-
Macleaya cordata (Willd.) R. Br., commonly known as boluohui in China, is a perennial, upright herbaceous plant belonging to the Papaveraceae family (Fig. 1)[1]. Modern pharmacological research has identified that plants of the Macleaya genus are rich in benzylisoquinoline alkaloids (BIAs), which exhibit significant anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, regulate intestinal microflora, and promote animal growth[2]. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has approved M. cordata as a safe plant for the manufacture of feed additives. In China, four alkaloids found in M. cordata, including sanguinarine (SAN), chelerythrine (CHE), allocryptopine (ALL), and protopine (PRO) have been successfully developed into veterinary medicines (Fig. 1).
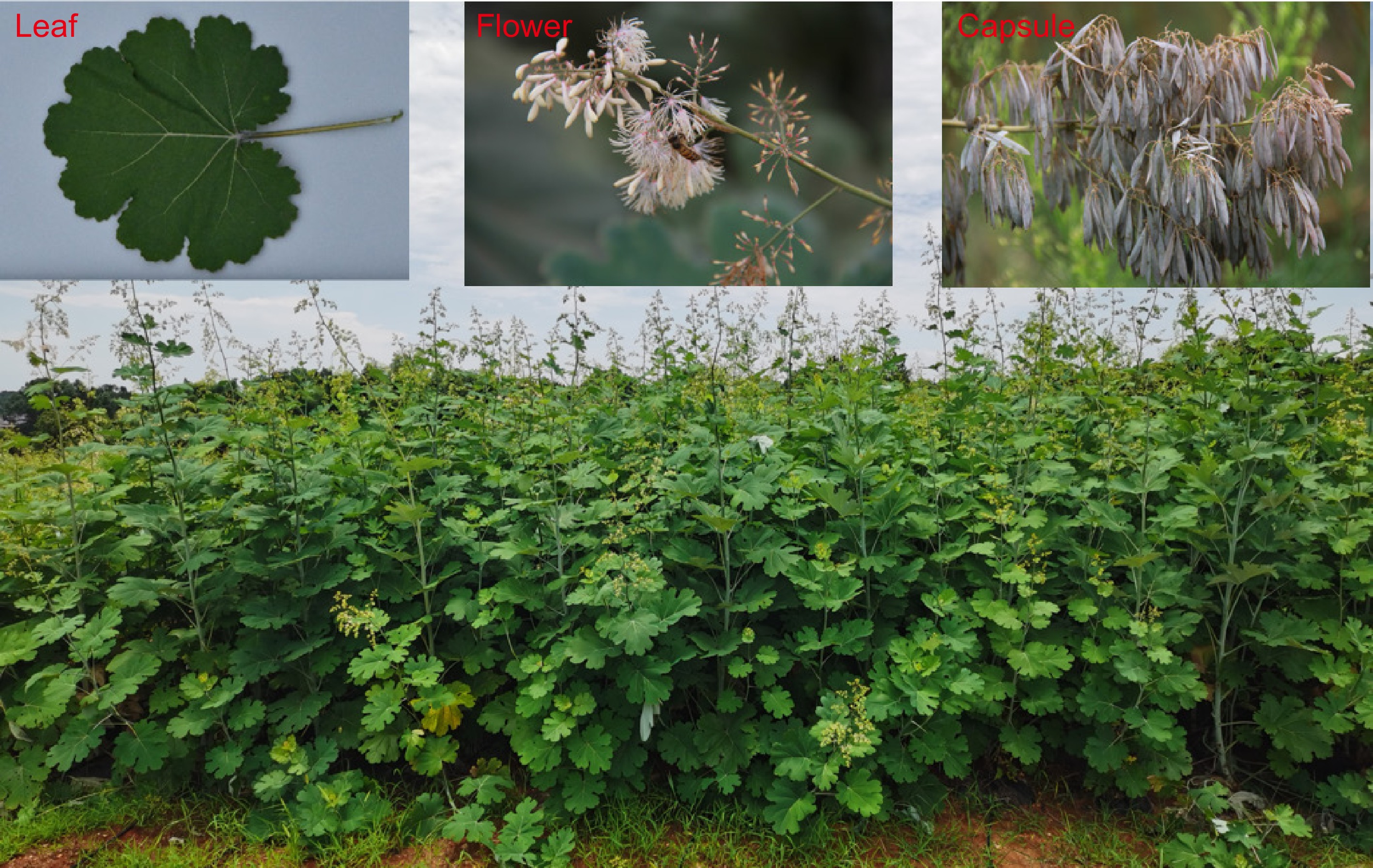

Figure 1.
Morphological characteristics of M. cordata. The figure shows various parts of M. cordata, commonly known as boluohui. The main image displays a field of mature plants with characteristic upright growth. The top left inset highlights a single leaf with a broad, lobed structure. The top middle inset shows the flower of M. cordata, featuring clustered blooms with delicate petals. The top right inset illustrates the capsule, the fruiting body containing seeds. These images collectively depict the key morphological features of M. cordata, which is valued for its rich content of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids.
This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements in the study of M. cordata. It will cover the plant's resources, chemical composition, pharmacological activities, biosynthesis mechanisms, and breeding strategies. By synthesizing current knowledge, this review seeks to offer a broad perspective on future research and potential applications of M. cordata in various fields.
-
The Macleaya genus comprises two species: M. cordata, and M. microcarpa. M. cordata is primarily distributed in China and Japan, originating in the regions south of the Yangtze River and north of the Nanling Mountains in China. It extends south to Guangdong, west to Guizhou, and northwest to southern Gansu. M. cordata predominantly grows in hills, low mountain forests, shrubs, or grasses at altitudes between 150 and 830 m. It is notably found in grasslands or shrubs on slopes at elevations ranging from 450 to 1,600 m in provinces such as Jiangsu, Jiangxi, Shanxi, Gansu, and Shaanxi.
