-
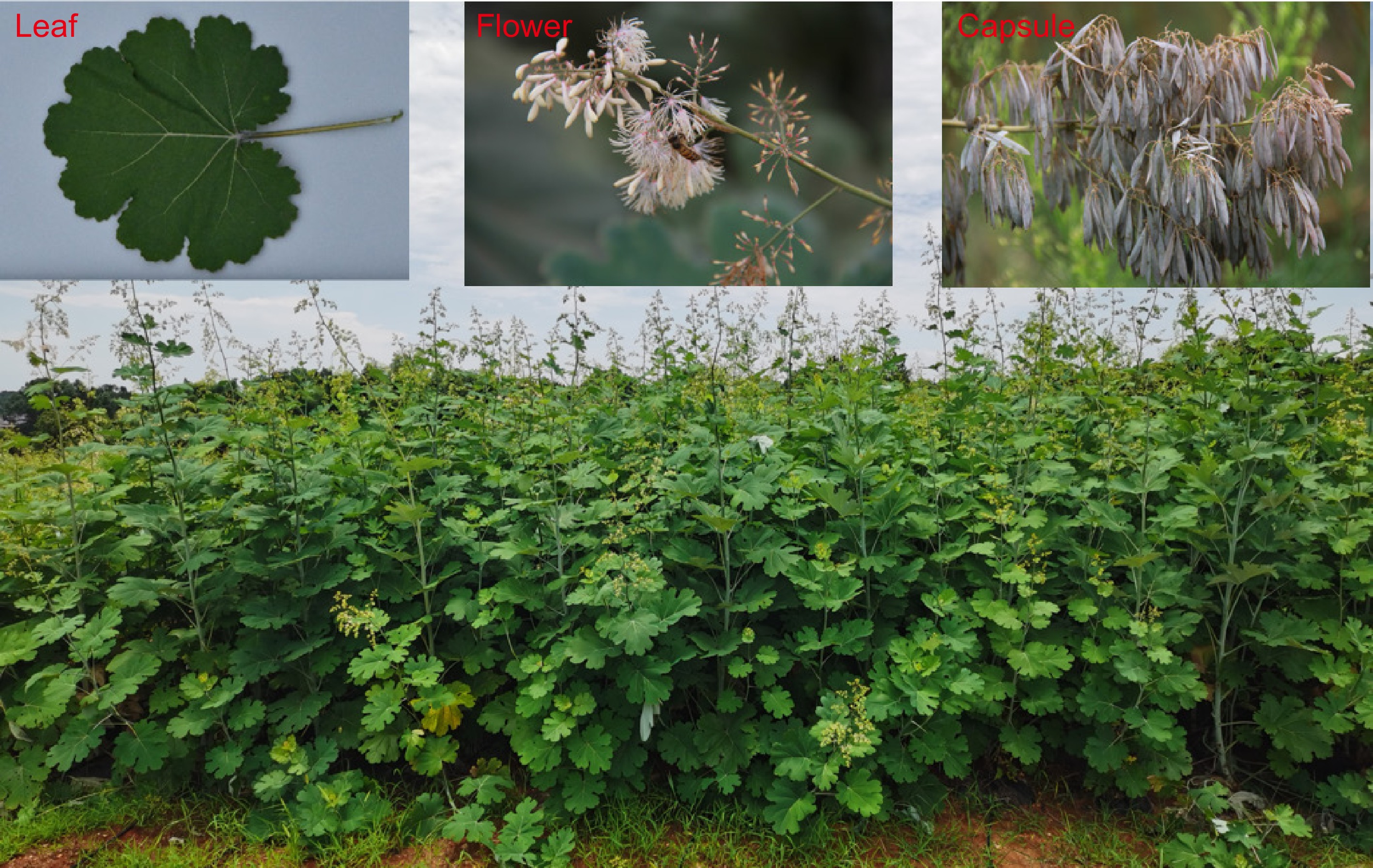

Figure 1.
