-
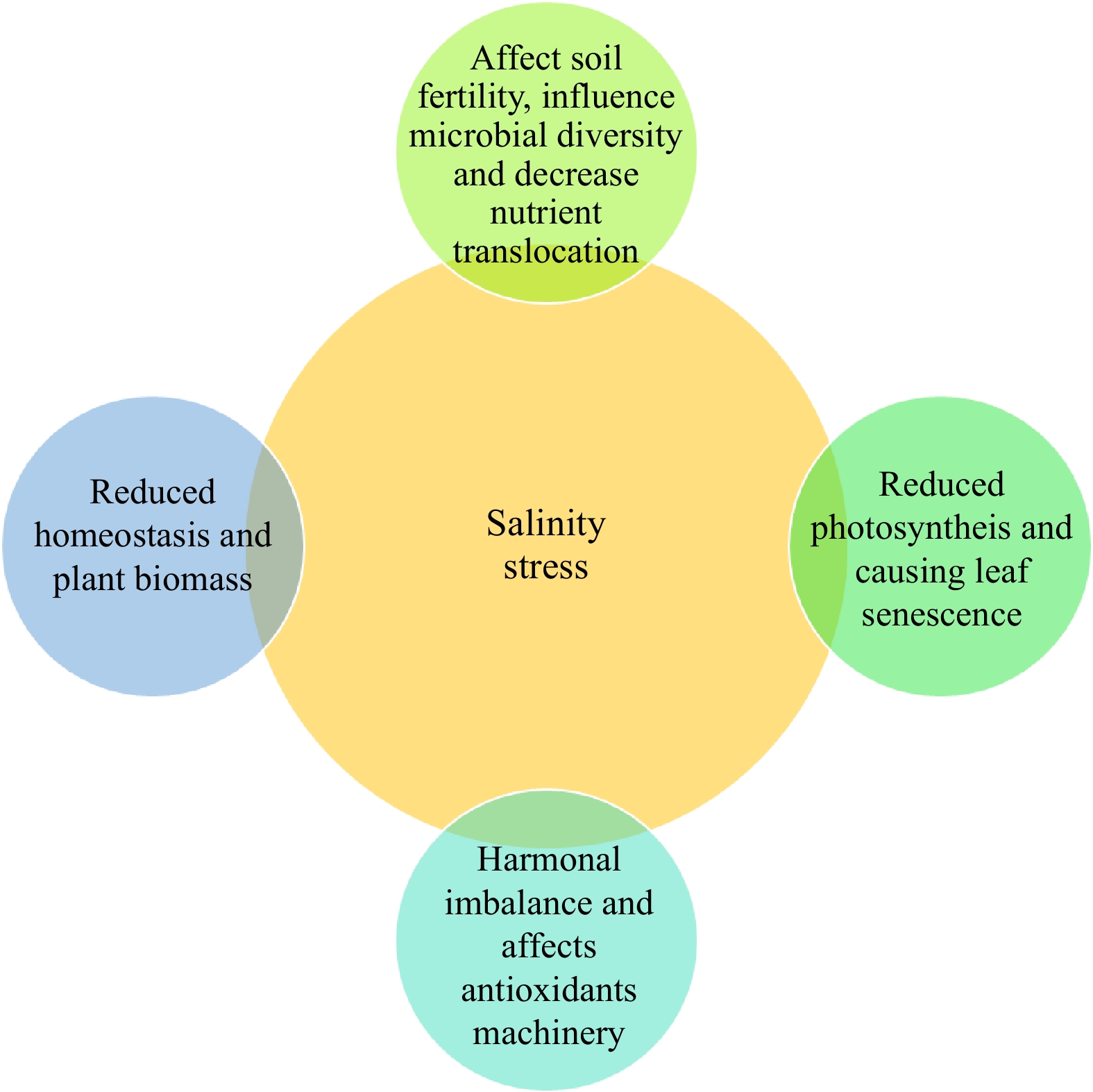
Figure 1.
Impact of salinity stresses on various plant growth characteristics.
