-
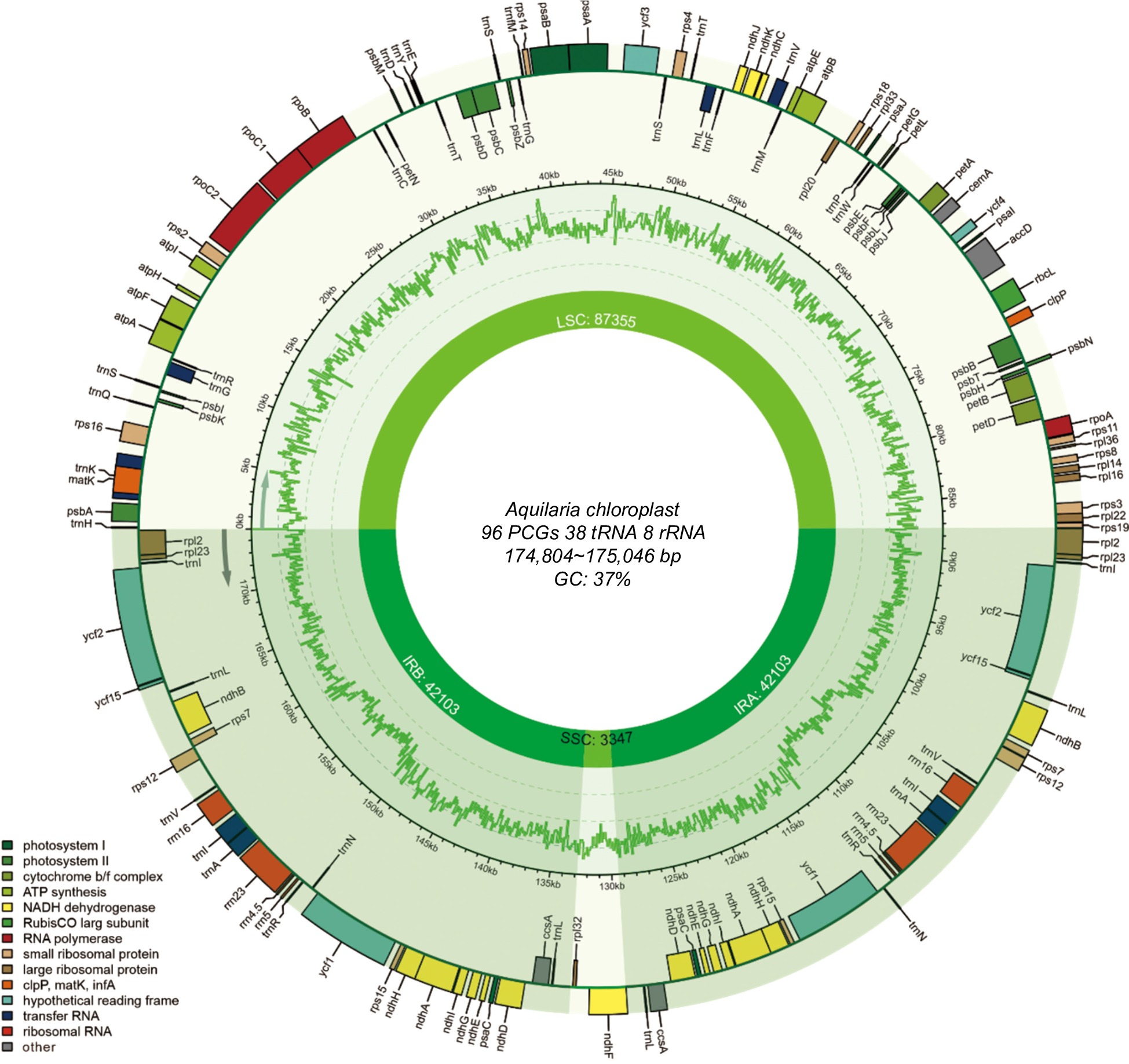
Figure 1.
Annotation map of the Aquilaria plastome. Genes listed inside and outside the circle are transcribed clockwise and counterclockwise, respectively, with genes color-coded based on functional classification.