Morphological characteristics of M. cordata. The figure shows various parts of M. cordata, commonly known as boluohui. The main image displays a field of mature plants with characteristic upright growth. The top left inset highlights a single leaf with a broad, lobed structure. The top middle inset shows the flower of M. cordata, featuring clustered blooms with delicate petals. The top right inset illustrates the capsule, the fruiting body containing seeds. These images collectively depict the key morphological features of M. cordata, which is valued for its rich content of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids.
-
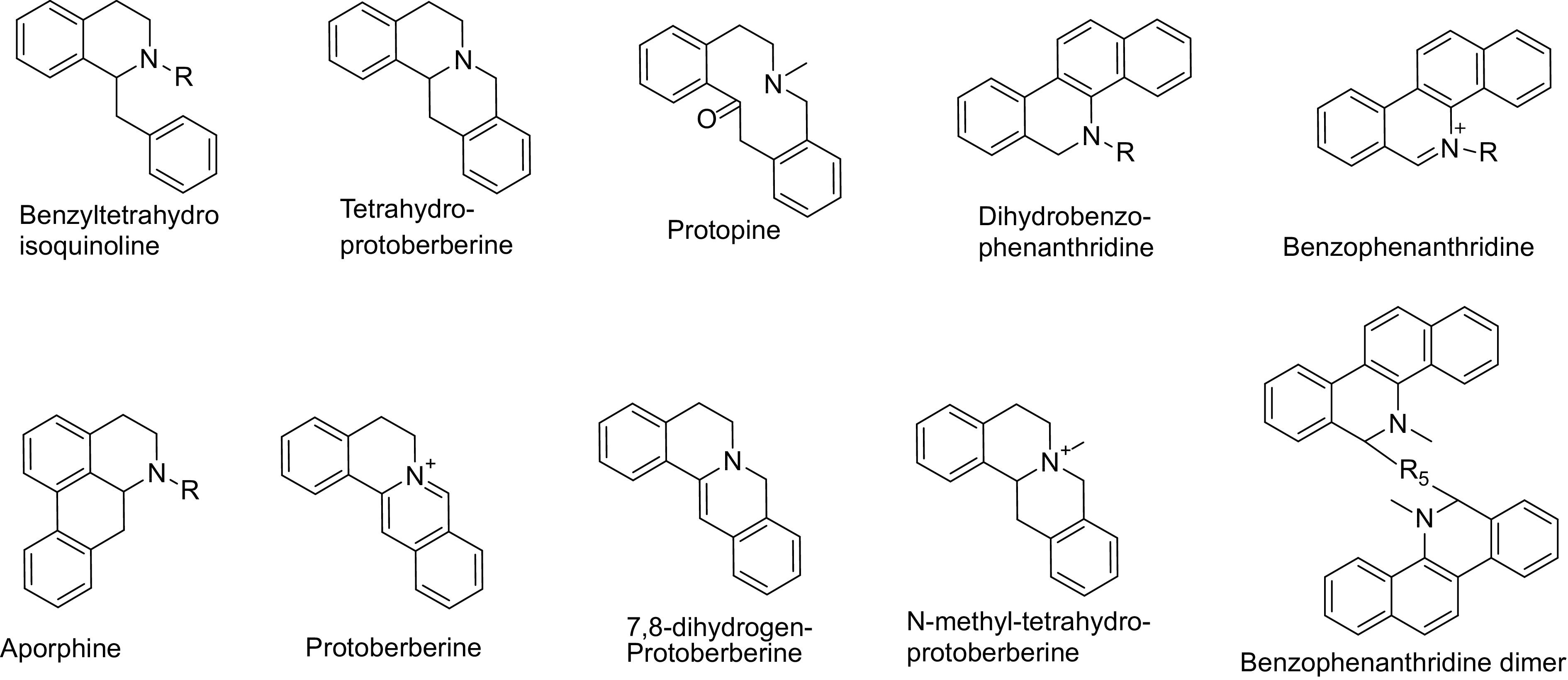
Figure 2.
Types of compounds identified in Macleaya species.
