-
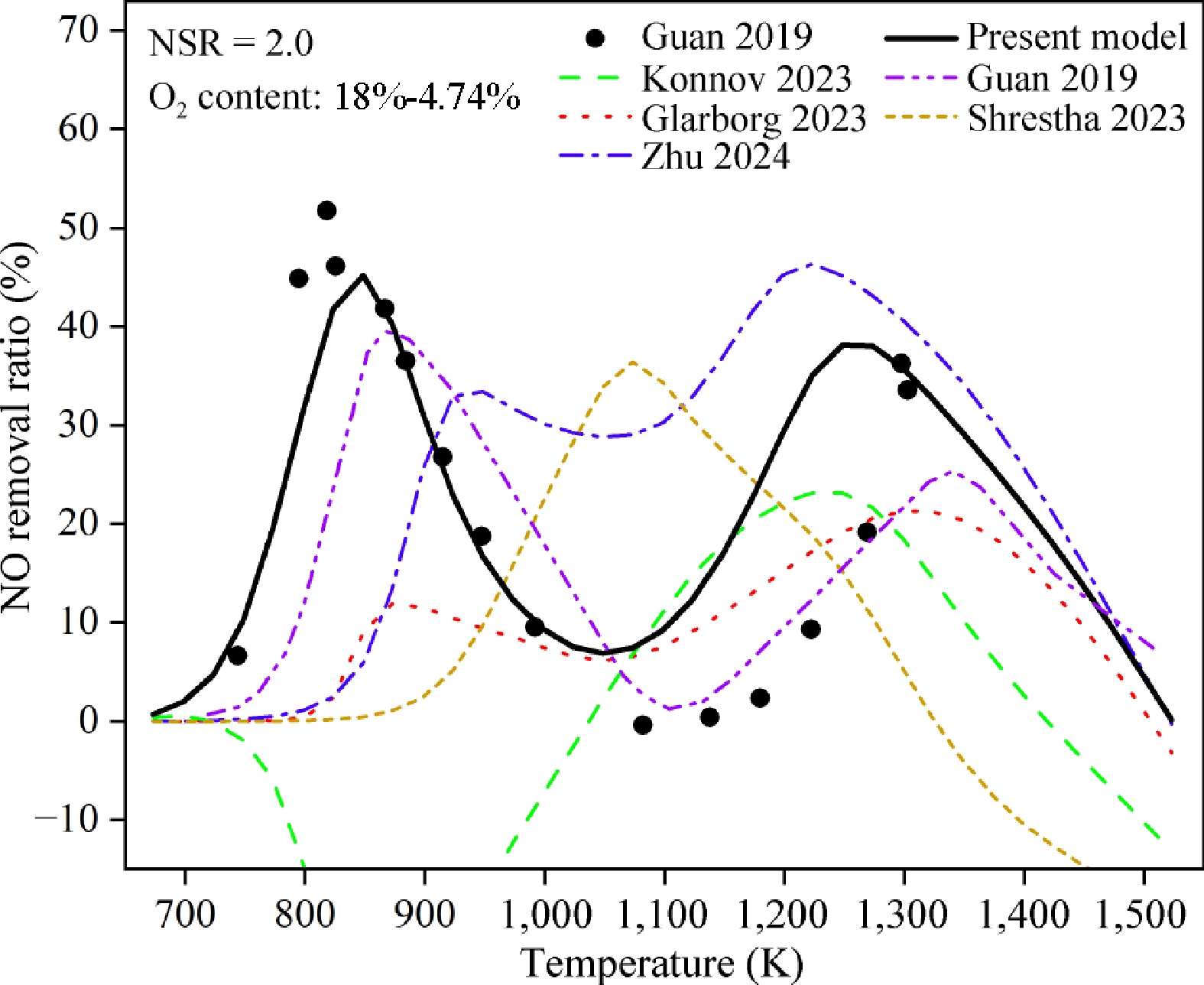
Figure 1.
NO removal ratios of N2H4/NO/O2 under condition 1. The symbols are experimental data from previous work[23]. The solid, dash dot dotted, dashed, dotted, short dashed, and dash dotted lines are the predicted results by the present, Guan 2019[23], Konnov 2023[51], Glarborg 2023[32], Shrestha 2023[52] and Zhu 2024[24] models, respectively.
