-
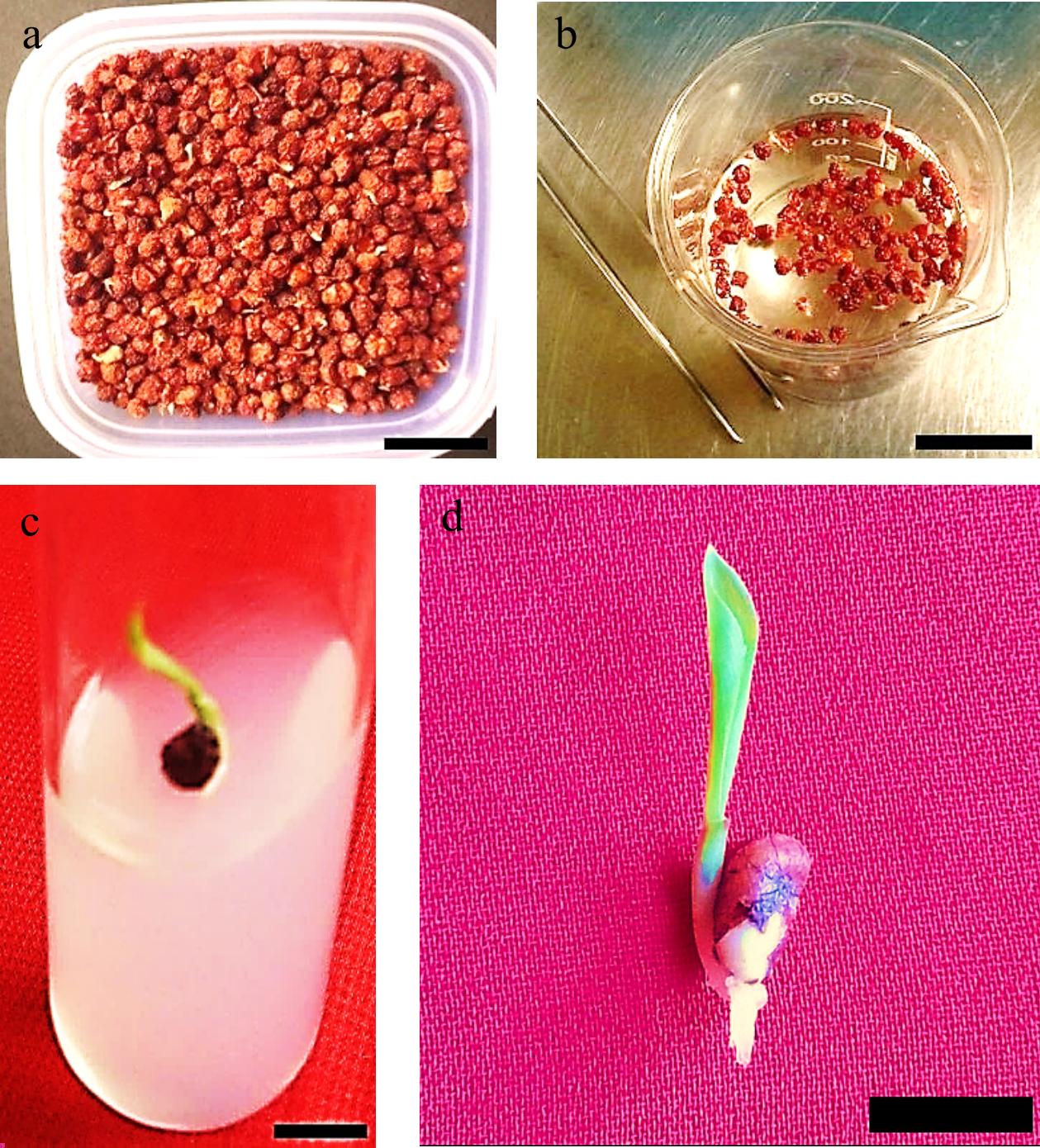
Figure 1.
Gloriosa superba L. seeds were obtained from the Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve (Madhya Pradesh, India) and cultured using in vitro techniques. (a) Batch of pre-sterilized seeds; (b) Seed sterilization process taking place in laminar air flow (LAF); (c) Seed germination; (d) Healthy in vitro seedling germination. Scale bar = 2 cm.
-
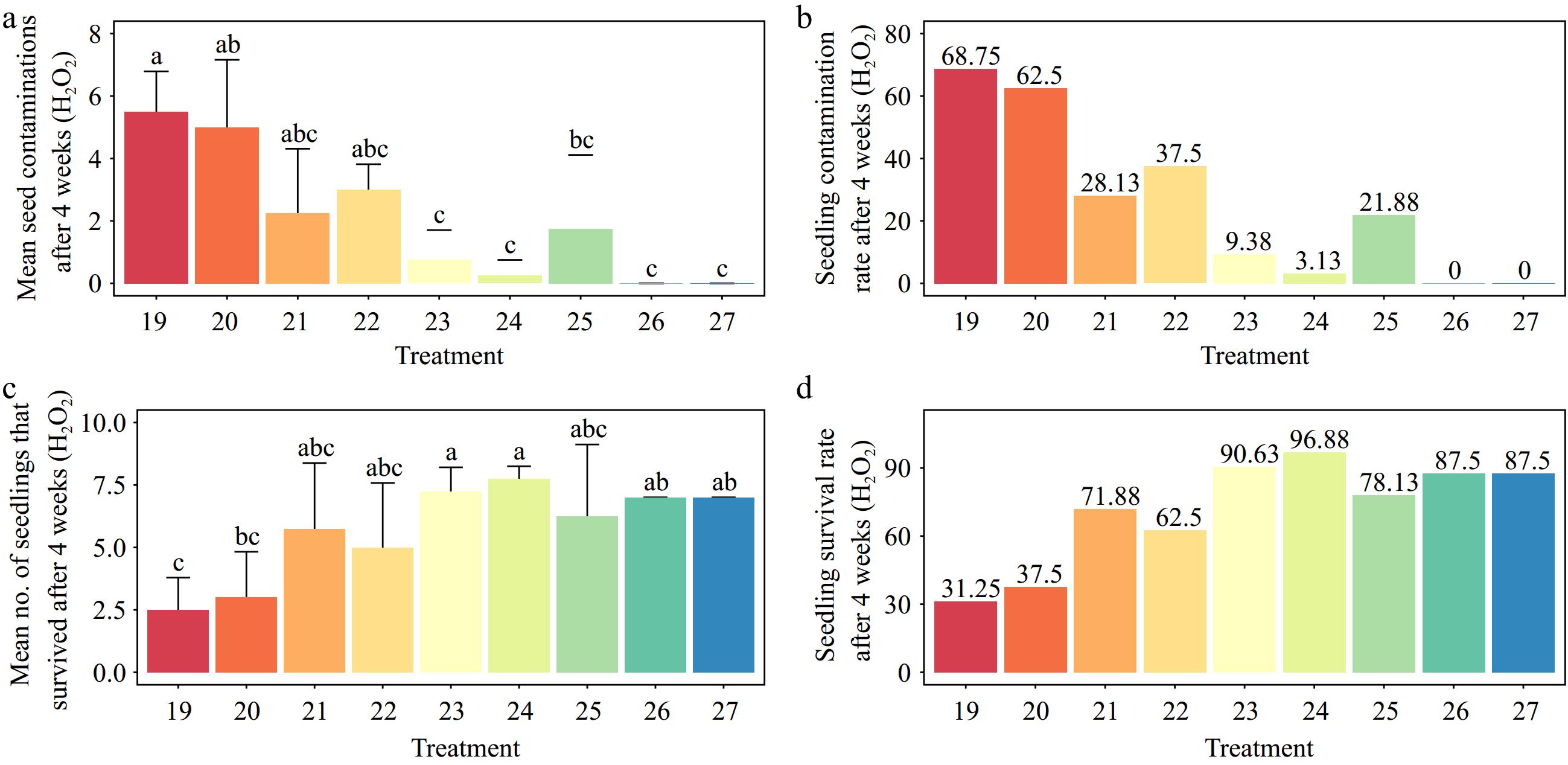
Figure 2.