Both M. cordata, and M. microcarpa are upright herbaceous plants with a woody base, producing a milky yellow sap. Their stems are hollow, with the upper parts branching out, and the leaves are broad ovate or nearly circular. They possess large conical inflorescences that can be both terminal and axillary, with a flowering and fruiting period from June to November. Plants of the Macleaya genus are rich in various chemical constituents, including alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenes, and phenylpropanoids, with alkaloids being the predominant components[3]. Benzylisoquinoline alkaloids, such as sanguinarine, are among the most active components in this genus. Sanguinarine is also abundant in other plants like poppy (Papaver somniferum) and bloodroot (Sanguinaria canadensis); however, due to regulatory restrictions and over-exploitation, these plants are no longer viable sources. Consequently, M. cordata has emerged as the primary commercial source of sanguinarine.
-
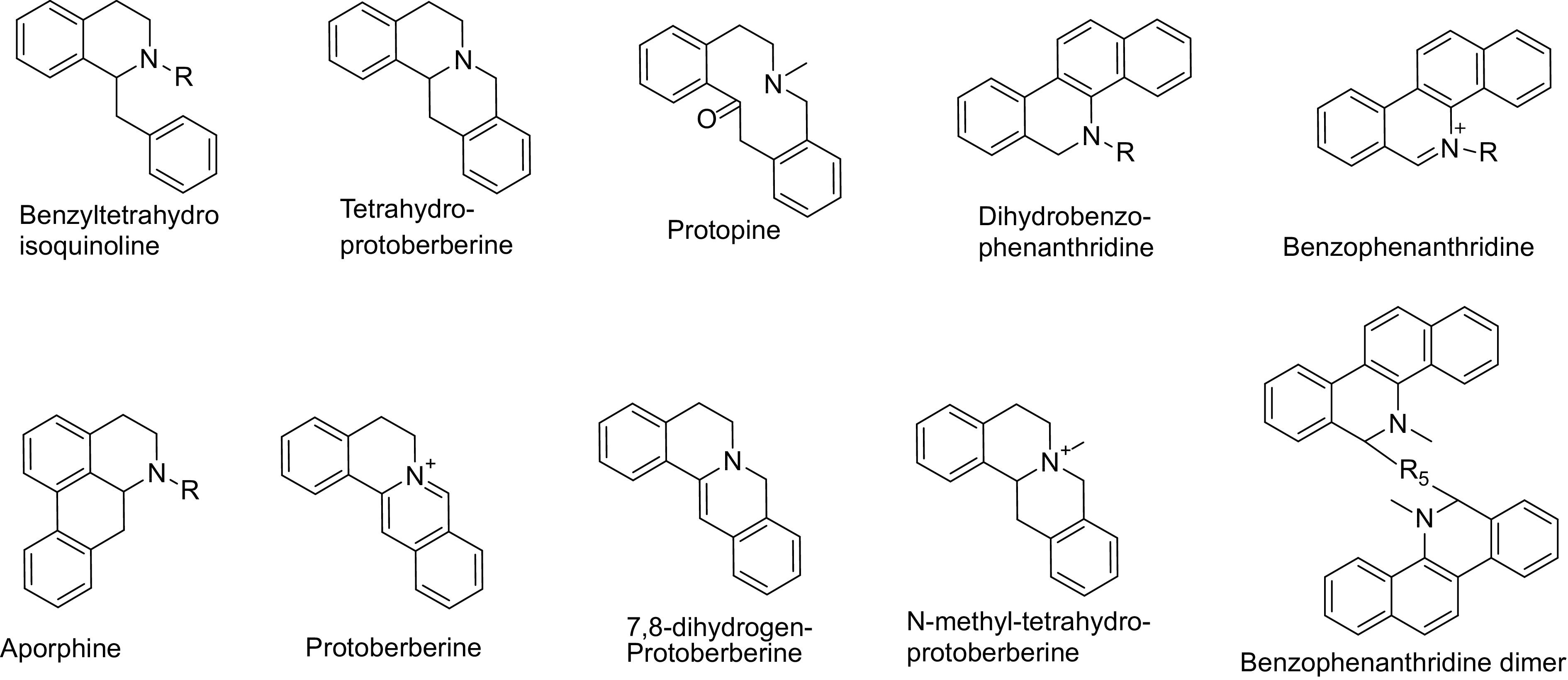
Japanese researchers such as Tani & Takao[4] and Takao[5] isolated alkaloids like sanguinarine, chelerythrine, berberine, and coptisine from M. cordata, initiating the study of its chemical constituents. Subsequently, numerous researchers contributed to the isolation and structural identification of secondary metabolites in the Macleaya genus[6−9]. From 2009 to 2024, Qing et al.[10] developed a new method for the discovery and structural identification of alkaloids in the Macleaya genus using mass spectrometry, identifying over 200 alkaloids. These alkaloids belong to ten major categories: benzylisoquinoline alkaloids, tetrahydroprotoberberine alkaloids, N-methyl-tetrahydroprotoberberine alkaloids, protopine alkaloids, protoberberine alkaloids, 7,8-dihydroprotoberberine alkaloids, aporphine alkaloids, benzophenanthridine alkaloids, dihydrobenzophenanthridine alkaloids, and benzophenanthridine dimers (Fig. 2). Using mass spectrometry-guided techniques, over 20 new compounds were isolated from Macleaya species, established a mass spectrometry database and metabolic profile for alkaloids in Macleaya, and proposed new biosynthetic pathways for berberine and sanguinarine[10−13]. In addition to a large number of alkaloids, Macleaya species also contain small amounts of flavonoids and polyphenols[3]. The rich chemical composition of Macleaya endows it with various biological activities. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that Macleaya possesses antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, insecticidal, antitumor, antifibrotic, hepatoprotective, antiviral, antioxidant, immune-enhancing, gut microbiota-regulating, animal growth-promoting, wastewater-purifying, and soil erosion-preventing properties[13−16].