-
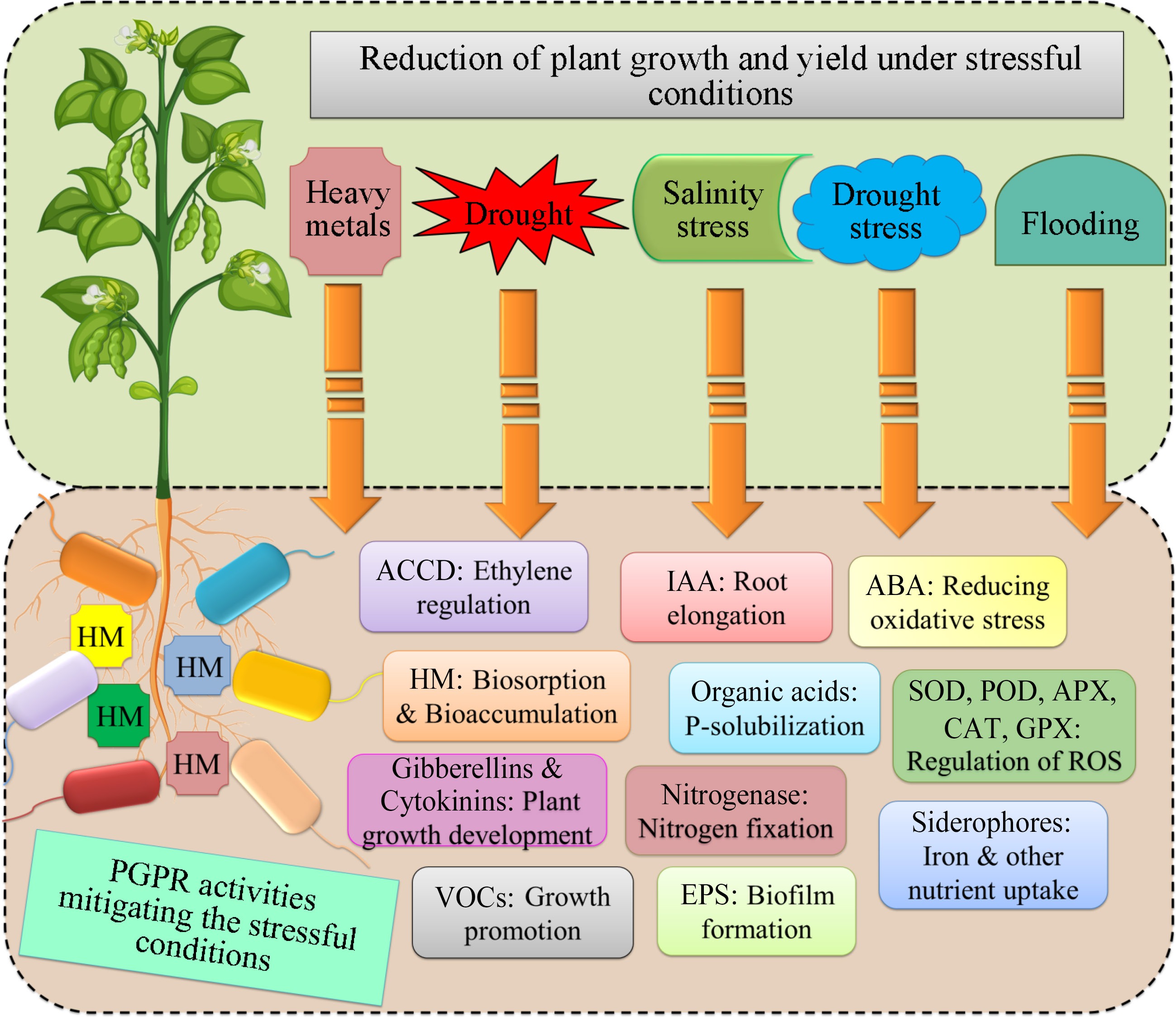
Figure 2.
Plant growth promotion activities of stresses tolerant PGPRs to enhanced the plant efficiency. HMs: Heavy metals; IAA: Indole-3 Acetic acid; ABA: Abscisic acid; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; POD: Peroxidases; APX: Ascorbate peroxidase; CAT: Catalase; GPX: Glutathione peroxidase; VOCs: Volatile organic compounds; EPS: Exopolysaccharides.