Effects of various concentrations of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and immersion times on Gloriosa superba L. seed sterilization after 4 weeks of culture. (a) Mean seed contamination, (b) seedling contamination rate, (c) mean number of seedlings that survived, and (d) seedling survival rate are shown. Treatments are T19: 5.0% H2O2 for 2 min; T20: 5.0% H2O2 for 5 min; T21: 5.0% H2O2 for 8 min; T22: 7.5% H2O2 for 2 min; T23: 7.5% H2O2 for 5 min; T24: 7.5% H2O2 for 8 min; T25: 10% H2O2 for 2 min; T26: 10% H2O2 for 5 min; T27: 10% H2O2 for 8 min. Bars indicate mean ± SE. Different letters indicate significant difference by Tukey's test at p ≤ 0.05.
-
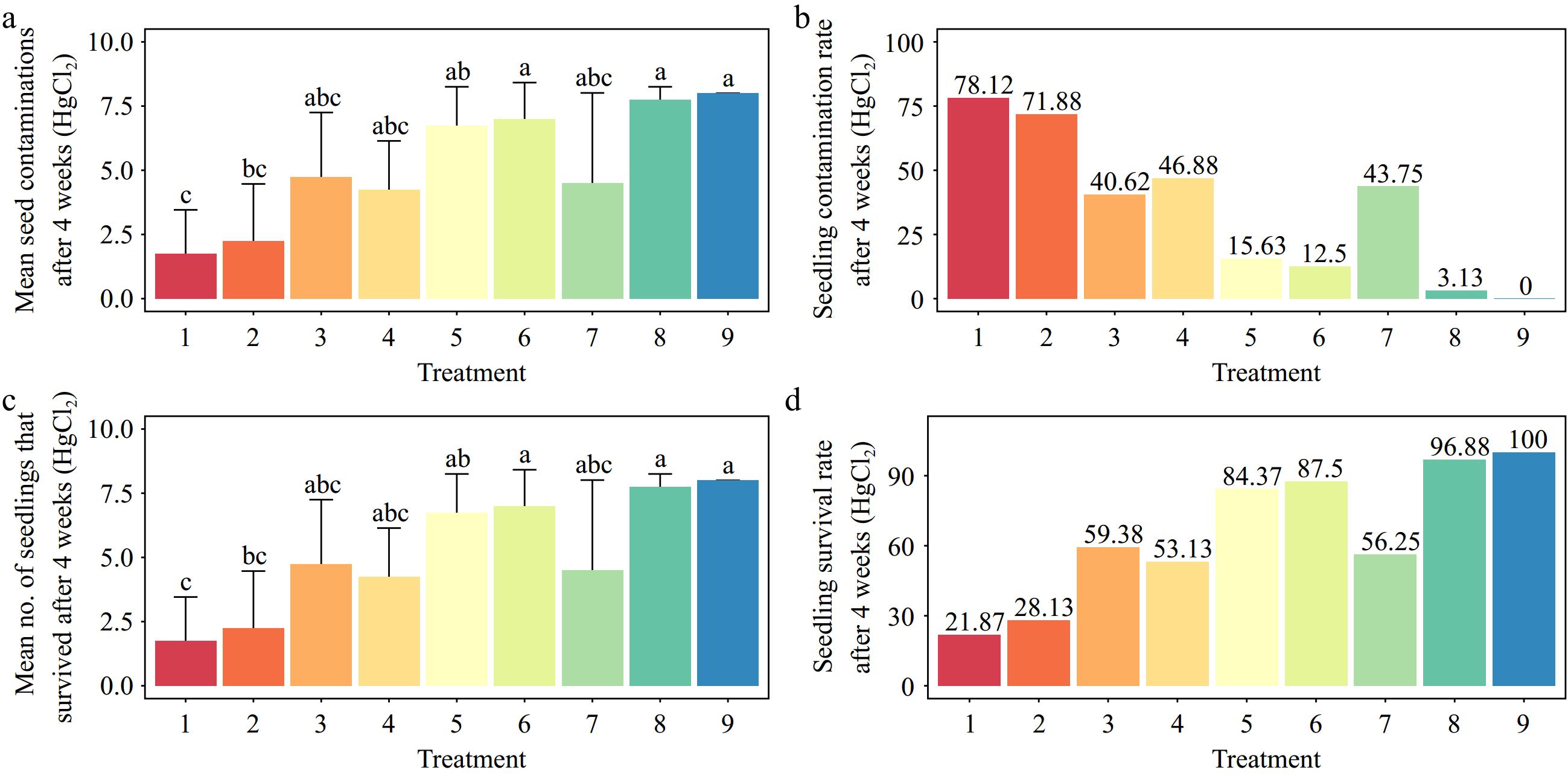
Figure 3.
Effects of various concentrations of mercuric chloride (HgCl2) and immersion times on Gloriosa superba L. seed sterilization after 4 weeks of culture. (a) Mean seed contamination, (b) seedling contamination rate, (c) mean number of seedlings that survived, and (d) seedling survival rate are shown. Treatments are T1: 0.05% HgCl2 for 2 min; T2: 0.05% HgCl2 for 5 min; T3: 0.05% HgCl2 for 8 min; T4: 0.1% HgCl2 for 2 min; T5: 0.1% HgCl2 for 5 min; T6: 0.1% HgCl2 for 8 min; T7: 0.15% HgCl2 for 2 min; T8: 0.15% HgCl2 for 5 min; T9: 0.15% HgCl2 for 8 min. Bars indicate mean ± SE. Different letters indicate significant difference by Tukey's test at p ≤ 0.05.
