-
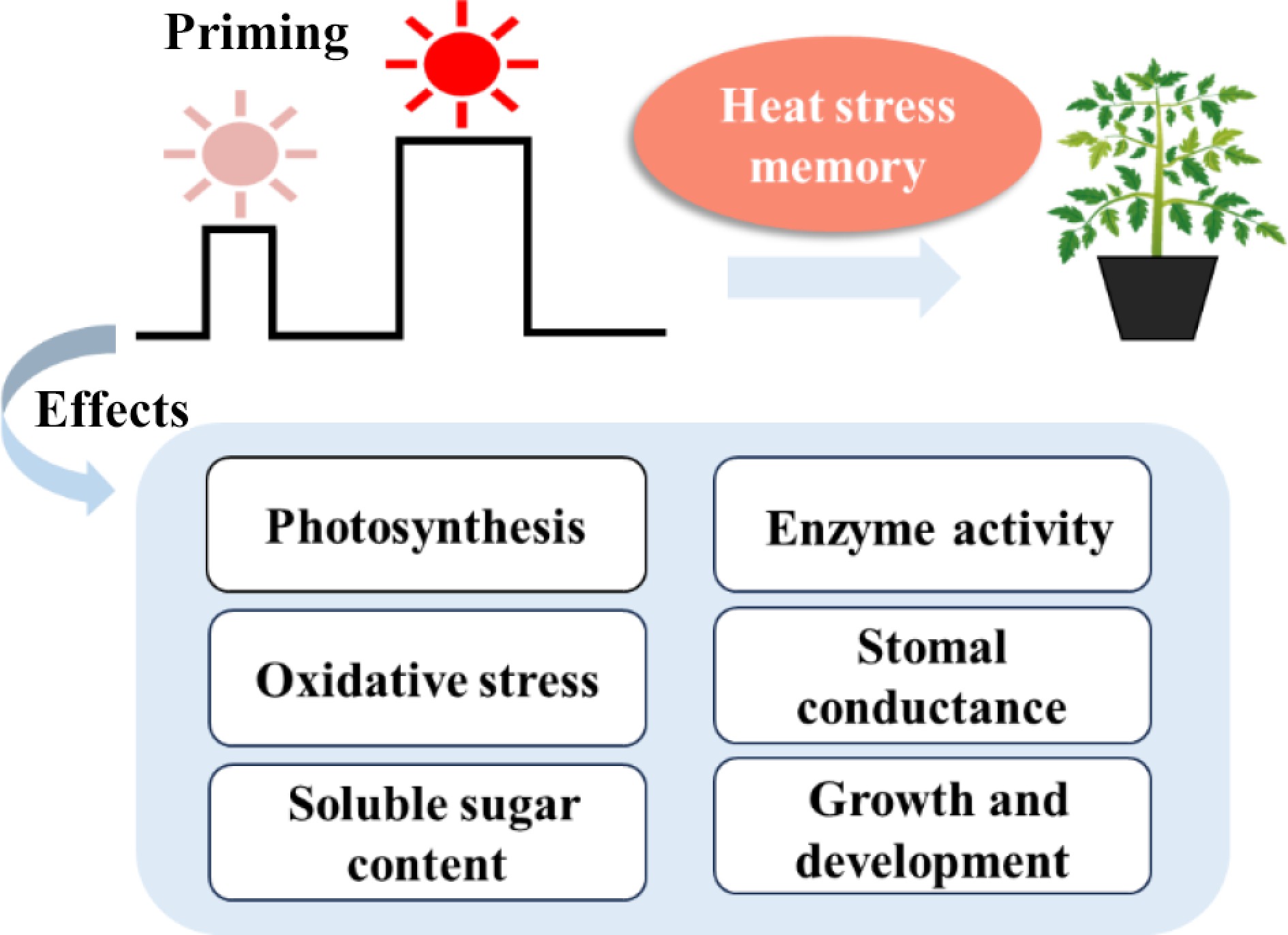
Figure 1.