-
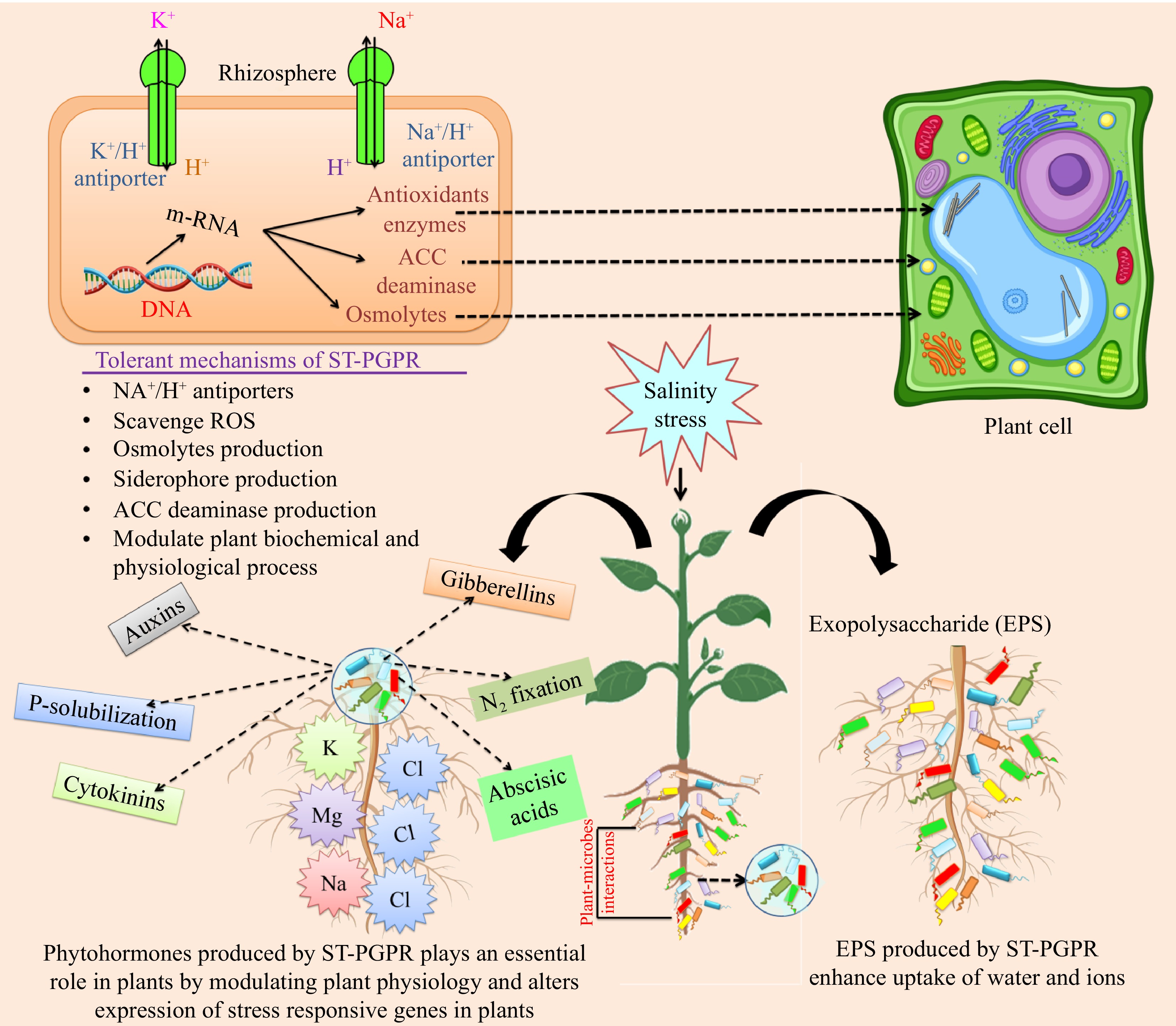
Figure 3.
Effect of ST-PGPR on plant growth, health, and stress tolerant. Salinity stress (inhibition of water uptake, reduction of cell elongation, and decrease in leaf growth), ionic stress, and nutrient imbalance (increase in Na+ and Cl− levels, reduction in Ca2+, K+, H+, N, and NO3− levels, and accelerate leaf senescence); oxidative stress (generation of ROS, DNA/RNA/protein/lipid membrane damage, depletion of antioxidants). ST-PGPR: salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria; EPS: Exopolysaccharide; ACC: 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate; Na+: sodium; Cl−: chloride; K+: potassium; H+: proton.
