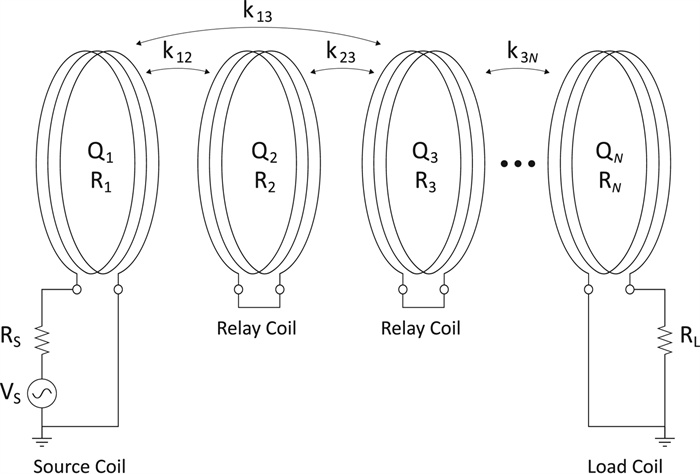
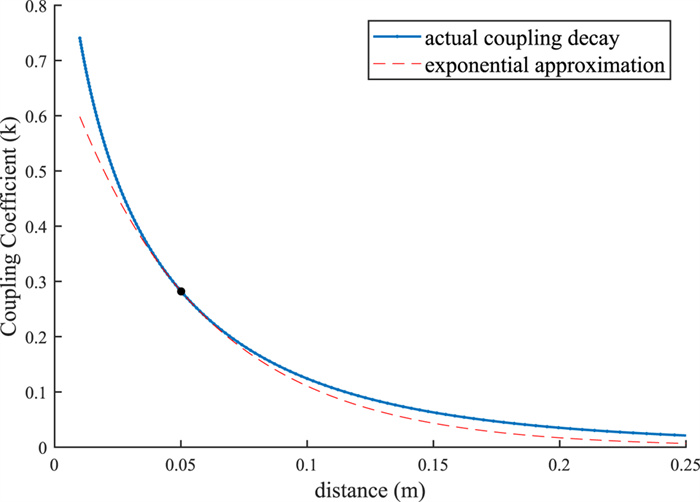
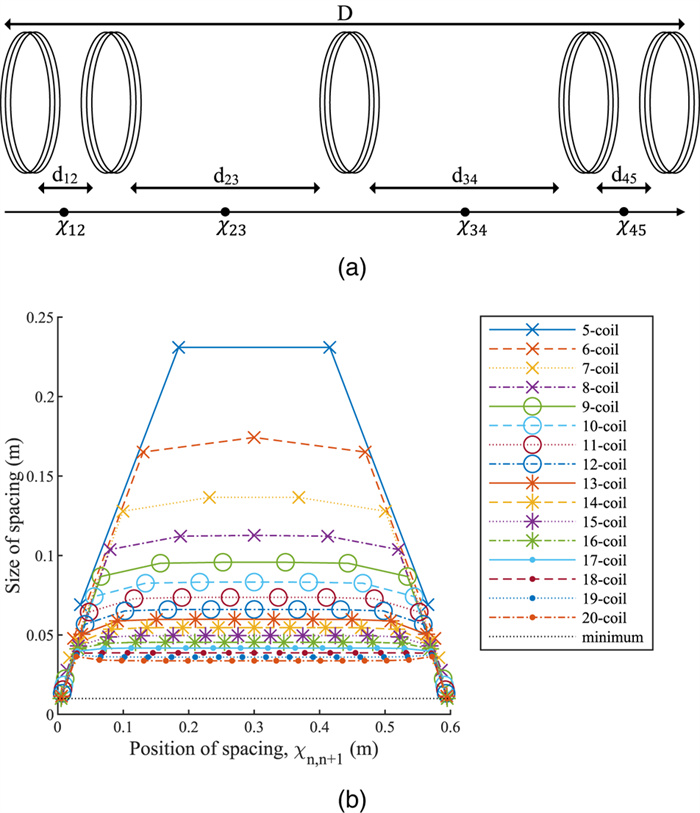
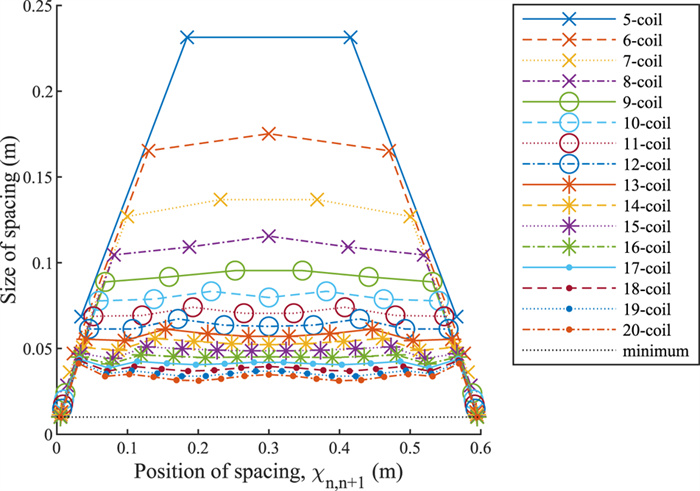
Convex optimization of coil spacing in cascaded multi-coil wireless power transfer
-
School of Engineering, University of British Columbia, Kelowna, BC, V1V 1V7, Canada
More Information
-
Author Bio:
 Connor Badowich
Connor Badowich obtained his B.A.Sc. and M.A.Sc. degrees in electrical engineering from the University of British Columbia (UBC), Kelowna, BC, Canada in 2016 and 2019, respectively. While completing his Master of Applied Science degree he worked as a graduate research assistant in the applied electromagnetics laboratory at UBC under the supervision of Dr. Markley. He is currently working in the aerospace industry and continues to collaborate with Dr. Markley. His research interests are in the field of electromagnetics, microwave engineering, and wireless power transfer.
 Jacques Rousseau
Jacques Rousseau received the B.A.Sc. degree in electrical engineering from the University of British Columbia, Kelowna, Canada, in 2019. As an undergraduate, he was involved in research on wireless power transfer and electronic gas sensor development.
 Loïc Markley
Loïc Markley received the B.A.Sc. degree in electronics engineering from Simon Fraser University, BC, Canada, in 2004, and the M.A.Sc. and Ph.D. degrees in electrical engineering from the University of Toronto, ON, Canada, in 2007 and 2013, respectively. He is currently an Assistant Professor in the School of Engineering at the University of British Columbia, Kelowna, BC, Canada. His research interests include applied electromagnetics, periodic structures and metamaterials, subwavelength imaging, frequency-selective surfaces, leaky-wave antennas, wireless sensing, and wireless power transfer. Since 2015, Prof. Markley has served as Associate Editor for IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters. In 2010 he was the recipient of the Tatsuo Itoh Best Paper Award for his paper on near-field focusing published in
IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters.