-
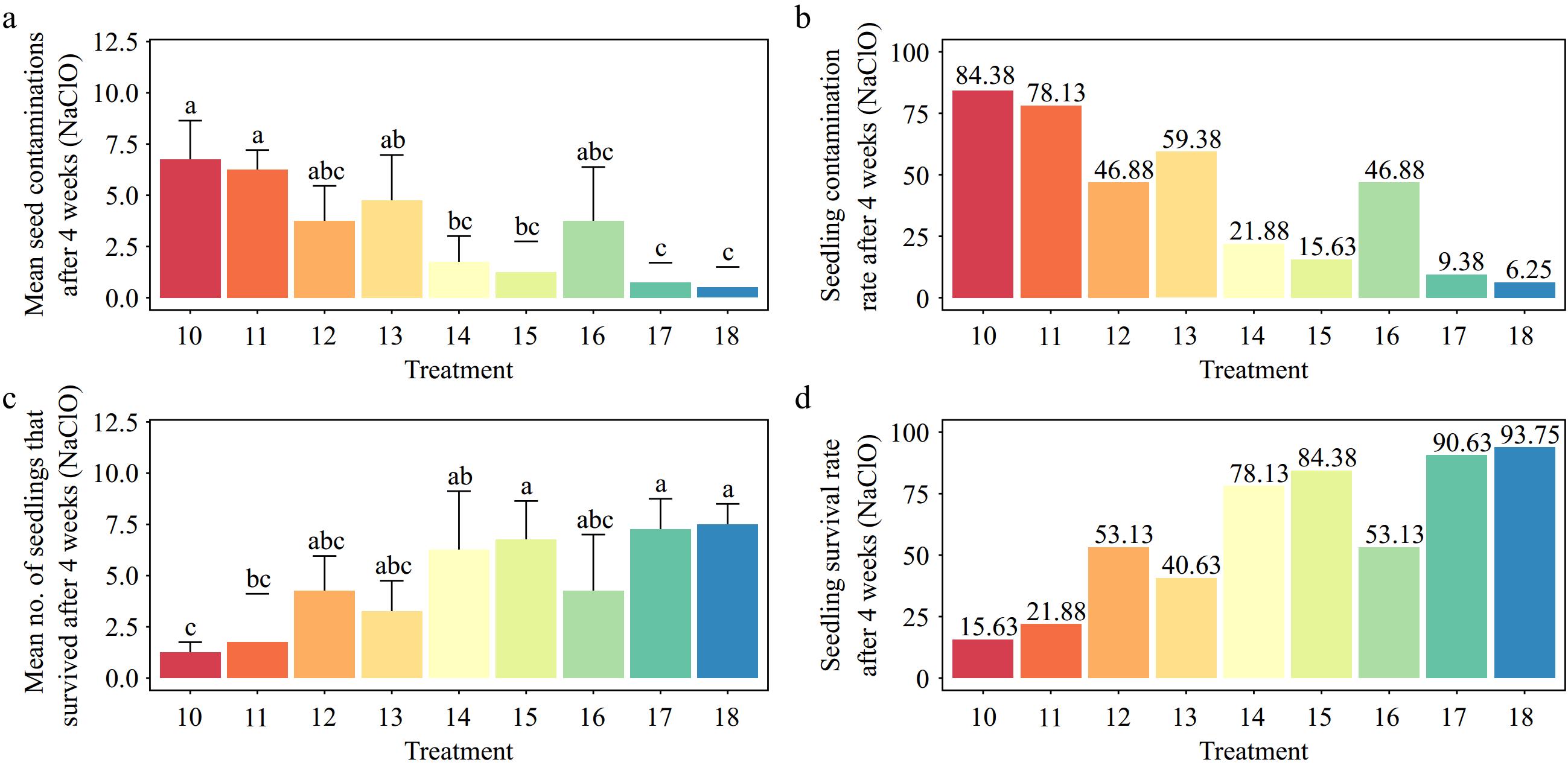
Figure 4.
Effects of different sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) concentrations and immersion times on Gloriosa superba L. seed sterilization after 4 weeks of culture. (a) Mean seed contamination, (b) seedling contamination rate, (c) mean number of seedlings that survived, and (d) seedling survival rate. Treatments are T10: 0.5% NaClO for 2 min; T11: 0.5% NaClO for 5 min; T12: 0.5% NaClO for 8 min; T13: 1.0% NaClO for 2 min; T14: 1.0% NaClO for 5 min; T15: 1.0% NaClO for 8 min; T16: 1.5% NaClO for 2 min; T17: 1.5% NaClO for 5 min; T18: 1.5% NaClO for 8 min. Bars indicate mean ± SE. Different letters indicate significant difference by Tukey's test at p ≤ 0.05.
-
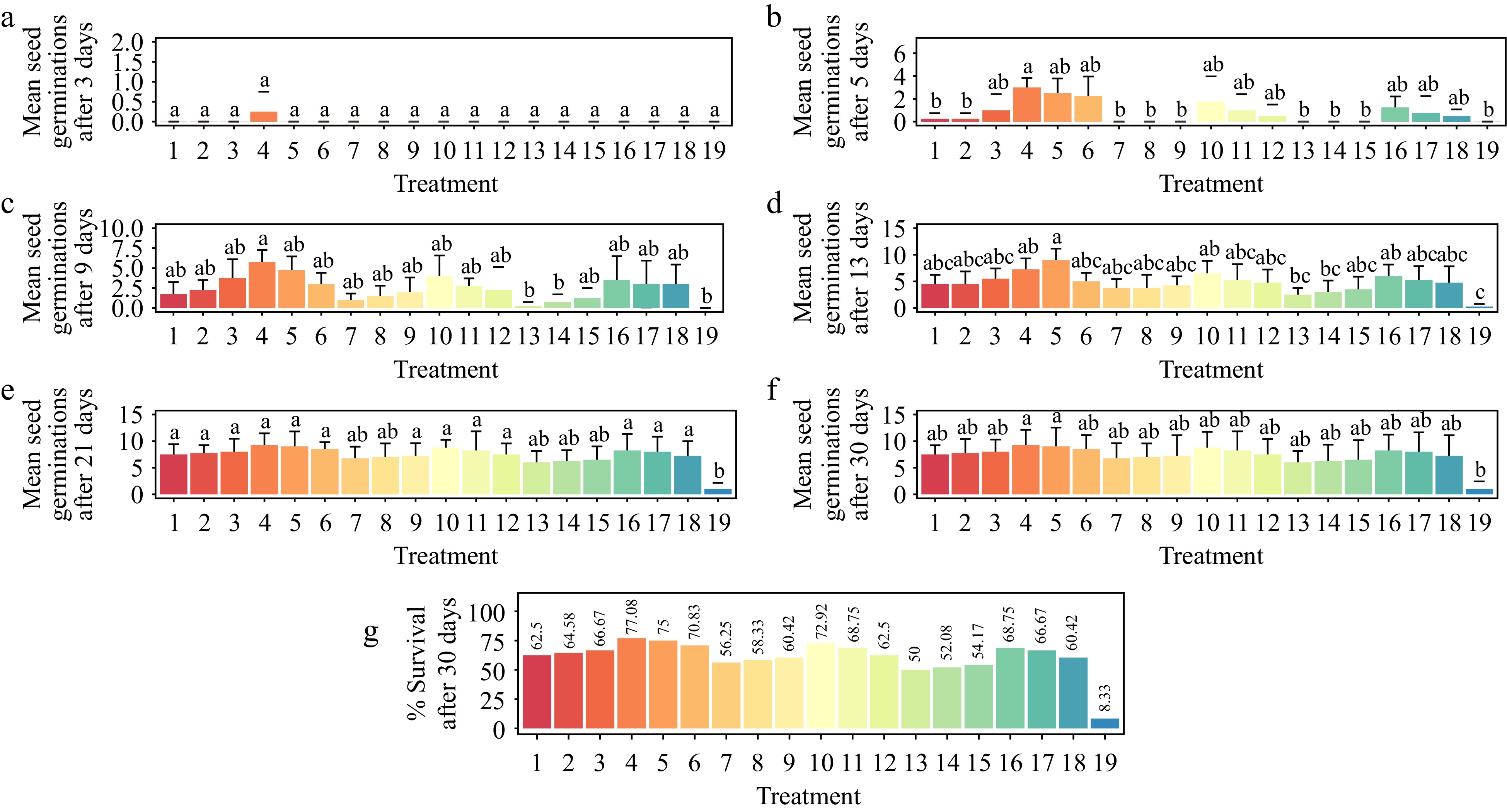
Figure 5.