-
The primary active secondary metabolites in Macleaya cordata are protopine alkaloids and quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids. To date, there have been no reports in the literature regarding the total chemical synthesis of protopine alkaloids. The total chemical synthesis of quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids is generally achieved through multi-step reactions using conventional chemical reagents[17]. In most reported synthetic routes, the cyclization reactions to form rings B and C constitute the final steps in constructing the tetracyclic system. Key chemical reactions for constructing ring B include Heck coupling to form the C10a-C11 bond[18], Pictet-Spengler reaction (PS reaction) or Bischler-Napieralski reaction (BN reaction) to form the C6-C6a bond[19,20], amidation to form the N5-C6 bond[21], and electrocyclization to form the N5-C5a bond[22]. For ring C, key reactions include enamide-aldehyde cyclization to form the C11-C11a bond[23] and Friedel-Crafts reaction to form the C12-C12a bond[24]. These reactions have been widely applied in the synthesis of benzo[c]phenanthridine derivatives with anticancer activity (Fig. 3).
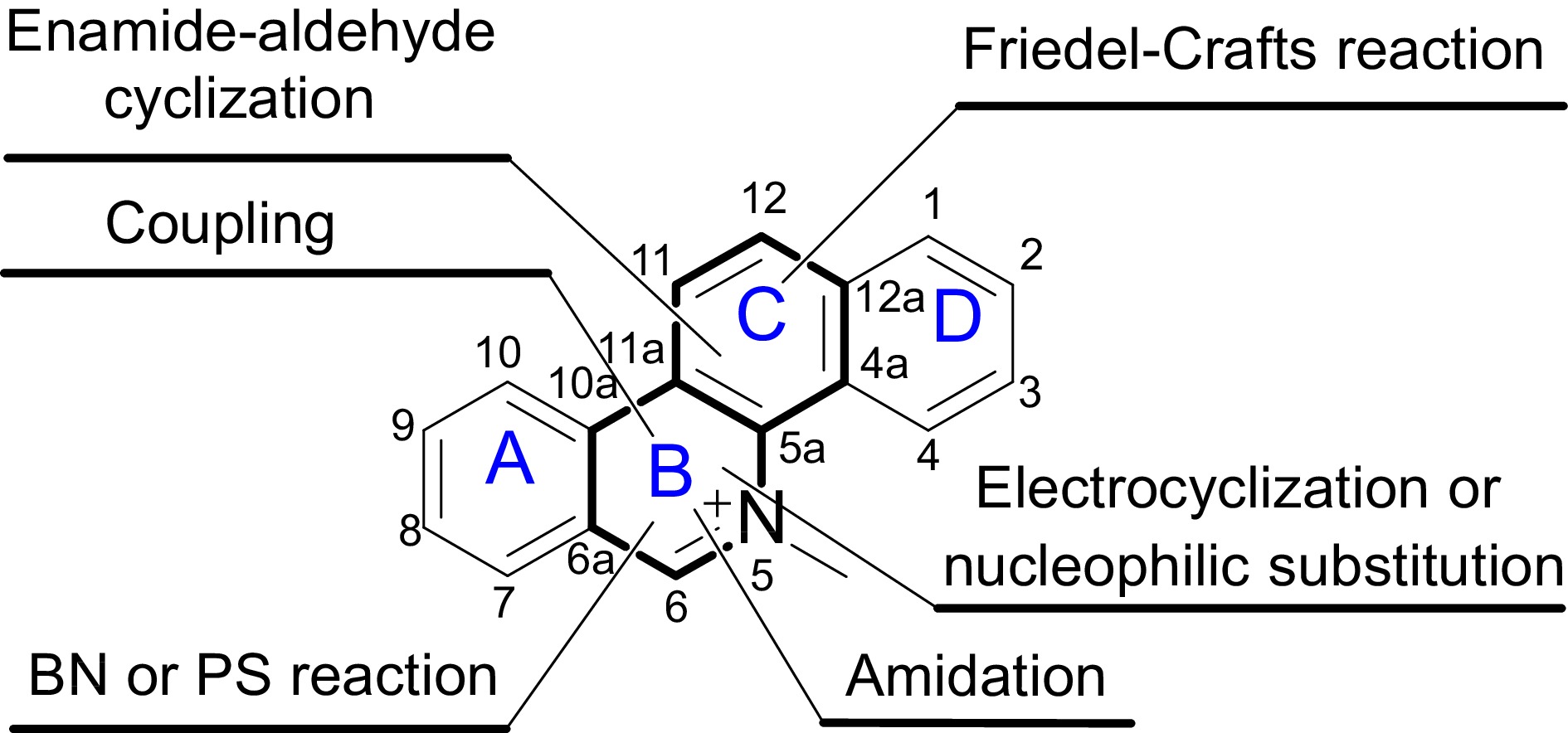
Figure 3.
Total synthesis of quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids, the major active components of M. cordata. This figure illustrates the chemical structure of quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids, highlighting the tetracyclic framework composed of rings A, B, C, and D. These alkaloids are notable for their complex ring system and significant biological activities. The positions of the rings are labeled for clarity, facilitating understanding of the synthetic pathways and structural modifications discussed in the study.
