-
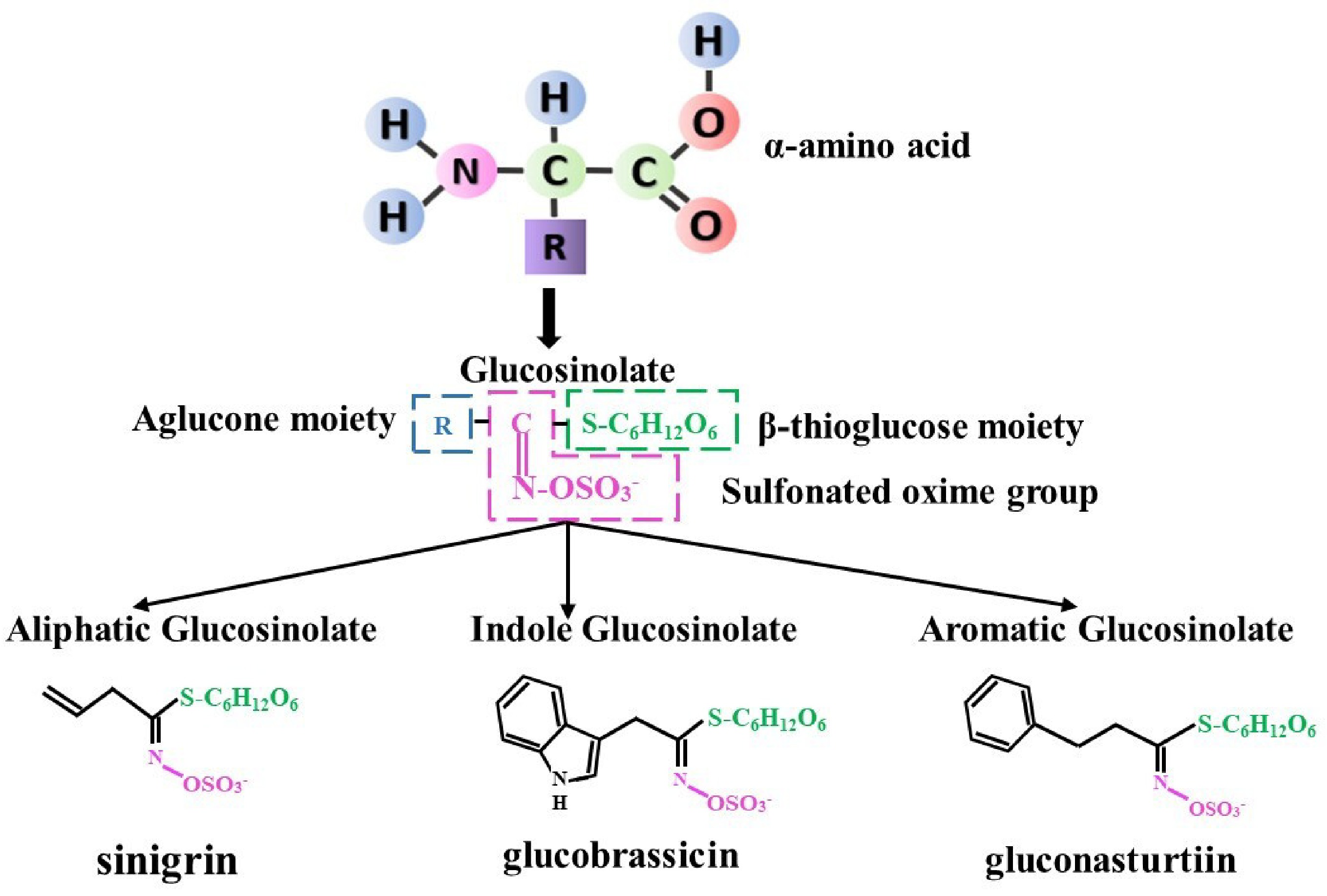
Figure 1.
Glucosinolate structure and type.