-
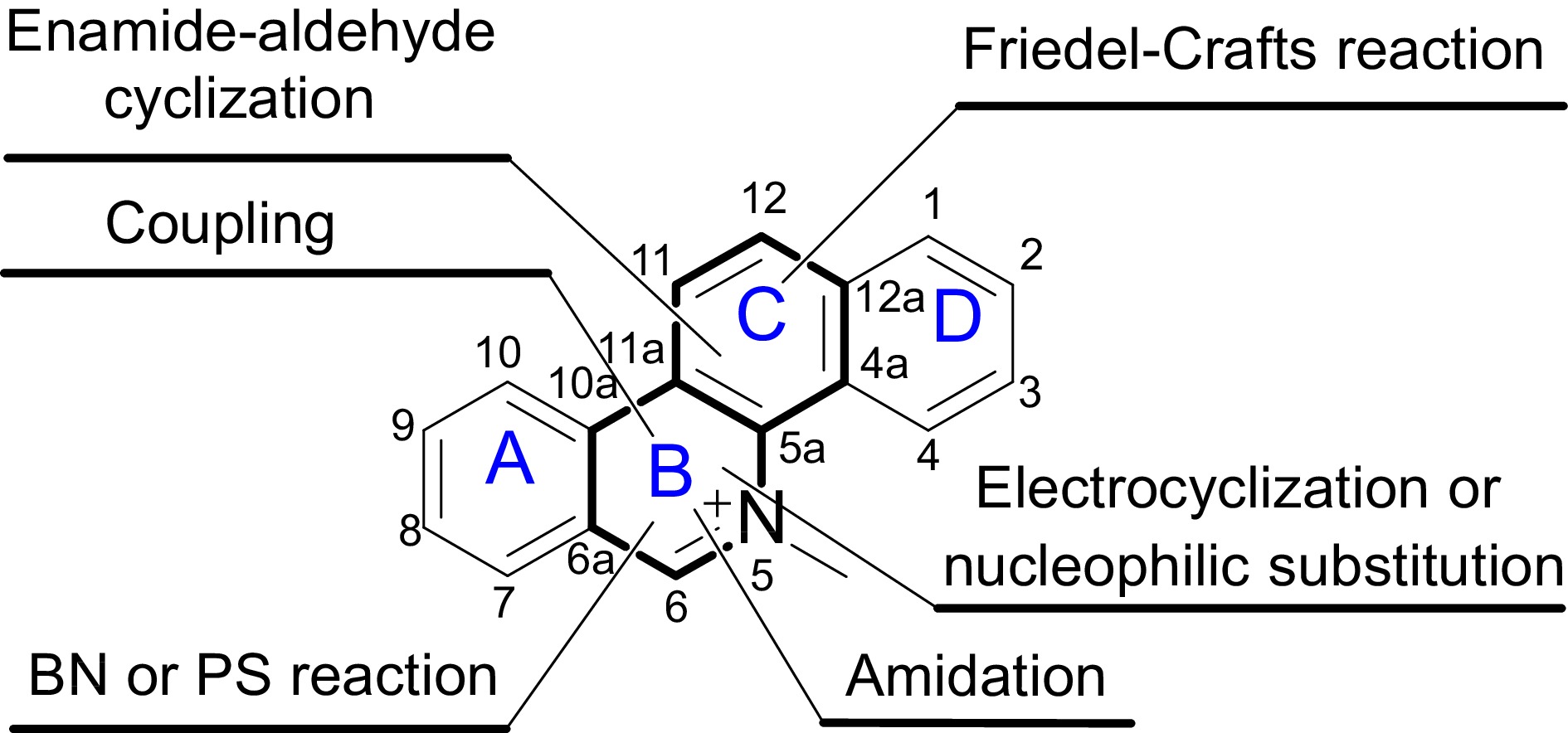
Figure 3.
Total synthesis of quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids, the major active components of M. cordata. This figure illustrates the chemical structure of quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids, highlighting the tetracyclic framework composed of rings A, B, C, and D. These alkaloids are notable for their complex ring system and significant biological activities. The positions of the rings are labeled for clarity, facilitating understanding of the synthetic pathways and structural modifications discussed in the study.