-

Figure 2.
NO removal ratios of N2H4/NO/O2 under condition 2. The symbols are experimental data from previous work[23]. The solid, dashed, dotted, short dashed, and dash dotted lines are the predicted results of the present, Konnov 2023[51], Glarborg 2023[32], Shrestha 2023[52], and Zhu 2024[24] models, respectively.
-

Figure 3.
NO removal ratios of N2H4/NO/O2 at condition 3. The symbols are experimental data from previous work[23]. The solid, dashed, dotted, short dashed, and dash dotted lines are the predicted results of the present, Konnov 2023[51], Glarborg 2023[32], Shrestha 2023[52], and Zhu 2024[24] models, respectively.
-
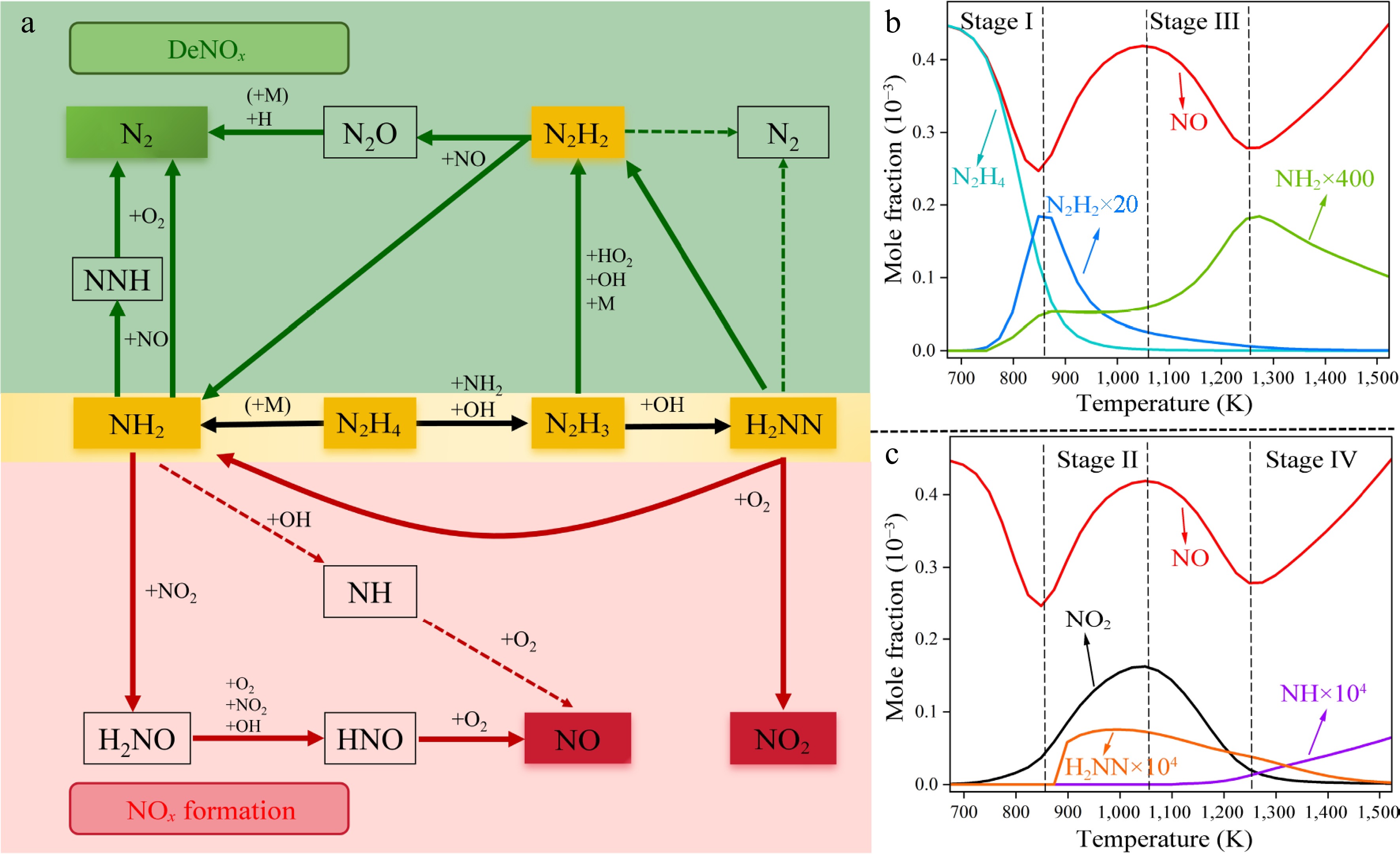
Figure 4.