-
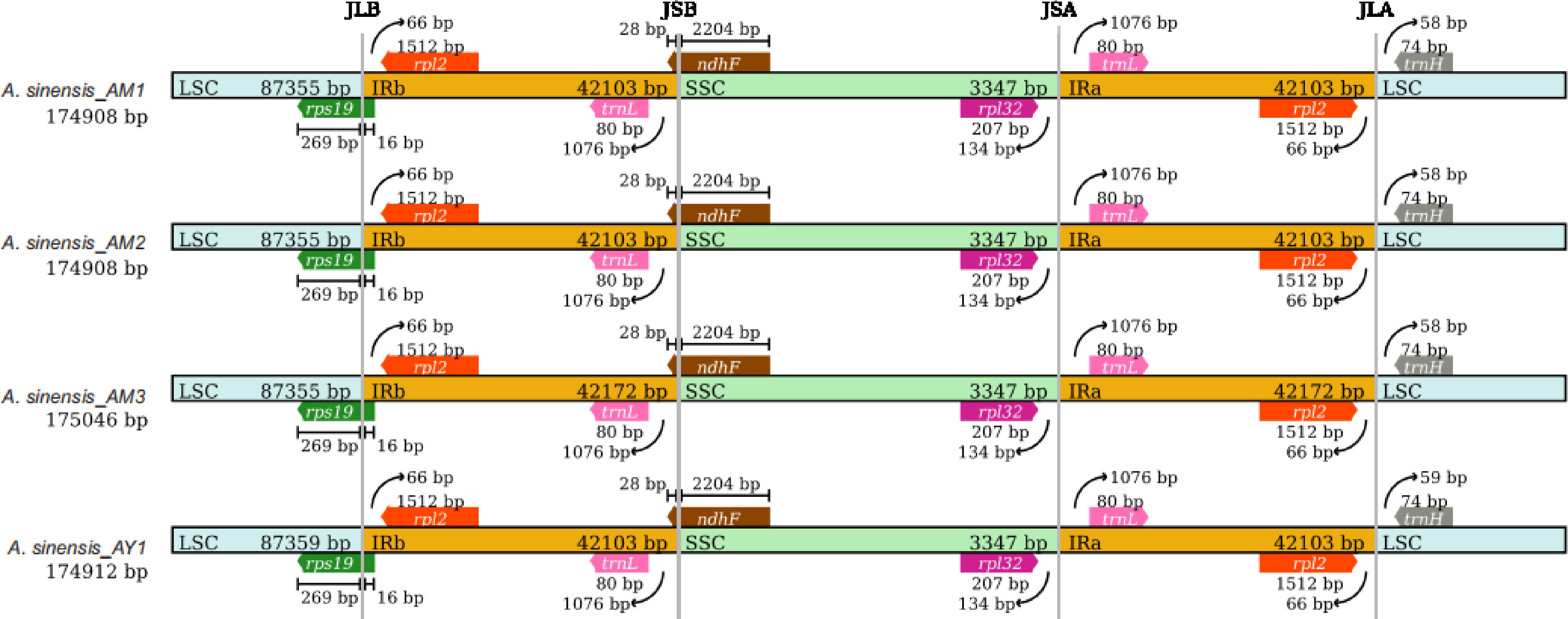
Figure 2.
Comparison of the large single-copy (LSC), small single-copy (SSC), and inverted repeat (IR) region borders of Aquilaria plastomes. The LSC, IR, and SSC regions are depicted with blue, orange, and green blocks, respectively. Gene boxes above the block are transcribed counterclockwise while those below the block are transcribed clockwise. (Representative plastomes from Supplemental Fig. S2).
-
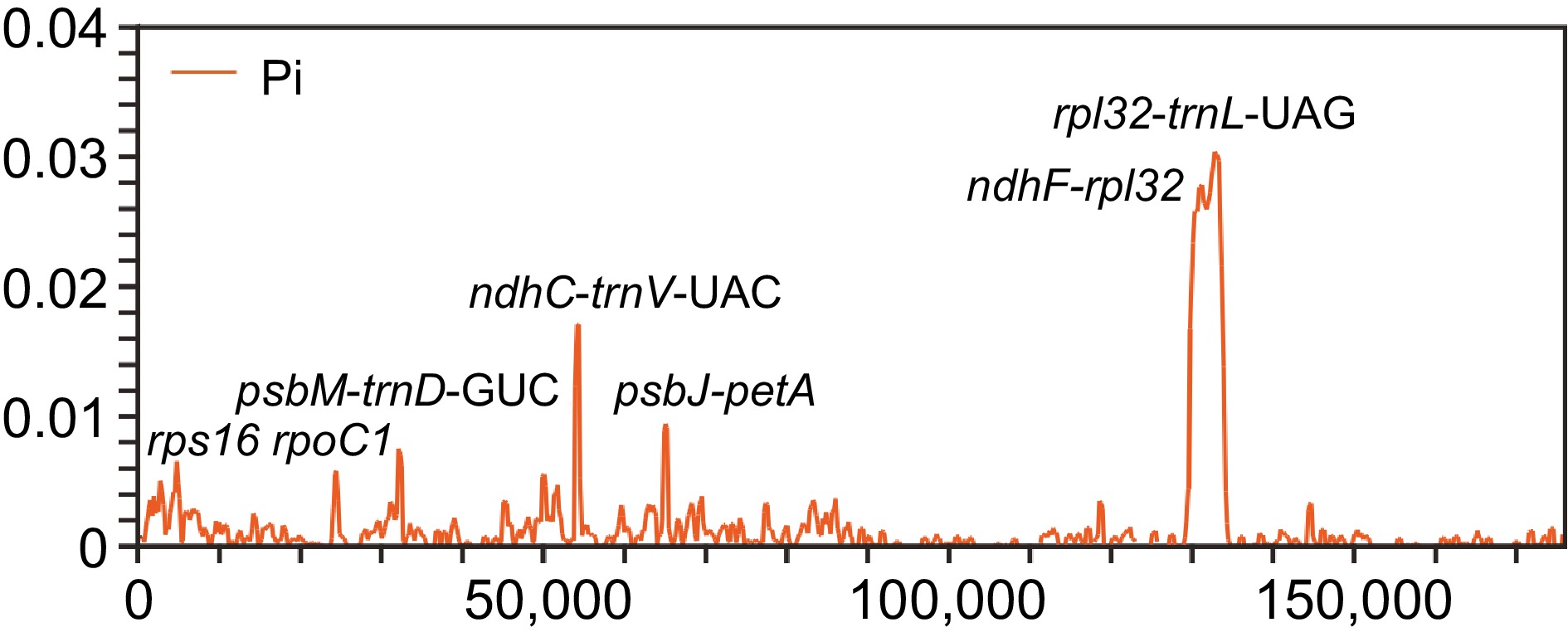
Figure 3.
Comparison of nucleotide variability values among 37 plastomes using window sliding analysis. The x-axis indicates the position of the midpoint of the window, while the y-axis indicates the nucleotide diversity of each window.
-
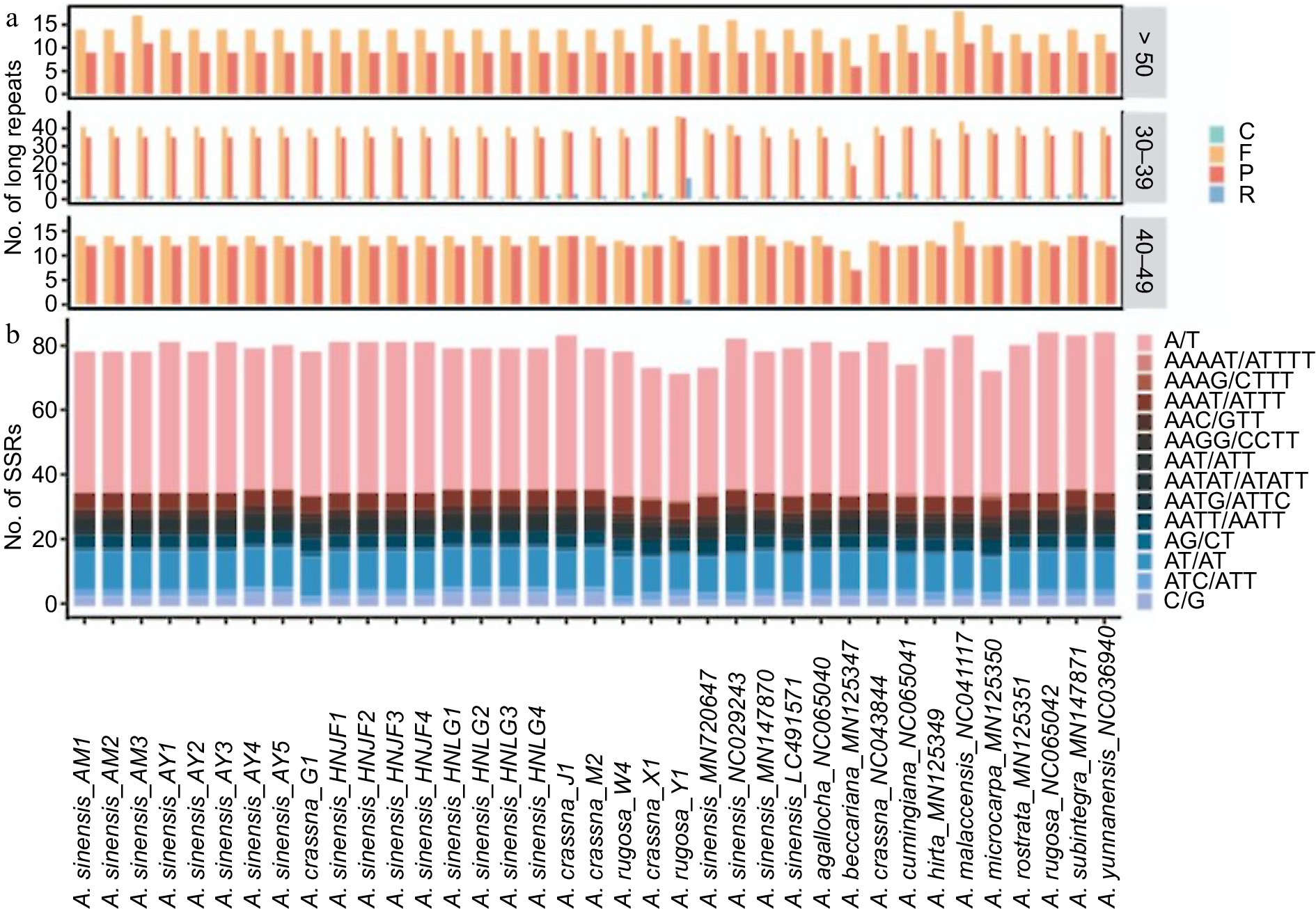
Figure 4.
(a) Distribution of different types of large sequences repeat (LSRs) in Aquilaria plastomes, including complementary (C), forward (F), palindromic (P), and reverse (R) type repeats. (b) Distribution of distinct types of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in Aquilaria plastomes.
-
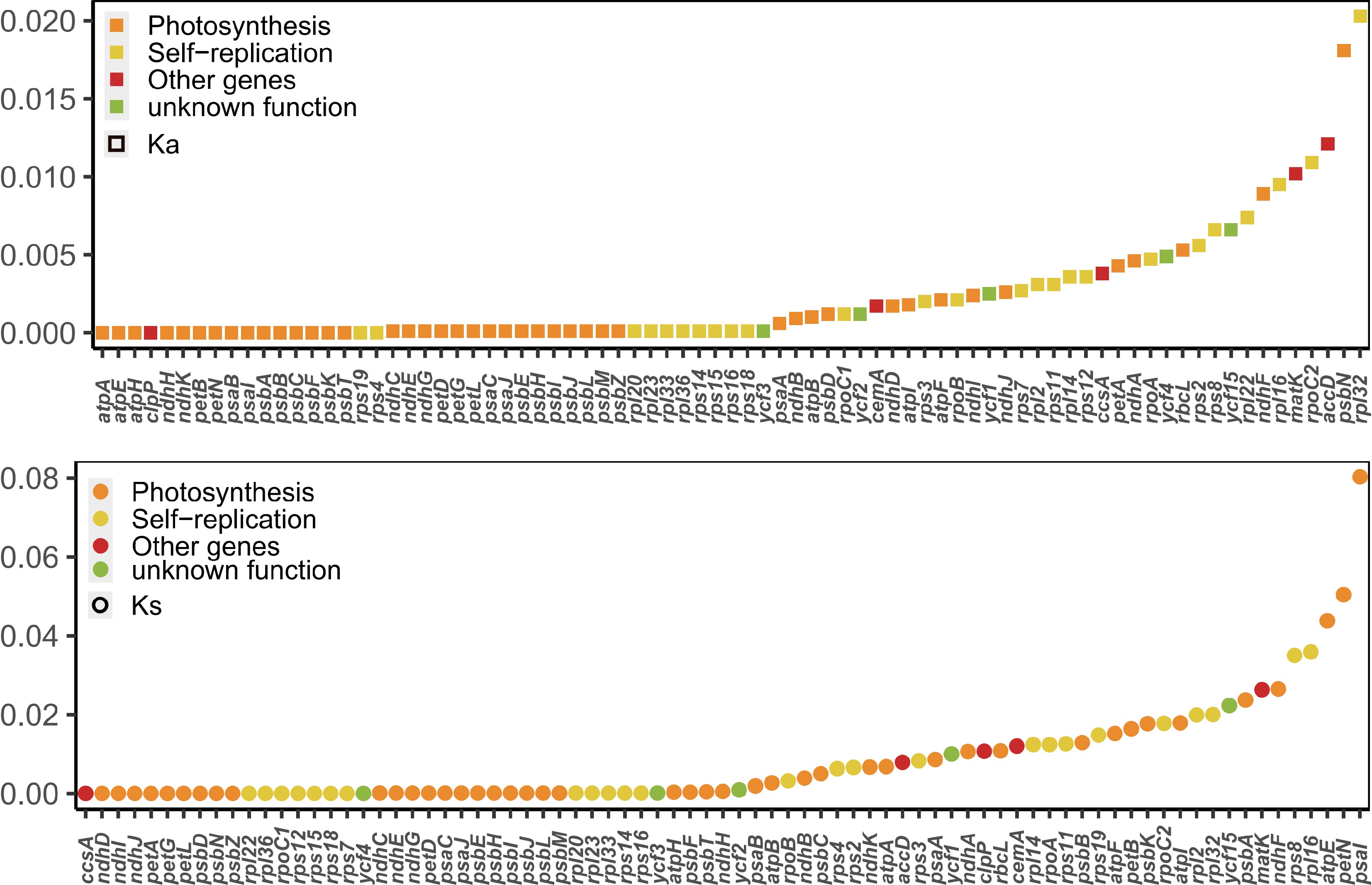
Figure 5.
Values of synonymous (Ks) and non-synonymous (Ka) substitution rates for 79 protein-coding genes in Aquilaria.