-
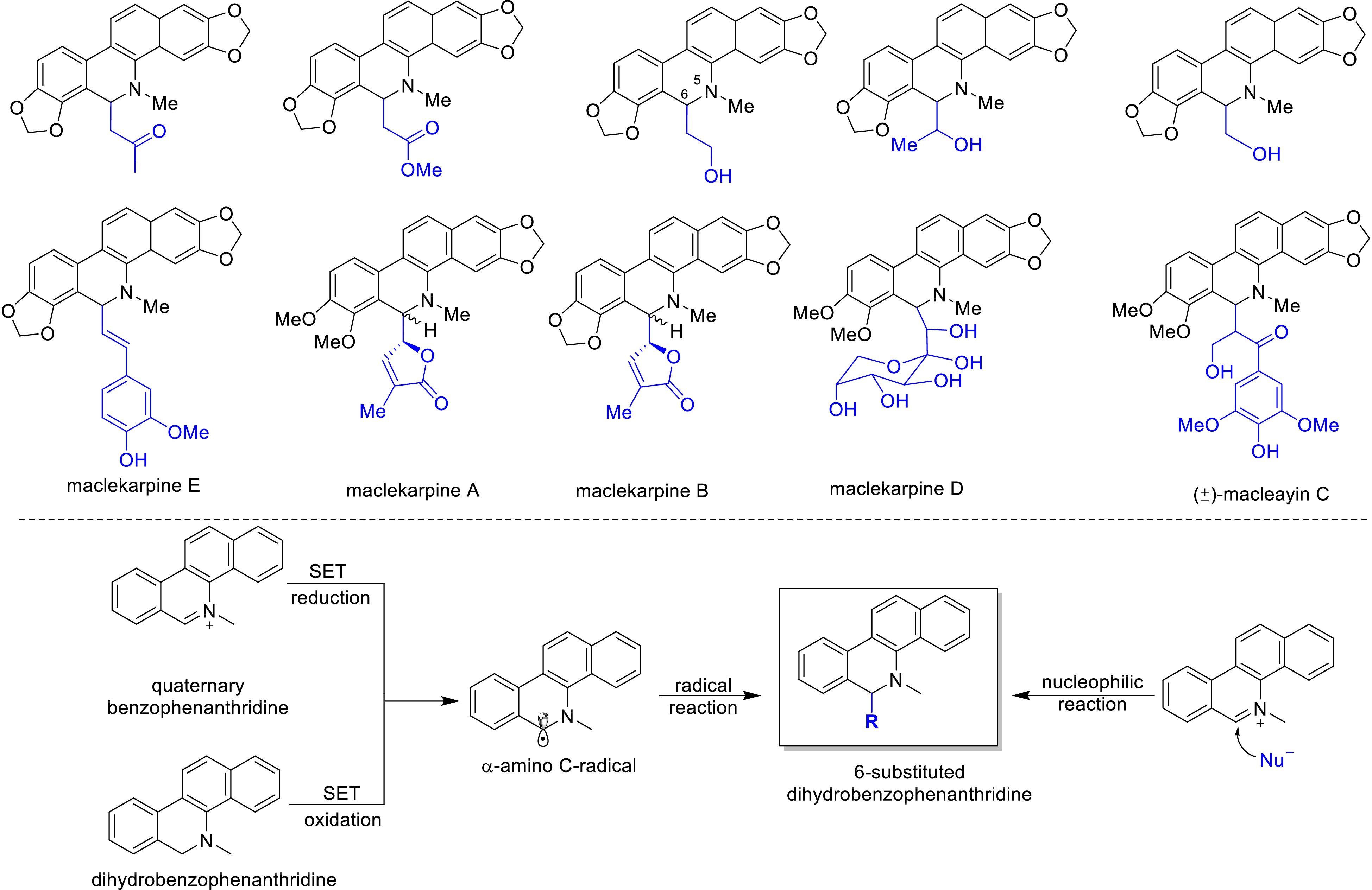
Figure 4.
Novel 6-substituted dihydrobenzophenanthridine alkaloids in Macleaya and their semi-synthesis.
