-
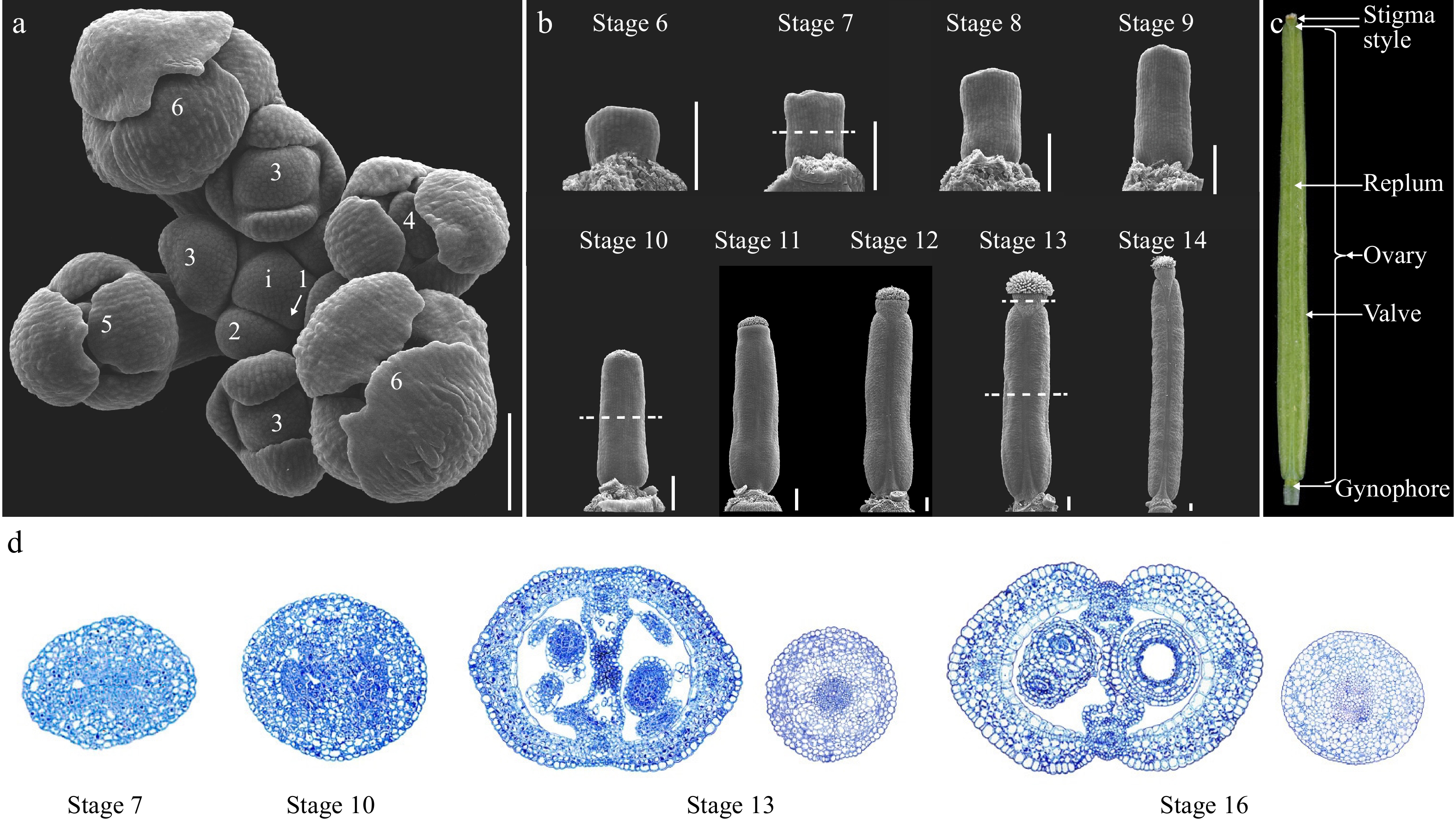
Figure 1.
Overview of the gynoecium development in Arabidopsis. (a) Top view of an Arabidopsis inflorescence meristem (IM) consisting of stage 1 to stage 6 floral primordia. Dashed lines indicate the position of the cross section shown in (d). (b) SEM micrographs of Arabidopsis gynoecium from stages 6 to 14. (c) A mature Arabidopsis fruit at stage 17 showing the full differentiation of distinct tissues. (d) Cross-section of the gynoecium at stage 7, 10, 13, and 16. For stage 13 and 16 samples, both the ovary and style were included for comparison of the symmetry. i: inflorescence meristem; the numbers indicate the developmental stages. Scale bars = 100 μm.