-
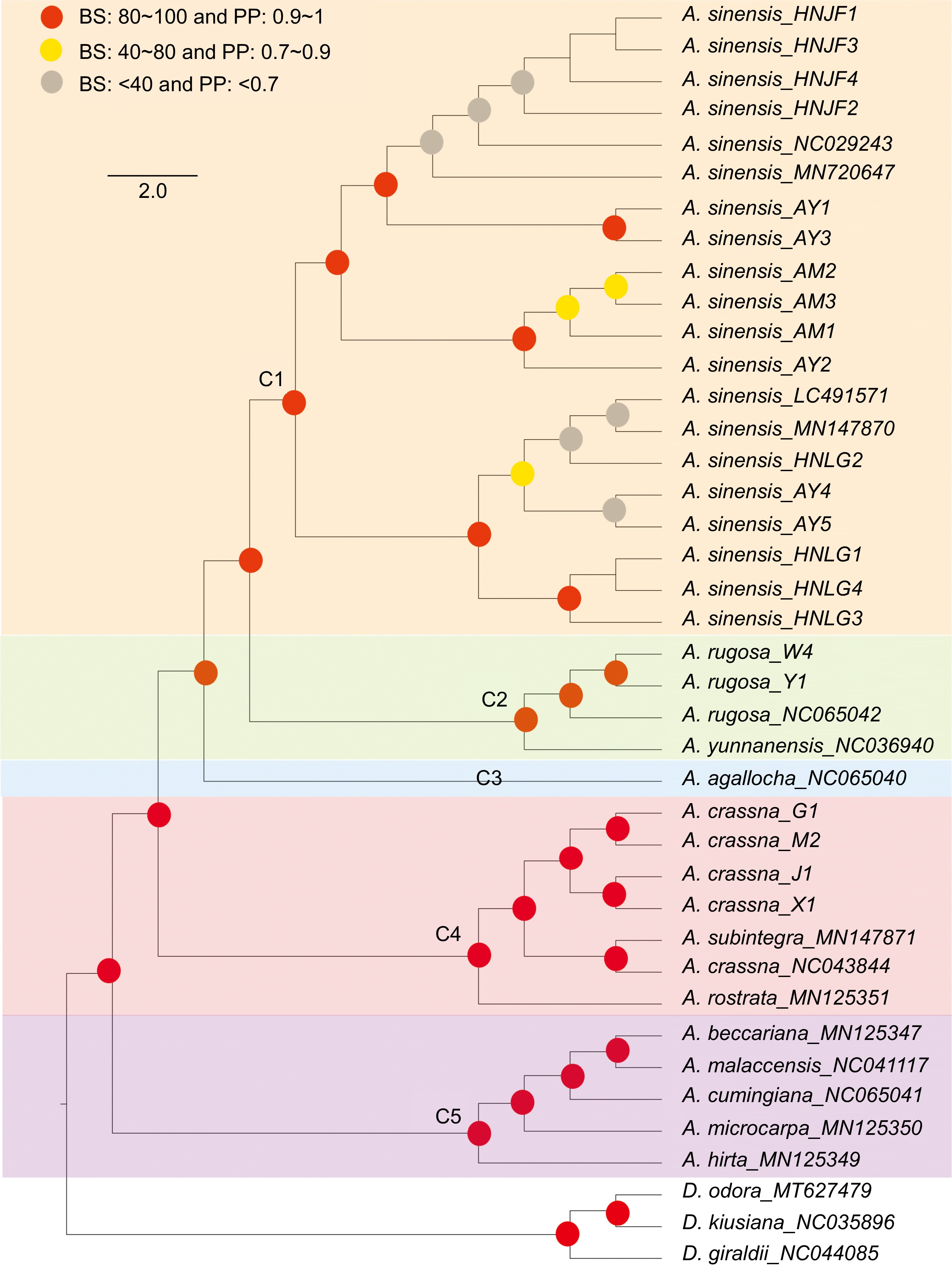
Figure 6.
Phylogenetic tree depicting relationships among Aquilaria species. Red circles indicates bootstrap support (BS) values greater than 80% and posterior probability (PP) values exceeding 1. Yellow circles indicates BS values ranging from 40% to 80%, and PP values ranging from 0.7 to 0.9. Grey circles indicates BS values below 40% and PP values less than 0.7.
-
Category Group of genes Names of genes Photosynthesis Subunits of photosystem I psaA, psaB, psaC(2), psaI, psaJ Subunits of photosystem II psbA, psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbN, psbT, psbZ Subunits of NADH dehydrogenase ndhA*(2), ndhB*(2), ndhC, ndhD(2), ndhE(2), ndhF, ndhG(2), ndhH(2), ndhI(2), ndhJ, ndhK Subunits