Effect of plant growth regulators (PGRs) on Gloriosa superba L. seed germination after 30 d of culture. (a) Mean seed germination after 3 d, (b) mean seed germination after 5 d, (c) mean seed germination after 9 d, (d) mean seed germination after 13 d, (e) mean seed germination after 21 d, (f) mean seed germination after 30 d, and (g) seedling survival rate after 30 d are shown. Treatments are T1: 0.2 mg·L−1 GA3 (Gibberellic acid), 0.2 mg·L−1 BAP (6-benzylaminopurine); T2: 0.5 mg·L−1 GA3, 0.5 mg·L−1 BAP; T3: 1.0 mg·L−1 GA3, 1.0 mg·L−1 BAP; T4: 1.5 mg·L−1 GA3, 1.5 mg·L−1 BAP; T5: 2.0 mg·L−1 GA3, 2.0 mg·L−1 BAP; T6: 2.5 mg·L−1 GA3, 2.5 mg·L−1 BAP; T7: 0.2 mg·L−1 GA3, 0.2 mg·L−1 KN (Kinetin); T8: 0.5 mg·L−1 GA3, 0.5 mg·L−1 KN; T9: 1.0 mg·L−1 GA3, 1.0 mg·L−1 KN; T10: 1.5 mg·L−1 GA3, 1.5 mg·L−1 KN; T11: 2.0 mg·L−1 GA3, 2.0 mg·L−1 KN; T12: 2.5 mg·L−1 GA3, 2.5 mg·L−1 KN; T13: 0.2 mg·L−1 GA3, 0.2 mg·L−1 NAA (1-Naphthalene acetic acid); T14: 0.5 mg·L−1 GA3, 0.5 mg·L−1 NAA; T15: 1.0 mg·L−1 GA3, 1.0 mg·L−1 NAA; T16: 1.5 mg·L−1 GA3, 1.5 mg·L−1 NAA; T17: 2.0 mg·L−1 GA3, 2.0 mg·L−1 NAA; T18: 2.5 mg·L− 1 GA3, 2.5 mg·L−1 NAA; T19: Control (media without PGRs). Bars indicate mean ± SE. Different letters indicate significant difference by Tukey's test at p ≤ 0.05.
-
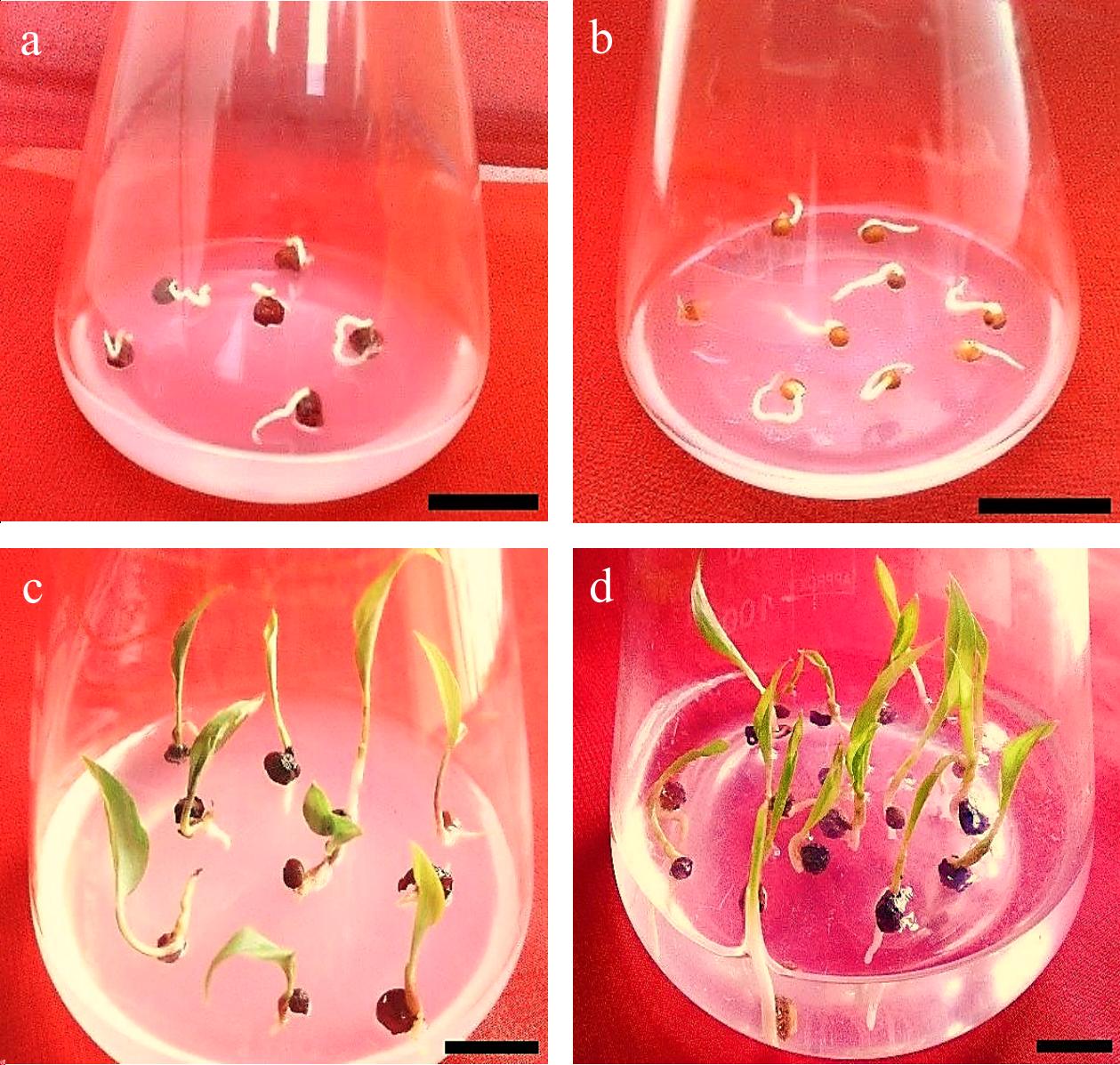
Figure 6.
Gloriosa superba L. seed germination. (a) & (b) Imbibition, seed swelling, and protrusion of the radicle. (c) & (d) Seed and seedling germination. Scale bar = 2 cm.
