-
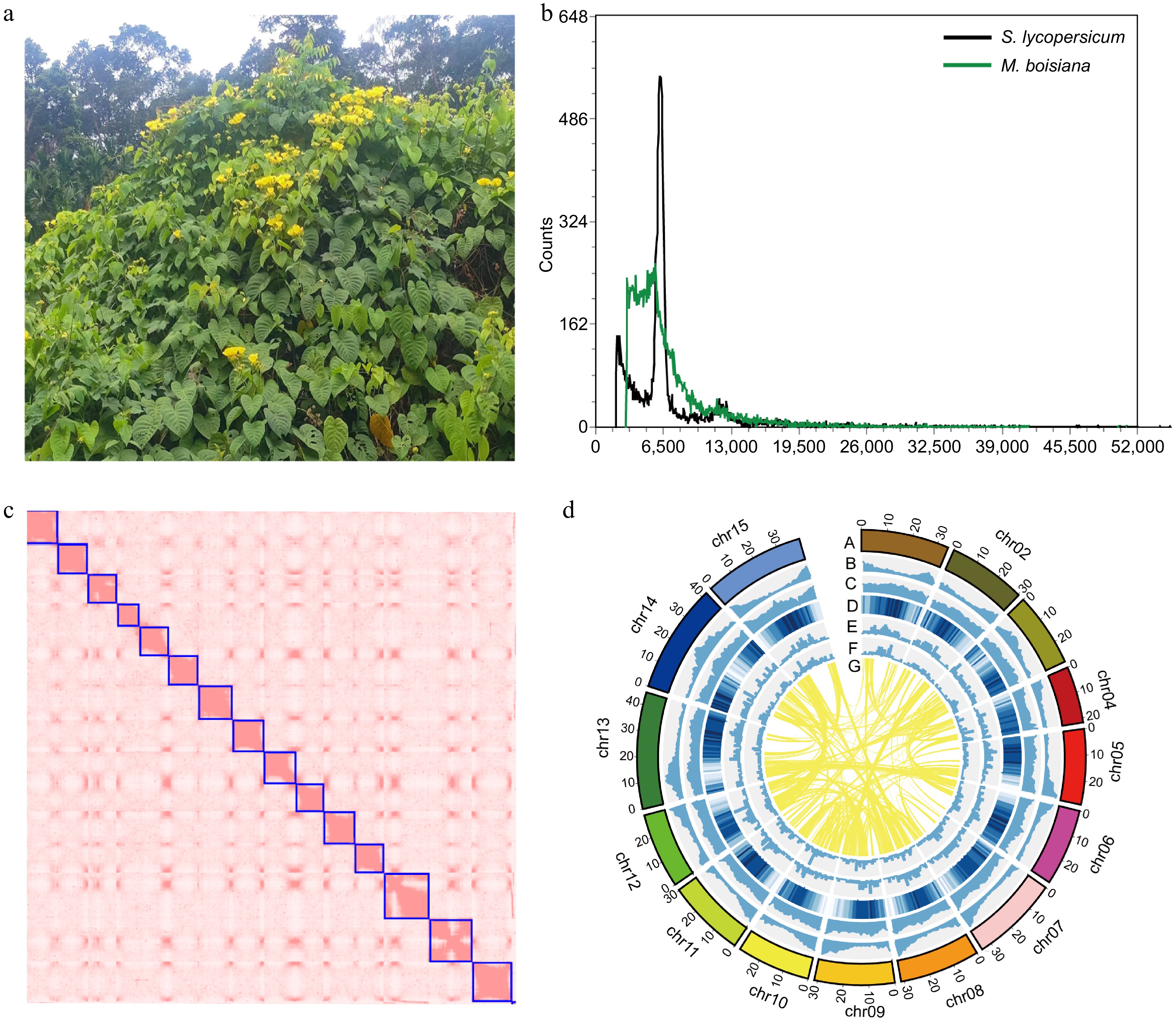
Figure 1.
Morphological traits and genome characterizations of M. boisiana. (a) The flower and leaf of M. boisiana. (b) Flow cytometry analysis results. (c) The Hi-C heatmap of the genome assembly. (d) Genome features of M. boisiana. (Chromosome karyotypes; Gene density; GC content per Mb; Repeat content per Mb; Gypsy content per Mb; Copia content per Mb; The syntenic regions between different chromosomes were identified)
-
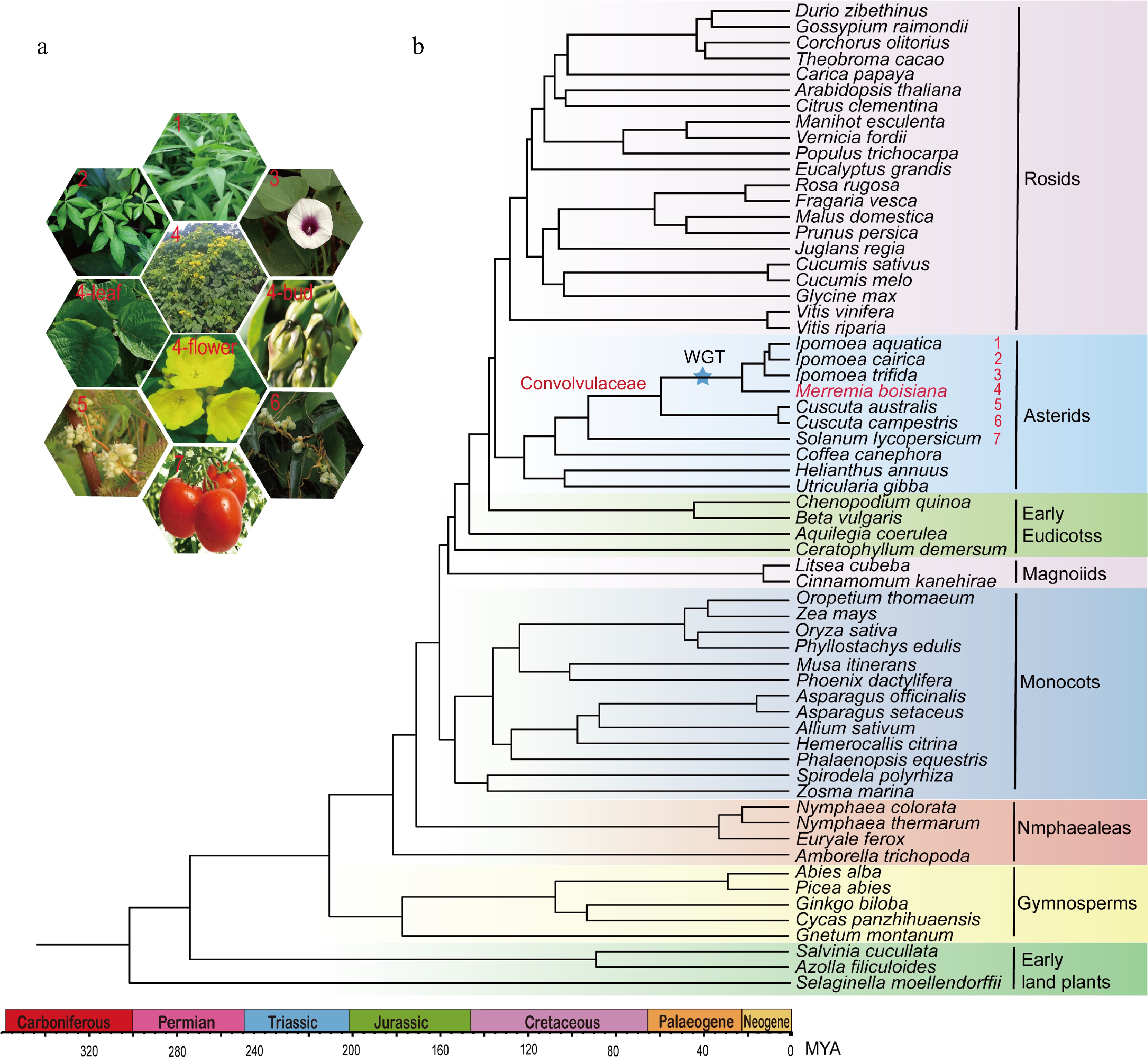
Figure 2.
Phylogenomic relationships of M. boisiana. (a) Pictures of six plants in the Convolvulaceae family. (b) Phylogeny and divergence time estimation of 60 plant species.