Semi-synthesis and structural modification of novel 6-substituted dihydrobenzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids in M. cordata
-
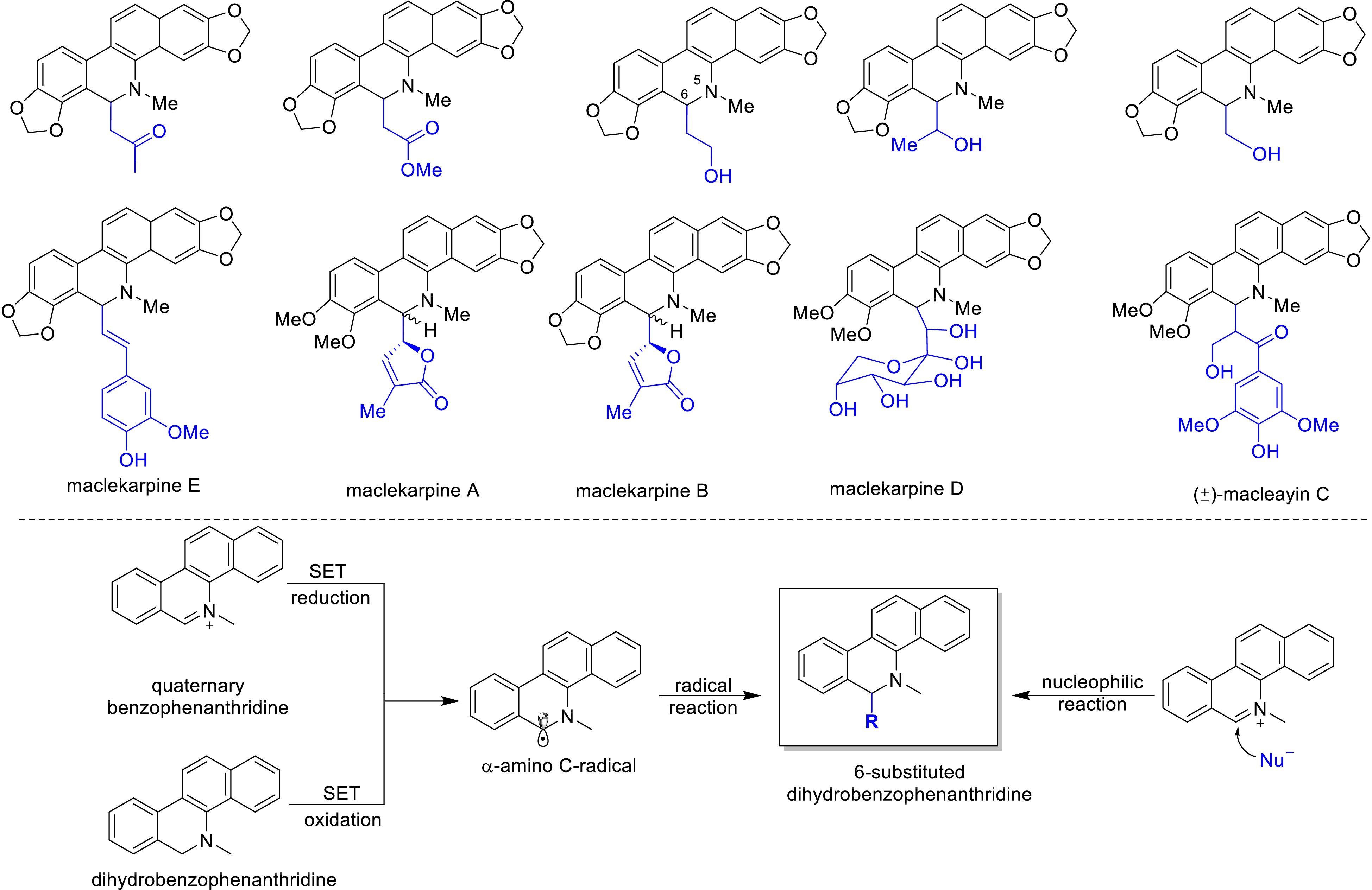
In recent years, with the deepening research on the chemical constituents of M. cordata, a series of 6-substituted dihydrobenzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids have been successively isolated and structurally confirmed (Fig. 4)[6,9,25,26]. Currently, studies on the biological activities of these alkaloids are still in their infancy, and no biosynthetic pathways for 6-substituted dihydrobenzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids have been reported. Based on the structural types and chemical properties of the C-6 substituents, it is speculated that these alkaloids may be biosynthesized in plants through radical reactions or nucleophilic substitution pathways. As shown in Fig. 4, quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids or dihydrobenzo[c]phenanthridine can be converted to α-amino carbon radicals through single-electron reduction[27,28] or oxidation[29,30]. These radicals can then undergo various types of radical reactions to achieve functionalization at C-6 of the benzo[c]phenanthridine ring structure, resulting in the semi-synthesis of the aforementioned alkaloids[31]. Additionally, the N5=C6 double bond in quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids can accept nucleophilic reagents, leading to the formation of 6-substituted dihydrobenzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids.
-
To date, nearly 300 secondary metabolites, including 204 isoquinoline alkaloids have been identified from M. cordata using untargeted LC-MS metabolomics technology[10]. This breakthrough surpasses the limitations of traditional methods for isolating and identifying secondary metabolites in plants, guiding the targeted analysis of alkaloid metabolism and metabolic profiling in M. cordata. Using untargeted LC-MS metabolomics technology, nearly 2,000 characteristic ions were discovered in M. cordata. Through stable isotope 13C6-labeled tyrosine tracing experiments, 179 13C6-labeled compounds were identified[1]. A database search for the non-labeled counterparts of these 13C6-labeled compounds quickly identified 40 alkaloids and four non-alkaloids, providing evidence for determining the biosynthetic pathways of sanguinarine and chelerythrine in M. cordata.
