-
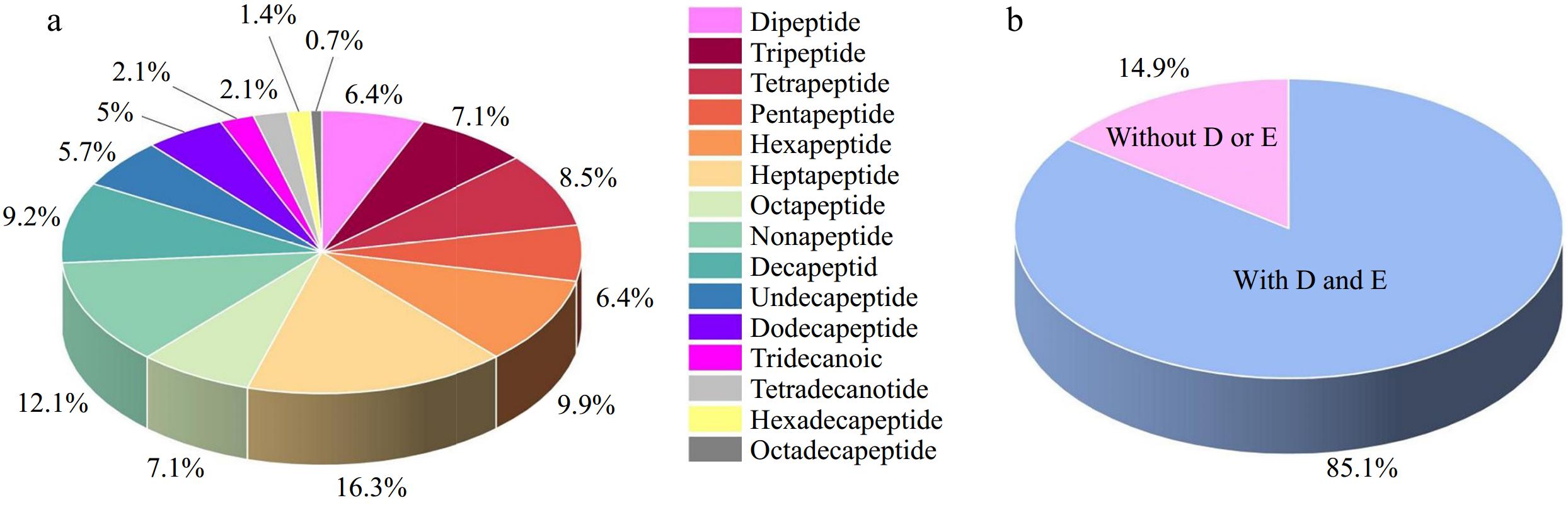
Figure 1.
The information of the identified marine umami peptides. (a) The distribution of the identified marine umami peptides. (b) The percentage of marine umami peptides with umami amino acid (D: aspartic acid, E: glutamic acid).