of cytochrome b/f complex petA, petB*, petD*, petG, petL, petN Subunits of ATP synthase atpA, atpB, atpE, atpF*, atpH, atpI Large subunit of rubisco rbcL Subunits photochlorophyllide reductase − Self-replication Proteins of large ribosomal subunit rpl14, rpl16, rpl2*(2), rpl20, rpl22, rpl23(2), rpl32, rpl33, rpl36 Proteins of small ribosomal subunit rps11, rps12**(2), rps14, rps15(2), rps16*, rps18, rps19, rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7(2), rps8 Subunits of RNA polymerase rpoA, rpoB, rpoC1*, rpoC2 Ribosomal RNAs rrn16(2), rrn23(2), rrn4.5(2), rrn5(2) Transfer RNAs trnA-UGC*(2), trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnF-GAA, trnG-GCC, trnG-UCC*, trnH-GUG, trnI-CAU(2), trnI-GAU*(2), trnK-UUU*, trnL-CAA(2), trnL-UAA*, trnL-UAG(2), trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU(2), trnP-UGG, trnQ-UUG, trnR-ACG(2), trnR-UCU, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnS-UGA, trnT-GGU, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC(2), trnV-UAC*,
trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA, trnfM-CAUOther genes Maturase matK Protease clpP Envelope membrane protein cemA Acetyl-CoA carboxylase accD c-type cytochrome synthesis gene ccsA Translation initiation factor − other − Genes of unknown function Conserved hypothetical chloroplast ORF ycf1(2), ycf15(2), ycf2(2), ycf3**, ycf4 Gene*: Gene with one intron; Gene**: Gene with two introns; Gene(2): Number of copies of multi-copy genes. Table 1.
Genes present within Aquilaria plastomes.
Figures
(6)
Tables
(1)