Targeted analysis of the metabolic accumulation patterns of intermediates in the biosynthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine in different developmental stages and organs of M. cordata, combined with transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics analysis revealed the biosynthetic tissues and gene expression patterns of alkaloid biosynthesis at different growth stages. This study elucidated the biosynthetic pathways of sanguinarine and chelerythrine and discovered the pattern of synthesis by 'root-pod compartmentalized synthesis', where precursor compounds like protopine are primarily synthesized in the roots and then transported to the pods for the synthesis of sanguinarine[1,32]. Laser microdissection with fluorescence detection was used to separate different tissue cells in the roots of M. cordata. Combined with LC-MS targeted analysis of trace alkaloids in each tissue, this approach accurately identified the storage cells of the alkaloids, clarifying the 'synthesis-storage-transport-resynthesis' biosynthetic mechanism of sanguinarine, chelerythrine, and their precursors[33] (Fig. 5).
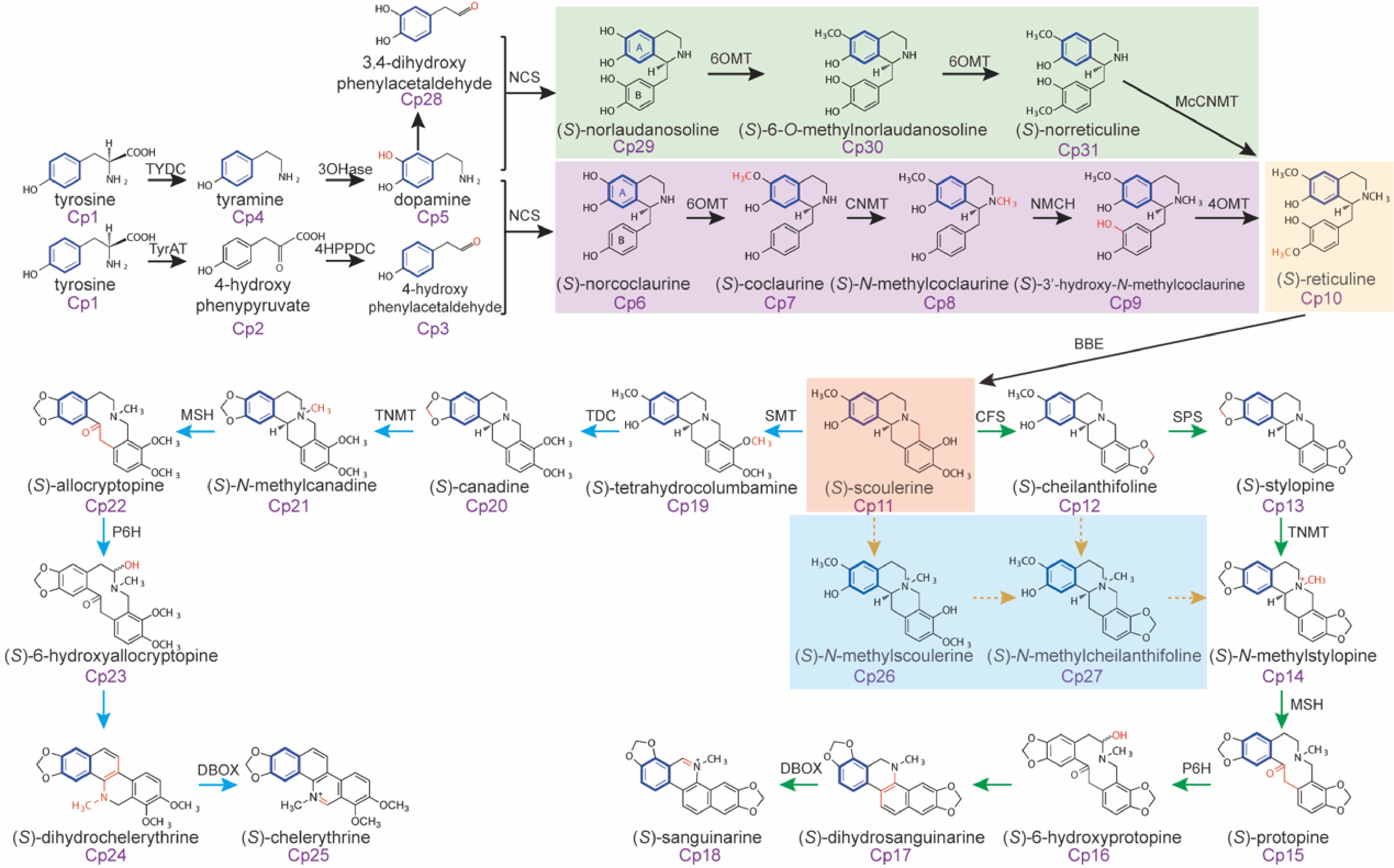
Figure 5.
Isotope tracing of the biosynthetic pathways of sanguinarine and chelerythrine in Macleaya.
Integrated analysis of genomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics, and proteomics in M. cordata to elucidate the mechanisms of sanguinarine storage, synthesis, and transport
-
In 2013, Zeng completed an integration of transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data to elucidate the biosynthesis of alkaloids in M. cordata and M. macrocarpa[32]. This study investigated the potential mechanisms of alkaloid biosynthesis in Macleaya species by analyzing transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data from 10 different samples collected at various times, tissues, and organs. The assembled and clustered transcriptomic data yielded 69,367 unigenes for M. cordata and 78,255 unigenes for M. macrocarpa. Through a multi-level comparative analysis of key gene expressions controlling enzymes in the alkaloid metabolic pathway, the research identified homologous genes for all functional genes in the sanguinarine biosynthesis pathway. This annotation provided foundational data for cloning functional genes in the sanguinarine pathway of M. cordata.