-
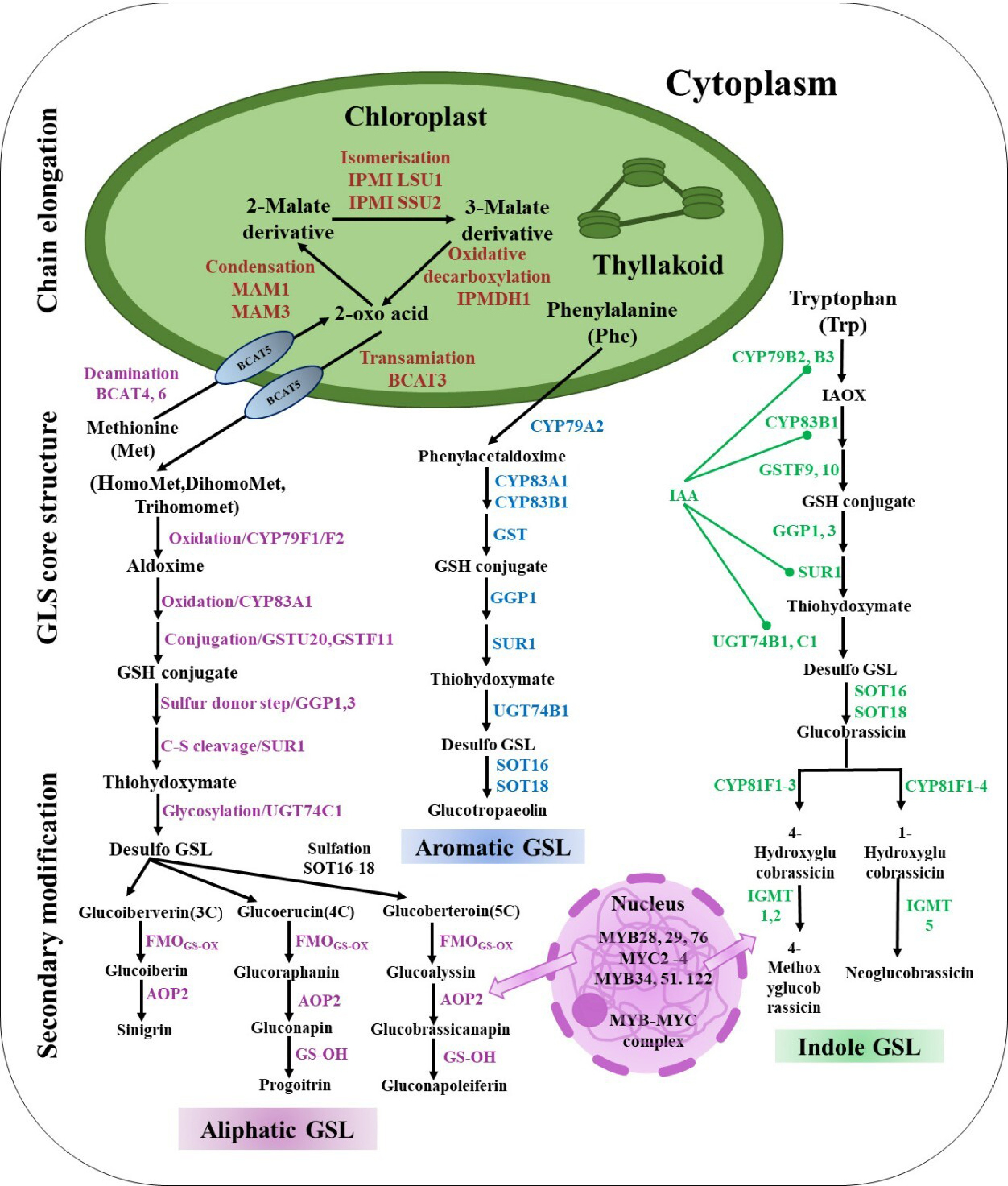
Figure 2.
Mechanisms in Brassicaceae synthesize GSLs: The biosynthesis of GSLs consists of three phases, including chain elongation, GSL core structure, and secondary modification. Met, methionine; Phe, phenyl alanine; Trp, tryptophan; BCAT, branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase; MAM, methylthioalkylmalate synthase; IPMI, isopropylmalate isomerase; IPMDH, isopropylmalate dehydrogenase; CYP79F1, cytochrome P450 79F1; CYP79F2, cytochrome P450 79F2; CYP79A2, cytochrome P450 79A2; CYP83A1, cytochrome P450 83A1; CYP83A2, cytochrome P450 83A2; CYP83B1, cytochrome P450 83B1; GSTU20, glutathione-S-transferases TAU 20; GSTF11, glutathione-S-transferases F11; GGP1, gamma-glutamyl peptidases 1; GGP3, gamma-glutamyl peptidases 3; SUR1, super root 1; UGT74C1, UDP-glycosyl transferase 74C1; UGT74B1, UDP-glycosyl transferase 74B1; SOT16, sulfotransferase 5a; SOT16, sulfotransferase 5c; SOT16, sulfotransferase 5b; FMO, flavin monooxygenase glucosinolate S-oxygenase; AOP2, alkenyl hydroxalkyl-producing 2; GS-OH, 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase; CYP81F1, cytochrome P450 81F1; CYP81F2, cytochrome P450 81F2; CYP81F3, cytochrome P450 81F3; CYP81F4, cytochrome P450 81F4; IGMT1, indole GSL O-methyltransferase 1; IGMT2, indole GSL O-methyltransferase 2; IGMT5, indole GSL O-methyltransferase 5.