-
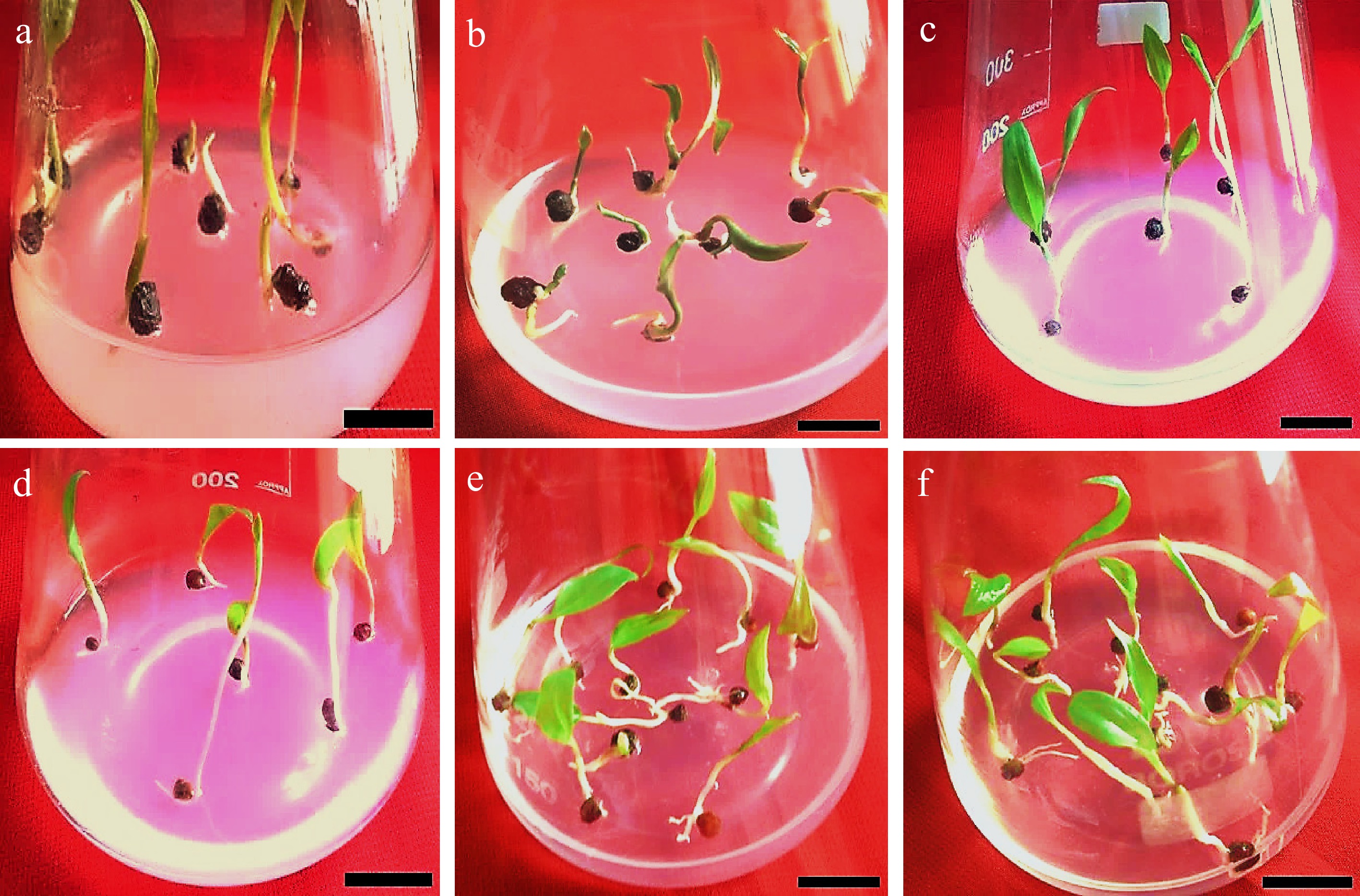
Figure 7.
Effects of various concentrations of PGRs (GA3, BAP, and NAA) on Gloriosa superba L. seed germination in full-strength MS medium supplemented with 30 g·L−1 sucrose after 30 d of culture. (a) & (b) Initial seedling developmental stage on 1.5 mg·L−1 GA3 (Gibberellic acid) + 1.5 mg·L−1 NAA (1-Naphthalene acetic acid) fortified medium. (c) & (d) Initial seedling developmental stage on 1.5 mg·L−1 GA3 + 1.5 mg·L−1 KN (Kinetin) fortified medium. (e) & (f) Initial seedling developmental stage on 1.5 mg·L−1 GA3 + 1.5 mg·L−1 BAP fortified medium. Scale bar = 2 cm.
-
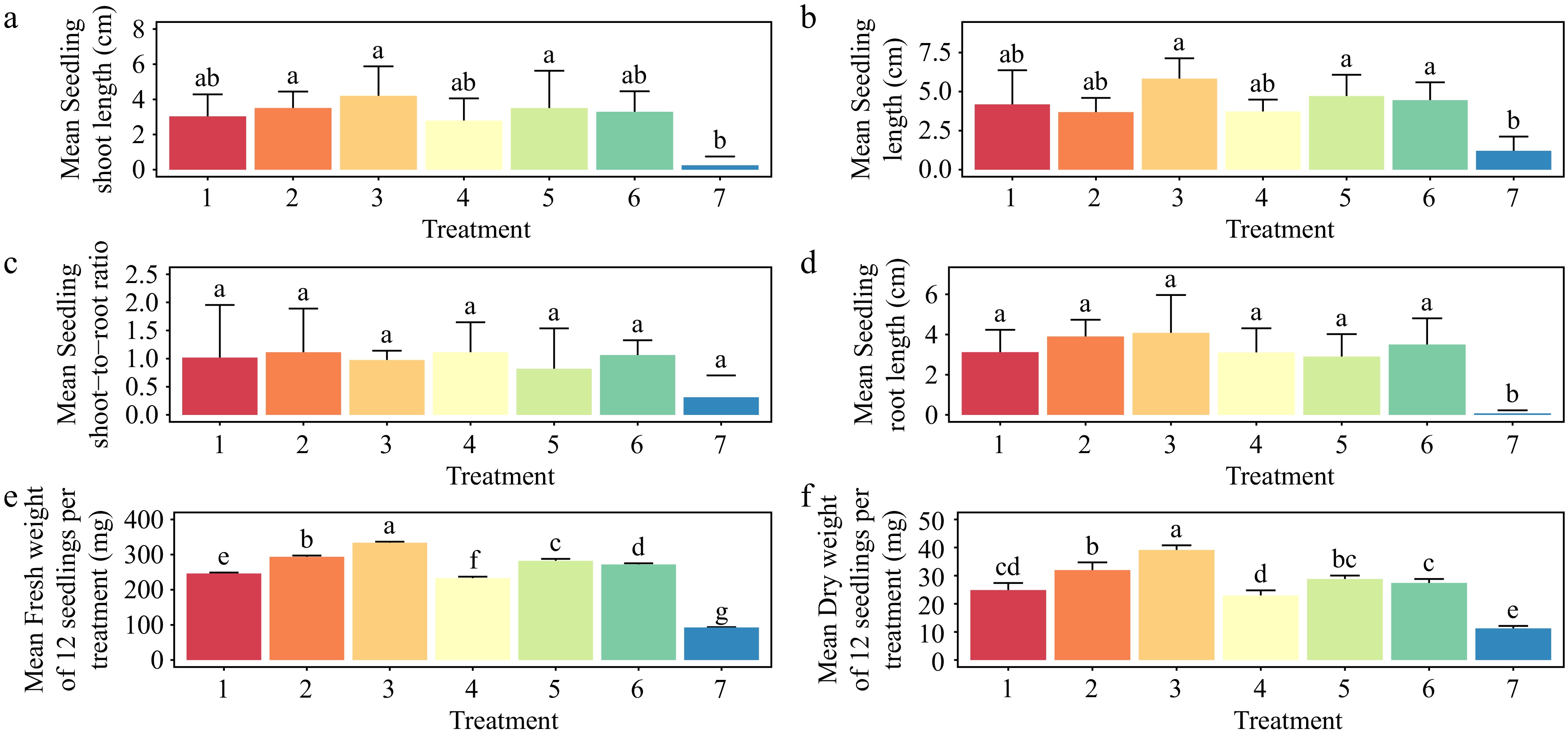
Figure 8.