In 2017, researchers first mapped the complete genome of M. cordata, making it the first Papaveraceae plant to have its whole genome sequenced[1]. The genomic results indicated that the genome size of M. cordata is 540.5 Mb with a heterozygosity rate of 0.92%, predicting 22,328 protein-coding genes, of which 43.5% are transposable elements. Additionally, 1,355 non-coding RNA (ncRNA) genes were identified in the M. cordata genome, including 216 rRNA, 815 tRNA, 75 miRNA, and 249 snRNA genes. Comparative genomics revealed a significant expansion of the flavoprotein oxidase gene family closely associated with sanguinarine synthesis, providing crucial insights into the evolutionary origin of the sanguinarine biosynthetic pathway in Macleaya. Through co-expression analysis of genes and metabolites, researchers successfully identified 14 genes, including flavoprotein oxidases, methyltransferases, and cytochrome P450 enzymes, involved in the biosynthesis of sanguinarine.
-
Recent advancements in genetic engineering have led to a series of modifications on the berberine bridge enzyme (McBBE), a rate-limiting enzyme in the biosynthesis of sanguinarine in M. cordata. These modifications included codon optimization and the design of N-terminal truncated mutants to enhance expression efficiency in heterologous hosts. By employing CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology, these optimized genes were successfully integrated into the genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This integration resulted in a significant increase in the production of the key precursor, chelerythrine, achieving a yield 58 times higher than the original level[34]. This accomplishment not only underscores the tremendous potential of genetic engineering in enhancing the synthesis of secondary metabolites but also provides a crucial foundation for subsequent industrial production. Furthermore, the research team developed innovative methods for producing sanguinarine through a 'plant-microbe' co-fermentation system. This system involved the co-cultivation of engineered yeast strains with the non-medicinal parts of M. cordata — specifically, the leaves — in a specially designed co-fermentation reactor[35]. This novel approach effectively converted precursor substances from the leaves into sanguinarine, maximizing the utilization of the non-medicinal parts of M. cordata and reducing production costs. This co-fermentation system not only offers an efficient and sustainable new pathway for the production of valuable bioactive compounds like sanguinarine but also exemplifies the integration of plant biology and microbial biotechnology.
In 2022, significant progress was made by Jiachang Lian's team, who successfully achieved the de novo biosynthesis of sanguinarine, reaching a yield of 16.5 mg/L[36]. After comprehensive metabolic engineering modifications, the current best-engineered yeast strain achieved a production titer of 448.64 mg/L for sanguinarine[37]. This achievement highlights the immense potential of modern biotechnology in promoting the effective utilization and industrial production of components from traditional medicinal plants. By leveraging advanced genetic engineering techniques, researchers have been able to enhance the efficiency of secondary metabolite production, opening up new possibilities for the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
The innovative approaches employed in this research, such as codon optimization, N-terminal truncation, and the use of CRISPR-Cas9 for gene editing, represent significant advancements in the field of synthetic biology. These methods not only improve the expression efficiency of key enzymes but also pave the way for the scalable production of complex bioactive compounds. The successful integration of plant and microbial systems in a co-fermentation setup demonstrates a promising strategy for sustainable and cost-effective production processes. This research not only advances our understanding of biosynthetic pathways but also sets the stage for future developments in the industrial application of traditional medicinal plant components
-
In the fields of plant science and biotechnology, artificial genetic transformation technology has become a key tool for molecular breeding. In 2016, a genetic transformation system for Macleaya cordata based on Agrobacterium tumefaciens was successfully established[38]. Utilizing this system, key genes involved in sanguinarine biosynthesis, such as berberine bridge enzyme MCBBE[39] and MCP6H[40], have been overexpressed, demonstrating the significant potential of genetic engineering in enhancing the production of plant secondary metabolites. Additionally, a hairy root culture system for M. cordata and M. microcarpa mediated by A. rhizogenes has also been successfully developed[41,42]. Recently, a CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing system for M. cordata has been established. By re-editing the sanguinarine biosynthesis pathway, researchers have achieved a significant increase in sanguinarine content in transgenic materials[43]. These advancements highlight the potential of molecular breeding techniques to enhance the yield of valuable secondary metabolites in M. cordata, providing a foundation for future research and industrial applications.
Study on the domestication and DUS testing guidelines of M. cordata
-
Previously, wild M. cordata capsules were the primary source of raw materials for M. cordata-related products. However, the popularity of these products has led to a significant decline in wild resources year by year. In response, domestic research teams have developed a standardized cultivation technology system for M. cordata. This system encompasses various techniques, including seedling raising, field management, pest and disease control, harvesting, and primary processing, facilitating the shift from wild to cultivated varieties. Additionally, comprehensive research on the current state of resources and breeding has led to the establishment of 30 traits which form the M. cordata DUS testing guidelines. As a result of these efforts, the team has preliminarily identified a superior strain, 'Meibo 1', known for its high fruit yield and elevated haematoxylin content.
-
Sanguinarine from M. cordata as a bioactive compound was initially used in Europe as feed additives to enhance flavor and stimulate appetite in food animals[44]. Studies have shown that M. cordata extracts are safe, with no adverse effects observed in target animals even at ten times the recommended clinical dose. Pharmacodynamic and clinical data indicate that long-term addition of M. cordata extracts at recommended doses has anti-inflammatory and growth-promoting effects, and total protopine alkaloids are effective in treating Escherichia coli-induced diarrhea in poultry.