-
ST-PGPR Mode of action Crops Ref. B. subtilis SU-12, Bradyrhizobium japonicum, and Serratia proteamaculans Antioxidant enzyme and Proline content Glycine max [60] K. oxytoca Rs-5, Bacillus sp. SL-44, Bacillus
sp. SL-14, and Bacillus sp. SL-13Antioxidant enzymes and photosynthetic pigment Gossypium hirsutum [61] P. pseudoalcaligens Siderophore, PO43‒ solubilization, and IAA production Cicer arietinum [62] Azotobacter chroococcum Improved K+/Na+ ratio, proline concentration, and polyphenol content Zea mays [63] Pseudomonas and Rhizobium sp. Water use efficiency, chlorophyll content, and photosynthetic rate Vigna radiata [64] Enterobacter cloacae N-fixation, Production of growth-promoting compounds Various vegetables and crops [65] P. aeruginosa EPS production Helianthus annuus [66] Klebsiella, Ochrobactrum, Pseudomonas,
and AgrobacteriumIAA production, PO43− solubilization, ACCD Arachis hypogaea [67] B. subtilis Nitrogen fixation PO43− solubilization, Production of plant hormones, Biocontrol of plant pathogens Most plants, including vegetables, cereals, and fruits [68] Rhizobium sp. ACCD, IAA production, and PO43‒ solubilization Brassica napus [69] Halobacillus sp. GSP 34 and
H. dabanensis SB-26N-fixation and IAA production O. sativa [70] P. aeruginosa GI-1, and
Burkholderia gladioli GI-6N assimilation, PO43‒ solubilization, IAA production, siderophores generation, and CAT activity Triticum aestivum L. [71,72] Bacillus and Pseudomonas sp. N-fixation and IAA production Pisum sativum L. [16] Bacillus sp. IAA production, PO43‒ solubilization, ACC deaminase, and HCN production P. sativum L. [2] B. cereus and B. marisflavi IAA production, PO43‒ solubilization, ACCD activity, Biofilm formation, HCN, and Siderophore production P. sativum and Z. mays [73] Arthrobacter sp., P. plecoglossicida,
Kocuria rosea, and Bacillus isolatesIAA production, Zn and PO43‒ solubilization, NH3 and siderophore production P. sativum [74] Enterobacter and Pseudomonas sp. ACCD activity O. sativa [75] P. aeruginosa HG28-5 Increased morphological and physiological parameters like elevating the antioxidants enzyme level, reducing oxidative stress, and up-regulating ABA pathway genes Solanum lycopersicum [48] Burkholderia sp. BK01 Enhanced enzymatic activities like SOD, POD, and CAT Arabidopsis thaliana [76] B. velezensis CC03 and
P. nicosulfuronedens AP01PO43‒ solubilization and pathogen suppression thereby increasing the RWC, PRP accumulation Hibiscus sabdariffa [77] N: Nitrogen; IAA: Indole-3-acetic acid; ACCD: 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase; P: Phosphate; HCN: Hydrogen cyanide; EPS: Exopolysaccharide; K+: Potassium; Na+: Sodium; Zn: Zinc; CAT: Catalase; ABA: Abscisic acid; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; POD: Peroxidase; RWC: Relative water content; PRP: Proline-rich protein. Table 1.
Salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and their potential involvement in increasing yield and growth in a variety of plants and crops.
-
PGPR Relationship to host Host crop Ref. Azospirillum sp. Rhizospheric Zea mays and O. Sativa [116,130] Azotobacter sp. Rhizospheric Z. mays and Triticum aestivum [128,131] Bacillus subtilis Rhizospheric T. aestivum [132,133] Burkholderia sp. Endophytic O. sativa [134] Cyanobacteria Rhizoshperic O. sativa and T. aestivum [135,136] Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus Endophytic Sorghum bicolor and Saccharum officinarum [137,138] Bacillus cereus and Bacillus marisflavi Rhizospheric Pisum sativum and Zea mays [16,73] Table 2.
PGPRs and their relationships to hosts on various crops.