-
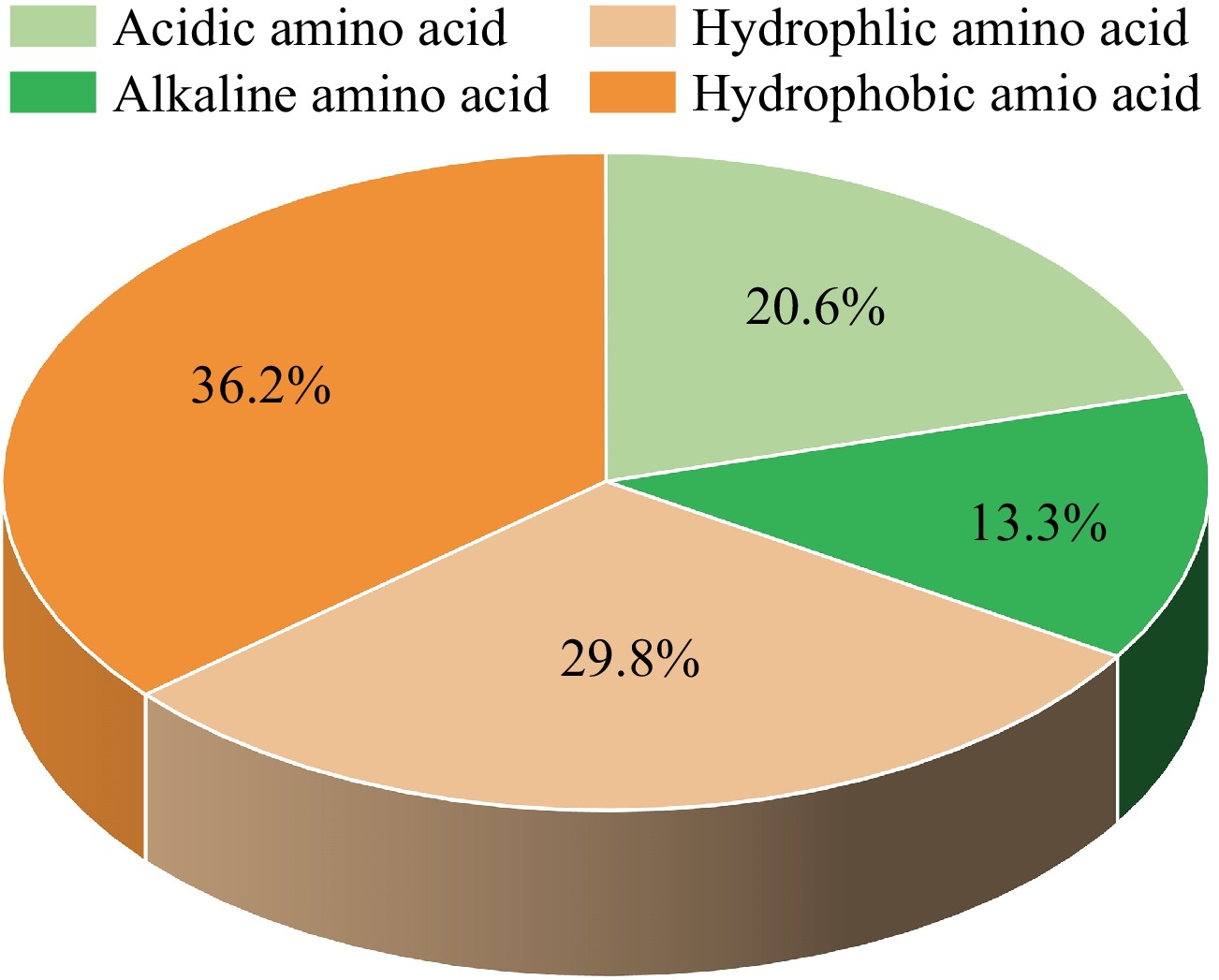
Figure 2.
The amino acid composition of the reported marine umami peptides according to the amino acid features.