Research on the mechanism of antibiotic substitution revealed that M. cordata extract enhances intestinal health by increasing the abundance of lactic acid bacteria, which inhibit pathogenic microorganisms through competitive exclusion[2]. Sanguinarine inhibits the phosphorylation and ubiquitination of I-κB proteins, reducing the dissociation of p50 and p60, thereby inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. This results in decreased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduced inflammation levels in animals[45]. Additionally, sanguinarine was found to enhance protein synthesis in animals by inhibiting tryptophan decarboxylase activity, thereby increasing amino acid utilization[46,47]. Based on the growth-promoting effects of M. cordata extract as an antibiotic substitute, Jianguo Zeng's team has developed a comprehensive feed technology focused on 'intestinal health, anti-inflammatory properties, and growth promotion'. This approach avoids the risk of antibiotic resistance associated with traditional growth-promoting antibiotics while still enhancing animal growth performance. This technology supports the development of antibiotic-free feed solutions and the use of non-antibiotic inputs in animal husbandry. Furthermore, chelerythrine in M. cordata, when used as an animal feed additive, interacts with phospholipids on bacterial membranes, increasing membrane fluidity and impairing respiration by disrupting proton motive force and generating reactive oxygen species, leading to reduced intracellular ATP levels. This dual action of downregulating the mobile colistin resistance gene mcr-1 and associated genes offers a new strategy to circumvent colistin resistance. These findings provide strong technical support for the development of antibiotic-free feeding practices and the creation of alternative growth-promoting solutions in animal production[48].
M. cordata extract is the first traditional Chinese veterinary medicine product approved for feed use in China. It is widely used to improve animal production performance, enhance animal health, and replace growth-promoting antibiotics in feed. Weaning stress is a major factor causing diarrhea and growth inhibition in piglets. Adding M. cordata extract to their diet can improve small intestine morphology, enhance intestinal barrier function, and regulate intestinal microbiota homeostasis, thereby reducing diarrhea and improving growth performance[49−52]. During pregnancy, progressive oxidative stress and parturition stress can lead to metabolic disorders and increased inflammation in sows. Supplementing their diet with M. cordata extract can reduce inflammation, enhance antioxidant capacity, shorten farrowing duration, increase feed intake and milk production during lactation, and ultimately increase the weaning weight of piglets[53,54]. Environmental stress and pathogenic infections are significant threats to poultry intestinal health. Adding M. cordata extract to poultry feed can improve intestinal mucosal morphology, enhance intestinal barrier function, regulate microbial populations, and improve broiler growth performance[55−58]. High-fat and high-protein feed can cause intestinal damage in fish. Supplementing their diet with M. cordata extract can enhance intestinal antioxidant capacity, alleviate intestinal barrier damage, improve microbiota homeostasis, and thus increase survival and growth rates[59−61]. Ruminants have a unique rumen physiology where the microbiota plays a crucial role in nutrient digestion and metabolism. Studies have shown that adding M. cordata extract to dairy cow diets can regulate rumen microbial populations and reduce methane emissions, alleviate intestinal inflammation in weaned lambs[62], promote growth in meat sheep[63], increase milk yield in dairy goats, reduce somatic cell counts in milk, and improves milk quality[64].
In addition to its applications in animal production, M. cordata extracts have been developed into various products due to their significant insecticidal and antibacterial properties. In 2021, they were registered as a new botanical pesticide in China and the United States for controlling greenhouse plant diseases such as powdery mildew and leaf spot disease. In the bioenergy sector, the combination of M. cordata extracts with trace elements cobalt and nickel can effectively accelerate the fermentation process of agricultural waste, increasing biogas production. Furthermore, Macleaya alkaloids are used in toothpaste and mouthwash for their sustained antibacterial activity, which helps treat periodontal disease and prevent bad breath[65]. These findings highlight the diverse applications and benefits of M. cordata in improving animal health and productivity, controlling plant diseases, and enhancing bioenergy production (Fig. 6).
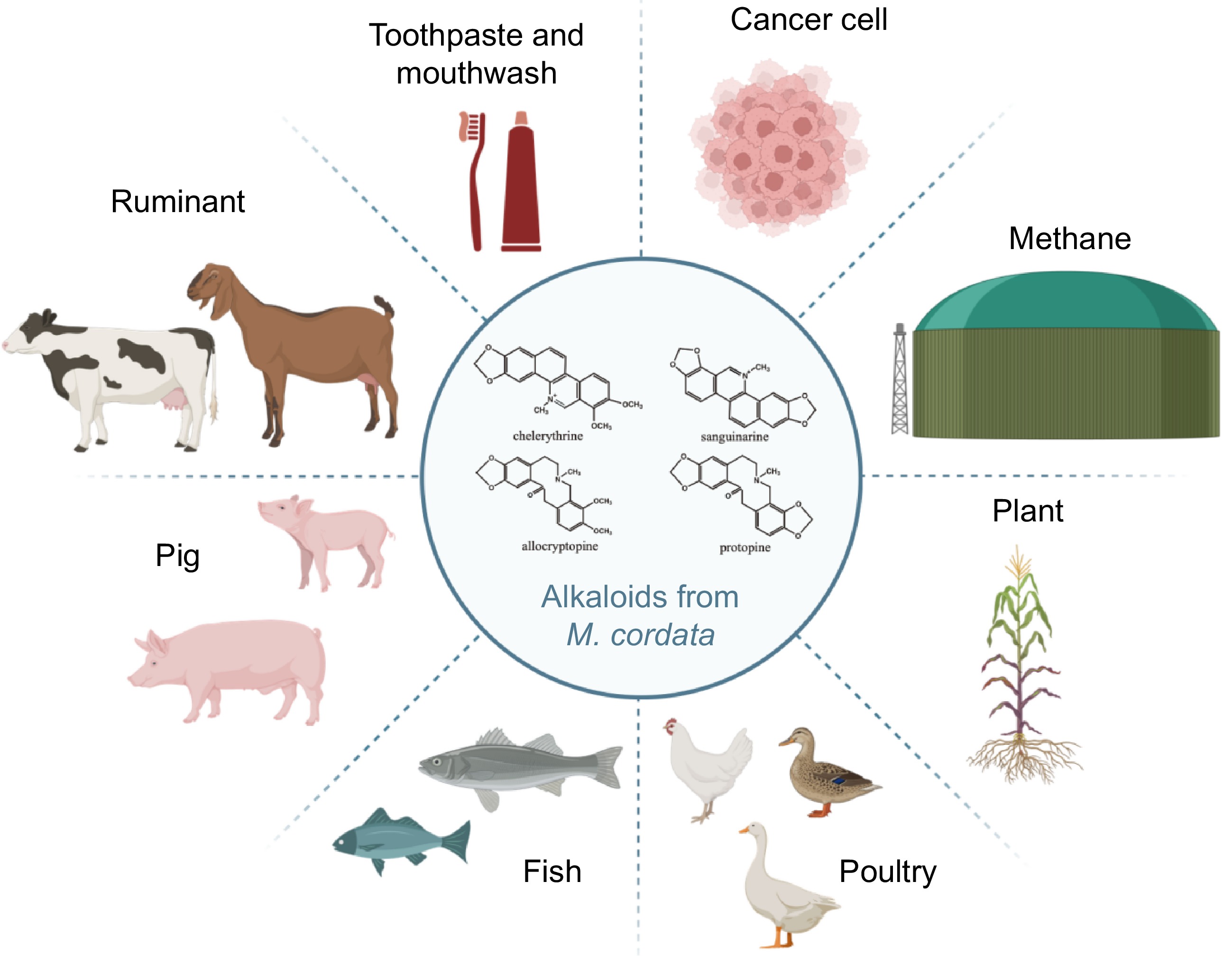
Figure 6.
