LOC108986228 ch10 1,575 524 59.87 7.97 JrPP2A09 B'' comp9850_c0 XM_018985083.2 LOC109005962 ch12 1,431 476 54.74 4.93 JrPP2A10 A comp28348_c0 XM_035685846.1 LOC109013629 ch15 1,764 587 65.61 4.88 JrPP2A11 B55 comp28413_c1 XM_018989098.2 LOC109008856 ch15 918 305 34.06 5.16 JrPP2A12 B55 comp28413_c1 XM_018989097.2 LOC109008856 ch15 651 216 24.15 6.21 JrPP2A13 C comp27670_c1 XM_018980847.2 LOC109002920 ch15 912 303 34.84 4.88 JrPP2A14 C comp23892_c0 XM_018963562.2 LOC108989812 ch16 921 306 35.01 4.83 JrPP2A15 B' comp13497_c0 XM_018951013.2 LOC108980163 ch16 1,530 509 58.52 7.18 Table 1.
Sequence characteristics of 15 JrPP2As.
-
Motif Width Motif consensus 1 41 TIVYGFYDETERHNGIAELLEIFGSIIDGFALPLKEEHKIF 2 50 KVAKRYIDHSFVLRLLDLFDSEDPREREYLKTILHRIYGKFMVHRPFIRK 3 50 HKPKSIGLYHQQLSYCITQFVEKDPKLADTVIRGLLKYWPVTNSQKEVMF 4 50 PAEFQRCMVPLFRQIGCCLNSSHFQVAERALFLWNNDHIVNLIAQNRNVI 5 50 NVQPVKSPVTICGDIHGQFHDLIELFRIGGNCPDTNYLFMGDYVDRGYYS 6 50 PIIFPALEKNARSHWNQAVQNLTLNVRKIFSEMDPELFEECQRQFQEDEA 7 48 DIKRQTLIELVDFVASGSGKFTETAIQEMIKMVSVNLFRVLPPKPREN 8 41 CLHGGLSPSIETLDNIRVIDRIQEVPHEGPMCDLLWSDPDD 9 29 EPSFDPAWPHLQJVYELLLRFVSSSETDA 10 37 VEALPAFKDVPNSEKQNLFISKLNLCCVVFDFSDPTK 11 29 ETFTLLLALKVRYPDRITJLRGNHESRQI 12 41 WGVSPRGAGYLFGGDVVSQFNHTNNLDLICRAHQLVMEGYK 13 27 WFQDKGIVTVWSAPNYCYRCGNVAAIL 14 38 SHADLDRQIEQLKECKPLPEAEVKVLCDKAKEILVEES 15 50 AHAHDFNINSISNNSDGETFISADDLRINLWNLEISNQCFNIIDMKPANM 16 50 YKTEFQSHEPEFDYLKSLEIEEKINKIRWCQTQNGALFLLSSNDKTIKFW 17 50 MDSGPVATFKVHENLRPKLCELYENDSIFDKFECCJSGDGJHFATGSYSN 18 38 EVITSAEFHPIHCNLLAYSSSRGFIRLIDMRCSALCDQ 19 17 TMIKQILSKLPRKPSKS 20 50 PLEWKFSQVFGERPAGEEVQEVDIISAIEFDKSGDHLAVGDRGGRVVJFE Table 2.
Motif sequences identified by the MEME tool.
Figures
(7)
Tables
(2)