(a) Reaction pathways of N2H4 under condition 1. The green and red boxes highlight reaction pathways involved in the DeNOx and NOx formation processes, respectively. The dashed arrows represent the pathways that are important only under high-temperature conditions. (b), (c) Simulated mole fractions of critical species in the N2H4/NO/O2 under condition 1.
-
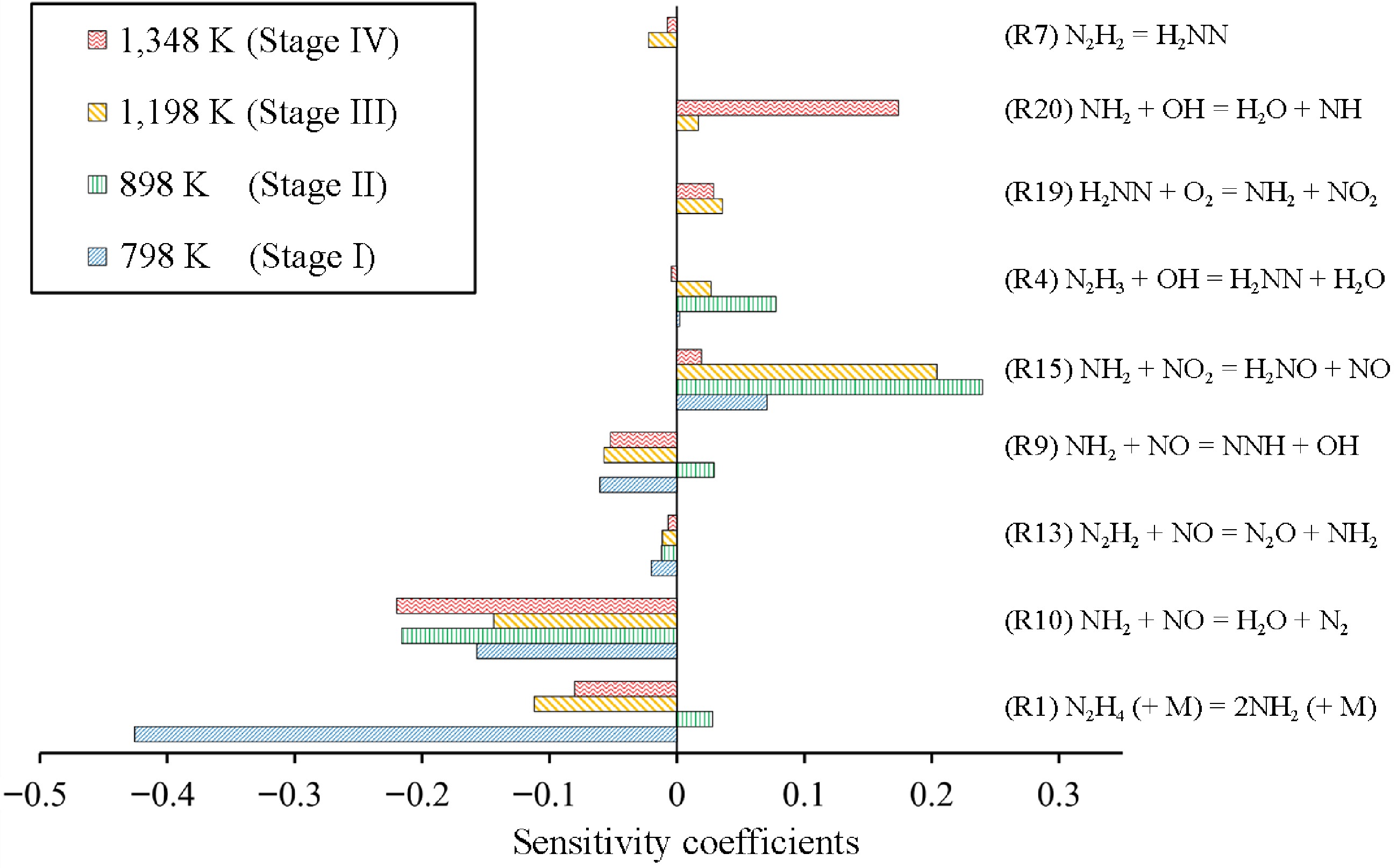
Figure 5.