This illustration showcases the versatile applications of alkaloids derived from M. cordata. The molecular structures of key alkaloids—chelerythrine, sanguinarine, allocryptopine and protopine—are depicted in the center. These alkaloids are utilized in enhancing digestion and improving feed efficiency in ruminants, boosting immunity and promoting growth in pigs, promoting health and growth in fish, improving health in poultry, serving as natural pesticides for crops, reducing methane emissions from ruminants to lower greenhouse gases, acting as antibacterial ingredients in toothpaste and mouthwash, and exhibiting potential anti-cancer activity in cancer treatment. The alkaloids from M. cordata demonstrate significant potential across various fields, from agriculture to medicine.
-
M. cordata, a plant rich in bioactive compounds, holds vast potential for applications in medical and agricultural fields. However, future research faces multiple challenges and opportunities. Firstly, although substantial research has been conducted on the primary alkaloids in M. cordata, their regulatory mechanisms remain unclear. Future studies need to integrate multi-omics data and systems biology approaches to elucidate the molecular mechanisms regulating alkaloid biosynthesis in M. cordata, providing a theoretical foundation for precise metabolic pathway regulation.
Secondly, the application of molecular breeding and metabolic engineering in M. cordata is still in its infancy. Effectively increasing the yield of specific bioactive compounds through genetic engineering, particularly achieving efficient biosynthesis and accumulation of key alkaloids like sanguinarine, will be a focus of future research. Despite the achievement of de novo synthesis of sanguinarine in yeast, the scalability of this production method remains challenging. It is necessary to assess the economic feasibility of these methods to ensure they can meet industrial demands without compromising quality or sustainability. Additionally, the long-term stability and consistency of genetically engineered strains and their products need to be ensured to avoid potential issues in production and application.
Lastly, as the medicinal value of M. cordata becomes better understood, ensuring its sustainable use and the conservation of wild resources, while developing more high-value products, will be crucial for future development. Large-scale cultivation and utilization of M. cordata may pose potential environmental impacts, including changes in soil health, biodiversity, and local ecosystems, which are not sufficiently studied and require further investigation and evaluation.
In summary, while the research and application prospects of M. cordata are promising, they also present a series of scientific and technical challenges. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and enhancing the integration of basic and applied research, these challenges can be overcome, enabling the efficient utilization and industrial development of M. cordata resources. Addressing the limitations in current research, particularly in ecological impact and production methods, will provide a more balanced perspective and guide future research toward sustainable and scalable solutions.
-
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: study conception and design: Huang P, Zeng J; draft manuscript preparation: Huang P, Cheng P, Sun M, Liu X, Qing Z, Liu Y, Yang Z, Liu H, Li C, Zeng J. All the authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
This work was supported by Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2023JJ40367 & 2023JJ30341).
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
- Copyright: © 2024 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press, Fayetteville, GA. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Huang P, Cheng P, Sun M, Liu X, Qing Z, et al. 2024. Systemic review of Macleaya cordata: genetics, biosynthesis of active ingredients and functions. Medicinal Plant Biology 3: e020 doi: 10.48130/mpb-0024-0019
Systemic review of Macleaya cordata: genetics, biosynthesis of active ingredients and functions
- Received: 20 May 2024
- Revised: 19 July 2024
- Accepted: 26 July 2024
- Published online: 09 October 2024
Abstract: Macleaya cordata, a medicinal plant in the Papaveraceae family, is rich in bioactive benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. Recent research has elucidated the mechanisms by which these active components promote livestock and poultry growth and exhibit anti-inflammatory effects on the intestines. These findings have led to the development of two raw medicinal materials and two veterinary drug formulations, widely used in China's livestock industry. Advances in multi-omics technologies, such as whole-genome sequencing and transcriptomics, have clarified the chemical composition of alkaloids and the biosynthesis of sanguinarine, enabling its de novo synthesis in yeast. Efforts in plant breeding have focused on cultivar selection and germplasm innovation, establishing DUS (Distinctness, Uniformity, and Stability) testing guidelines. Genetic engineering techniques have re-edited the sanguinarine pathway and induced hairy roots and cell suspension cultures in M. cordata. These advancements reduce production costs, ensure product stability, and promote sustainable production. This paper reviews the species origin, current research status, and prospects of M. cordata, offering guidance for further research on this valuable resource.
-
Key words:
- Review /
- Macleaya cordata /
- Systemic /
- Genetics /
- Biosysnthesis /
- Active