Effect of plant growth regulators (PGRs) on Gloriosa superba L. seedling morphological traits after four weeks of culture. (a) Mean seedling shoot length, (b) mean seedling length, (c) mean seedling shoot-to-root ratio, (d) mean seedling root length, (e) mean seedling fresh weight, and (f) mean seedling dry weight are shown. Treatments are T1: 0.5 mg·L−1 BAP (6-benzylaminopurine), 0.2 mg·L−1 NAA (1-Naphthalene acetic acid); T2: 1.0 mg·L−1 BAP, 0.5 mg·L−1 NAA; T3: 1.5 mg·L−1 BAP, 1.0 mg·L−1 NAA; T4: 0.5 mg·L−1 2iP (N6-(2-isopentenyl) adenine), 0.2 mg·L−1 IAA (Indole 3-acetic acid); T5: 1.0 mg·L−1 2iP, 0.5 mg·L−1 IAA; T6: 1.5 mg·L−1 2iP, 1.0 mg·L−1 IAA; T7: control (media without PGRs). Bars indicate mean ± SE. Different letters indicate significant difference by Tukey's test at p ≤ 0.05.
-
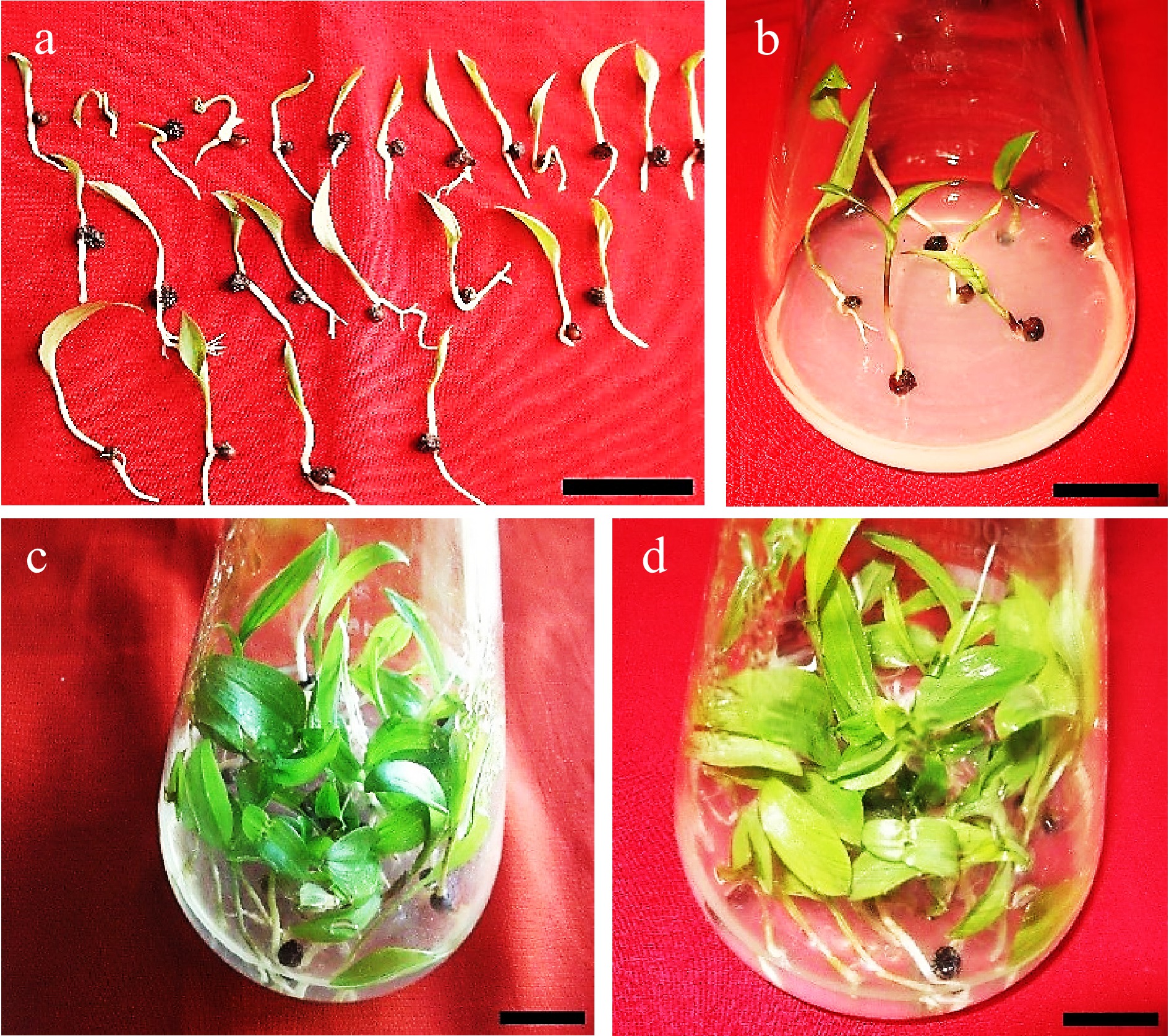
Figure 9.
Seedlings of Gloriosa superba L. cultured in shooting and seedling enhancement media to test the effects of different plant growth regulator combinations on the morphological traits and biomass of seedlings. (a) Germinated seeds before transfer into seedling enhancement media. (b) Initiation of seedling development on 1.5 mg·L−1 BAP (6-benzylaminopurine) + 1.0 mg·L−1 NAA (1-Naphthalene acetic acid). (c)−(d) Seedling growth on 1.5 mg·L−1 BAP + 1.0 mg·L−1 NAA after 4 weeks. Scale bar = 2 cm.