-
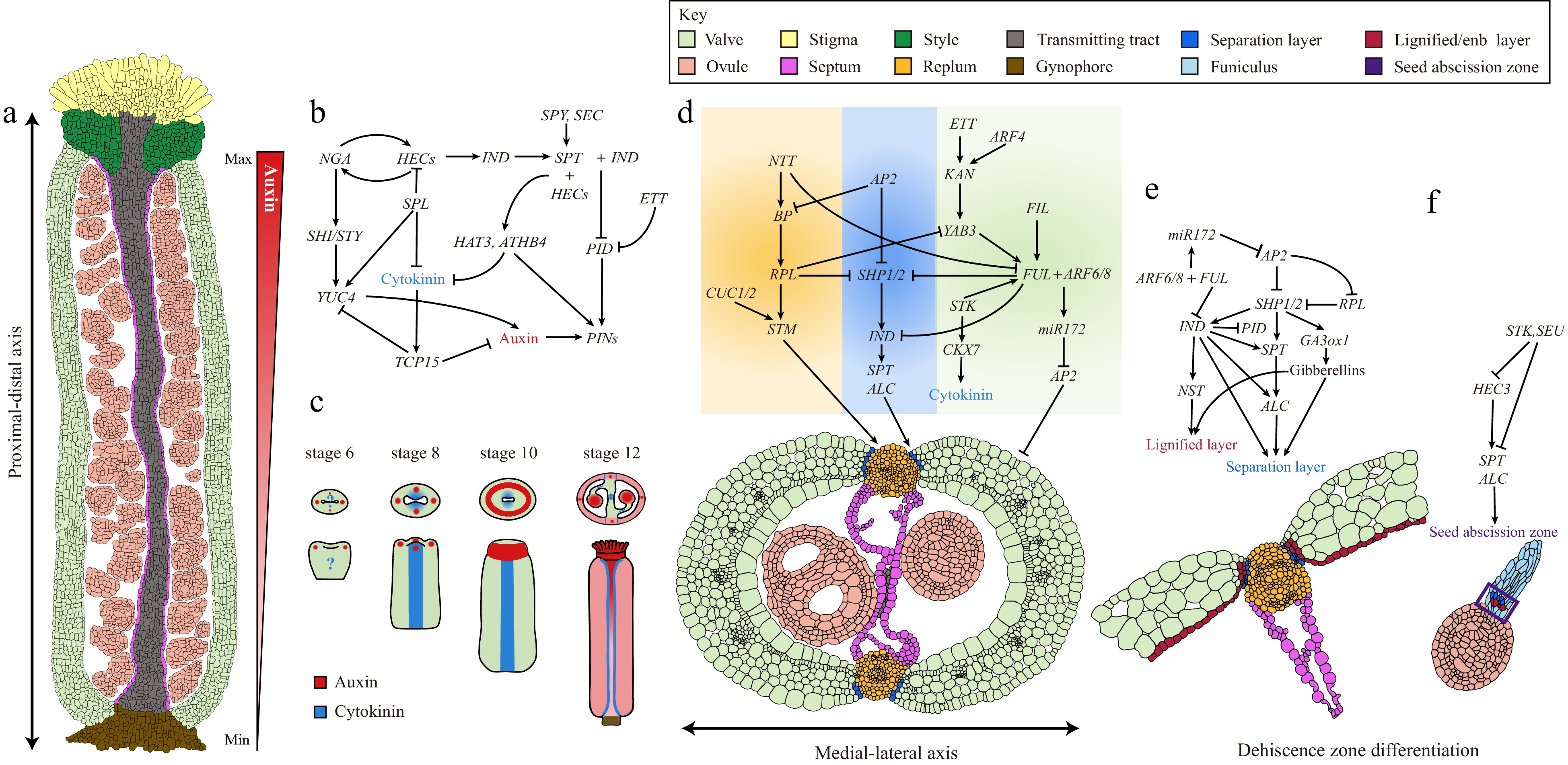
Figure 2.
Complex GRNs underlie gynoecium patterning and fruit development in Arabidopsis. (a) A longitudinal section of a stage 11/12 Arabidopsis gynoecium showing the differentiation of complex tissues along the proximal-distal axis. The auxin gradient along the proximal-distal axis is shown by a triangular red gradient. (b) GRNs and the hormone dynamic patterning the gynoecium apical region. (c) Auxin and cytokinin signaling distribution pattern during gynoecium development from stage 6 to 12. (d) GRNs governing the differentiation of medial-lateral axis of Arabidopsis gynoecium. (e) GRNs and the hormone dynamic controlling the dehiscence zone differentiation. (f) GRNs controlling the cell differentiation responsible for seed abscission.