-
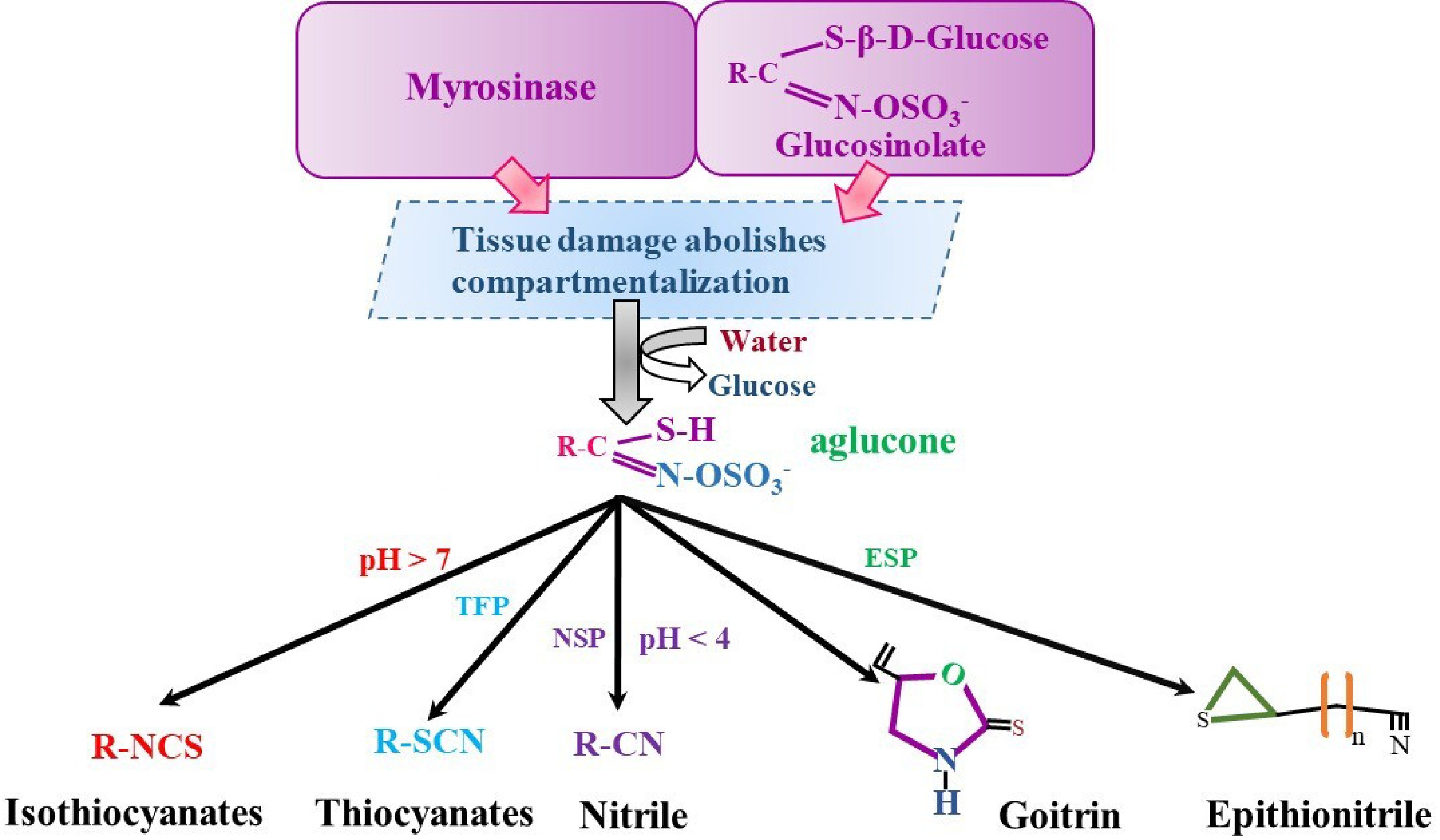
Figure 3.