-
Corresponding author:
Loïc Markley, School of Engineering, University of British Columbia, Kelowna, BC, V1V 1V7, Canada. E-mail: loic.markley@ubc.ca
-
Abstract
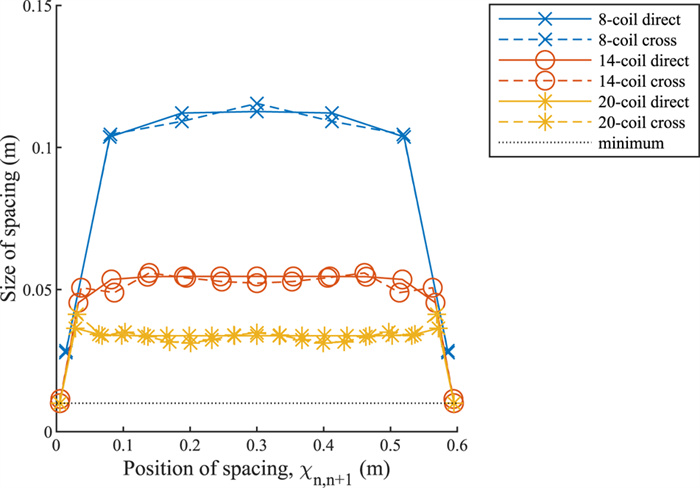
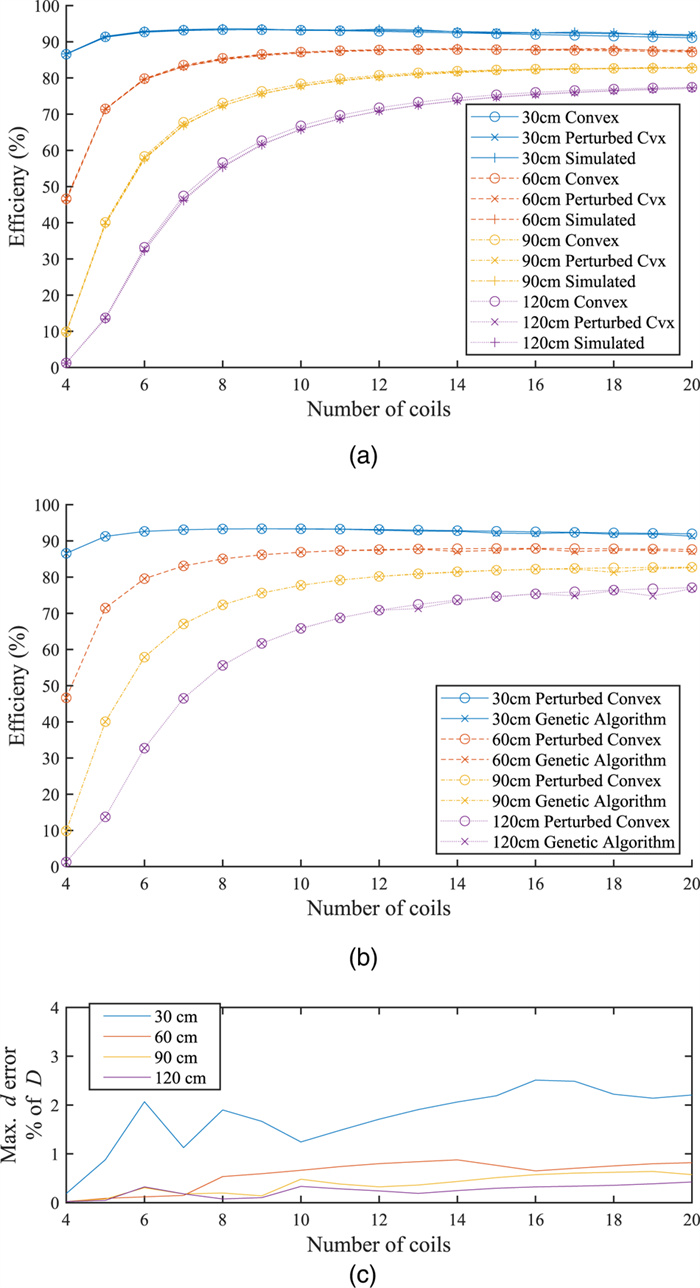
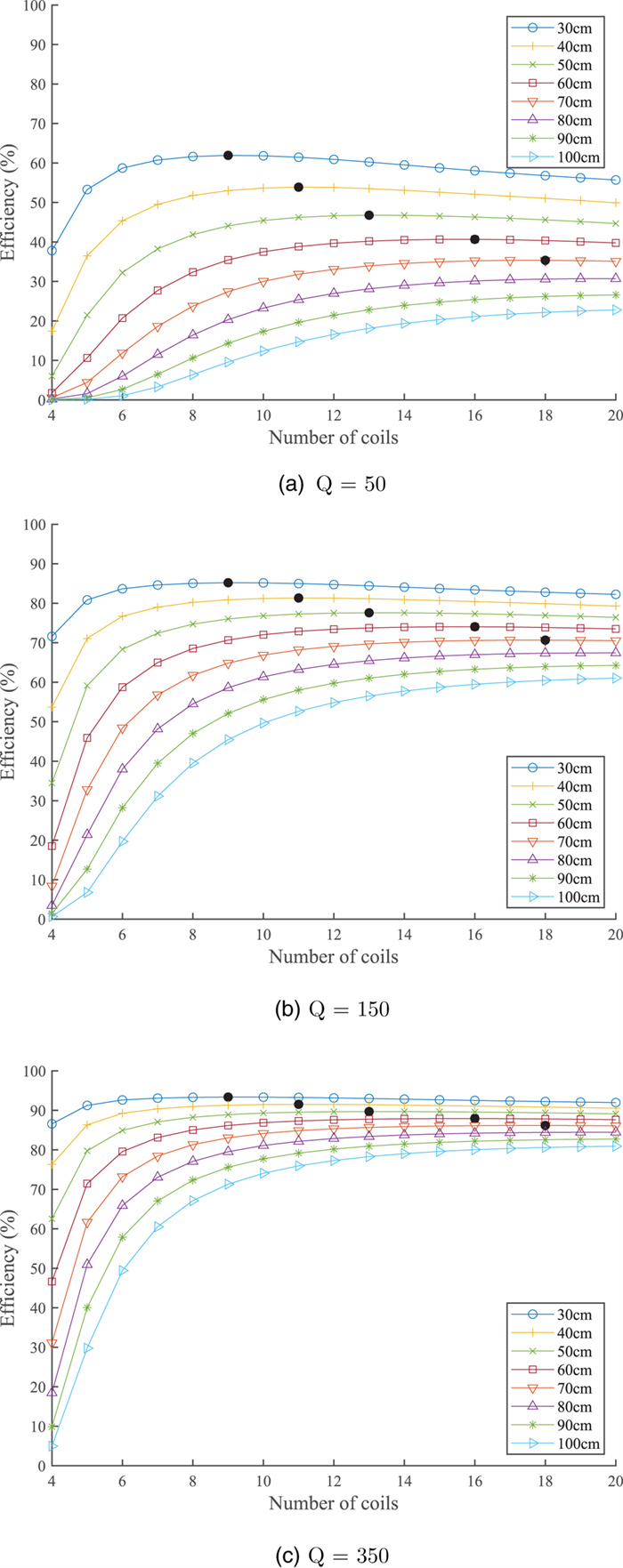
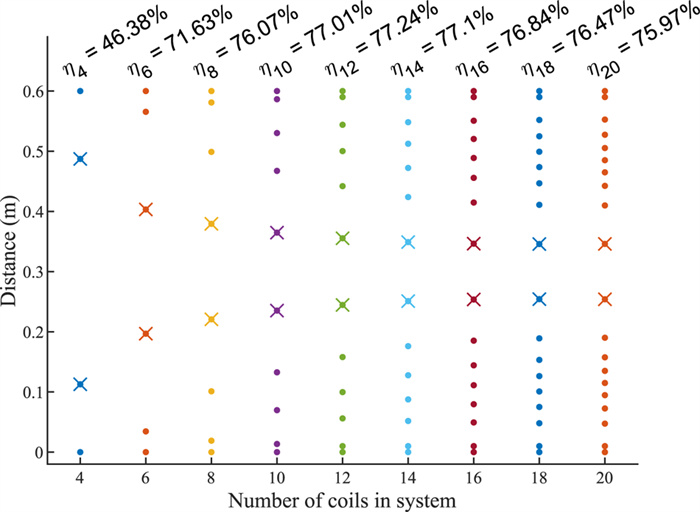
In this paper, we use convex optimization to maximize power efficiency through cascaded multi-coil wireless power transfer systems and investigate the resulting characteristic spacing. We show that although the efficiency is generally a non-convex function of the coil spacing, it can be approximated by a convex function when the effects of higher-order couplings are small. We present a method to optimize the spacing of cascaded coils for maximum efficiency by perturbing the solution of the convex approximation to account for higher-order interactions. The method relies on two consecutive applications of a local optimization algorithm in order to enable fast convergence to the global optimum. We present the optimal configurations of coil systems containing up to 20 identical coils that transfer power over distances up to 4.0 m. We show that when spacing alone is optimized, there exist an optimal number of coils that maximize transfer efficiency across a given distance. We also demonstrate the use of this method in optimizing the placement of a select number of high-Q coils within a system of low-Q relay coils, with the highest efficiencies occurring when the high-Q coils are placed on either side of the largest gaps within the relay coil chain.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Badowich C, Rousseau J, Markley L. 2020. Convex optimization of coil spacing in cascaded multi-coil wireless power transfer. Wireless Power Transfer 7(1): 42-50 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2020.5