-

Figure 3.
Expression patterns of the genetic factors involved in gynoecium patterning. A visual depiction of the expression patterns of genetic factors involving in the development and specification of gynoecium tissues. Longitudinal and cross sections of the gynoecium at stages 6, 10, and 13 are shown. Expression is indicated by the red color exclusively within the gynoecium tissues (gene expression patterns are derived from original research articles; the relevant sources can be found in Table 1).
-
Gene name AG code Family Function Ref. AGAMOUS (AG) AT4G18960 MADS-box Gynoecium primordium specification [27] ALCATRAZ (ALC) AT5G67110 bHLH Separation layer development [117] APETALA 2 (AP2) AT4G36920 AP2/EREBP Valve development [110,120] ARABIDOPSIS RESPONSE REGULATORS 1(ARR1) AT3G16857 ARR CMM development [83] ARABIDOPSIS RESPONSE REGULATORS 10 (ARR10) AT4G31920 ARR CMM development [83] ARABIDOPSIS RESPONSE REGULATORS 12 (ARR12) AT2G25180 ARR CMM development [83] AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR 3/ ETTIN (ARF3/ETT) AT2G33860 ARF Distal end of the gynoecium and in replum development [71] BRASSINOSTEROID ENHANCED EXPRESSION1 (BEE1) AT1G18400 bHLH Reproductive tract development [105] BRASSINOSTEROID ENHANCED EXPRESSION3 (BEE3) AT1G73830 bHLH Reproductive tract development [105] BREVIPEDICELLUS (BP) AT4G08150 Homeobox Replum development [104] CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON 1 (CUC1) AT3G15170 NAC SAM development and organ boundary definition [88,89] CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON 2 (CUC2) AT5G53950 NAC SAM development and organ boundary definition [88] CRABS CLAW (CRC) AT1G69180 YABBY Gynoecium primordium specification [47] FILAMENTOUS FLOWER (FIL) AT2G45190 YABBY Valve development [101] FRUITFULL (FUL) AT5G60910 MADS-box Valve development [102] HALF FILLED (HAF) AT1G25330 bHLH Reproductive tract development [105] HECATE 1 (HEC1) AT5G67060 bHLH adaxial-identity in gynoecium [61] HECATE 2 (HEC2) AT3G50330 bHLH adaxial-identity in gynoecium [61] HECATE 3 (HEC3) AT5G09750 bHLH adaxial-identity in gynoecium [61] INDEHISCENT (IND) AT4G00120 bHLH Valve margin tissue development and seed dispersal [55,125] NGATHA (NGA) AT2G46870 AP2/B3-like Style specification [64,65] NO TRANSMITTING TRACT (NTT) AT3G57670 C2H2 Transmitting tract development [98−100] PIN-FORMED 1 (PIN1) AT1G73590 PIN Proximal-distal axis establishment [53] PIN-FORMED 3 (PIN3) AT1G70940 PIN Proximal-distal axis establishment [127,128] REPLUMLESS (RPL) AT1G02065 Homeobox CMM development and replum morphogenesis [97] SEPALLATA (SEP) AT5G15800 MADS-box Gynoecium identity [28] SHATTERPROOF 1 (SHP1) AT3G58780 MADS-box Dehiscence zone differentiation [114] SHATTERPROOF 2 (SHP2) AT2G42830 MADS-box Dehiscence zone differentiation [114] SPATULA (SPT) AT4G36930 bHLH Style development [55,84] SEEDSTICK (STK) AT4G09960 MADS-box Funiculus and ovule development [111] STYLISH (STY) AT3G51060 SHI Gynoecium apex development [67] SHOOT MERISTEMLESS (STM) AT1G62360 Homeobox SAM development [94,95] TEOSINTEBRANCHED1 / CYCLOIDEA / PCF15 (TCP15) AT1G69690 TCP Gynoecium apex development [75] YABBY 3 (YAB3) AT4G00180 YABBY Valve development [101] YUCCA 4 (YUC4) AT5G11320 YUC Gynoecium primordium specification and gynoecium apex [66] WUSCHEL (WUS) AT2G17950 Homeobox FMs development [29] Table 1.
A list of genes involved in the gynoecium patterning and fruit development.
Figures
(3)
Tables
(1)