Glucosinolates hydrolysis in Brassica plant cells. NSP, nitrile specifier proteins; ESP, epithiospecifier proteins; TSP, thiocyanate specifier proteins.
-
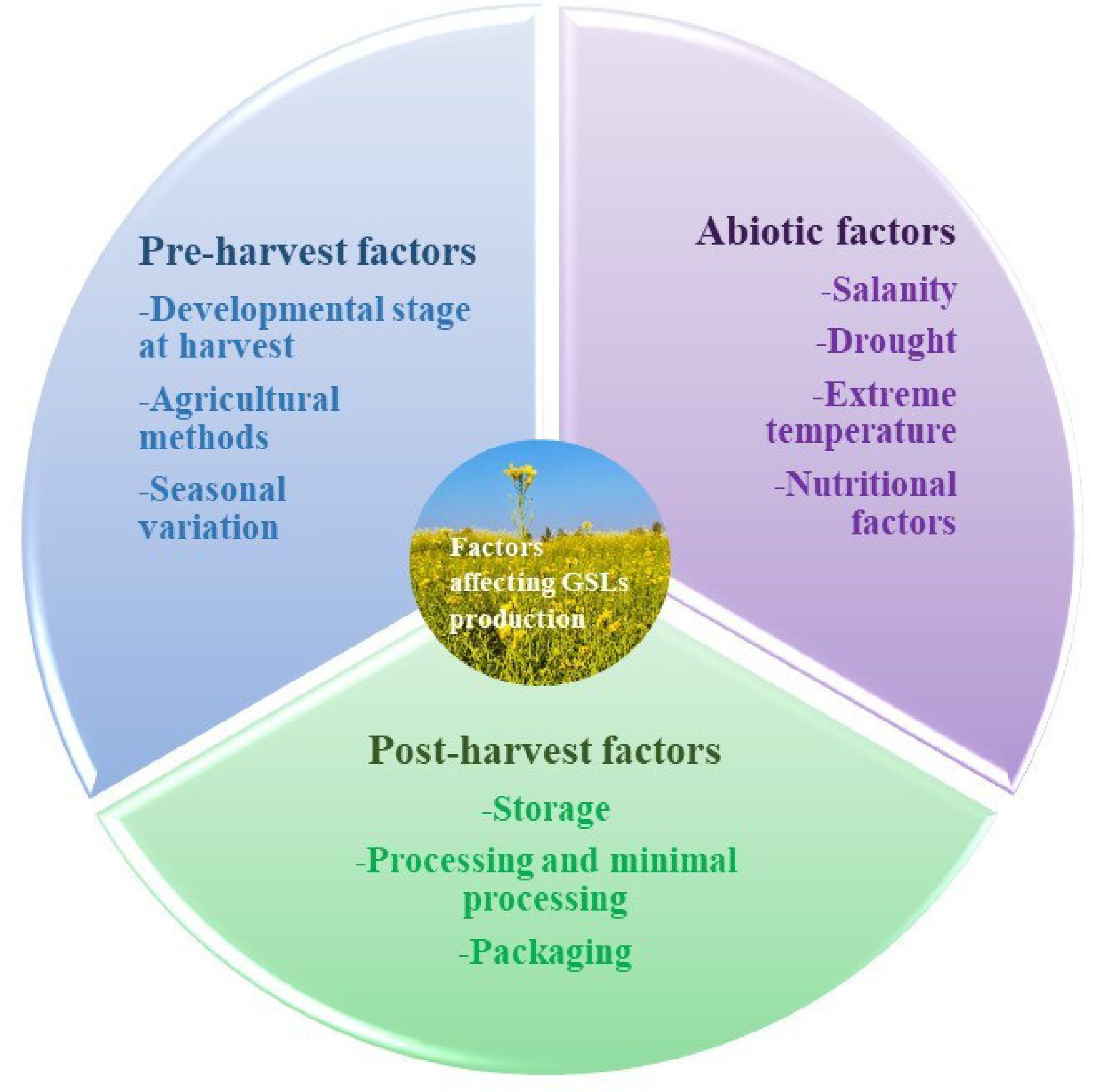
Figure 4.