-
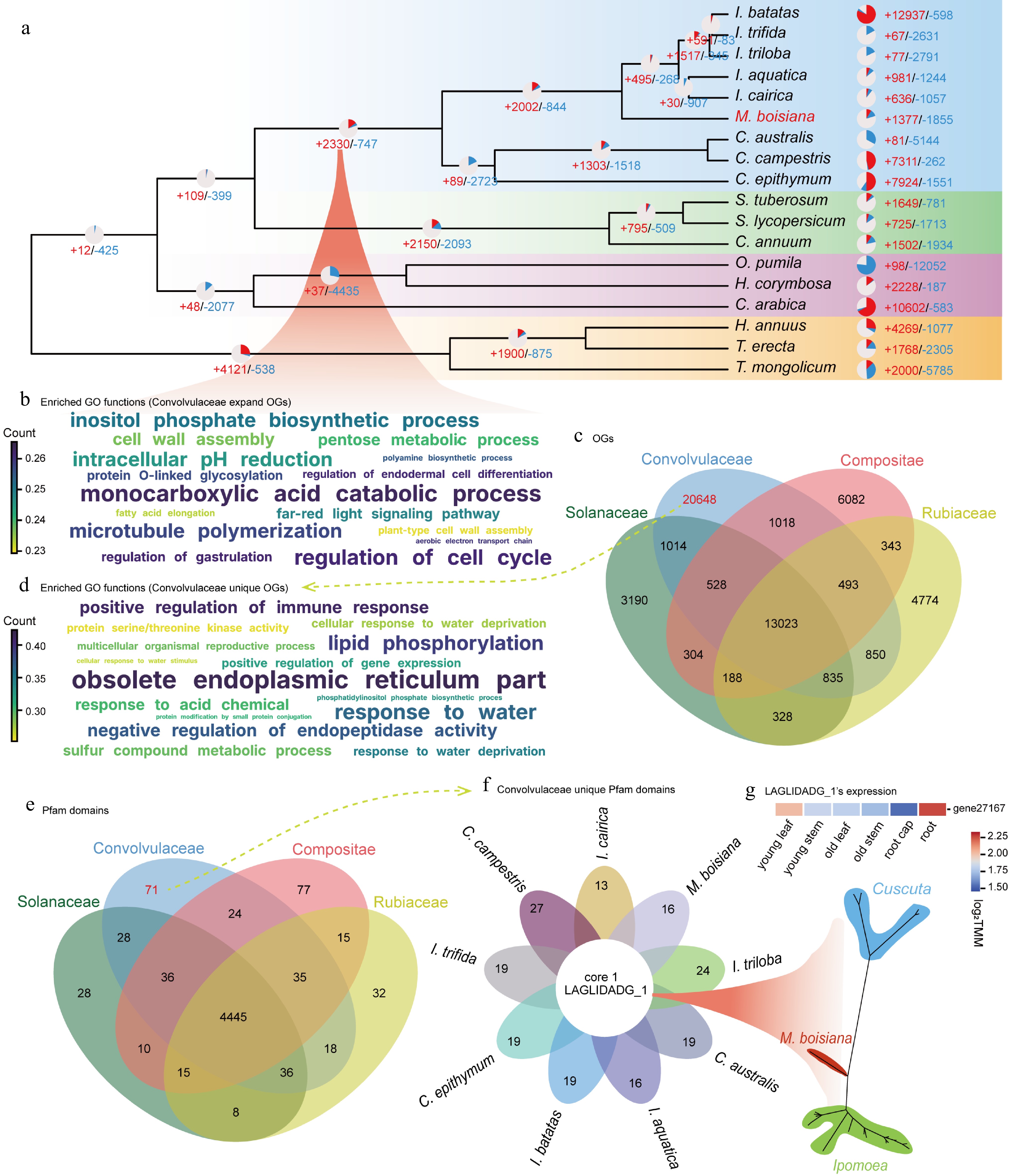
Figure 3.
Enriched orthogroups and domains in the Convolvulaceae family (a) Gene family expansion and contraction of M. boisiana. (b) Functional (GO) enrichment for the Convolvulaceae node. (c) Functional (GO) enrichment for the Convolvulaceae unique. (d) OGS overlap among Convolvulaceae, Solanaceae, Rubiaceae, and Asteraceae. (e) LAGLIDADG_1's expression of M. boisiana. (f) Convolvulaceae unique Pfam domains. (g) Pfam domains overlap among Convolvulaceae, Solanaceae, Rubiaceae, and Asteraceae.
-
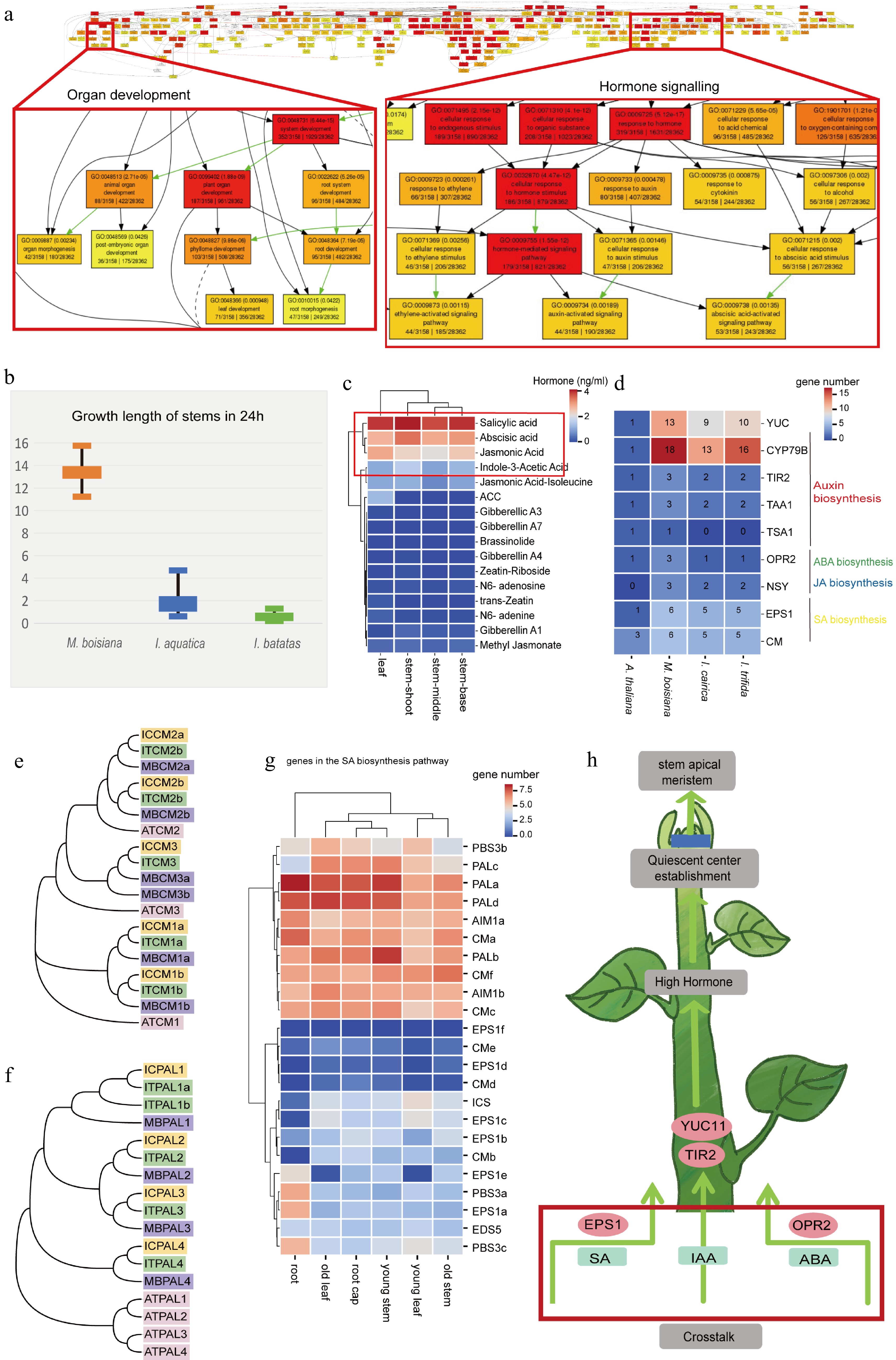
Figure 5.
The phytohormones regulate the rapid growth of roots in M. boisiana. (a) Go annotation of M. boisiana, a focus on organ development and hormone signalling in red boxes. (b) The rapid growth of M. boisiana, I. aquatica, and I. batatas. (c) The hormone content in different organs, among which four kinds of hormones (SA, ABA, JA, and IAA) have higher content across all organs. (d) Compared to plants such as I. aquatica, I. cairica, and A. thaliana, there is an expansion of key genes related to hormone synthesis in M. boisiana. These key genes promote root development. (e) Phylogenetic tree of M. boisiana, and A. thaliana CM. (f) Phylogenetic tree of M. boisiana, and A. thaliana PAL. (g) Highly expressed genes involved in SA hormone synthesis. (h) These key genes promote stem development.
-
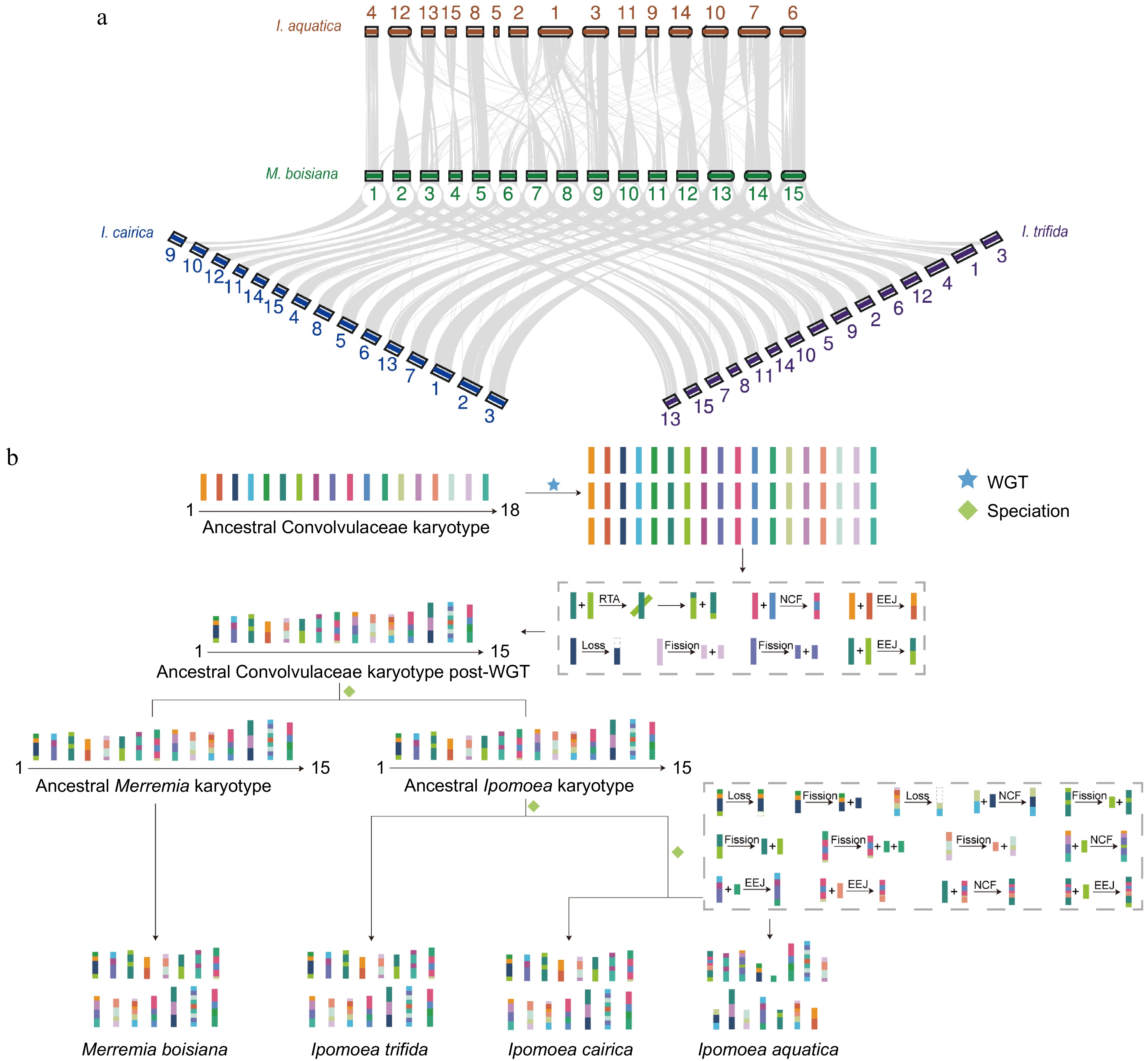
Figure 4.
Collinearity and karyotype analysis of M. boisiana. (a) Collinearity between M. boisiana and I. aquatica, I. cairica, and I. trifida. (b) WGD and chromosome-level genomic evolution of M. boisiana.
-
Genomic feature Merremia boisiana Estimated genome size (Mb) 523.64 Genome size (Mb) 510.9 Heterozygous (%) 1.02 Contig N50 (Mb) 21.24 Length of N50 (bp) 50,755 Number of contigs 141 Number of chromosomes 15 Repeat sequence content (%) 60.93 GC content (%) 36.23 Number of genes 37,389 Genome completeness (BUSCO) 98.7 Gene completeness (BUSCO) 99.2 Genomic LAI 11.27 (reference level) Genomic Merqury 33.2 (reference level) Table 1.
The genome features of M. boisiana.
Figures
(5)
Tables
(1)