-
PGPR Plant species Expressed gene Role of gene expression under SS Ref. B. megaterium Zea mays ZmPIP Increased root hydraulic conductivity [153] B. amyloliquefaciens O. sativa NADPMe2, EREBP, SOS1, BADH,
and SERK1Increased plant growth and salt tolerance [154] Pseudomonas putida Solanum lycopersicum Toc GTPase Imported chloroplast protein [155] Enterobacter sp. Solanum lycopersicum DREB2b, RD29A, RD29B, RAB18, P5CS1, P5CS2, MPK, and MPK6 Antioxidant activity enhanced; increased
proline biosynthesis[156] B. amyloliquefacis Zea mays RBCS, RBCL, H+-PPase, HKT1,
NHX1, NHX2, and NHX3Promoted seedling growth and Chl content; Improved POD/CAT activity and glutathione content; Decreased Na+ toxicity [87] Dietzia natronolimnaea Triticum aestivum APX, MnSOD, CAT, POD, GPX, GR, TaABARE, TaOPR1, TaMYB, and TaWRKY Increased proline content and antioxidant enzymes [157] Enterobacter sp Abelmoschus esculentus and Arabidopsis sp. APX and CAT Increased antioxidant enzyme activities [158] Arthrobacter protophormiae and B. subtilis Triticum aestivum TaCTR1 and TaDRE2 Enhanced salt stress tolerance [159] Pseudomonas simiae
strain AUGlycine Max L. DREB2A, EREB, GOLS, and
P5CS, PIP, and TIPUp-regulated TF, osmoprotectants, and water transporters by enhancing drought and salt tolerance by regulating stress-responsive genes [160] Bacillus sp. SR-2-1/1 Zea mays RBCL, CAT1, APX1, APX2, NHX1, SOS1, H+-PPase, and HKT1 Enhances photosynthesis efficiency, maintains ion homeostasis, regulates vacuolar proton pump, and minimizes oxidative stresses [161] Bradyrhizobium japonicum
and Enterobacter Delta PSKGlycine Max ‒ Enhanced the morphological parameters and chl a, decreased the electrolyte leakage, malondialdehyde, and H2O2 thereby mitigating OS [162] P. aeruginosa HG28-5 Solanum lycopersicum L. NCED, ABF4, ABI5, and AREB Regulating Na+/K+ homeostasis and ABA signaling pathway [48] ‒ Arabidopsis thaliana SOS1 and HKT1 Regulate efflux of Na+ ad enhancing SS tolerance [163] Beijerinckia fluminensis Arabidopsis thaliana SOS1, NHX1, and MYB genes Modulation of SS tolerance using signal response pathways and regulating ion homeostasis [164] SS: Salinity stress; RBCS: encodingribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) small subunit; RBCL: encoding ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase largesubunit; H+-PPase: encoding H+-pumping pyrophosphatase; HKT1: encoding high-affinity K+ transporter 1; NHX: encoding Na+/H+ antiporter; ABARE: ABA-signalling cascade; PIP: Plasma membrane intrinsic protein; CTR: Copper uptake protein; DRE2: Dehydration responsive element 2; APX: Ascorbate peroxidase; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; CAT: Catalase; POD: Peroxidase; GPX: Glutathione peroxidase; GR: Glutathione reductase; OPR1: Oxophytodienoate reductase; MYB: Myeloblastosis; Toc GTPase: Translocons of the outer; DREB2b: Dehydration-responsive element-binding protein 2B; RD29A: Response to Desiccation; RAB18: Ras-related protein; P5CS1: Delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase 1; MPK: MAP kinase; NADPMe2: NADP-malic enzyme; EREBP: Ethylene-responsive element binding protein; SOS1: Salt-overly sensitive; BADH: Betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase; SERK1: Somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase 1; DREB2A: Dehydration-responsive element binding protein2a; EREB: Ethylene responsive protein; GOLS: Galactinol synthase; P5CS: 1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase; PIP: Plasma membrane intrinsic protein; TIP: Tonoplast Intrinsic Proteins; RBCL: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain; OS: Osmotic stress; NHX1: Sodium/hydrogen exchanger 1; SOS1: Salt Overly Sensitive 1; H+-PPase: Proton-pumping pyrophosphatase; NCED: 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase; ABF4: ABRE (abscisic acid-responsive elements) binding factor 4; ABI5: ABA-insensitive5; AREB: ABA-responsive element binding protein. Table 3.
Influence of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on gene expression regulation under SS conditions.
Figures
(3)
Tables
(3)