Factors influencing the glucosinolate content of Brassica.
-
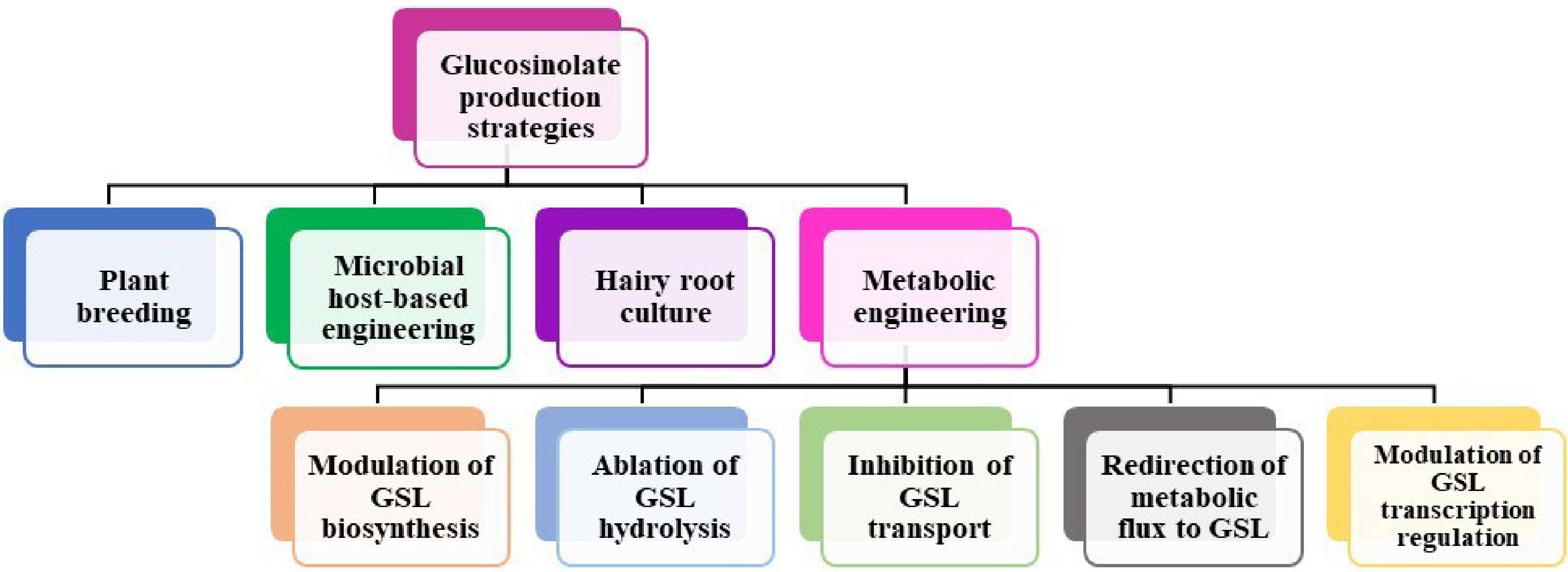
Figure 5.
Strategies to improve glucosinolate production in Brassicaceae.
-
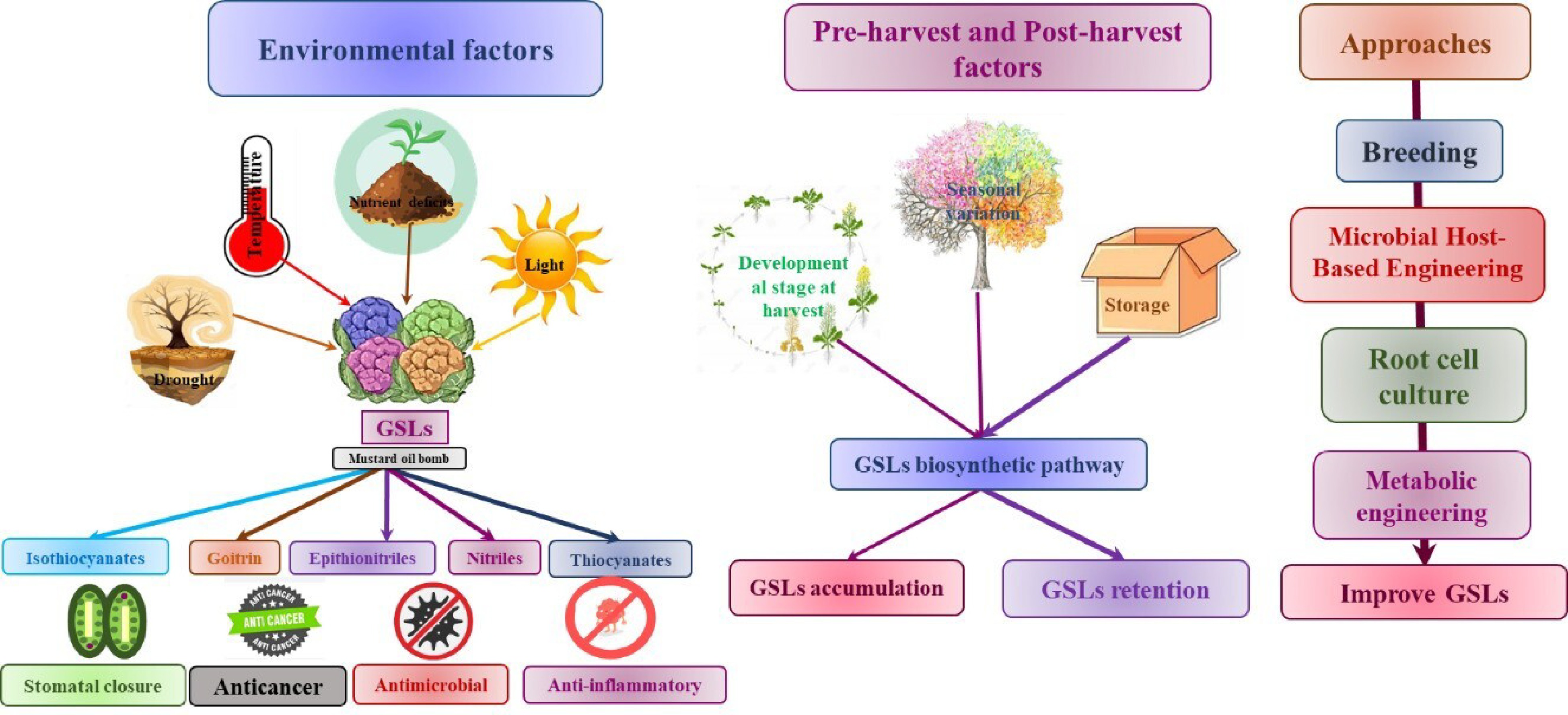
Figure 6.
Regulatory network of GSLs metabolism and sustainable managements for GSLs improvement in Brassicaceae.
-
Common name Chemical name
(side chain R)Molecular weight (g·mol−1) Prominently observed in Benefits to health or toxicity Ref. Aliphatic glucosinolate Three carbon chain length Sinigrin 2-Propenyl GSL 359 Mustard green, white and red cabbage, cauliflower, kale and kohlrabi Anticarcinogenic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, wound-healing properties, and antioxidant activity [9−13] Glucoiber verin 3-Methylthio propyl GSL 407 White and red cabbage,
cauliflower and kaleAntimicrobial activity [9,11−14] Glucoiber in 3-Methylsulfi nylpropyl GSL 423 Cabbage, broccoli and cauliflower Antimicrobial activity [9,11−14] Four carbon chain length Gluconapi n 3-Butenyl GSl 373 Chinese cabbage, mustard spinach, cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower and rapeseed Anticarcinogenic activity, prevention of postprandial hypertriglyceridemia and antimicrobial activity [9,11−13,
18,21,22]Progoitrin (2R) 2-Hydroxy- 3-butenyl GSL 389 Chinese cabbage, mustard spinach, turnip, broccoli, cauliflower and rapeseed Antiviral activity, effect of goitrogens, and suppression of the synthesis of thyroid hormones [9,11−13,
15−17]Glucoeruc in 4-Methylthio butyl GSL 421 Garden rocket Anticarcinogenic activity, antioxidant activity and anti-obesity activity [9,11−13,
23−25]Glucorap hanin 4-Methylsulfi nylbutyl GSL 437 Broccoli, garden rocket, cauliflower and kohlrabi Anti-inflammatory activity, recovery and prevention of muscle atrophy and alcohol intolerance preventive [9,11−13,
26−28]Five carbon chain length Glucobras sicanapin 4-Pentenyl GSL 387 Chinese cabbage, turnip, turnip green and swede Antimicrobial activity [9,11−13,18] Glucoalyssin 5-Methylsulfi nylpentyl GSL 451 Ethiopian mustard Anticarcinogenic activity and antimicrobial activity [11−14,29,30] Aromatic glucosinolate Gluconast urtiin 2-Phenethyl GSL 423 Watercress and horseradish Anticarcinogenic activity, cardioprotective and neuroprotective activity [11−13,22,
31,32]Glucotrop aeolin Benzyl GSL 409 Red cabbage Antidiabetic, neuroprotective activity and prevention of
multiple sclerosis
[11−13,22,33]Indole glucosinolate Glucobras sicin 3-lndolyl methyl GSL 448 Green cabbage, broccoli, chinese and red cabbage Impediment to cancer in prostate [11−13,19,20] Neogluco brassicin 1-Methoxy-3- indolymethyl GSL 478 Red cabbage, Chinese cabbage, broccoli, and green cabbage Inhibition of cancer in prostate [11−13,19,20] Table 1.