-
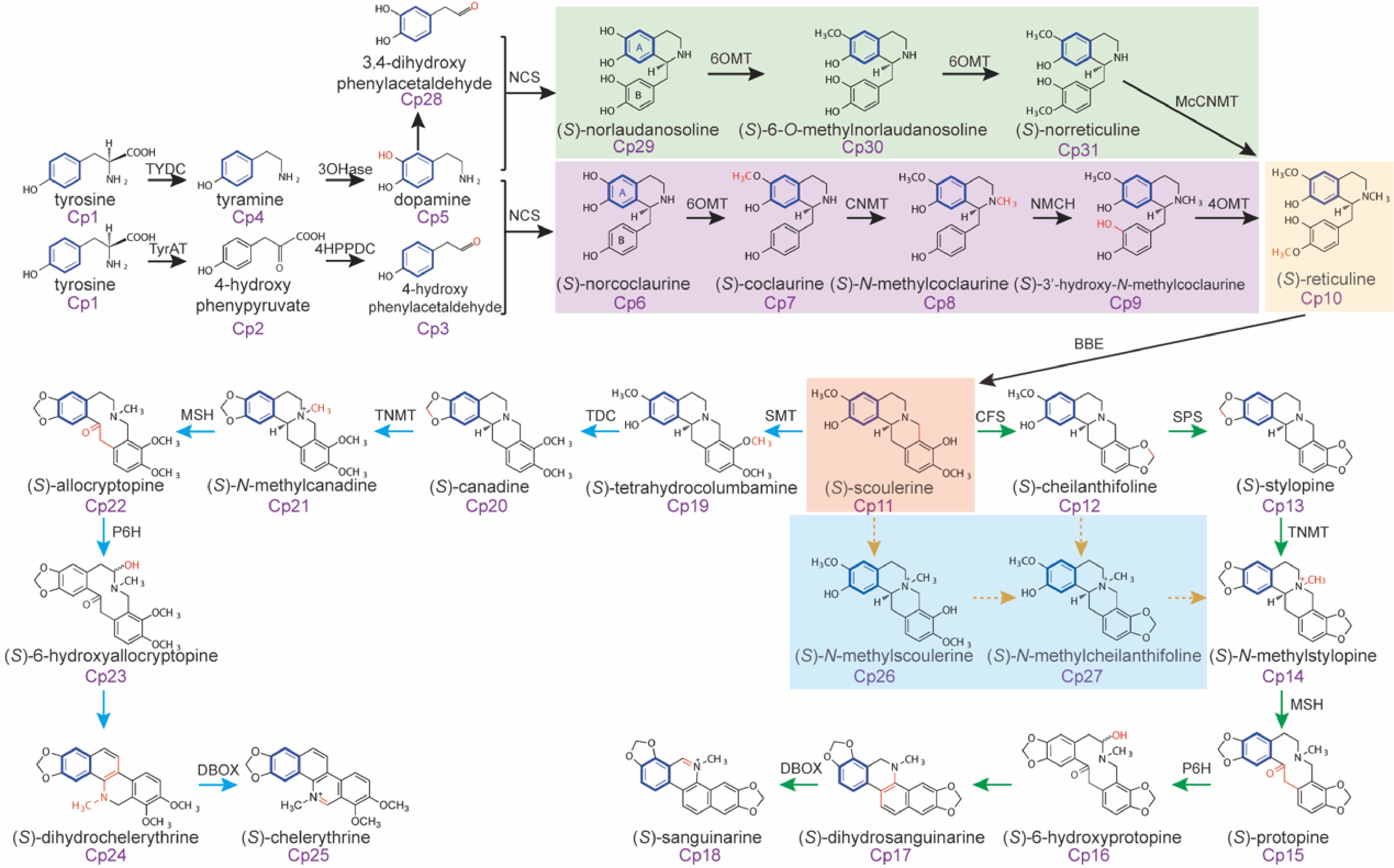
Figure 5.
Isotope tracing of the biosynthetic pathways of sanguinarine and chelerythrine in Macleaya.
