-
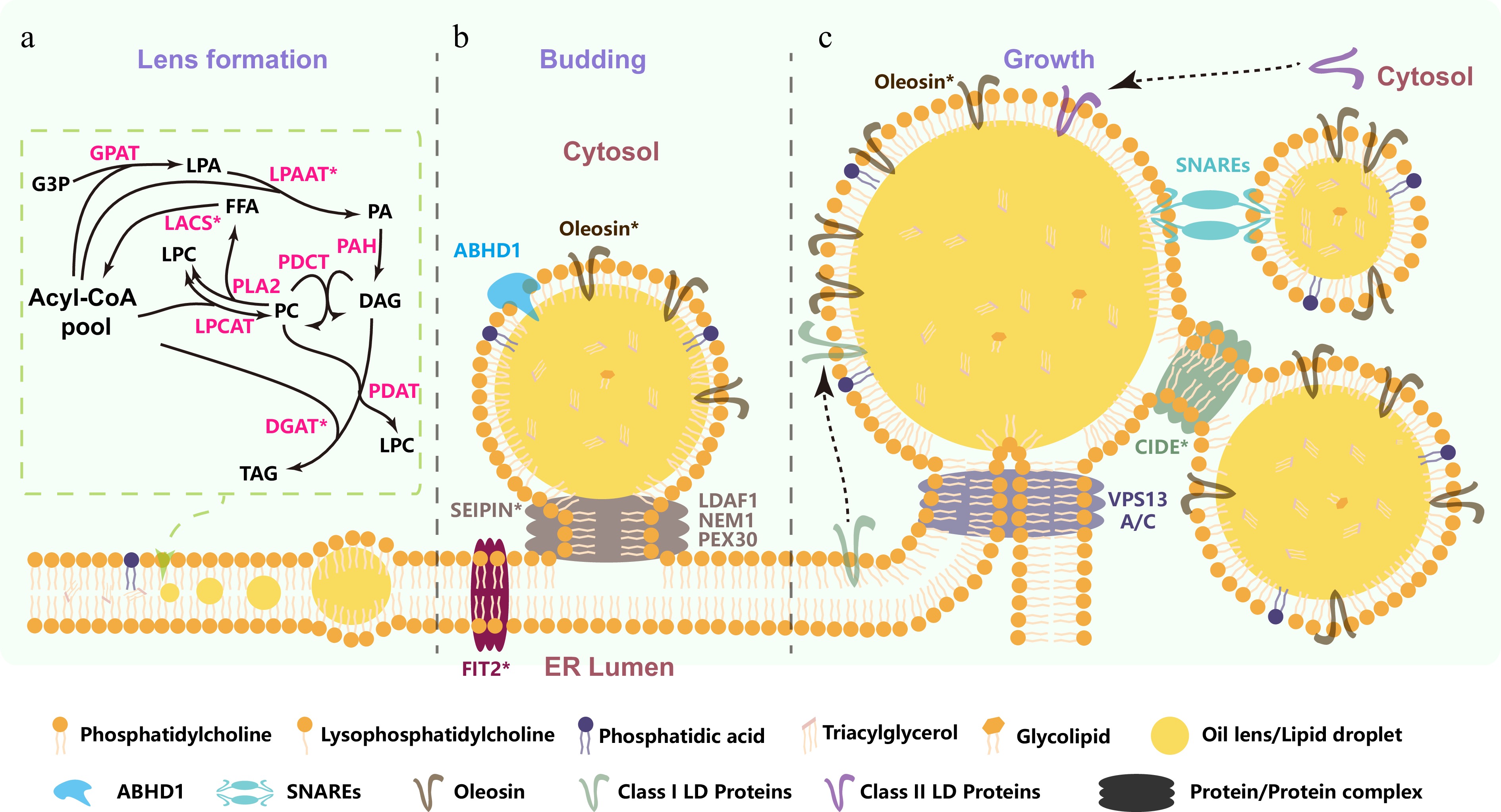
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of TAG biosynthesis and lipid droplet formation. (a) TAG biosynthesis and lens formation: TAG assembly occurs in the ER via the Kennedy pathway (G3P → LPA → PA → DAG → TAG), supplemented by acyl-CoA flux from acyl editing at PC and acyl-transfer from PC via PDAT or PDCT. Newly synthesized TAG aggregate into lens-like structures via phase separation on the leaflets of the ER bilayer. (b) SEIPIN-driven lipid droplet budding: SEIPIN interacts with specific proteins and lipids to drive lipid droplet budding via phase separation and membrane remodeling. (c) LD growth and fusion mechanisms: cytosolic LDs grow via Ostwald ripening and fuse through protein-mediated mechanisms. G3P, sn-3 glycerol 3-phosphate; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; PA, phosphatidic acid; PC, phosphatidylcholine; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; DAG, 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol; FFA, free fatty acids; TAG, triacylglycerol; DGAT, diacylglycerol acyltransferase; GPAT, sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase; LACS, long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase; LPAAT, lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase; LPCAT, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase; PDAT, phospholipid:diacylglycerol acyltransferase; PDCT, phosphatidylcholine:diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferase; PLA2, phospholipase A2; PAH, phosphatidate phosphatase; FIT2, fat storage-inducing transmembrane protein 2 from mammals; LDAF1, lipid droplet assembly factor 1 from mammals; NEM1, Nuclear Envelope Morphology 1 from mammals; PEX30, Peroxin 30 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae; ABHD1, α/β hydrolase domain-containing protein 1 from Chlamydomonas; VPS13A/C, Vacuolar Protein Sorting-associated Protein 13 A/C from mammals; SNARE, Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors from mammals; CIDE, Cell Death-Inducing DFFA-like Effector from mammals. Overexpression of asterisk-marked proteins enhances seed oil content.
-
Stage Protein Function Plant oil content enhancement Ref. TAG assembly and lens Formation GPAT G3P to LPA using acyl-CoA-derived acyl / LPAAT LPA to PA using acyl-CoA-derived acyl Yes [20] PAH PA to DAG / DGAT1 DAG to TAG using acyl-CoA-derived acyl Yes [22] PDAT1 DAG to TAG using PC-derived acyl No [5] LACS FFA to FA-CoA Yes [21] PLA2 PC to LPC and FFA / LPCAT LPC to PC using acyl-CoA-derived acyl / PDCT Transfer of the headgroup from PC to DAG / LD budding FIT2 Converts luminal phospholipids to DAG, driving LD
budding toward the cytoplasmYes [25] SEIPIN Drive lipid phase separation, triggering LD nucleation Yes [24] LDAF Member of SEIPIN Complex / LDAP Member of SEIPIN Complex No [34] NEM1 Member of SEIPIN Complex / PEX30 Member of SEIPIN Complex / LDIP Member of SEIPIN Complex / LD growth and fusion VPS13A/C Facilitate neutral lipid transport from the ER to LDs / SNAREs Facilitate LD membrane fusion machinery, enabling
inter-organelle bridges/ CIDEs Mediate TAG transfer between LDs Yes [18,26] Table 1.
Protein candidates to enhance plant oil content,
Figures
(1)
Tables
(1)