Sensitivity analysis of NO at 798, 898, 1,198, and 1,348 K, corresponding to Stage I to IV, under condition 1.
-

Figure 6.
Effect of O2 content on the removal of NO at [NO]initial = 500 ppm, NSR = 4.0 at 1 atm and τ = 0.3 s. Symbols are experimental data from Guan 2019[23], while lines are the predicted results by the present model.
-
Reactions A
(cm3·mol−1·s−1)β
(unitless)Ea
(cal·mol− 1)Ref. R1 N2H4 (+ M) = 2NH2 (+ M) 5.0E14 0.000 251.22 [21] Low/ 1.5E15 0.000 39000 N2/ 2.4/ NH3/ 3.0/ N2H4/ 4.0/ R2 N2H4 + OH = N2H3 + H2O 4.0E13 0.000 0.0000 [35] R3 N2H4 + NH2 = N2H3 + NH3 3.8E01 3.440 −574.00 [40] R4 N2H3 + OH = H2NN + H2O 3.0E13 0.000 0.0000 [41] R5 N2H3 + HO2 = N2H2 + H2O2 2.8E04 2.690 −1600.0 [41] R6 N2H3 + OH = N2H2 + H2O 1.2E06 2.000 −1192.0 [41] R7 N2H2 = H2NN 1.0 E01 0.000 0.0000 [41] PLOG / 1.0E-01 9.2E38 −9.010 67727/ PLOG / 1.0E+00 2.0E41 −9.380 68452/ PLOG / 1.0E+01 1.3E45 −1.013 70757/ R8 H2NN = H2 + N2 5.0E13 0.000 52785 [34] R9 NH2 + NO = NNH + OH 4.3E10 0.294 −866.00 [43] R10 NH2 + NO = H2O + N2 2.6E19 −2.369 870.00 [43] R11 NNH = N2 + H 3.0E08 0.000 0.0000 [41] R12 NNH + O2 = N2 + HO2 5.6E14 −0.385 −13.000 [44] R13 N2H2 + NO = N2O + NH2 4.0E12 0.000 11922 [41] R14 N2O + H = N2 + OH 6.7E10 0.000 5390.0 [45] Duplicate 4.4E14 0.000 18900 R15 NH2 + NO2 = H2NO + NO 1.1E12 0.110 −1186.0 [31−33] Duplicate −4.3E17 −1.874 588.00 R16 H2NO + NO2 = HNO + HONO 3.0E11 0.000 2000.0 [46] R17 H2NO + O2 = HNO + HO2 2.3E05 2.190 18000 [46] R18 HNO + O2 = HO2 + NO 2.0E13 0.000 14000 [41] R19 H2NN + O2 = NH2 + NO2 1.5E12 0.000 5961.0 [41] R20 NH2 + OH = H2O + NH 3.3E06 1.949 −217.00 [47] R21 NH + O2 = HNO + O 3.3E09 1.034 11420 [3] R22 NH + O2 = NO + OH 4.5E08 0.790 1195.0 [48] Table 1.
Important reactions in the N2H4/NO/O2 system. The parameters for use are in the modified Arrhenius expression k = ATβexp[-E/(RT)].
-
Parameters Condition 1 Condition 2 Condition 3 T (K) 673−1,523 773−1,398 773−1,348 P (atm) 1 1 1 τ (s) 0.3 0.3 0.3 NO (ppm) 450 500 500 N2H4 (ppm) 450 1,000 1,000 NSR 2 4 4 O2 (%) 18−4.74 7.4−16.5 9.9−16.8 CO2 (%) 5 5 5 H2O (%) 10 10 10 N2 (%) Balance Balance Balance Table 2.
Validation conditions[23] of the present model.
Figures
(6)
Tables
(2)