Major glucosinolates and their health benefits in Brassicaceae.
-
Variable Plant species Change in glucosinolate level Ref. Abiotic factors Soil salinity Brassica oleracea var. italica (broccoli) and B. rapa var. pekinensis (Chinese cabbage) Increase total GSLs (40, 80 mM) [44] R. sativus (radish), Brassica oleracea var. botrytis
(cauliflower) and B. oleracea var. italica (broccoli)Increase total GSLs with reduced water [56] Water availability B. oleracea var. capitata (cabbage), Brassica napus (rapeseed) and Brassica oleracea var. italica (Broccoli) Increase total GSLs with severe drought [44] Brassica carinata (Ethiopian mustard) and B. oleracea
var. gemmifera (Brussels sprouts)No effect under mild drought [44,56] B. rapa var. rapa (turnip) Increase total GSLs with mild drought [44] Brassica oleracea var. capitata (cabbage) and
Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress)Decrease total GSLs under mild and severe drought [44] Temperature stress B. oleracea var. italica (broccoli), B. oleracea var.
botrytis (cauliflower)At a moderate temperature of 14 °C and increase total GSLs [56] B. oleracea var. capitata (cabbage), B. oleracea L. var. gemmifera (Brussels sprouts) and B. oleracea var.
acephala (kale)Total GSLs diminish as temperature rises [61] B. napus (swede) Progoitrin and glucoberteroin should be increased to 21 °C [113] B. rapa var. pekinensis (Chinese cabbage) Vary the total GSLs from 21 to 34 °C [44] B. oleracea var. italica (broccoli) and B. oleracea var.
botrytis (cauliflower)Increase overall GSLs under bright conditions
(450 μmol·m−2·s−1)[56] B. oleracea var. italica (broccoli) and B. oleracea var.
botrytis (cauliflower)Reduce glucoraphanin levels during harvest using high light [44] Light intensity B. oleracea var. italica (broccoli) Diminish overall GSLs with light [44] B. oleracea var. capitata (cabbage) and B. oleracea var. gemmifera (Brussels sprouts) Variation in total and indole GSLs with respect to light intensity and duration [61] Cardamine fauriei (Ezo-wasabi) Total GSLs increase; red + blue luminescence [68] Brassica oleracea var. acephala (kale) Change in total and indole GSLs with respect to light intensity and day length [61] Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) Light increases total GSLs, while darkness reduces total GSLs [44] Sulfur application B. oleracea var alboglabra (Chinese kale) Blue light diminishes gluconapin levels [114] B. oleracea var. italica (broccoli) Enhance indole and alkyl GSLs (60 mg of S plant−1) [56] Raphanus sativus (radish) Boost alkenyl GSLs (30 mg·plant−1) [56] Brassica rapa var. rapa (turnip) Promote overall GSLs (60 kg S ha−1) [44] Potassium application Brassica rapa var. rapa (turnip) Decrease total GSLs with K+ deficiency [44] Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) Increase overall GSLs when K+ is lacking [44] Nitrogen application B. oleracea var. botrytis (cauliflower), B. oleracea var.