-
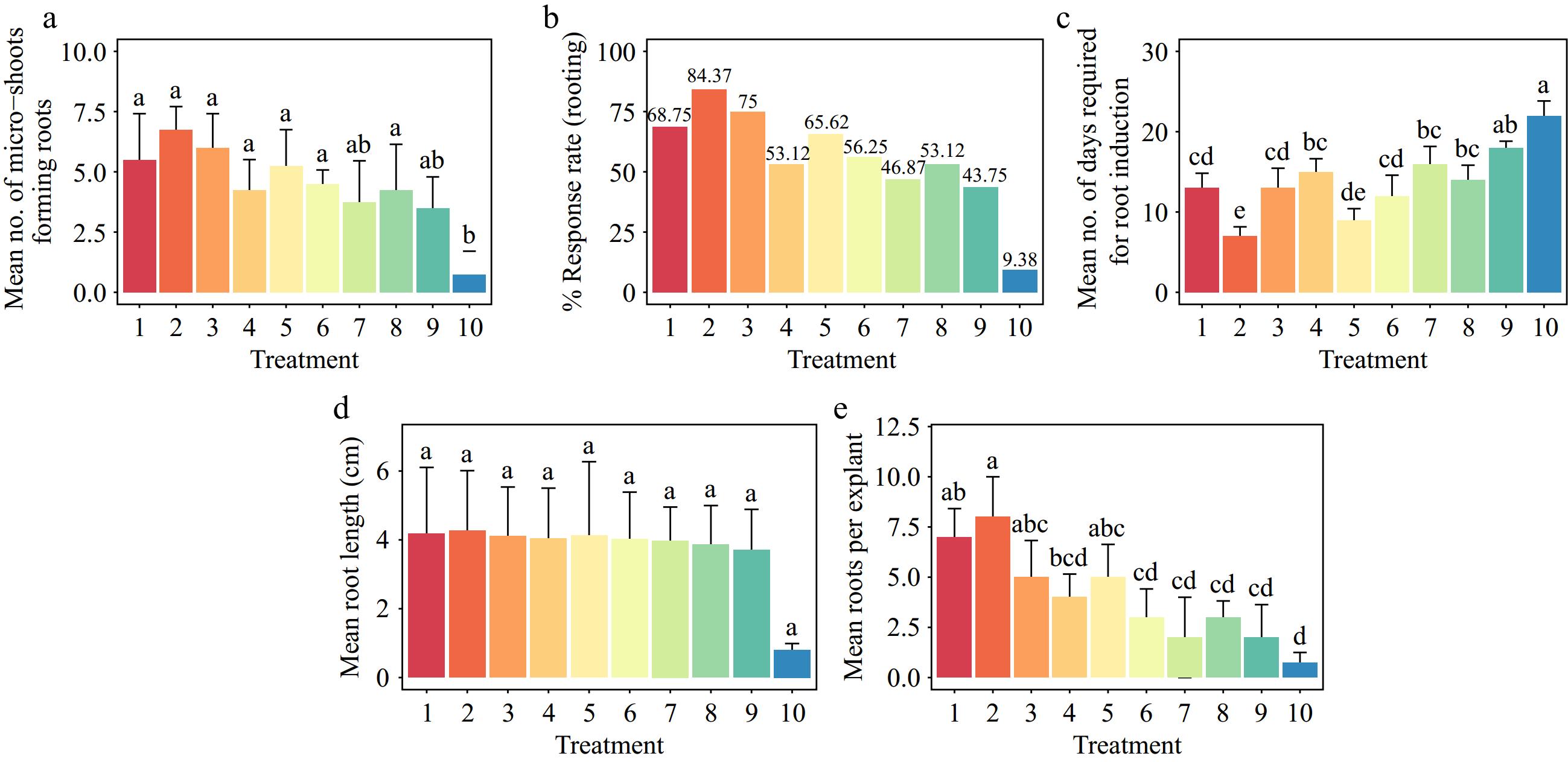
Figure 10.
Effect of PGRs on Gloriosa superba L in vitro morphogenetic response to root induction from seedling derived microshoot explants. (a) Mean microshoots forming roots, (b) response rate to rooting treatment, (c) mean days required for root induction, (d) mean root length, and (e) mean root per explant. Treatments are T1: 0.5 mg·L−1 IBA (Indole-3-butyric acid); T2: 1.0 mg·L−1 IBA; T3: 1.5 mg·L−1 IBA; T4: 0.5 mg·L−1 IAA (Indole 3-acetic acid); T5: 1.0 mg·L−1 IAA; T6: 1.5 mg·L−1 IAA; T7: 0.5 mg·L−1 NAA (1-Naphthalene acetic acid); T8: 1.0 mg·L−1 NAA; T9: 1.5 mg·L−1 NAA; T10: Control (media without PGRs). Bars indicate mean ± SE. Different letters indicate significant difference by Tukey's test at p ≤ 0.05.
-
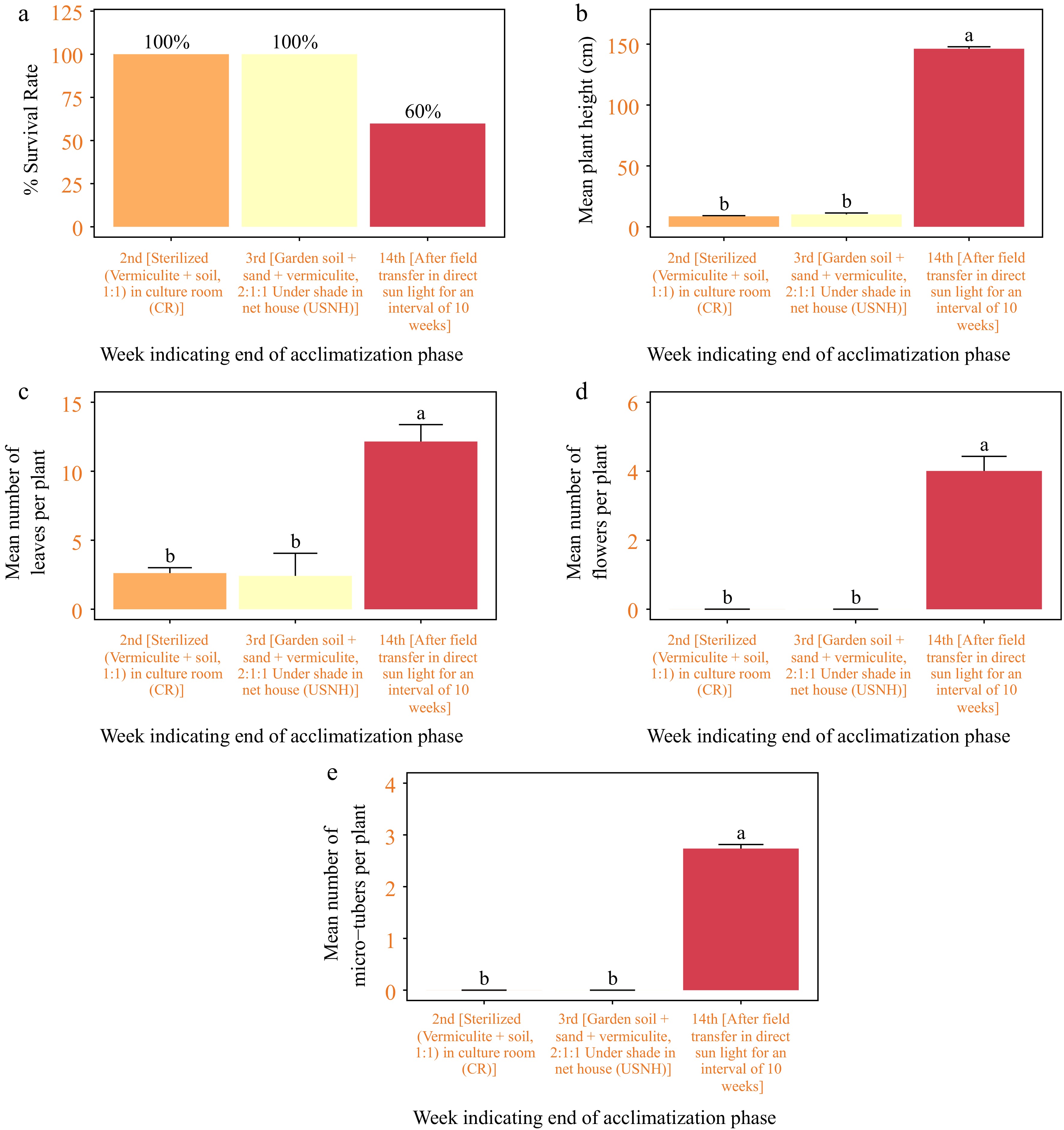
Figure 11.
Acclimatization of in vitro regenerated seedlings of Gloriosa superba L. (a) Plant survival, (b) plant height in cm, (c) number of leaves per plant, (d) number of flowers per plant, and (e) number of microtubers per plant, measured after 2 weeks of transplant in sterilised (vermiculite + soil, 1:1) grown in culture room (CR); 1 week of transplant in garden soil + sand + vermiculite, 2:1:1 under shade in net house (USNH), and finally, 11 weeks of transplant in the field under direct sun light (DSL).