|
Badowich C, Rousseau J, Markley L. 2020. Convex optimization of coil spacing in cascaded multi-coil wireless power transfer. Wireless Power Transfer 7(1): 42-50 doi: 10.1017/wpt.2020.5
|









 Connor Badowich obtained his B.A.Sc. and M.A.Sc. degrees in electrical engineering from the University of British Columbia (UBC), Kelowna, BC, Canada in 2016 and 2019, respectively. While completing his Master of Applied Science degree he worked as a graduate research assistant in the applied electromagnetics laboratory at UBC under the supervision of Dr. Markley. He is currently working in the aerospace industry and continues to collaborate with Dr. Markley. His research interests are in the field of electromagnetics, microwave engineering, and wireless power transfer.
Connor Badowich obtained his B.A.Sc. and M.A.Sc. degrees in electrical engineering from the University of British Columbia (UBC), Kelowna, BC, Canada in 2016 and 2019, respectively. While completing his Master of Applied Science degree he worked as a graduate research assistant in the applied electromagnetics laboratory at UBC under the supervision of Dr. Markley. He is currently working in the aerospace industry and continues to collaborate with Dr. Markley. His research interests are in the field of electromagnetics, microwave engineering, and wireless power transfer.  Jacques Rousseau received the B.A.Sc. degree in electrical engineering from the University of British Columbia, Kelowna, Canada, in 2019. As an undergraduate, he was involved in research on wireless power transfer and electronic gas sensor development.