italica (broccoli) and Raphanus sativus (radish)Increase total GSLs by decreasing nitrogen [56] Brassica oleracea var. italica (broccoli) Increase average GSLs while decreasing N (1 g of
N plant−1)[44] Brassica oleracea var. italica (broccoli) Raise the overall GSLs by 5.2 mM Se [44] Selenium application Raphanus sativus (radish) Enrich the soil with total GSLs and glucoraphanin [81] Pre-harvest factors Brassica oleracea var. italica (broccoli) Increase indole GSLs in immature florets, increase glucoraphanin between transplanting and harvest [61,115] Developmental stage
at harvestB. oleracea var. capitata (cabbage), B. oleracea var. gemmifera (Brussels sprouts), B. oleracea var. botrytis (cauliflower) and B. oleracea var. acephala (kale) Increase glucoraphanin between transplanting and harvest [61] Seasonal variation B. oleracea var. italica (broccoli) and Brassica oleracea
var. botrytis (cauliflower)Enhance overall GSLs in spring and autumn [56] B. oleracea var. capitata (cabbage) and B. oleracea var. gemmifera (Brussels sprouts) Increase glucoiberin and glucobrassicin in spring [84] Agricultural practices B. oleracea var italica (broccoli) The levels of 3-indolylmethyl-GSL were considerably elevated in crops grown organically [91] Post-harvest factors Storage B. oleracea var. italica (broccoli) The content of 4-methylsulfinylbutyl-GSL in florets exhibited an increase subsequent to a 6-d storage period, which was followed by a decrease in temperature [94] Processing and minimal processing B. oleracea var. italica (broccoli) An increase of 490% in total GSLs, 4,200% in 4-hydroxy-3-indolylmethyl-GSL, and the rise of 1,300% in 1-methoxy-3-indolylmethyl-GSL was reported after 24 h of incubation at a temperature of 20 °C [103] Packaging Brassica oleracea var. italica (broccoli) Compared to fresh florets, storage in a regulated atmosphere consisting of 0.5% O2, 20% CO2 and air. resulted in a 21%–42% increase in total GSL [112] Table 2.
Impact of abiotic stress, pre-harvest, and post-harvest factors on Brassicaceae glucosinolate levels.
-
Approach Invoved process Strategy Gene name Target species Source species Effect on GSLs Ref. Modulation of GSL biosynthesis Side chain elongation KO MAM1 Chinese cabbage Arabidopsis thaliana Increased aliphatic GSL (3-butenyl-GSL, 4-pentenyl-GSL) [129] Glucone formation KO CYP79F1 Chinese cabbage Arabidopsis thaliana Increased levels of 2-hydroxy-4-pentenyl-GSL, indol-3-ylmethyl-GSL, 4-methoxy-indol-3-ylmethyl-GSL, decreased concentrations of 3-butenyl-GSL and 4-pentenyl-GSL, and increased concentration of 4 hydroxyindol-3-ylmethyl-GSL [140] Glucone formation KO CYP83A1 Chinese cabbage Arabidopsis thaliana Increased aliphatic GSL [129] Secondary
modificationOE FMOGS-OX Brassica rapassp. rapa Brassica rapa
ssp. rapaElevated aliphatic GSL [130] Glucone formation OE CYP79B2, CYP79B3, CYP83B1 Brassica rapa Arabidopsis thaliana Increased indolic GSL [131,141] Glucone formation OE UGT74B1 B. napus Brassica napus Elevate aliphatic GSL and indolic GSL [132] Ablation of GSL hydrolysis GSL hydrolysis Co- expression Myr1.Bn1 B. napus Brassica napus Seeds' myrosinase storing idioblasts were eliminated [133] Inhibition of GSL transport GSL transport KO GTR B. rapa Brassica rapa Lowered GSL content in seedlings [135] Redirection of metabolic flux to GSL Engineering metabolic flux Mutation TDC Brassica napus Catharanthus roseus Diminished indolic GSL in both seedlings and entire plants [136] Transcriptional regulation GS MYB28 Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra Raised in aliphatic GSLs [137] Modulation of GSL transcription regulation Transcriptional regulation OE MYB28 Brassica rapa Brassica rapa Aliphatic GSL and indolic GSL are elevated [138] Transcriptional regulation OE MYB29 Brassica oleracea Brassica oleracea Enhanced aliphatic GSL concentration (2-propenyl glucoraphanin GSL) [139] Table 3.
Metabolic engineering of glucosinolate in Brassicaceae.
Figures
(6)
Tables
(3)