-
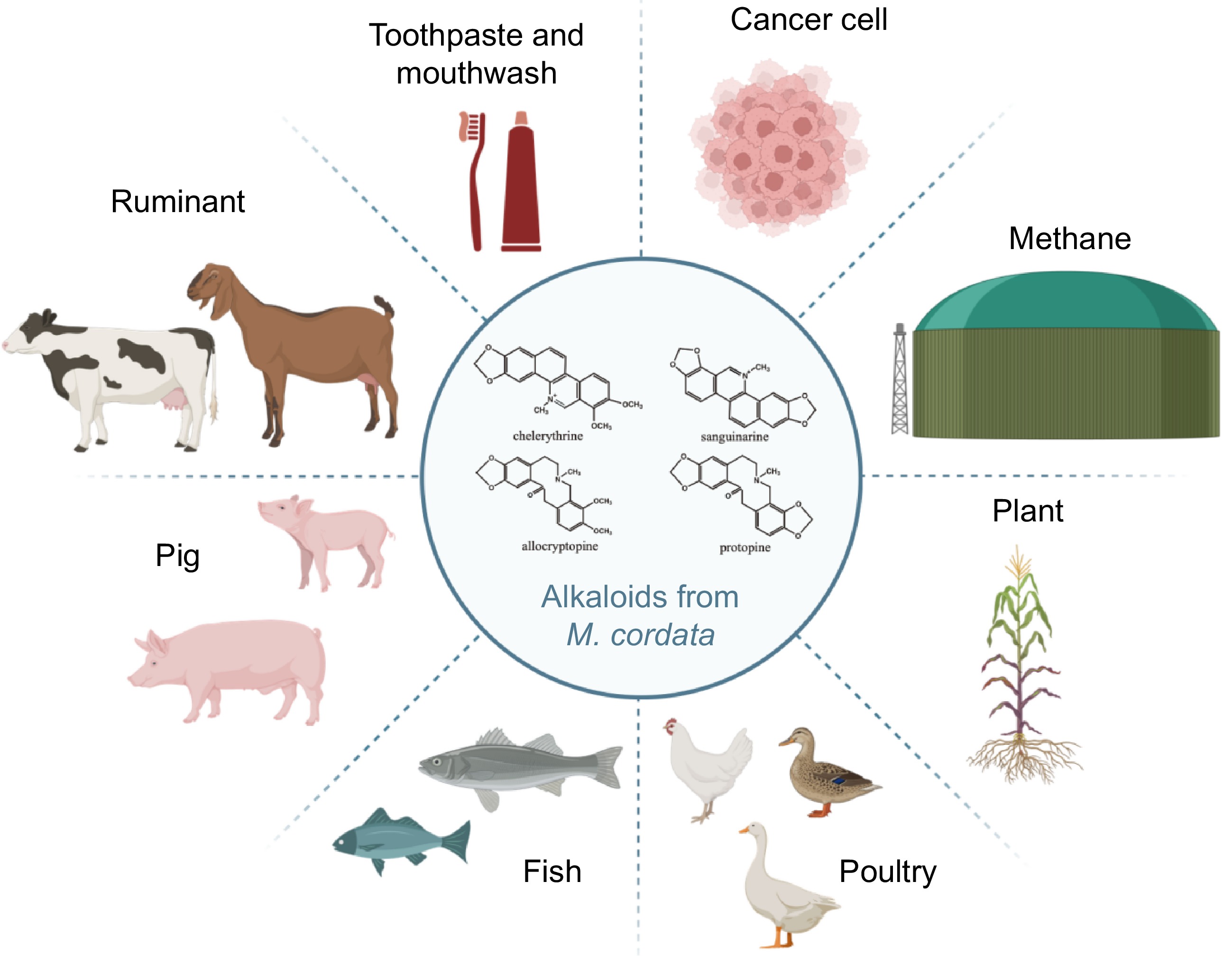
Figure 6.
This illustration showcases the versatile applications of alkaloids derived from M. cordata. The molecular structures of key alkaloids—chelerythrine, sanguinarine, allocryptopine and protopine—are depicted in the center. These alkaloids are utilized in enhancing digestion and improving feed efficiency in ruminants, boosting immunity and promoting growth in pigs, promoting health and growth in fish, improving health in poultry, serving as natural pesticides for crops, reducing methane emissions from ruminants to lower greenhouse gases, acting as antibacterial ingredients in toothpaste and mouthwash, and exhibiting potential anti-cancer activity in cancer treatment. The alkaloids from M. cordata demonstrate significant potential across various fields, from agriculture to medicine.
Figures
(6)
Tables
(0)