-
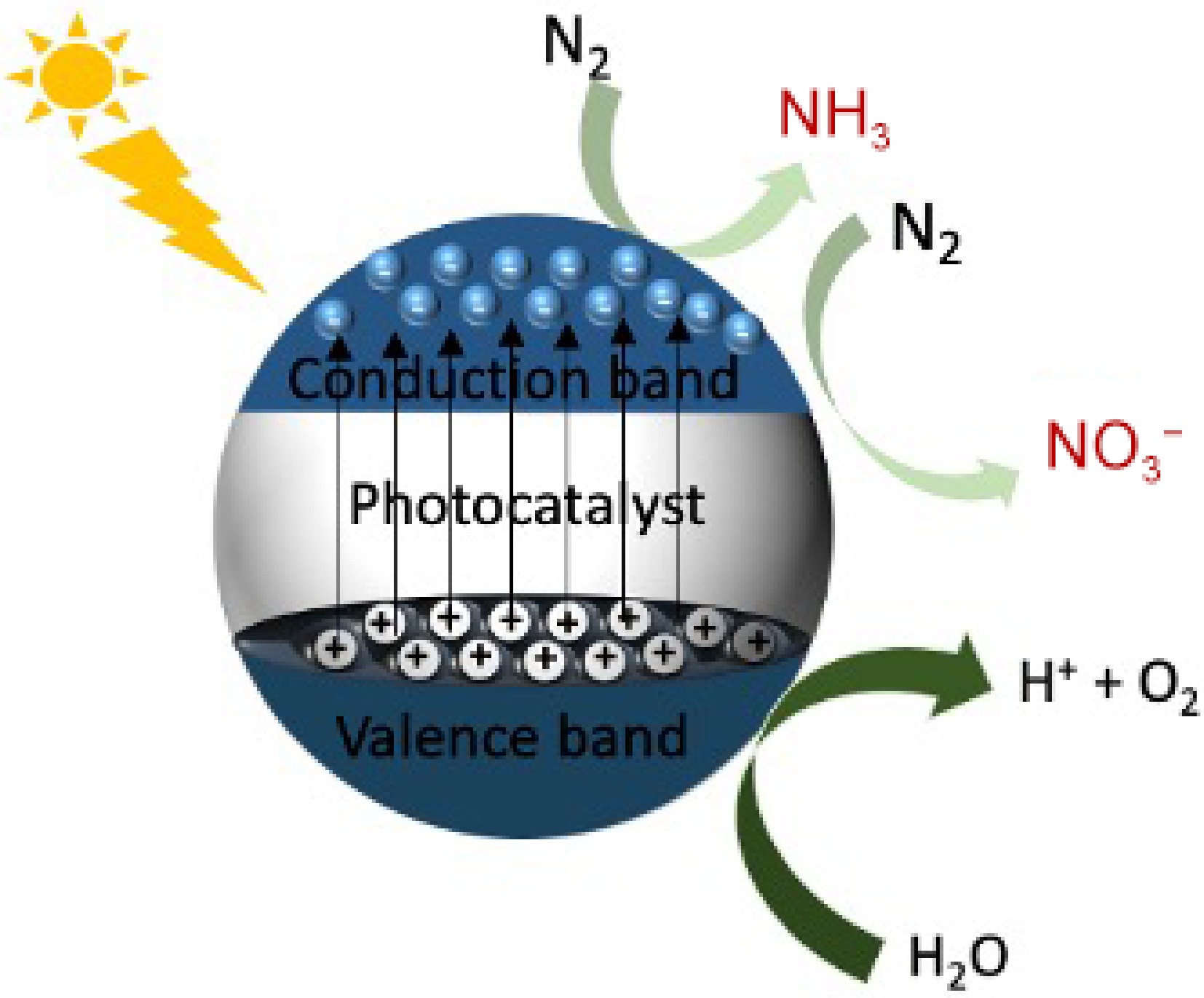
Figure 1.
Photocatalytic reduction/oxidation of N2 to NH3/NO3−.