Jacques Rousseau received the B.A.Sc. degree in electrical engineering from the University of British Columbia, Kelowna, Canada, in 2019. As an undergraduate, he was involved in research on wireless power transfer and electronic gas sensor development.  Loïc Markley received the B.A.Sc. degree in electronics engineering from Simon Fraser University, BC, Canada, in 2004, and the M.A.Sc. and Ph.D. degrees in electrical engineering from the University of Toronto, ON, Canada, in 2007 and 2013, respectively. He is currently an Assistant Professor in the School of Engineering at the University of British Columbia, Kelowna, BC, Canada. His research interests include applied electromagnetics, periodic structures and metamaterials, subwavelength imaging, frequency-selective surfaces, leaky-wave antennas, wireless sensing, and wireless power transfer. Since 2015, Prof. Markley has served as Associate Editor for IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters. In 2010 he was the recipient of the Tatsuo Itoh Best Paper Award for his paper on near-field focusing published in IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters.
Loïc Markley received the B.A.Sc. degree in electronics engineering from Simon Fraser University, BC, Canada, in 2004, and the M.A.Sc. and Ph.D. degrees in electrical engineering from the University of Toronto, ON, Canada, in 2007 and 2013, respectively. He is currently an Assistant Professor in the School of Engineering at the University of British Columbia, Kelowna, BC, Canada. His research interests include applied electromagnetics, periodic structures and metamaterials, subwavelength imaging, frequency-selective surfaces, leaky-wave antennas, wireless sensing, and wireless power transfer. Since 2015, Prof. Markley has served as Associate Editor for IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters. In 2010 he was the recipient of the Tatsuo Itoh Best Paper Award for his paper on near-field focusing published in IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters.