-
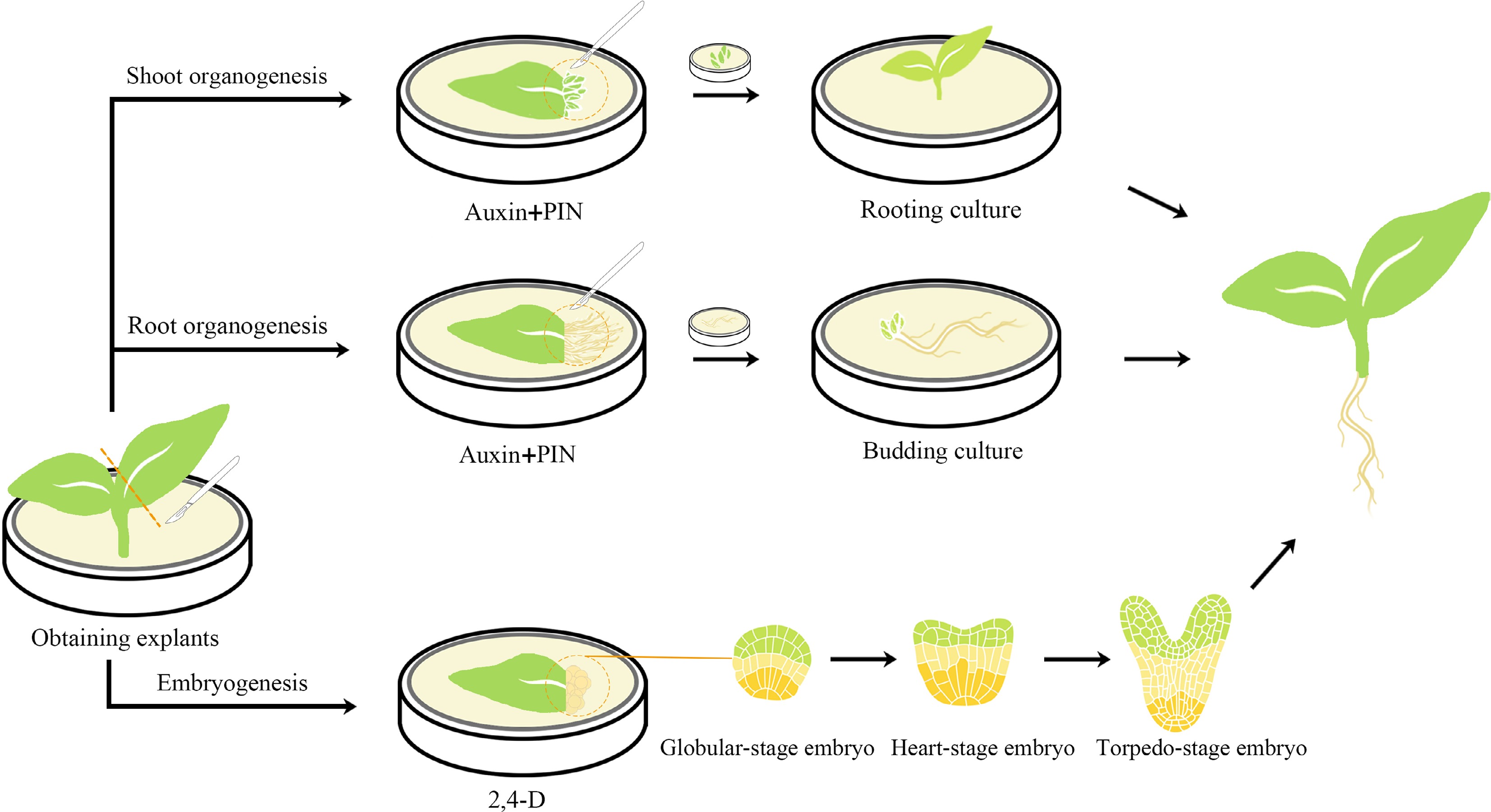
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis processes in plant regeneration. Organogenesis can be achieved through the induction of bud formation, followed by in vitro culture of the newly formed buds and subsequent cultivation of independent plants through root culture. Alternatively, root formation can be induced, and the roots can be cultured in vitro to stimulate bud formation and generate new individuals. The majority of somatic embryogenesis processes necessitate induction with 2,4-D, and after successful induction, somatic embryos go through several stages before shoot formation.
-
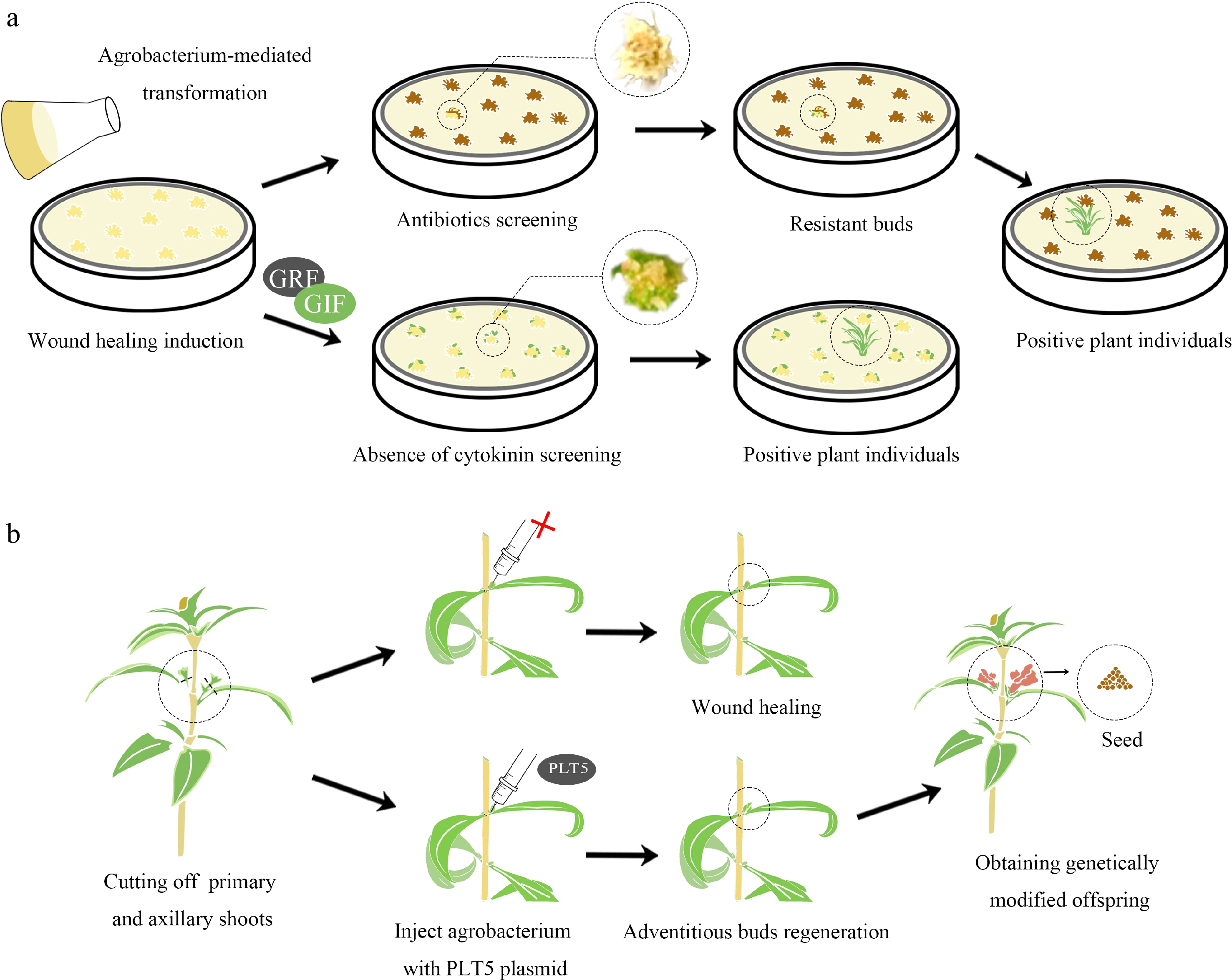
Figure 2.
Screening genetically modified plants by enhancing their regeneration ability. (a) Traditionally, the process of transformational screening involves the introduction of Agrobacterium into plant explants, which carries a resistance gene in the T-DNA region of its plasmid. These explants are then screened in specific antibiotics to obtain resistant shoots. When explants are infected with GRF-GIF chimeric protein, they are placed in a cytokinin-free medium for regeneration. Shoots produced without the need for cytokinins could potentially be positive and selected in an antibiotic-free manner. (b) Snapdragons were injected with plasmids containing or lacking the PLT5 gene. After injection with agrobacterium carrying the PLT5 gene, small buds formed at the wound sites of the goldfish plants, which could give rise to positive seeds. In contrast, wounds injected with Agrobacterium lacking the PLT5 gene healed without bud formation.
-
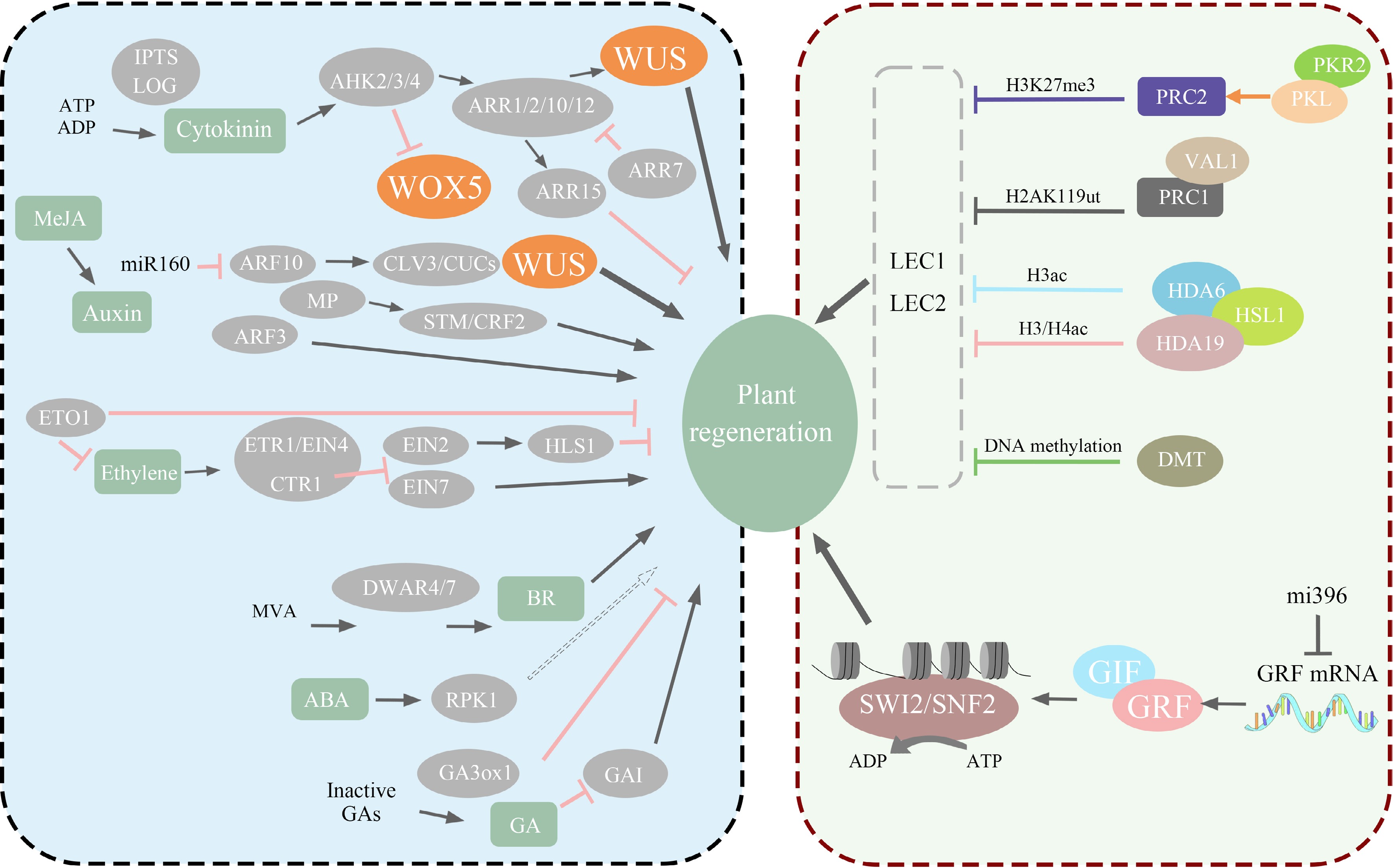
Figure 3.
The left half of the diagram illustrates how various genes related to regeneration directly or indirectly regulate plant regeneration through different pathways, such as WUS and WOX. The right half of the diagram portrays the impact of epigenetics on plant regeneration, including histone modifications and nucleosome structure remodeling.
-
Species Plant category Plant regeneration pathway Ref. Chrysanthemum morifolium Dicotyledonous herbaceous plant Organogenesis [27] Dianthus chinensis Organogenesis [16] Tanacetum cinerariifolium Organogenesis [17] Origanum vulgare Organogenesis [18] Taraxacum koksaghyz Organogenesis [19] Tulipa gesneriana Somatic embryogenesis [20] Smusa spp. Monocotyledonous herbaceous plant Somatic embryogenesis [21] Crinum
malabaricumSomatic embryogenesis [28] Fritillaria meleagris Somatic embryogenesis [29] Lilium longiflorum Somatic embryogenesis [22] Sansevieria trifasciata Organogenesis [26] Lilium candidum Organogenesis [23] Aeschynanthus pulcher Woody plant Organogenesiss [30] Robinia pseudoacacia Organogenesis [31] Koelreuteria paniculata Somatic embryogenesis [32] Cinnamomum camphora Somatic embryogenesis [33] Platanus acerifolia Organogenesis [25] Table 1.
Regeneration mode of some ornamental plants.
Figures
(3)
Tables
(1)