Heat priming induced heat stress memory, allowing the tomato plants to acquire heat tolerance via physiological and morphological regulation.
-
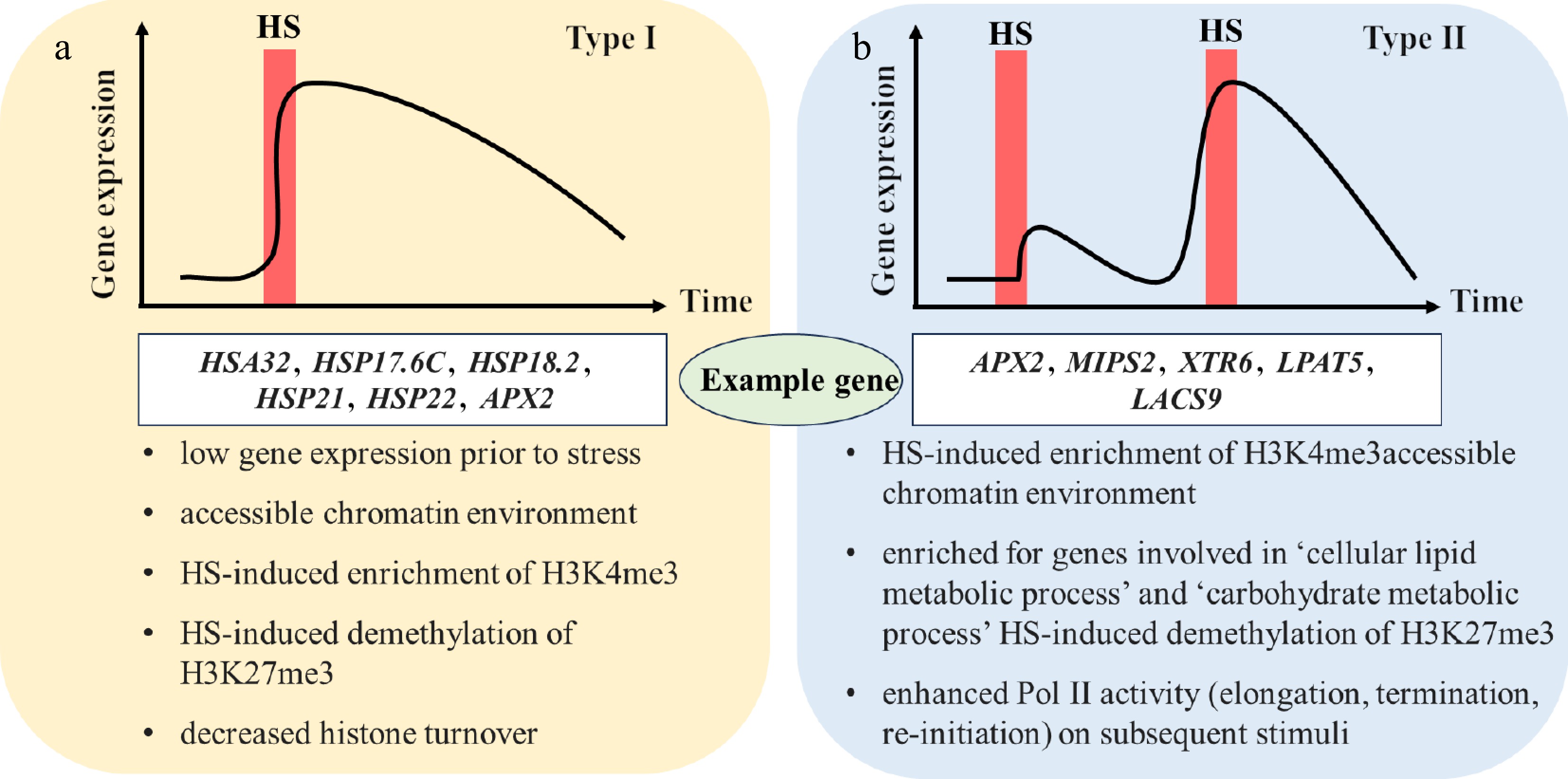
Figure 2.