-
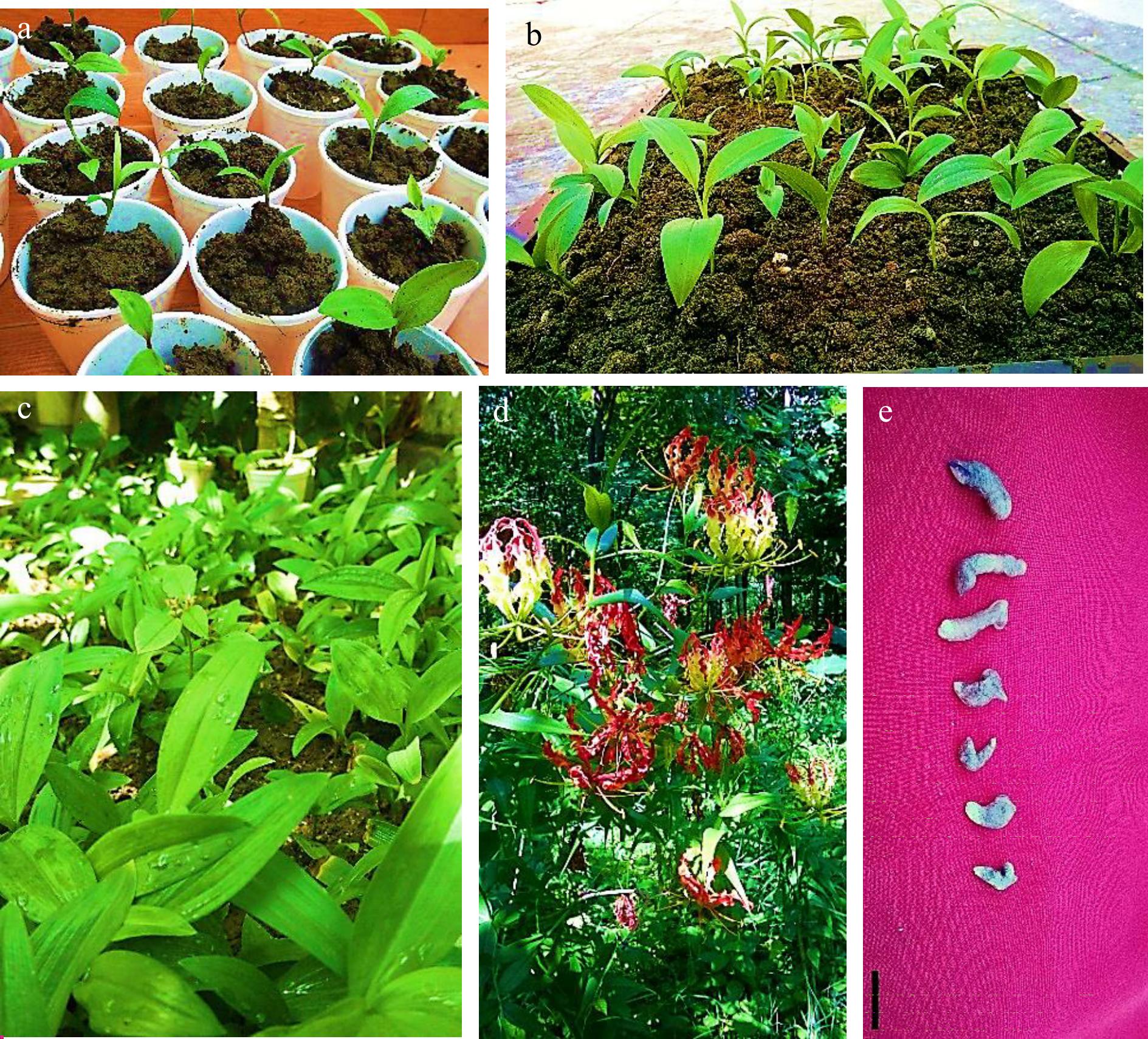

Figure 12.
Acclimatization of in vitro regenerated seedlings of Gloriosa superba L. (a) Microshoots transplanted into sterilized substrate (vermiculite + soil, 1:1) grown in culture room (CR). (b) Plantlets in chill trays containing a mixture of garden soil + sand + vermiculite, 2:1:1 under shade in net house (USNH). (c) Direct transplantation in the field under direct sun light (DSL). (d) Fully grown plant with developed flowers at the later stage of acclimatization in the field under direct sun light (DSL). (e) Some microtubers harvested at the later stage of acclimatization. Scale bar = 2 cm.
-
Treatments Sterilant Concentration (w/v) Exposure time (min) T1 HgCl2 0.05% 2 T2 0.05% 5 T3 0.05% 8 T4 0.1% 2 T5 0.1% 5 T6 0.1% 8 T7 0.15% 2 T8 0.15% 5 T9 0.15% 8 T10 NaClO 0.5% 2 T11 0.5% 5 T12 0.5% 8 T13 1.0% 2 T14 1.0% 5 T15 1.0% 8 T16 1.5% 2 T17 1.5% 5 T18 1.5% 8 T19 H2O2 5.0% 2 T20 5.0% 5 T21 5.0% 8 T22 7.5% 2 T23 7.5% 5 T24 7.5% 8 T25 10% 2 T26 10% 5 T27 10% 8 Table 1.
Concentrations and exposure durations of mercuric chloride (HgCl2), sodium hypochlorite (NaClO), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) used to assess the contamination levels and survival rate of in vitro germinated Gloriosa superba L. seedlings.
-
Treatment PGRs (mg L−1) GA3 BAP T1 0.2 0.2 T2 0.5 0.5 T3 1.0 1.0 T4 1.5 1.5 T5 2.0 2.0 T6 2.5 2.5 GA3 KN T7 0.2 0.2 T8 0.5 0.5 T9 1.0 1.0 T10 1.5 1.5 T11 2.0 2.0 T12 2.5 2.5 GA3 NAA T13 0.2 0.2 T14 0.5 0.5 T15 1.0 1.0 T16 1.5 1.5 T17 2.0 2.0 T18 2.5 2.5 T19 (Control) 0 0 Table 2.
Various concentrations and combinations of Gibberellic acid (GA3), 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP), Kinetin (KN), and 1-naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) used to evaluate in vitro germination of Gloriosa superba L. seeds.
-
Treatments PGRs (mg·L−1) BAP NAA T1 0.5 0.2 T2 1.0 0.5 T3 1.5 1.0 2ip IAA T4 0.5 0.2 T5 1.0 0.5 T6 1.5 1.0 T7 (control) 0 0 Table 3.
Various concentrations and combinations of 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP), 1-naphthalene acetic acid (NAA), N6-(2-Isopentenyl) adenine (2-iP), and Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) used to evaluate in vitro growth and development Gloriosa superba L. seedlings.
-
Treatments 1/2 MS + auxins (mg·L−1) IBA T1 0.5 T2 1.0 T3 1.5 IAA T4 0.5 T5 1.0 T6 1.5 NAA T7 0.5 T8 1.0 T9 1.5 T10 (control) 0.0 Table 4.
Various concentrations of Indole-3-butyric acid (IBA), Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), and 1-naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) used to assess in vitro root development in young shoots excised from Gloriosa superba L. seedlings.
Figures
(12)
Tables
(4)