-
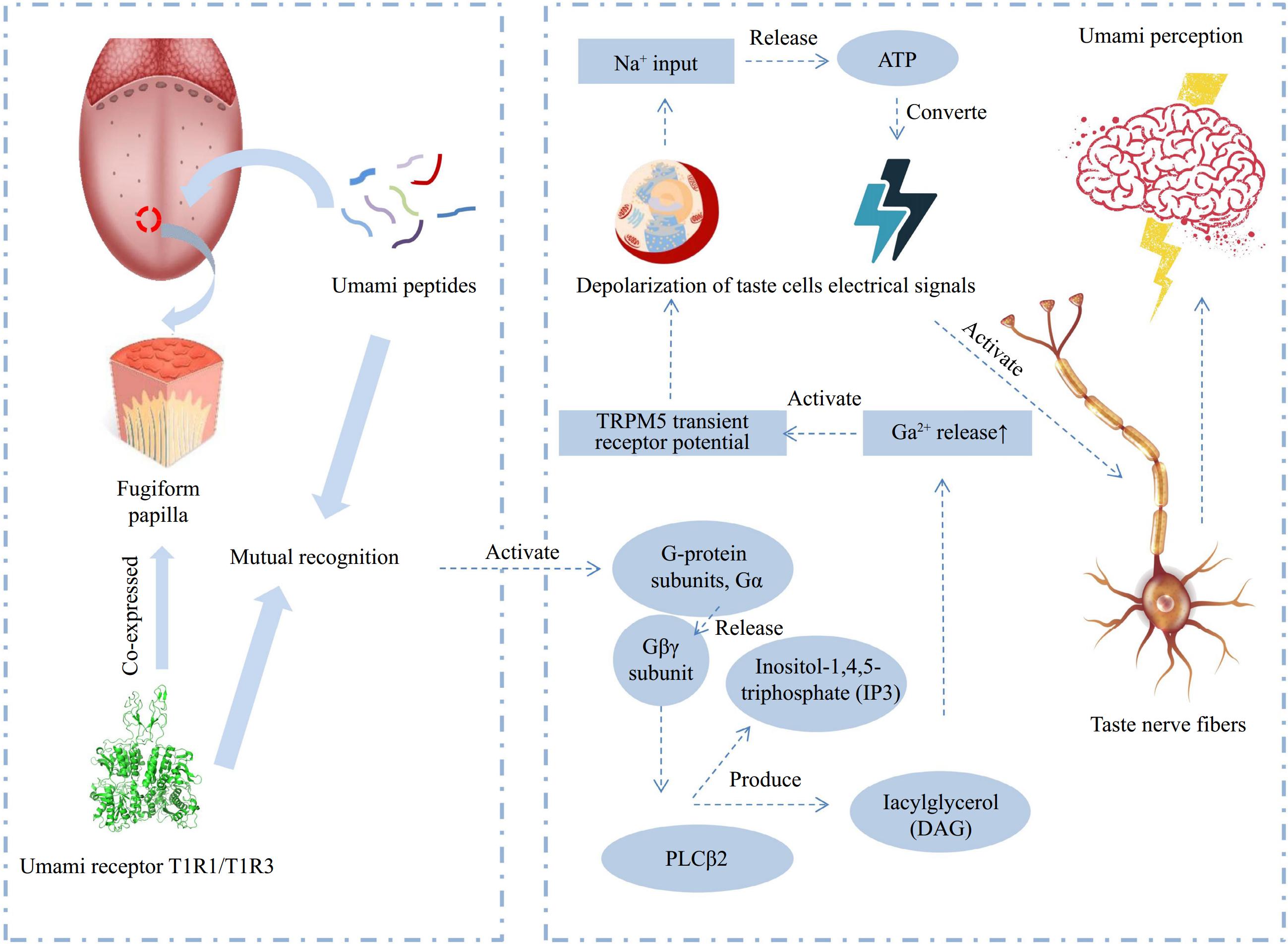
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the flavor mechanism of umami peptides (adapted from[32]).
-

Figure 4.
The application prospect of Industry 4.0 in marine umami peptides.
-
Methods Mechanism Advantages Disadvantages Ref. Microbial fermentation Microbial metabolism degrades marine proteins into peptides Simple operation, safety and low cost High environmental requirements [50,87] Enzymatic hydrolysis Proteases specifically cleave hydrolytic peptide bonds Mild reaction conditions, green environmental protection, and high yield Poor control of the reaction leads to the production of undesirable by-products [21,50,51,54] Acid hydrolysis Proteins are hydrolyzed under acidic conditions Low cost and high yield Toxic substances are easily produced in the reaction process [66,100] High-temperature
processingProtein degrades into small parts under thermal treatment Simple operation and high efficiency High energy consumption and high requirements for equipment [30,68−72] Solvent extraction The majority of umami peptides are soluble in water Simple operation and low cost Low efficiency [44,75] Table 1.
Overview of the preparation methods for marine umami peptides.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(1)