-
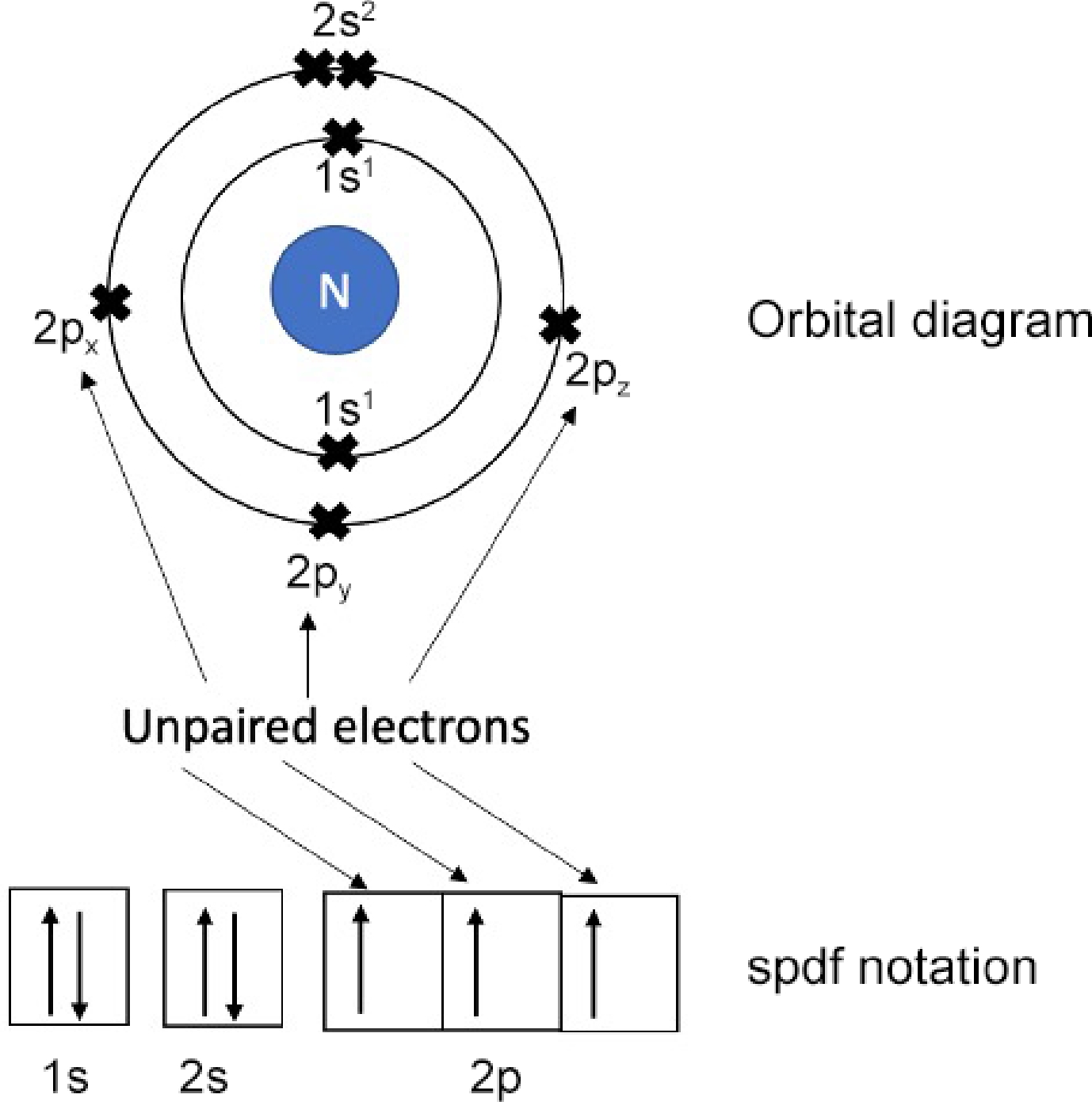
Figure 2.
Electronic configuration of a nitrogen atom.
-
Photocatalyst Band gap
energy (eV)Yield (NH3) Ref. Bi2O2CO3 2.65 1,175.78 μmol·L−1·g−1·h−1 Feng et al.[101] I-g-C3H4 2.68 200.8 mg·L−1·g−1 Hu et al.[102] La2TiO5 4.07 158.13 μmol·g−1·h−1 Song et al.[103] C-BiOI 1.81 311 μmol·g−1·h−1 Zeng et al.[92] g-C3H4 2.74 150 mg·L−1·h−1·g−1 Hu et al.[104] FeS2/Fe-Pal 1.30 147 μmol·g−1·h−1 Ye et al.[105] In2O3/In2S3 2.77 40.04 μmol·g−1·h−1 Xu et al.[106] Ag/B-g-C3H4 2.82 5.19 mg·h−1·g−1 Yao et al.[107] N-g-C3H4 2.60 531.24 μmol·L−1·g−1·h−1 Liu et al.[108] Bi2S3 1.48 51.04 μmol·g−1·h−1 Lan et al.[109] Bi2S3@PCN-2 1.61 3,880 μg·h−1·g−1 Chen et al.[110] W18O49/g-C3N4 2.83 64.8 μmol·gcat−1·h−1 Huang et al.[111] TCN/ZnS/ZnIn2S4 2.59 136.56 μmol·L−1 Sun et al.[112] Table 1.
Photocatalyst for photocatalytic nitrogen fixation.
Figures
(2)
Tables
(1)