Two types of transcriptional memory: (a) Type I, sustained induction; (B) Type II, enhanced re-induction. This was made according to Pratx et al.[26], with some revisions. The red bar represents HS (heat stress), and x and y axes represents time and gene expression, respectively. The white boxes correspond to the related genes of the two types, followed by their features below the box. HSA, heat-induced protein; HSP, heat shock protein; APX, ascorbate peroxidase; MIPS, enzyme l-myo-inositol 1-phosphate synthase; XTR, xyloglucan endotransglycosylase; LPAT, lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase; LACS, long-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthetase.
-
Type Function Ref. HsfA2/
HsfA3HsfA2 and HsfA3 maintain sustained expression of thermal memory-related genes by recruiting the methylation of histone H3K4. This epigenetic modification contributes to chromatin opening, which promotes the transcriptional activation of genes. [29] HsfA2 HsfA2 binds to heat memory gene promoters, sustaining their high expression after heat stress and prolonging the duration of AT via maintained HSP expression. It also regulates the H3K4me3 memory locus, preserving chromatin's openness for continuous transcription. [30] HsfA2 HsfA2 is able to bind to the promoter of the plastidial metalloproteinase FtsH6 gene and activate its expression. FtsH6 resets the thermal memory during the heat recovery phase by degrading HSP21 to the priming level. [31] HsfA1 HsfA1 is rapidly activated under heat stress conditions and coordinates heat tolerance in tomato by initiating the transcription of a large number of downstream heat-responsive genes. [32] HSP21 Sustained high expression of HSP21 is a key factor in the maintenance of thermal memory. During the thermal memory phase, the level of HSP21 determines the duration of thermal memory. [33] HSP101/
HSA32HSP101 and HSA32 play important roles in heat acclimation memory in Arabidopsis through the formation of positive feedback loops, post-transcriptional regulation, and maintenance of protein stability. [34] sHSP22 sHSP22 plays a role in the formation and maintenance of thermal memory by regulating growth hormones' polar transport and ABA signaling. [35] Hsfs, heat shock transcription factor; H3K4, histone H3 lysine 4; AT, acquired thermotolerance; HSPs, heat shock proteins; H3K4me3, histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation; FtsH6, filamentation temperature-sensitive H6; HSA32, heat-induced 32-kD protein; sHSP22, small heat shock protein 22. Table 1.
Plant heat stress memory-related Hsfs and HSPs
-
Type Function Ref. SDG25/
ATX1Mutations in SDG25 and ATX1 decrease histone H3K4me3 levels, increase DNA cytosine methylation, and suppress the expression of a subset of heat stress-responsive genes during stress recovery in Arabidopsis thaliana. [38] H3K4me3/H3K4me2 H3K4me2 and H3K4me3 are involved in transcriptional memory transmission during heat shock memory. [39] JMJ JMJ has H3K27me3 demethylase activity and is able to remove H3K27me3 modifications on heat memory-related genes such as HSP22 and HSP17.6C. [43] CSN5A The CSN5A subunit can regulate heat stress memory by resetting the heat stress memory genes APX2 and HSP22 and affecting H3K4me3. [44] ATX1 ATX1 is an H3K4 methyltransferase that has been shown to regulate H3K4me3 levels at the promoter of heat stress recovery genes. [45] SDG25, Set Domain Group; ATX1, Arabidopsis homolog of trithorax; H3K4me3, histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation; H3K4me2, histone H3 lysine 4 dimethylation; JMJ, Jumonji domain-contaning protein; H3K27me3, histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation; HSPs, heat shock proteins, CSN5A, constitutive photomorphogenesis 9 signalosome 5A; APX2, ascorbate peroxidase. Table 2.
Histone-modifying epigenetic genes for heat stress memory in plants.
Figures
(2)
Tables
(2)